Japan Telemedicine Market Expected to Reach USD 20 Billion by 2033 - IMARC Group
Japan Telemedicine Market Statistics, Outlook and Regional Analysis 2025-2033
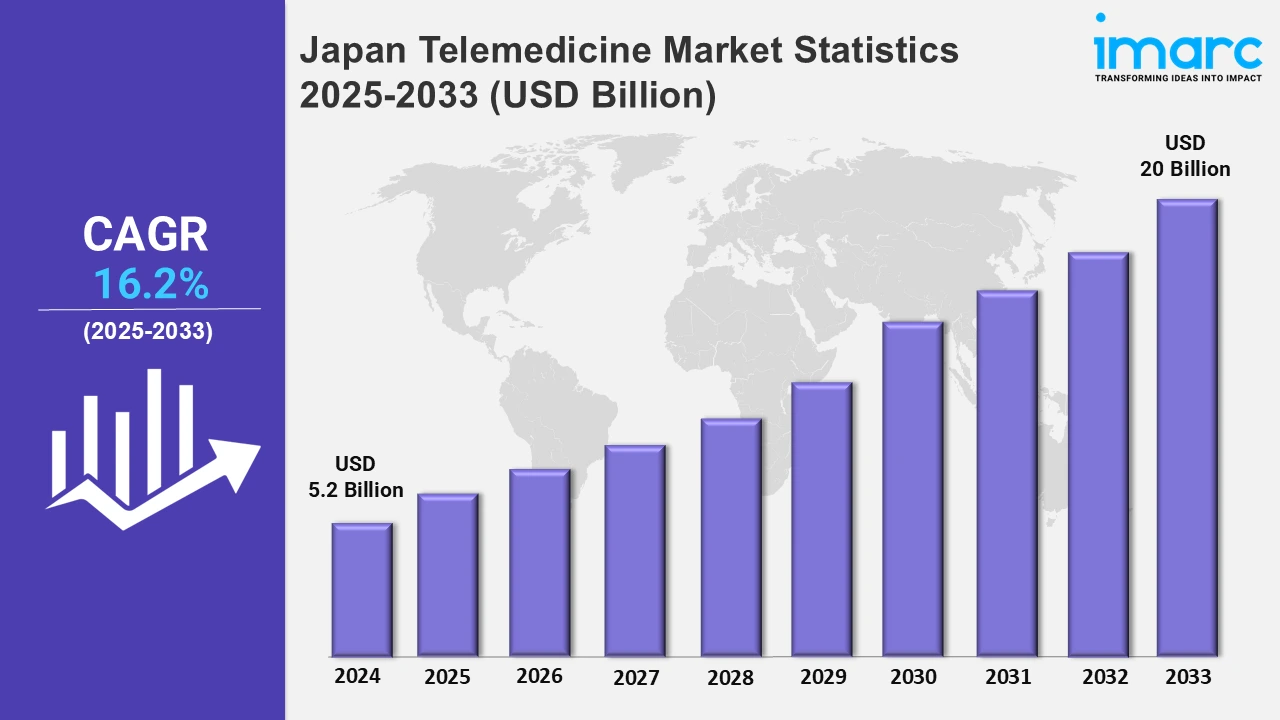
The Japan telemedicine market size was valued at USD 5.2 Billion in 2024, and it is expected to reach USD 20 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 16.2% from 2025 to 2033.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
The growing adoption of telemedicine in Japan is primarily driven by technological advancements, regulatory support, and demographic challenges. The rising elderly population and the shortage of healthcare professionals are increasing the demand for digital healthcare solutions. With telemedicine offering remote consultations and AI-driven diagnostics, healthcare accessibility is improving significantly. In addition, Japan’s revised Google policy in January 2025 permits licensed online pharmacies and telemedicine providers to advertise prescription drug services. This regulatory shift enhances digital healthcare reach, allowing patients to receive medical consultations and medications remotely, thereby improving convenience and accelerating the adoption of telemedicine. The growing emphasis on digital transformation in Japan’s healthcare sector is also fueling investments in AI-powered medical technologies. In this context, hospital resources are optimized, and patient care is improved by the growing use of intelligence in diagnostics and virtual consultations. According to a Nikkei Asia report published in March 2024, Japan has advanced AI-driven telemedicine to address the shortage of healthcare workers. AI-powered tools are enhancing operational efficiency by automating routine consultations and assisting doctors with faster, more accurate diagnostics.
