
Qatar Advanced Industries Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Industry Segment, Business Model, Activity Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar Advanced Industries Market Summary:
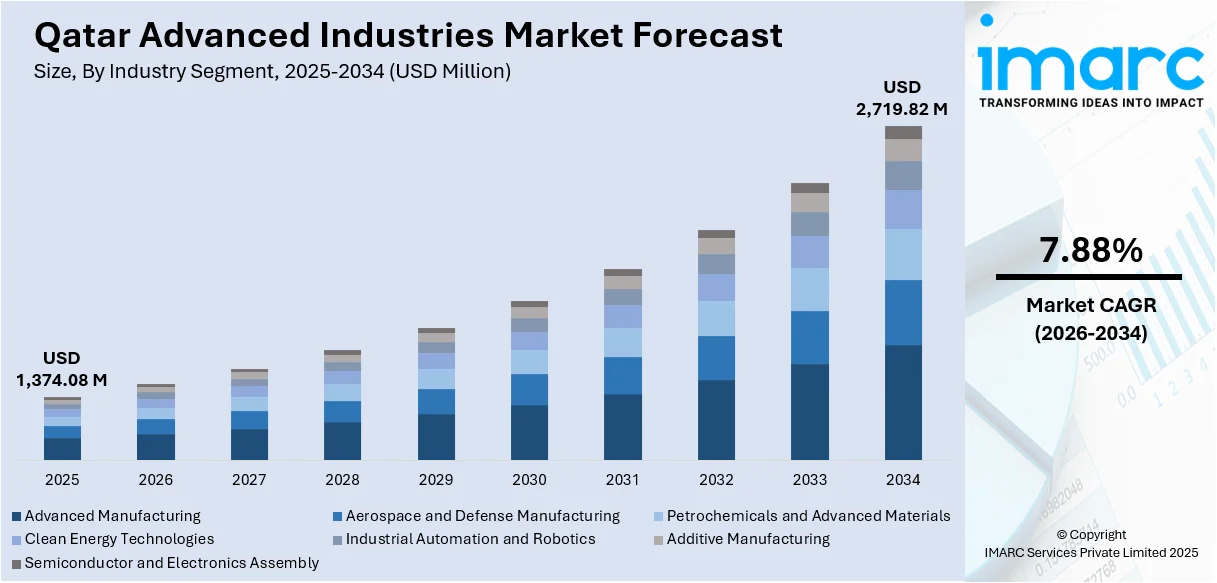
The Qatar advanced industries market size reached USD 1,374.08 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 2,719.82 Million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.88% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by the government's comprehensive industrial diversification strategy through the Qatar National Manufacturing Strategy 2024-2030, which emphasizes technological innovation and Industry 4.0 adoption. Significant investments in petrochemicals infrastructure, including the USD 6 Billion Ras Laffan Petrochemical Complex, are also expanding production capabilities and supporting export growth. Rapid integration of smart manufacturing technologies and additive manufacturing capabilities is further enhancing the Qatar advanced industries market share.
|
Particulars |
Details |
|
Market Size (2025) |
USD 1,374.08 Million |
|
Forecast (2034) |
USD 2,719.82 Million |
|
CAGR (2026-2034) |
7.88% |
|
Key Segments |
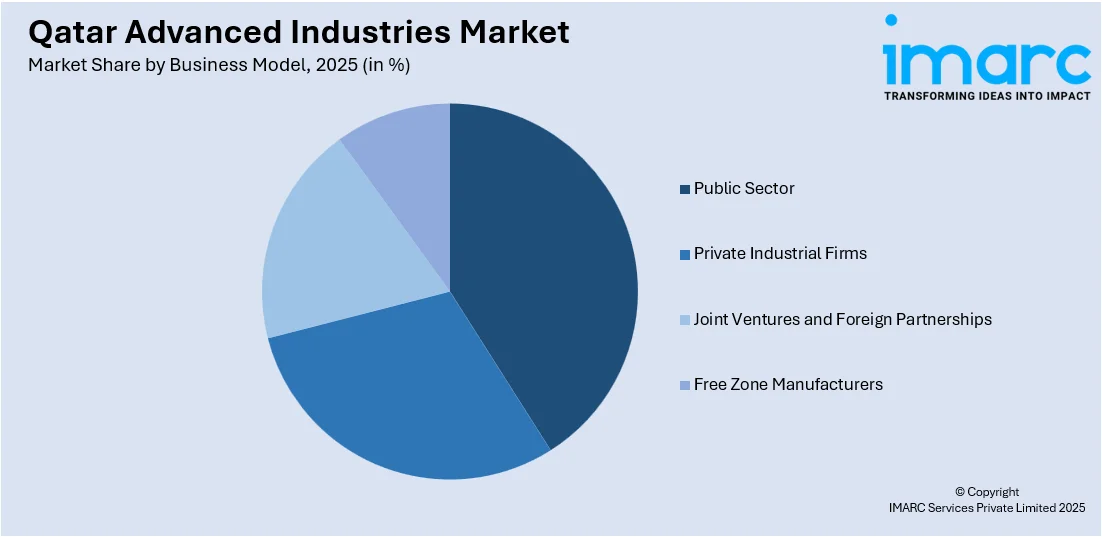
Industry Segment (Advanced Manufacturing, Aerospace and Defense Manufacturing, Petrochemicals and Advanced Materials, Clean Energy Technologies, Industrial Automation and Robotics, Additive Manufacturing, Semiconductor and Electronics Assembly), Business Model (Public Sector, Private Industrial Firms, Joint Ventures and Foreign Partnerships, Free Zone Manufacturers), Activity Type (Research and Development (R&D), Manufacturing and Production, System Integration and Advanced Services) |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
Qatar Advanced Industries Market Outlook (2026-2034):
The Qatar advanced industries market is poised for robust expansion, driven by the government's strategic focus on economic diversification beyond hydrocarbons through the Third National Development Strategy. Significant investments in Industry 4.0 technologies, including AI-powered automation and digital manufacturing platforms, will enhance operational efficiency and competitiveness. The development of world-class research facilities such as the GORD 3D Center of Excellence and partnerships with global technology leaders will foster innovation ecosystems. Furthermore, the expansion of Qatar Free Zones with attractive incentives including tax exemptions and 100% foreign ownership will continue attracting international manufacturers seeking to serve EMEA markets.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Impact of AI:
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally reshaping Qatar's advanced industries through multiple transformative pathways. With AI-driven automation improving supply chain management, quality assurance, and production processes, the government's USD 2.5 Billion AI incentive package, which was unveiled in 2024, is hastening adoption across manufacturing sectors. To reduce downtime and increase equipment efficiency, smart factories are using AI-powered predictive maintenance solutions. The market for AI industrial robotics is expected to rise at a compound yearly growth rate of more than 24 percent, from USD 7.86 Million in 2024 to USD 29.37 Million by 2030. Additionally, AI applications in digital twin technology and advanced analytics are enabling manufacturers to simulate operations and optimize resource allocation before physical implementation.
Market Dynamics:
Key Market Trends & Growth Drivers:
Strategic Government Investment and Industrial Policy Framework
Qatar's advanced industries sector is experiencing unprecedented momentum fueled by comprehensive government strategies aimed at transforming the nation into a regional manufacturing powerhouse. The Qatar National Manufacturing Strategy 2024-2030 represents a landmark policy initiative encompassing 15 key programs with 60 distinct projects designed to elevate strategic industries including aluminum processing, advanced plastics, specialty pharmaceuticals, and precision medical devices. This ambitious framework establishes concrete targets of increasing the manufacturing sector's value-added contribution to QAR 70.5 billion while simultaneously boosting non-hydrocarbon exports to QAR 49.1 billion by the decade's end. The strategy explicitly prioritizes attracting QAR 2.75 billion in annual industrial investments, demonstrating the government's commitment to creating an ecosystem conducive to advanced manufacturing. In January 2025, Qatar officially launched the Ministry of Commerce and Industry Strategy 2024-30, which builds on the manufacturing strategy and targets 3.4 percent annual growth in non-hydrocarbons GDP alongside up to USD 100 Billion in foreign direct investment by 2030. The Third National Development Strategy identifies chemicals and low-carbon metals as priority growth areas, aligning industrial policy with global sustainability trends. Government incentives through programs like the Advanced Industries Package target technology-driven sectors including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, automotive components, and electronics manufacturing, providing tax exemptions, subsidized utilities, and expedited licensing to attract international players. This coordinated policy approach, combining financial support, regulatory streamlining, and strategic sector targeting, creates powerful tailwinds for the Qatar advanced industries market growth.
