
Philippines Insurance Market Size, Share, Trends, and Forecast by Type and Region, 2026-2034
Philippines Insurance Market Size and Share:
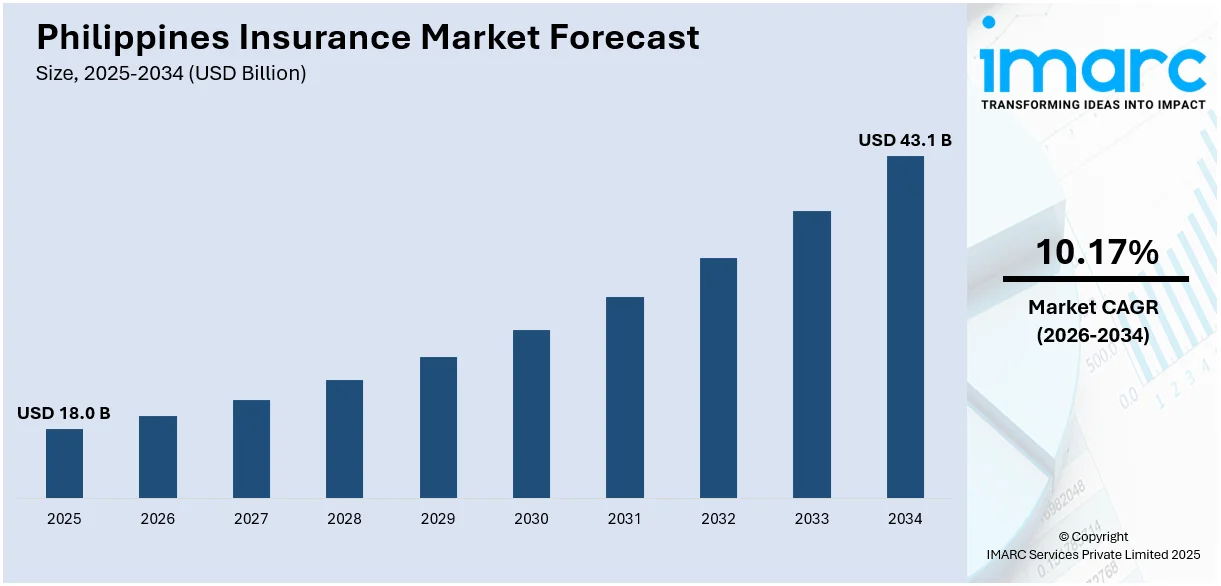
The Philippines insurance market size reached USD 18.0 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 43.1 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 10.17% during 2026-2034. The market is expanding due to the rising economic growth, increasing disposable incomes, rapid digital transformation, heightened awareness of health and life protection, and the imposition of supportive regulations.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 18.0 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 43.1 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 10.17% |
Key Trends of Philippines Insurance Market:
Increasing Economic Growth and Rising Disposable Income
Country’s consistent economic growth is one of the major influential factors underlying the growth of insurance market in the Philippines. According to industry reports, for 2023, the domestic productivity growth rate of the country exceeded expectation with a 5.6% growth, which is beyond earlier projections ranging from 5 to 6.3 percent. Moreover, the growing middle class and rising disposable incomes that encourage individuals and families to allocate funds toward insurance products, is creating a positive outlook for the market. In 2023, the country witnessed a 3.7% rise in per capita disposable income. This economic progress has led to an increase in financial literacy and awareness about the importance of insurance as a tool for risk management and financial security.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Growing Digital Transformation and Rapid Technological Advancements
Advancing technologies that increase access and personalization of insurance products will in fact give a favorable outlook to the marketplace. The introduction of insurtech solutions which help insurers to cover underserved areas using a digital platform will also drive market growth. This will be supplemented by the increasing use of mobile applications, online portals, and artificial intelligence (AI)-based customer service to facilitate purchases and management of insurance policies. For instance, in January 2024, Manulife Philippines revealed the growth of its digital initiatives to satisfy the increasing need for insurance and investment offerings. Industry reports indicate that 82% of Filipinos utilize finance apps for making cashless transactions and investments. Manulife Philippines has launched various digital services aimed at streamlining the purchasing of insurance and the processing of claims for their clients. They are making use of platforms such as Manulife Online that allow its users to purchase affordable insurance products online at their own convenience.
