
Japan Smart Power Transmission Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Technology, Voltage Level, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
Japan Smart Power Transmission Market Overview:
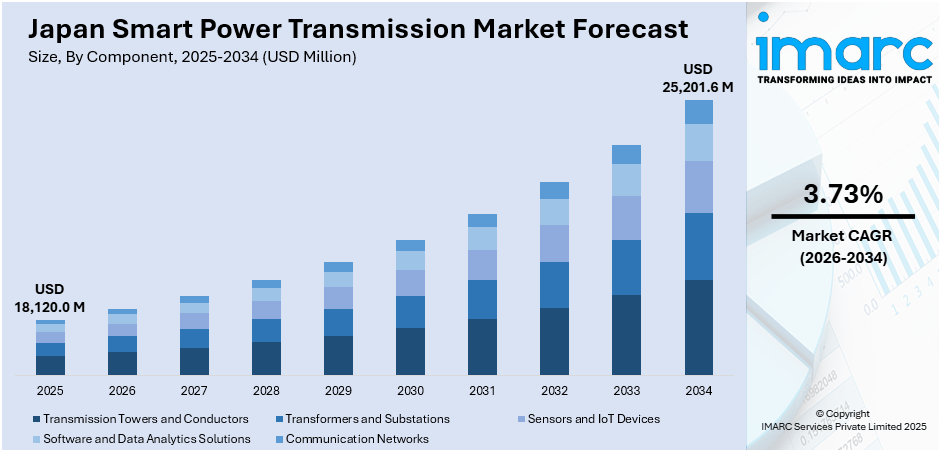
The Japan smart power transmission market size reached USD 18,120.0 Million in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 25,201.6 Million by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 3.73% during 2026-2034. The market includes the country’s transition to renewable energy, requiring grid upgrades to handle variable supply from sources like solar and wind. Rising electricity demand from artificial intelligence (AI) technologies and data centers further accelerates the need for modern infrastructure. Government policies supporting carbon neutrality and energy efficiency encourage utilities to adopt smart grid solutions. Additionally, the Japan smart power transmission market share is surged by the rising distributed energy resources and consumer demand for energy resilience and control are propelling investments in smart transmission technologies across the country.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 18,120.0 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 25,201.6 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 3.73% |
Japan Smart Power Transmission Market Trends:
Grid Modernization for Renewables and AI Integration
Japan is profoundly expanding its transmission network of power to support growing integration of the renewable energy resources and growing demands from AI technology and data centers. The transformation includes increasing the transmission lines and constructing new substations to promote the shift away from fossil fuel. As AI technologies and digital infrastructure expand further, so does electricity demand, which requires an efficient and expandable transmission system. In response to these challenges, corporations such as Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings will invest more than $3 billion in transmission systems by 2027. Japan will be modernizing its grid systems in an effort to maintain stability as it balances the unpredictability of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar. The initiative comes within Japan's overall sustainability goals, putting its power grid in place to cope with future technological changes as well as environmental aims successfully.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Flexible Grid Access and Market-Based Management
Japan is adopting flexible power transmission policies to make more space for renewable energy. Conventional grid systems, with assured access for every source of energy, tended to result in congestion and inefficiencies. The new system facilitates the connection of renewable energy sources to the grid with greater ease, even though their supply has to be curbed on occasion, allowing for quicker integration of clean energy. This transition assists in balancing system-wide demands while maintaining grid stability. Japan is also implementing market-based mechanisms to prioritize low-environmental-impact energy sources, making the grid more responsive and adaptive. These policy reforms seek to maximize energy flow, minimize congestion, and facilitate Japan's shift toward a cleaner and more sustainable energy mix, consistent with larger environmental objectives.
Deployment of Smart Grid Technologies
Japan is adopting smart grid technologies to make its electricity transmission system more efficient and responsive. With the deployment of around 60 million smart meters, Japan makes real-time monitoring and accurate energy management possible, which assists utilities in managing supply and demand fluctuations more effectively, especially as renewable power sources such as solar and wind become more dominant. Besides smart meters, Japan is rolling out data-driven controls and automation equipment to enhance the operation of the grid. Japan is also encouraging decentralized power systems, e.g., rooftop solar panels and residential batteries, that can be combined into virtual power plants. This technology enables communities to produce and exchange electricity, helping toward a more robust and flexible grid. These initiatives form part of Japan's overall aspiration to strengthen consumers, promote sustainability, and shift towards a greener energy future.
Japan Smart Power Transmission Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on component, technology, voltage level, and end user.
Component Insights:
- Transmission Towers and Conductors
- Transformers and Substations
- Sensors and IoT Devices
- Software and Data Analytics Solutions
- Communication Networks
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the component. This includes transmission towers and conductors, transformers and substations, sensors and IoT devices, software and data analytics solutions, and communication networks.