Accelerated Industry 4.0 Implementation and Smart Manufacturing Adoption
With Industry 4.0 technology becoming deeply ingrained in manufacturing operations across the nation, Qatar has established itself as a leader in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Acknowledging that digital transformation is critical for global competitiveness, the Third National Development Strategy specifically encourages the adoption of Industry 4.0 methods and circular economy concepts across all manufacturing sub-sectors. This dedication is demonstrated by large investments in Internet of Things sensor networks, automation systems, industrial robotics, AI applications, and integrated digital platforms that allow for real-time production monitoring and optimization. The establishment of Factory One in collaboration with McKinsey & Company exemplifies this commitment, providing manufacturers with access to world-class lean operations expertise and hands-on training in advanced production methodologies. In March 2024, the Gulf Organisation for Research and Development officially launched the GORD 3D Center of Excellence at the Doha International Maritime Defence Exhibition and Conference. This state-of-the-art facility serves vital industries like aerospace, energy, defense, and life sciences with advanced additive manufacturing technologies like bound metal deposition, metal powder bed fusion, selective laser sintering, and large-format robotic arm extrusion systems. The facility is a symbol of Qatar's resolve to become a regional leader in cutting-edge production technologies. An whole display section of Project Qatar 2025 was devoted to smart manufacturing, showcasing advancements in robotics, automation, AI-powered quality control systems, IoT-enabled smart logistics, sustainable production techniques, and all-inclusive digital industrial transformation solutions. The government's willingness to invest in capability-building programs, research infrastructure, and technology partnerships demonstrates recognition that smart manufacturing excellence requires systematic ecosystem development rather than isolated initiatives.
Expansion of Petrochemicals and Advanced Materials Production Infrastructure
Qatar's petrochemicals and advanced materials sector is undergoing transformational expansion driven by strategic investments leveraging the nation's abundant natural gas resources and global market positioning. The Ras Laffan Petrochemical Complex, a massive USD 6 Billion joint venture between QatarEnergy (70% equity) and Chevron Phillips Chemical (30% equity), is the most notable development. Construction on the complex began in February 2024 after His Highness Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani laid the foundation stone. This massive plant will have an ethane cracker that can produce 2.1 million tons of ethylene annually, making it the biggest ethane cracker in the Middle East and one of the biggest in the world. Additionally, the complex includes two high-density polyethylene derivative units with a combined yearly production capacity of 1.7 million tons, which increases Qatar's capacity to produce polyethylene by around 50%. The plant will significantly improve Qatar's standing in international petrochemical markets when it is operational in 2026, increasing the country's overall petrochemical production capacity to almost 14 million tons per year. The project employs modern energy-efficient technologies and utilizes ethane feedstock, which, combined with other operational measures, is expected to yield lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to similar facilities worldwide. QatarEnergy's complementary investments include the Golden Triangle Polymers Plant in Texas, a parallel USD 8.5 Billion venture with Chevron Phillips Chemical that further demonstrates Qatar's commitment to integrated global petrochemicals value chains. These massive infrastructure projects position Qatar to capitalize on growing global demand for polyethylene products used in packaging, durable goods manufacturing, and numerous industrial applications, while creating substantial opportunities for downstream industries and supporting economic diversification objectives aligned with Qatar National Vision 2030.
Key Market Challenges:
Skilled Workforce Development and Persistent Talent Gaps
Despite Qatar's ambitious industrial transformation agenda, the development of a sufficiently skilled workforce capable of operating and innovating within advanced manufacturing environments remains a formidable challenge. The quick uptake of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as complex automation systems, robotics integration, AI applications, and data analytics platforms, necessitates technical skills beyond the capability of the current workforce. Government programs like QDB Jahiz, which offers industrial workshops and training programs for entrepreneurs, and Factory One, which was established in collaboration with McKinsey & Company to provide world-class lean operations training, have established significant capability-building infrastructure, but they have not yet reached the scale necessary to completely close current skills gaps. The cybersecurity domain exemplifies this challenge particularly acutely, with Qatar's National Cyber Security Agency establishing the National Cyber Security Academy in 2024 specifically to address critical workforce deficiencies in this strategic sector. The academy aims to serve as a regional training hub, acknowledging that talent shortages extend beyond Qatar's borders throughout the Gulf Cooperation Council region. Advanced manufacturing requires multidisciplinary expertise spanning mechanical engineering, software development, data science, materials science, and systems integration, which are competencies that cannot be developed overnight through short-term training interventions. The challenge is compounded by Qatar's relatively small national population and historical reliance on expatriate labor, which creates uncertainties around workforce stability and knowledge retention. Additionally, the pace of technological change means that even recently trained workers require continuous upskilling to remain current with evolving manufacturing methodologies and digital tools. Addressing this challenge demands sustained investment in education system transformation, partnerships with international universities and technical institutions, structured apprenticeship programs linking academic preparation with industrial experience, and potentially immigration policies that attract and retain highly skilled technical professionals from global talent markets.
