
Qatar E-Retail Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product Category, Sales Channel, Customer Type, Payment Method, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar E-Retail Market Summary:
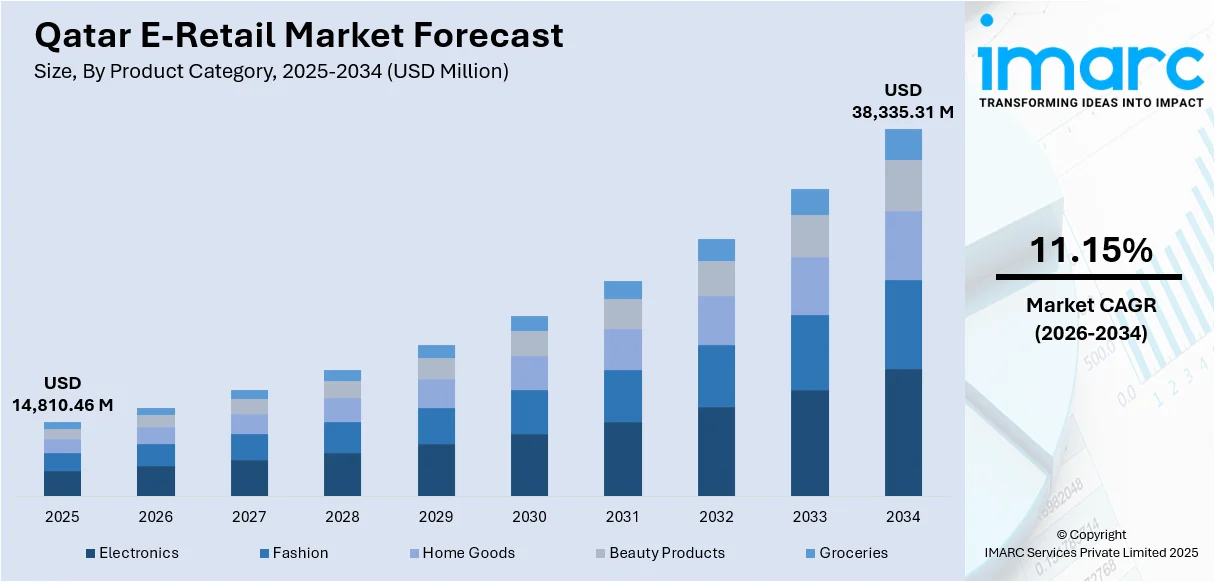
The Qatar e-retail market size reached USD 14,810.46 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 38,335.31 Million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 11.15% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by comprehensive government-led digital infrastructure investments through the National Digital Agenda 2030, the overwhelming dominance of mobile-first shopping experiences enabled by 95 percent smartphone penetration, and the rapid expansion of modern digital payment infrastructure including Buy-Now-Pay-Later services. Legacy of infrastructure upgrades from the FIFA 2022 World Cup, including nationwide fiber coverage and modernized payment rails, continues to underpin e-commerce operations. These factors collectively support the expanding Qatar e-retail market share.
|
Particulars |
Details |
|
Market Size 2025 |
USD 14,810.46 Million |
|
Forecast 2034 |
USD 38,335.31 Million |
|
CAGR (2026-2034) |
11.15% |
|
Key Segments |
Product Category (Electronics, Fashion, Home Goods, Beauty Products, Groceries), Sales Channel (Mobile Applications, Websites, Social Media, Marketplaces), Customer Type (Individual Consumers, Business Consumers, Bulk Buyers), Payment Method (Credit Card, Digital Wallet, Bank Transfer, Cash on Delivery) |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
Qatar E-Retail Market Outlook (2026-2034):
The Qatar e-retail market is poised for sustained expansion, underpinned by the government's ambitious National Digital Agenda 2030, which emphasizes digital infrastructure development, innovation, and economic diversification. The proliferation of 5G connectivity and advanced cloud computing capabilities will enable immersive shopping experiences including augmented reality product visualization and live-stream commerce. Strategic investments in logistics infrastructure, including the expansion of Hamad Port and the development of inland logistics parks, will enhance delivery efficiency and reduce last-mile costs. Furthermore, the growing adoption of artificial intelligence for personalized recommendations and predictive analytics will drive customer engagement and retention throughout the forecast period.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Impact of AI:
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally transforming Qatar's e-retail sector by enabling sophisticated personalization engines, dynamic pricing algorithms, and predictive demand forecasting. Retailers are deploying AI-powered chatbots and digital assistants to provide round-the-clock customer support in both Arabic and English, while machine learning models optimize inventory management and reduce stockouts. Qatar's strategic positioning of AI as a priority sector, supported by substantial government investments including the February 2025 allocation of USD 550 million toward AI and data centers, is accelerating technology adoption across the market. As platforms integrate computer vision for visual search and natural language processing for voice commerce, AI will increasingly drive operational efficiency and enhance the overall customer experience.