Technology Insights:
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems
- Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs)
- Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS)
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Smart Transformers
- High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission
- Wide-Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS)
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology have also been provided in the report. This includes supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, phasor measurement units (PMUS), flexible ac transmission systems (FACTS), advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), smart transformers, high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission, and wide-area monitoring systems (WAMS).
Voltage Level Insights:
- Extra High Voltage (EHV) Transmission (≥ 220 kV)
- High Voltage (HV) Transmission (66 kV - 220 kV)
- Medium Voltage (MV) Transmission (11 kV - 66 kV)
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the voltage level. This includes extra high voltage (EHV) transmission (≥ 220 kV), high voltage (HV) transmission (66 kV - 220 kV), and medium voltage (MV) transmission (11 kV - 66 kV).
End User Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
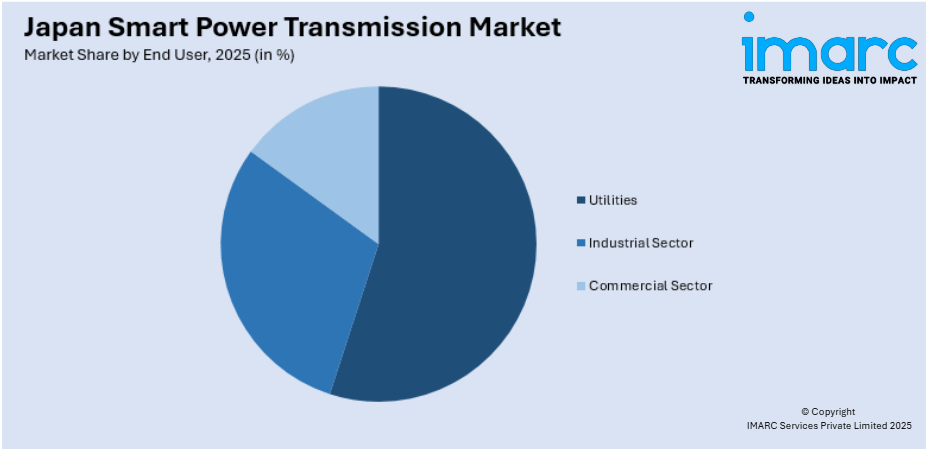
- Utilities
- Industrial Sector
- Commercial Sector
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user have also been provided in the report. This includes utilities, industrial sector, and commercial sector.
Regional Insights:
- Kanto Region
- Kansai/Kinki Region
- Central/ Chubu Region
- Kyushu-Okinawa Region
- Tohoku Region
- Chugoku Region
- Hokkaido Region
- Shikoku Region
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Kanto, Kansai/Kinki, Central/ Chubu, Kyushu-Okinawa, Tohoku, Chugoku, Hokkaido, and Shikoku Region.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Japan Smart Power Transmission Market News:
- In April 2025, Chugoku Electric Power partnered with Sense in Japan to initiate a high-resolution smart metering platform. The partnership introduces AMI 2.0 edge intelligence, enabling real-time grid image and data processing up to 1MHz. This technology will help utilities better manage infrastructure, enhance grid resilience, and improve power forecasting. The smart meters will also support demand response, detect faults, and provide consumers with actionable energy insights, boosting efficiency and cost savings.
- In July 2024, Japan is set to support ASEAN in expanding its power transmission networks to promote renewable energy and decarbonization. Prime Minister Fumio Kishida will announce the initiative at the Asia Business Summit in July 2024. Japan plans to fund projects like Kansai Electric Power Co.’s inter-island transmission in Indonesia. This effort, part of the "Asia Zero Emission Community" goals, aims to boost Japan’s influence in the regional energy sector and promote its technology exports.
Japan Smart Power Transmission Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Transmission Towers and Conductors, Transformers and Substations, Sensors and IoT Devices, Software and Data Analytics Solutions, Communication Networks |
| Technologies Covered | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems, Phasor Measurement Units (PMUs), Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS), Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI), Smart Transformers, High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission, Wide-Area Monitoring Systems (WAMS) |
| Voltage Levels Covered | Extra High Voltage (EHV) Transmission (≥ 220 kV), High Voltage (HV) Transmission (66 kV - 220 kV), Medium Voltage (MV) Transmission (11 kV - 66 kV) |
| End Users Covered | Utilities, Industrial Sector, Commercial Sector |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kansai/Kinki Region, Central/ Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Japan smart power transmission market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Japan smart power transmission market on the basis of component?
- What is the breakup of the Japan smart power transmission market on the basis of technology?
- What is the breakup of the Japan smart power transmission market on the basis of voltage level?
- What is the breakup of the Japan smart power transmission market on the basis of end user?
- What is the breakup of the Japan smart power transmission market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Japan smart power transmission market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Japan smart power transmission market?
- What is the structure of the Japan smart power transmission market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Japan smart power transmission market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Japan smart power transmission market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Japan smart power transmission market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Japan smart power transmission industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