Rising Awareness about Health and Life Protection
The increasing awareness of the need for health and life insurance among individuals is another major factor boosting the Philippines insurance market share. Along with this, the rising healthcare crisis that underscores the importance of financial preparedness for medical emergencies is fueling the market growth. As per an industry survey, 78% of Filipinos agreed that increasing their insurance coverage and benefits is essential for future financial well-being. Along with this, the introduction of various government programs and partnerships with private insurers to help increase awareness about the benefits of insurance coverage is fostering market growth.
Growth Drivers of Philippines Insurance Market:
Regulatory Reforms Supporting Market Expansion
The Insurance Commission of the Philippines has introduced forward-looking reforms aimed at strengthening and modernizing the insurance sector. Updated risk-based capital frameworks have improved financial stability, while regulatory clarity around microinsurance licensing has enabled smaller providers to enter the market more easily. These changes have not only enhanced transparency and compliance but also attracted new investors and encouraged innovation in product design. Moreover, simplified policy issuance and digital onboarding processes—promoted under these regulatory updates—have made it easier for insurers to scale outreach. These reforms align with the country’s broader financial inclusion goals and have led to a more competitive and inclusive insurance environment. As a result, both local and foreign players are now more confident in expanding their operations within the Philippines.
Financial Inclusion and Bancassurance Expansion
Financial inclusion initiatives have significantly widened the insurance market in the Philippines by making products more accessible to underserved populations. One of the key drivers is the growing reach of bancassurance, where insurance policies are offered through banks and credit cooperatives. This channel has proven effective in building trust and improving financial literacy among rural and low-income communities. Additionally, partnerships between insurers and digital financial service providers—such as mobile wallets and fintech platforms—are helping bridge access gaps by enabling simple, paperless policy issuance and premium payments. These innovations are especially critical for reaching unbanked individuals. The ease of distribution and lower acquisition costs through these channels are expanding insurance penetration in remote regions, making financial protection more attainable for millions of Filipinos.
Public-Private Partnerships in Social Protection
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) have emerged as a vital mechanism for expanding insurance coverage to vulnerable and low-income groups in the Philippines, which is driving the Philippines insurance market demand. The government, in collaboration with private insurers, has launched programs targeting critical needs such as agricultural risk insurance, disaster resilience, and basic healthcare coverage. For example, initiatives that provide crop insurance to farmers or health benefits to informal workers demonstrate the effectiveness of combining government subsidies with private-sector efficiency. These partnerships not only improve social safety nets but also foster trust in the insurance system. Moreover, they help insurers gather data and gain insights into underserved populations, enabling the design of more relevant, affordable products. As these collaborations mature, they are expected to play an increasingly strategic role in broadening market reach and impact.
Opportunities of Philippines Insurance Market:
Growth of Climate and Disaster Risk Insurance
The Philippines ranks among the most disaster-prone countries globally, frequently experiencing typhoons, floods, earthquakes, and other natural calamities. This vulnerability is driving demand for climate and disaster risk insurance, especially among small businesses, farmers, and communities in high-risk zones. Insurers have the opportunity to develop innovative, parametric, or event-based policies that offer faster payouts with simpler claim processes. Climate-smart insurance products can be bundled with agricultural loans or government aid, increasing uptake among low-income groups. As climate change intensifies the frequency and severity of natural disasters, insurers who proactively address this risk can gain market leadership. Additionally, public-private collaborations in climate resilience planning can further accelerate adoption and help insurers tailor policies for long-term risk mitigation in vulnerable sectors.