The government is also promoting reimbursement policies for telemedicine services, encouraging both providers and patients to integrate digital healthcare into regular medical practices. Leading technology firms and healthcare providers are collaborating to develop AI-integrated telemedicine platforms that offer seamless remote patient monitoring and digital prescription services. Concurrently, the EU-Japan Centre for Industrial Cooperation article from March 2024 highlights Japan’s launch of the INNOVCARE project, which integrates AI, robotics, and telemedicine for elderly care. This initiative supports independent living, reduces caregiver workload, and improves remote patient monitoring, offering a sustainable solution for Japan’s aging society. The synergy of AI, robotics, and telemedicine is expected to redefine elderly healthcare by enhancing efficiency and accessibility, further driving the expansion of Japan’s telemedicine market.
Japan Telemedicine Market Statistics, By Region
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Kanto region, Kinki region, Central/Chubu region, Kyushu-Okinawa region, Tohoku region, Chugoku region, Hokkaido region, and Shikoku region. The aging population with chronic diseases, tech advancements, digital health demand, lifestyle shifts, and government initiatives are fueling market growth.
Kanto Region Telemedicine Market Trends:
The Kanto region is witnessing a rapid spread of telemedicine because of its tech-driven lifestyle and large metropolitan population. Online medical consultations are becoming popular, particularly for treatments related to dermatology and mental health. In line with this, hospitals are under less strain due to Tokyo-based systems like LINE Healthcare, which enable video consultations. Increasing partnerships between hospitals and digital health startups are further driving telemedicine integration into mainstream healthcare services.
Kinki Region Telemedicine Market Trends:
In Kyoto, the telemedicine market is expanding through AI-assisted diagnostic platforms. Kyoto University Hospital launched a remote dermatology consultation service in 2023, utilizing AI to analyze skin conditions. Along with that, it improves early diagnosis of conditions like melanoma and shortens patients’ wait times. The initiative supports rural healthcare facilities, where dermatologists are scarce, aligning with Japan’s broader digital healthcare strategy to improve accessibility across the Kinki region’s underserved areas.
Chubu Region Telemedicine Market Trends:
Chubu, home to Nagoya, is prioritizing telemedicine in occupational health and industrial worker safety. Many manufacturing firms are implementing virtual healthcare programs, reducing absenteeism by offering remote consultations for common ailments. Nagoya-based automotive companies use corporate telehealth services to ensure worker wellness. Rising government support for telemedicine adoption in workplaces is driving demand for AI-powered diagnosis tools and wearable health monitoring devices.
Kyushu-Okinawa Region Telemedicine Market Trends:
Access to healthcare is difficult in Kyushu and Okinawa because of their island geography. Particularly in Okinawa, where locals use telehealth platforms to consult experts in Fukuoka, telemedicine solutions are helping to close this gap. Besides this, Okinawan hospitals used remote diagnostic services, which lessened the need for patients to go to distant locations. Government-backed digital health programs are improving connectivity and expanding medical support across multiple islands.
Tohoku Region Telemedicine Market Trends:
The Tohoku region is growing in the telemedicine sector to fill the deficiencies in healthcare in rural and isolated locations. Moreover, hospitals in Sendai are using telemedicine networks to provide rehabilitative services and psychological counseling to improve accessibility for patients with mobility challenges. Besides this, remote diagnosis is improved by AI-powered medical imaging technologies, especially in smaller communities. These innovations ensure that patients receive timely medical attention while reducing the need for extensive travel to urban healthcare facilities.
Chugoku Region Telemedicine Market Trends:
The Chugoku region, with Hiroshima as a key city, is advancing telemedicine for rural healthcare. Many villages lack immediate access to specialists, which makes telehealth essential for consultations in cardiology and neurology. Hiroshima University Hospital has launched a virtual care program connecting rural clinics to city-based experts. These developments are enhancing diagnostic accuracy and reducing patient travel time for specialized treatments.