Dependence on Global Supply Chains for Critical Inputs and Technologies
Qatar's advanced industries, despite ambitious localization objectives, remain substantially dependent on international supply chains for critical manufacturing inputs, specialized equipment, and cutting-edge technologies that cannot yet be produced domestically. This dependency creates multiple vulnerabilities that constrain industrial resilience and strategic autonomy. The semiconductor sector provides a particularly instructive example: while semiconductors are essential for virtually all advanced manufacturing applications including automation systems, robotics, AI infrastructure, and smart manufacturing platforms, Qatar has not developed domestic semiconductor fabrication capabilities due to the enormous capital requirements, technical complexity, and established global supply chain structures that favor concentrated production in specialized regions. Instead, Qatar has pursued strategies to secure reliable access to cutting-edge chips through partnerships with leading international suppliers, but this approach leaves the market exposed to geopolitical tensions, export controls, and supply disruptions like those experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic when semiconductor shortages cascaded through global manufacturing systems. Similar dependencies exist across numerous other domains including specialized manufacturing machinery typically sourced from Germany, Japan, and other industrialized nations; advanced materials and specialty chemicals that require sophisticated production processes; precision components and sub-assemblies integral to complex products; and proprietary software platforms that control modern manufacturing operations. While Qatar's strategic partnerships with international technology leaders including joint ventures, licensing agreements, and technology transfer arrangements provide valuable access to capabilities and knowledge, these relationships inherently limit strategic autonomy and expose Qatar to risks of technological dependencies. Geopolitical shifts, trade policy changes, or deteriorating international relationships could potentially disrupt access to essential inputs and technologies, undermining industrial operations and competitiveness.
Intense Regional and Global Competition for Manufacturing Investment
Qatar's advanced industries face formidable competition from well-established manufacturing centers throughout the Gulf Cooperation Council region, broader Middle East, and Asia that possess significant structural advantages accumulated over decades of industrial development. Countries such as the United Arab Emirates, particularly Abu Dhabi and Dubai, have built sophisticated manufacturing ecosystems with extensive supplier networks, mature logistics infrastructure, large pools of experienced technical workers, and proven track records attracting international manufacturers. Saudi Arabia's massive Vision 2030 initiative dedicates enormous financial resources toward industrial development with scale advantages Qatar cannot match given its smaller economy and population. Asian manufacturing powerhouses including China, Vietnam, Thailand, and Malaysia offer dramatically lower labor costs, established component supplier clusters that reduce production costs and lead times, deep manufacturing expertise spanning multiple industries, and government policies explicitly designed to maintain cost competitiveness. These structural advantages create substantial barriers for Qatar's efforts to attract and retain international manufacturers despite the incentives offered through Qatar Free Zones including 100% foreign ownership, tax exemptions, subsidized utilities, and streamlined regulatory processes. Competing jurisdictions continuously enhance their value propositions through infrastructure investments, regulatory reforms, and targeted incentive programs, creating a dynamic competitive environment where Qatar must constantly demonstrate differentiated value. The challenge extends beyond initial investment attraction to long-term retention, as manufacturers continuously evaluate production location strategies based on evolving cost structures, market access considerations, supply chain optimization, and geopolitical risk assessments. Qatar's relatively small domestic market limits opportunities for import substitution manufacturing, meaning industrial facilities must primarily target export markets where they compete directly with producers in lower-cost jurisdictions. Overcoming these competitive disadvantages requires Qatar to leverage distinctive advantages including strategic geographic positioning between European, African, and Asian markets; world-class logistics infrastructure anchored by Hamad International Airport and Hamad Port; abundant energy resources enabling competitive utility pricing; political stability and business-friendly governance; and increasingly, specialized capabilities in high-value niches like additive manufacturing, advanced petrochemicals, and technology-intensive sectors where cost advantages matter less than innovation, quality, and technical expertise.
Qatar Advanced Industries Market Report Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Qatar advanced industries market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on industry segment, business model, and activity type.
Analysis by Industry Segment:
- Advanced Manufacturing
- Aerospace and Defense Manufacturing
- Petrochemicals and Advanced Materials
- Clean Energy Technologies
- Industrial Automation and Robotics
- Additive Manufacturing
- Semiconductor and Electronics Assembly
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the industry segment. This includes advanced manufacturing, aerospace and defense manufacturing, petrochemicals and advanced materials, clean energy technologies, industrial automation and robotics, additive manufacturing, and semiconductor and electronics assembly.