Youth and Millennial Market Engagement
The Philippines has a young and highly digital population, with millennials and Gen Z comprising a significant share of the workforce and consumer base. This tech-savvy demographic prefers convenient, on-demand services—including insurance products that can be accessed via smartphones. Insurers have a growing opportunity to design mobile-first, customizable policies tailored to the lifestyle preferences of younger consumers. Popular categories include gadget protection, travel insurance, wellness packages, and flexible health plans with subscription-style premiums. These users value transparency, affordability, and seamless digital interactions, making user-friendly apps and chatbots essential. By leveraging social media marketing and influencer collaborations, insurers can engage this segment effectively. Capturing the loyalty of this demographic can result in long-term client relationships and stronger brand equity in the digital age.
Untapped MSME and Informal Sector Coverage
The Philippines has a vast network of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs), as well as a large informal workforce that remains largely uninsured. According to the Philippines insurance market analysis, these segments face risks ranging from property damage and theft to illness and income disruption, yet often lack access to affordable, relevant insurance products. This creates a major opportunity for insurers to develop microinsurance and group policies specifically tailored to the cash flow and risk profiles of these sectors. Bundling coverage with business loans, digital payment services, or government support programs can further ease adoption. By providing low-cost, simplified plans with minimal paperwork, insurers can address both financial and trust barriers. Expanding coverage to these underserved groups not only boosts market penetration but also strengthens the economic resilience of local communities.
Challenges of Philippines Insurance Market:
Low Insurance Penetration and Awareness in Rural Areas
While insurance adoption in urban centers has steadily increased, rural areas in the Philippines continue to face significant barriers. Limited infrastructure, low financial literacy, and cultural hesitation toward formal insurance systems hinder widespread penetration. Many rural residents are unaware of the benefits insurance can provide, or they associate it with long, complex processes. Moreover, a lack of physical branches and agent representation in remote areas limits product accessibility. To close this gap, insurers must invest in community-level education campaigns and build trust through local partnerships and microagents. Leveraging mobile technology and simplified enrollment processes can also improve access. Expanding into rural areas is essential not just for market growth but also for strengthening financial protection among the country’s most vulnerable populations.
Affordability and Perceived Value Gaps
One of the biggest challenges in the Philippine insurance market is making insurance products feel both affordable and worthwhile, especially to low-income households. For many, the concept of paying premiums without seeing immediate or tangible benefits makes insurance seem like a non-essential expenditure. In some cases, prior negative experiences—such as delayed claims processing or complex policy terms—have eroded consumer trust. Additionally, conventional insurance packages often fail to align with the irregular incomes of informal workers or the specific needs of rural communities. To address these concerns, insurers must design flexible, low-cost policies with transparent terms and quick, reliable claims processing. Building trust through financial literacy programs and community testimonials is also key to changing perceptions and encouraging broader adoption.
Operational and Underwriting Risks
Insurance providers in the Philippines face mounting operational and underwriting challenges due to environmental, economic, and data-related factors. The country’s frequent natural disasters—including typhoons, earthquakes, and floods—make risk assessment and claims forecasting more difficult and costly. Rising healthcare inflation further complicates pricing for health and life insurance products, increasing the likelihood of claims exceeding premiums. Additionally, many insurers struggle with limited access to accurate data for underwriting, particularly in informal or rural markets. This leads to risk miscalculations and impacts profitability. For smaller insurers or new entrants, these challenges can be particularly overwhelming. Addressing these issues will require investment in predictive analytics, better data infrastructure, and collaborative risk-sharing mechanisms to improve accuracy and resilience across the insurance value chain.
Philippines Insurance Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on type.