Hokkaido Region Telemedicine Market Trends:
Hokkaido’s vast, sparsely populated landscape makes telemedicine essential for medical outreach. Telecardiology programs allow specialists in Sapporo to monitor heart patients in remote towns like Asahikawa. Residents can now perform virtual examinations due to the installation of leading-edge healthcare kiosks in community centers. Furthermore, the government is funding high-speed internet expansion to improve telemedicine access in isolated regions.
Shikoku Region Telemedicine Market Trends:
Shikoku is leveraging telemedicine to support its aging rural population. Teleophthalmology programs are expanding, enabling eye disease screenings via virtual consultations. Matsuyama Medical Center offers AI-assisted remote diagnostics, helping detect conditions such as diabetic retinopathy early. Also, mobile telehealth units are being deployed to underserved areas, ensuring elderly residents receive timely healthcare without needing to travel long distances.
Top Companies Leading in the Japan Telemedicine Industry
Japan is strengthening its position in digital healthcare, with the August 2024 Japan-ASEAN agreement advancing telemedicine, cybersecurity, and medical data integration. This initiative improves cross-border healthcare access and accelerates telehealth adoption. The report provides a detailed competitive analysis, covering industry structure, positioning major players, and company evaluations. It also includes in-depth profiles of major companies driving Japan’s digital health expansion, positioning the country as a leader in telemedicine and regulatory advancements in the region.
Japan Telemedicine Market Segmentation Coverage
- On the basis of the component, the market has been bifurcated into product (hardware, software, and others), and services (tele-consulting, tele-monitoring, and tele-education). These solutions enhance healthcare accessibility, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes by enabling real-time interaction between patients and healthcare professionals through secure digital channels.
- Based on the modality, the market is categorized into real-time, store and forward, and others. Real-time telemedicine enables immediate consultations via video conferencing, while store-and-forward technology facilitates data sharing for later evaluation. Meanwhile, other approaches, such as remote monitoring, track patient vitals continuously, enhancing chronic disease management.
- On the basis of the delivery mode, the market has been divided into web/mobile (audio/text-based and visualized) and call centers. Web and mobile applications streamline telemedicine by offering virtual consultations, appointment scheduling, and electronic prescriptions. In contrast, call centers support telehealth services by providing triage, medical advice, and emergency response.
- Based on the facility, the market is categorized into tele-hospital and tele-home. Tele-hospital services connect specialists with hospitals for remote consultations, second opinions, and surgical guidance. At the same time, tele-home solutions allow patients to receive virtual care, chronic disease management, and post-discharge support from their homes.
- On the basis of the application, the market has been divided into teledermatology, teleradiology, telepsychiatry, telepathology, telecardiology, and others. Teledermatology enables remote skin condition assessments, while teleradiology facilitates digital imaging review by off-site radiologists. On the contrary, telepsychiatry provides mental health consultations, telepathology supports pathology slide analysis, telecardiology allows cardiac monitoring, and other telemedicine specialties enhance medical expertise accessibility.
- Based on the end-user, the market has been divided into providers, payers, patients, and others. Telemedicine involves providers delivering remote care, payers covering virtual health services, and patients accessing medical support conveniently. Meanwhile, others contribute to the ecosystem, ensuring secure, efficient, and compliant digital healthcare solutions.
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 5.2 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 20 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 16.2% |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered |
|
| Modalities Covered | Real-Time, Store and Forward, Others |
| Delivery Modes Covered |
|
| Facilities Covered | Tele-hospital, Tele-home |
| Applications Covered | Teledermatology, Teleradiology, Telepsychiatry, Telepathology, Telecardiology, Others |
| End Users Covered | Providers, Payers, Patients, Others |
| Regions Covered | Kanto Region, Kinki Region, Central/Chubu Region, Kyushu-Okinawa Region, Tohoku Region, Chugoku Region, Hokkaido Region, Shikoku Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Browse IMARC Related Reports on Telemedicine Market:
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.

 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure




.webp)




.webp)












