
Qatar Distributed Solar Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Application, Ownership Type, End User, Financing Option, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar Distributed Solar Market Summary:
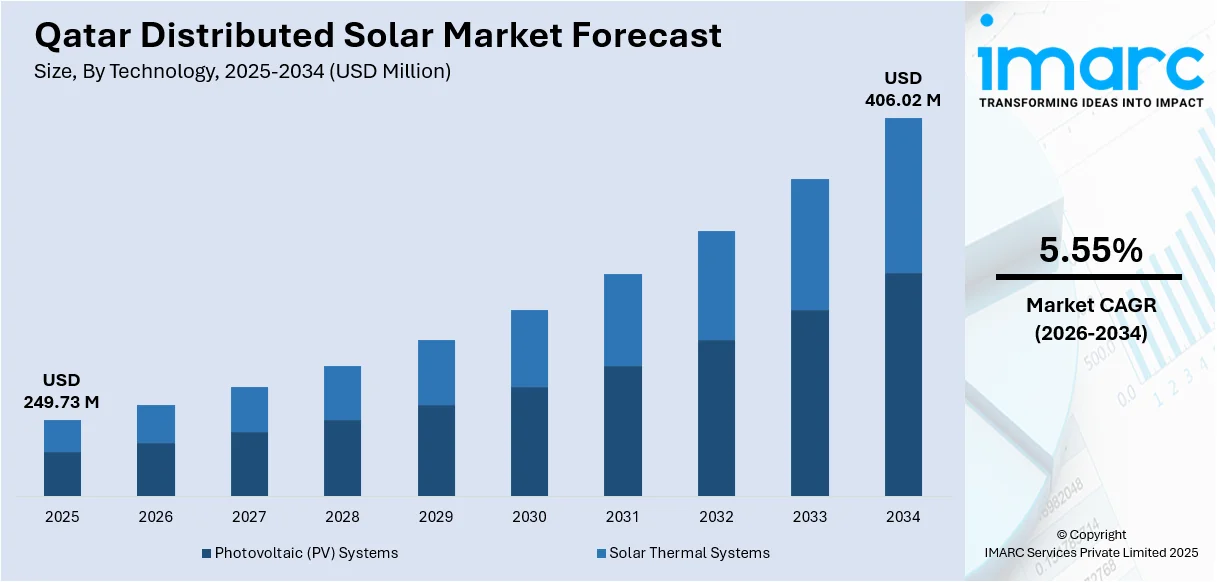
The Qatar distributed solar market size reached USD 249.73 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 406.02 Million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 5.55% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by Qatar's ambitious renewable energy targets under Qatar National Vision 2030, which mandates a significant increase in solar power generation capacity. Additionally, favorable government policies, including net metering regulations and financial incentives for solar installations, are encouraging residential, commercial, and industrial adoption. The growing awareness of environmental sustainability, coupled with declining solar technology costs and Qatar's abundant solar irradiance, is further expanding the Qatar distributed solar market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 249.73 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 406.02 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 5.55% |
| Key Segments | Technology (Photovoltaic (PV) Systems, Solar Thermal Systems), Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Utility-scale), Ownership Type (Owner-operated, Third-party Ownership, Community Solar Programs), End User (Residential Users, Commercial Businesses, Government Institutions, Non-profit Organizations), Financing Option (Cash Purchases, Loans and Financing Models, Leasing Options, Government Incentives and Grants) |
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
Qatar Distributed Solar Market Outlook (2026-2034):
The Qatar distributed solar market is poised for substantial growth as the nation intensifies efforts to diversify its energy portfolio beyond fossil fuels. Government-backed initiatives, including substantial investments in solar infrastructure and regulatory frameworks supporting distributed generation, will drive market expansion. Rising electricity demand from rapid urbanization and mega-projects related to economic diversification is creating opportunities for decentralized solar solutions. Additionally, technological advancements in photovoltaic efficiency and energy storage systems will enhance the economic viability of distributed solar installations across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors throughout the forecast period.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Impact of AI:
Artificial intelligence is beginning to optimize distributed solar operations in Qatar through predictive maintenance algorithms that identify potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. AI-powered energy management systems are enabling better demand forecasting and grid integration, particularly important in Qatar's extreme climate conditions. Machine learning models are being deployed to optimize panel orientation and cleaning schedules based on dust accumulation patterns and weather data. As the technology matures, AI is expected to play an increasingly critical role in maximizing energy yield, managing battery storage systems, and facilitating virtual power plant operations across Qatar's distributed solar network.