Analysis by Business Model:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Public Sector
- Private Industrial Firms
- Joint Ventures and Foreign Partnerships
- Free Zone Manufacturers
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the business model have also been provided in the report. This includes public sector, private industrial firms, joint ventures and foreign partnerships, and free zone manufacturers.
Analysis by Activity Type:
- Research and Development (R&D)
- Manufacturing and Production
- System Integration and Advanced Services
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the activity type. This includes research and development (R&D), manufacturing and production, and system integration and advanced services.
Analysis by Region:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar advanced industries market exhibits a moderately concentrated competitive structure characterized by strategic collaboration between government-backed entities, multinational corporations, and emerging local enterprises. Competition dynamics vary significantly across industry segments, with petrochemicals dominated by state-owned Qatar Energy and its international joint venture partners, while sectors like additive manufacturing and smart technologies feature more diverse participation from specialized technology providers and innovative startups. The market increasingly emphasizes technology transfer partnerships and joint ventures that combine international expertise with local market knowledge and access to government support mechanisms. Qatar Free Zones play a catalytic role in attracting foreign manufacturers by offering 100% foreign ownership, tax exemptions, and proximity to world-class logistics infrastructure. Competitive positioning increasingly depends on technological capabilities, particularly Industry 4.0 readiness, sustainability credentials, and ability to meet international quality standards. The government's role as both market participant through state-owned enterprises and ecosystem enabler through industrial policy creates unique competitive dynamics where public-private collaboration often supersedes traditional competitive rivalries in advancing national strategic objectives.
Qatar Advanced Industries Industry Latest Developments:
- November 2024: The US-based leader in advanced battery technology and manufacturing, Inventus Power, inaugurated its Technical Center EMEA and manufacturing facility at Ras Bufontas in Qatar Free Zones. The facility acts as a center of excellence for the organization in digitalization, smart IoT batteries, energy storage systems, and lead-acid battery conversion, while also offering complete manufacturing capabilities to assist military, government, security, and commercial clients throughout the European, Middle Eastern, and African markets.
- May 2025: Project Qatar 2025 was launched at the Doha Exhibition and Convention Center under the theme "Innovation & Sustainability: Qatar's Path to 2030" with participation from 200 local and international companies. The event featured a dedicated Qatar Smart Manufacturing Exhibition showcasing cutting-edge Industry 4.0 technologies including robotics, automation, Internet of Things applications, artificial intelligence, smart logistics, and sustainable production systems, which further support the Qatar National Manufacturing Strategy 2024-2030 aimed at localizing manufacturing and attracting global industrial partnerships.
- February 2025: Qatar formally joined the Integrated Industrial Partnership for Sustainable Economic Development during a meeting held in Egypt. The meeting welcomed Qatar's accession as added value owing to the country's competitive advantages, positive economic prospects, and advanced infrastructure. Multiple agreements were ratified between private sector companies from member states across sectors including agriculture, food, fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, textiles, chemicals, plastics, manufacturing products, and metals.
Qatar Advanced Industries Market Report Coverage:
|
Report Features |
Details |
|
Base Year of the Analysis |
2025 |
|
Historical Period |
2020-2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
|
Units |
Million USD |
|
Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
|
Industry Segments Covered |
Advanced Manufacturing, Aerospace and Defense Manufacturing, Petrochemicals and Advanced Materials, Clean Energy Technologies, Industrial Automation and Robotics, Additive Manufacturing, Semiconductor and Electronics Assembly |
|
Business Models Covered |
Public Sector, Private Industrial Firms, Joint Ventures and Foreign Partnerships, Free Zone Manufacturers |
|
Activity Types Covered |
Research and Development (R&D), Manufacturing and Production, System Integration and Advanced Services |
|
Regions Covered |
Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
|
Customization Scope |
10% Free Customization |
|
Post-Sale Analyst Support |
10-12 Weeks |
|
Delivery Format |
PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Qatar advanced industries market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar advanced industries market on the basis of industry segment?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar advanced industries market on the basis of business model?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar advanced industries market on the basis of activity type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar advanced industries market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Qatar advanced industries market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Qatar advanced industries market?
- What is the structure of the Qatar advanced industries market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Qatar advanced industries market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC's industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Qatar advanced industries market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Qatar advanced industries market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Qatar advanced industries industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