Type Insights:
Access the Comprehensive Market Breakdown Request Sample
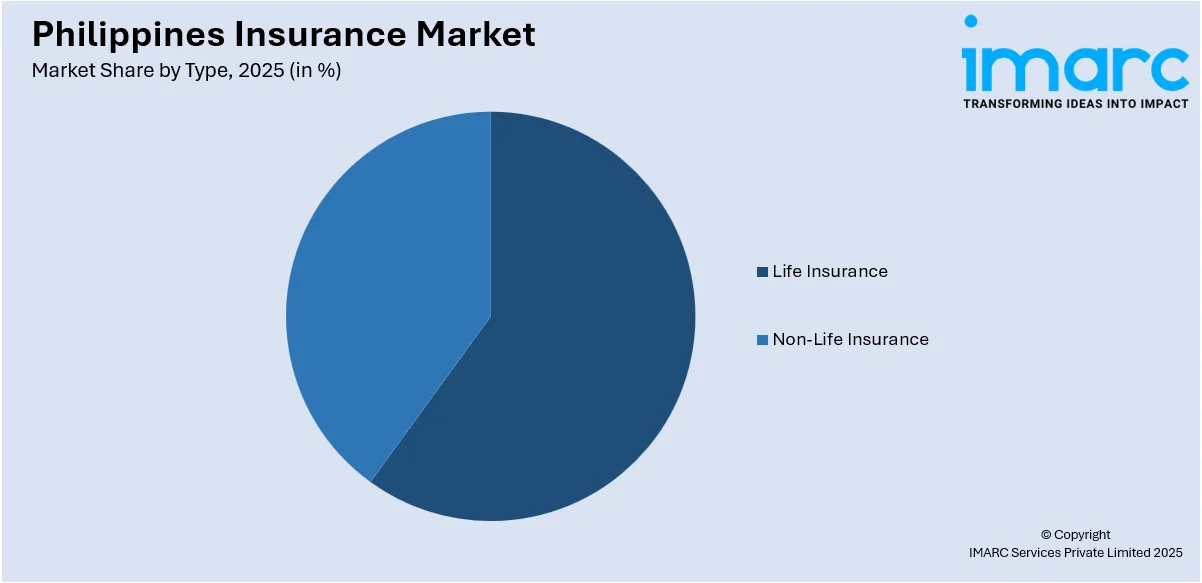
- Life Insurance
- Non-Life Insurance
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes life insurance and non-life insurance.
Regional Insights:
- Luzon
- Visayas
- Mindanao
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Philippines Insurance Market News:
- In May 2024, International Finance Corporation (IFC) announced that it is investing up to $10 million by joining a consortium of investors led by Triple P Capital to acquire an 85% stake in MAA General Assurance Philippines Inc. (MAAGAP). This partnership will boost non-life insurance coverage for small businesses and vulnerable households in the Philippines.
- In January 2024, Manulife Philippines announced a partnership with Forticare Health Systems International, Inc., one of the foremost health maintenance organizations in the country, to make Manulife the exclusive underwriter of group life insurance together with the current HMO products of Forticare.
Philippines Insurance Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Life Insurance, Non-Life Insurance |
| Regions Covered | Luzon, Visayas, Mindanao |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Philippines insurance market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Philippines insurance market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Philippines insurance industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The insurance market in the Philippines was valued at USD 18.0 Billion in 2025.
The Philippines insurance market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 10.17% during 2026-2034.
The Philippines insurance market is projected to reach a value of USD 43.1 Billion by 2034.
The Philippines insurance market is evolving through digitalization, with mobile platforms and AI enhancing customer engagement. Additionally, ESG-aligned insurance products and growing interest in cyber and health coverage reflect shifting consumer priorities and emerging risk profiles.
Economic development, expanding middle-class income, and increased financial literacy are driving insurance demand in the Philippines. Post-pandemic health awareness has boosted life and medical coverage uptake. Government support, regulatory reforms, and digital distribution channels, including insurtech partnerships, are further enabling market expansion across both urban and underserved rural populations.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