Market Dynamics:
Key Market Trends & Growth Drivers:
National Renewable Energy Strategy and Policy Support
Qatar's commitment to renewable energy is anchored in its Qatar National Vision 2030 and the National Development Strategy, which establish clear targets for solar energy deployment as part of the country's economic diversification efforts. The government has implemented comprehensive regulatory frameworks, including net metering policies that allow distributed solar users to export excess electricity to the grid and receive credits, making installations financially attractive. Qatar General Electricity and Water Corporation (Kahramaa) has launched initiatives such as the Tarsheed program to promote energy efficiency and renewable energy adoption among residential and commercial consumers. The establishment of feed-in tariffs and power purchase agreements for distributed solar projects provides revenue certainty for investors and property owners. Additionally, streamlined permitting processes and technical standards for grid-connected solar systems have reduced bureaucratic barriers to entry. These policy measures are creating an enabling environment that encourages private sector participation and accelerates the Qatar distributed solar market growth.
Declining Technology Costs and Improved System Efficiency
The distributed solar market in Qatar is benefiting from global trends in photovoltaic technology advancement and cost reduction. The levelized cost of solar energy has decreased dramatically over the past decade, making distributed solar increasingly competitive with conventional electricity sources, even in a country with historically low utility rates. Improvements in solar panel efficiency, particularly high-efficiency monocrystalline modules that perform better in Qatar's high-temperature environment, are enabling greater energy production from limited rooftop space. The development of bifacial solar panels that capture reflected sunlight from Qatar's predominantly light-colored built environment further enhances energy yield. Advanced inverter technologies with smart grid capabilities are improving system reliability and enabling better integration with Qatar's electricity network. Additionally, declining costs of battery energy storage systems are making solar-plus-storage solutions economically viable, addressing the intermittency challenges of solar power and providing backup during peak demand periods. These technological improvements are reducing payback periods for distributed solar investments and attracting a broader range of adopters across residential, commercial, and industrial segments. In September 2024, Qatar-based Nebras Power partnered with international technology providers to deploy next-generation bifacial solar modules across multiple commercial installations in Doha, demonstrating performance improvements of up to twenty-eight percent compared to conventional panels in the local climate conditions.
Growing Environmental Awareness and Corporate Sustainability Commitments
Environmental consciousness is rising rapidly in Qatar, driven by government campaigns, educational initiatives, and increasing global attention to climate change issues. The country's hosting of major international events has heightened awareness of sustainability practices and green building standards among both public and private sectors. Commercial enterprises and industrial facilities are increasingly adopting distributed solar as part of corporate social responsibility strategies and sustainability reporting requirements. International companies operating in Qatar are implementing solar installations to meet parent company environmental targets and demonstrate leadership in renewable energy adoption. The Qatar Green Building Council has been promoting sustainable construction practices, including the integration of solar energy systems in new developments. Real estate developers are recognizing that buildings with solar installations command premium valuations and attract environmentally conscious tenants. Educational institutions and healthcare facilities are installing distributed solar systems as demonstration projects that showcase a commitment to sustainability while reducing operational costs. This cultural shift toward environmental stewardship is creating sustained demand for distributed solar solutions across multiple end-user segments.
Key Market Challenges:
Extreme Climate Conditions and Operational Constraints
Qatar's harsh desert climate presents significant challenges for distributed solar installations. Ambient temperatures regularly exceed 45 degrees Celsius during summer months, which substantially reduces photovoltaic panel efficiency and accelerates equipment degradation. The high-temperature environment increases thermal stress on electrical components, inverters, and mounting structures, potentially shortening system lifespan and increasing maintenance requirements. Frequent dust storms and persistent airborne particles accumulate on solar panels, reducing light transmission and energy output by up to forty percent if not regularly cleaned. However, water scarcity makes conventional panel cleaning costly and environmentally problematic, requiring innovative dry-cleaning solutions or automated robotic systems. The corrosive salt-laden air from the Arabian Gulf poses additional challenges, particularly for coastal installations, necessitating specialized protective coatings and corrosion-resistant materials. High humidity levels combined with temperature fluctuations create condensation issues that can damage electrical connections and reduce system reliability. These environmental factors increase both initial installation costs, due to the need for premium equipment and protective measures, and ongoing operational expenses for maintenance and cleaning, potentially extending payback periods and deterring some potential adopters from investing in distributed solar systems.
Limited Grid Infrastructure for Distributed Generation Integration
Qatar's electrical grid was historically designed for centralized power generation from large natural gas facilities rather than distributed renewable energy sources. The existing grid infrastructure lacks the advanced smart grid capabilities necessary for efficiently managing bidirectional power flows from numerous distributed solar installations. Grid stability concerns arise when significant amounts of solar generation are introduced, particularly during periods of low demand when excess solar power must be absorbed or curtailed. The absence of comprehensive energy storage infrastructure at the distribution level limits the ability to store excess solar generation for use during evening peak demand periods. Technical challenges related to voltage regulation, power quality, and frequency control become more complex as distributed solar penetration increases. Utility companies must invest substantially in grid modernization, including advanced metering infrastructure, distribution automation systems, and sophisticated forecasting tools to accommodate growing distributed solar capacity. The relatively slow pace of grid infrastructure upgrades compared to the accelerating interest in solar installations creates bottlenecks in interconnection approvals and may limit the number of systems that can be safely connected without grid reinforcement. These infrastructure constraints require coordinated planning and significant capital investment from utility companies and government entities to ensure the grid can support the anticipated growth in distributed solar deployment.
Economic Competitiveness with Subsidized Conventional Electricity
Qatar's electricity and water are heavily subsidized for citizens and residents, resulting in some of the lowest utility rates globally. For Qatari nationals, residential electricity costs are minimal, significantly reducing the economic incentive to invest in distributed solar systems despite declining technology costs. Even for commercial and industrial consumers, who pay higher rates than residential users, electricity prices remain below the global average due to Qatar's abundant natural gas resources and government energy subsidies. This pricing structure extends payback periods for solar investments and makes the financial case for distributed solar less compelling compared to countries with higher electricity rates. The opportunity cost of capital becomes particularly relevant when potential solar investors compare modest utility bill savings against alternative investment opportunities in Qatar's economy. Furthermore, the lack of time-of-use pricing that would reward solar generation during peak demand periods diminishes the value proposition of distributed solar systems. While environmental benefits and energy independence are important considerations, many potential adopters prioritize financial returns, and subsidized electricity rates create a significant barrier to market growth. Reforming energy subsidies to reflect true generation costs would dramatically improve the economics of distributed solar, but such policy changes face political and social challenges given the expectations of affordable energy among Qatar's population.
Qatar Distributed Solar Market Report Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Qatar distributed solar market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on technology, application, ownership type, end user, and financing option.
Analysis by Technology:
- Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
- Solar Thermal Systems
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology. This includes photovoltaic (PV) systems and solar thermal systems.
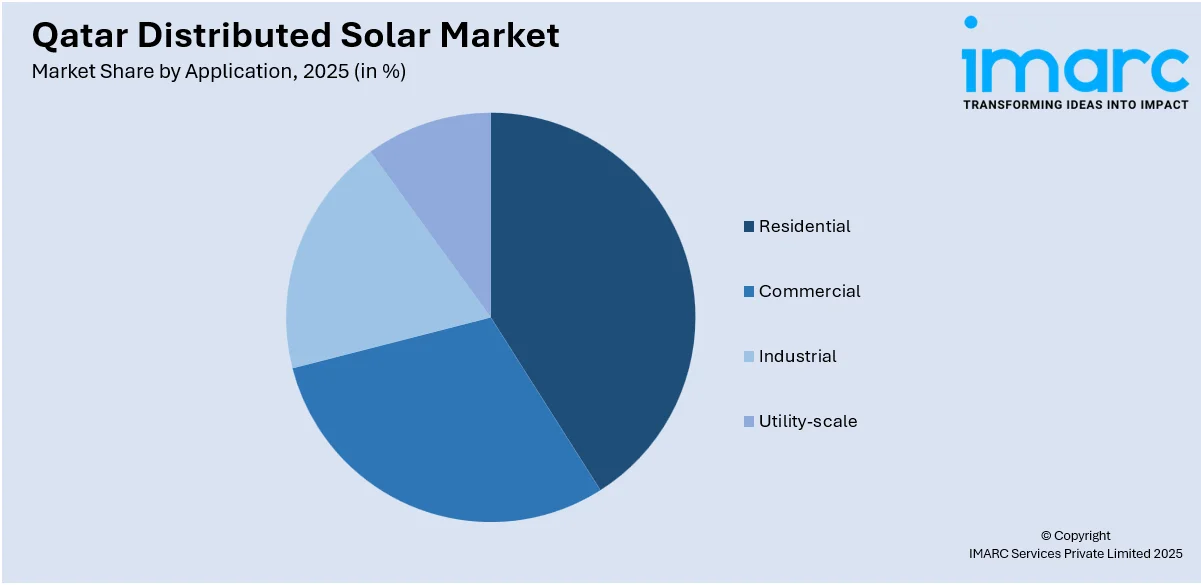
Analysis by Application:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Utility-scale
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application have also been provided in the report. This includes residential, commercial, industrial, and utility-scale.
Analysis by Ownership Type:
- Owner-operated
- Third-party Ownership
- Community Solar Programs
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the ownership type. This includes owner-operated, third-party ownership, and community solar programs.
Analysis by End User:
- Residential Users
- Commercial Businesses
- Government Institutions
- Non-profit Organizations
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user have also been provided in the report. This includes residential users, commercial businesses, government institutions, and non-profit organizations.
Analysis by Financing Option:
- Cash Purchases
- Loans and Financing Models
- Leasing Options
- Government Incentives and Grants
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the financing option. This includes cash purchases, loans and financing models, leasing options, and government incentives and grants.
Analysis by Region:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar distributed solar market exhibits a developing competitive structure characterized by a mix of international solar technology providers, regional engineering firms, and emerging local companies specializing in renewable energy solutions. Competition centers on system quality, installation expertise, financing options, and after-sales service capabilities. International players leverage established brand recognition, proven technology platforms, and access to global supply chains to capture large commercial and industrial projects. Regional firms compete by offering localized service, familiarity with Qatar's regulatory environment, and customized solutions tailored to the specific climatic challenges of the Gulf region. Local companies are increasingly partnering with international manufacturers to combine global technology with local market knowledge and installation networks. The market is also seeing the emergence of specialized financing companies and energy service providers offering innovative business models such as solar leasing and power purchase agreements to reduce upfront costs for customers.
Qatar Distributed Solar Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Photovoltaic (PV) Systems, Solar Thermal Systems |
| Applications Covered | Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Utility-scale |
| Ownership Types Covered | Owner-operated, Third-party Ownership, Community Solar Programs |
| End Users Covered | Residential Users, Commercial Businesses, Government Institutions, Non-profit Organizations |
| Financing Options Covered | Cash Purchases, Loans and Financing Models, Leasing Options, Government Incentives and Grants |
| Regions Covered | Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Qatar distributed solar market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar distributed solar market on the basis of technology?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar distributed solar market on the basis of application?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar distributed solar market on the basis of ownership type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar distributed solar market on the basis of end user?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar distributed solar market on the basis of financing option?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar distributed solar market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Qatar distributed solar market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Qatar distributed solar market?
- What is the structure of the Qatar distributed solar market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Qatar distributed solar market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC's industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Qatar distributed solar market from {Stakeholder1}.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Qatar distributed solar market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Qatar distributed solar industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