Market Dynamics:
Key Market Trends & Growth Drivers:
Government-Led Digital Infrastructure Investment Accelerating E-Commerce Growth
Qatar's government has implemented a comprehensive digital transformation strategy that serves as a fundamental catalyst for e-retail market expansion. Digital infrastructure, digital governance, digital innovation, digital technology, digital economy, and digital society are the six main pillars of the National Digital Agenda 2030, which was unveiled by the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology in April 2024. This framework aims to position Qatar as a knowledge-based economy with advanced digital capabilities, directly supporting e-commerce development through enhanced connectivity, streamlined digital services, and robust cybersecurity frameworks. In February 2025, Qatar invested QR 2 billion (USD 550 million) in artificial intelligence and data centers, unlocking advanced personalization, predictive logistics, and scalable cloud services for the e-retail market. These investments build upon earlier achievements, including Microsoft's opening of its first global datacenter region in Qatar in 2022 and Google Cloud's launch of its Doha cloud region in 2023, creating a technology ecosystem that has the potential to contribute over USD 18 billion and create tens of thousands of jobs. The government's commitment extends to workforce development, with training programs targeting 50,000 individuals by 2025 on advanced digital skills. This comprehensive approach to digital infrastructure development provides e-retailers with the technological foundation necessary to implement advanced features such as real-time inventory management, seamless omnichannel integration, and sophisticated customer analytics, thereby driving sustained Qatar e-retail market growth.
Mobile-First Commerce Dominance Reshaping Consumer Shopping Behavior
Mobile devices have fundamentally transformed the Qatar e-retail landscape, establishing themselves as the primary channel through which consumers discover, evaluate, and purchase products. Mobile commerce generated approximately 70 percent of online sales revenue in 2024, reflecting the country's near-universal smartphone adoption rate of 95 percent and one of the highest mobile penetration rates globally. This mobile-first paradigm is reinforced by Qatar's extensive 5G network infrastructure, which provides the low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity essential for rich multimedia experiences including live-streaming product demonstrations, augmented reality try-on features, and interactive video content. E-retail platforms have responded by prioritizing mobile-optimized interfaces featuring intuitive navigation, one-click checkout processes, and biometric authentication options including fingerprint and facial recognition. The integration of mobile wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and local solutions has streamlined the payment experience, reducing friction and cart abandonment rates. Mobile applications now incorporate sophisticated features including push notifications for personalized promotions, location-based services for identifying nearby pickup points, and social sharing capabilities that leverage Qatar's high social media engagement. To supply the Qatari corporation with its cutting-edge AI technology, Nvidia partnered with telecom operator Ooredoo in June 2024. This was Nvidia's first major Middle East launch and furthered Ooredoo Group's goal of becoming the top provider of digital infrastructure in the MENA area. The convenience of mobile shopping, which allows consumers to browse and purchase products at any time from any location, aligns perfectly with Qatar's fast-paced lifestyle and tech-savvy population demographics. As mobile devices continue to evolve with enhanced processing capabilities and larger, higher-resolution displays, the mobile-first trend is projected to strengthen further, with mobile commerce forecast to grow at an 11.4 percent CAGR through 2030, cementing its dominance in the e-retail ecosystem.
Rapid Expansion of Digital Payment Infrastructure and Buy-Now-Pay-Later Services
Qatar's payment landscape has undergone a remarkable transformation, characterized by the proliferation of innovative digital payment solutions that are removing traditional barriers to e-retail adoption. The Qatar Central Bank's Fawran instant payment network, which settles fund transfers in under 15 seconds, represents a quantum leap in payment processing speed and has processed over QR 2.11 billion by April 2025, signaling rapid consumer acceptance of real-time payment mechanisms. The Himyan debit card scheme has further expanded digital payment accessibility by providing a unified national payment card infrastructure. A watershed moment occurred in July 2024 when regulatory authorities granted approval for Buy-Now-Pay-Later (BNPL) services, addressing substantial pent-up consumer demand for flexible payment options without interest charges. Following regulatory approval in July 2024, Buy-Now-Pay-Later providers including Spendwisor, PayLater, and others signed up 220,000 users in Qatar within six months, underscoring significant latent demand for installment payment plans without interest charges. BNPL services are particularly appealing to younger demographics who value financial flexibility and prefer to spread payments over time without incurring interest fees. The rapid adoption trajectory positions BNPL to grow at an 18.3 percent CAGR through 2030, potentially disrupting the traditional dominance of credit and debit cards, which currently account for 40 percent of transaction value. Digital wallets have gained concurrent traction, benefiting from QR code acceptance infrastructure deployed across both physical retail establishments and online checkout processes. The government's policy initiatives promoting cashless transactions, combined with enhanced payment security protocols and consumer protection regulations, have built trust in digital payment channels. This modernized payment ecosystem not only enhances convenience and checkout conversion rates but also generates valuable transaction data that e-retailers can leverage for customer insights and personalized marketing strategies.
Key Market Challenges:
Last-Mile Delivery Complexity and Cost Pressures Outside Urban Centers
The efficient delivery of products to customers' doorsteps remains one of the most significant operational challenges facing Qatar's e-retail sector, particularly for deliveries outside the densely populated capital region of Doha. While Doha accounts for approximately three-quarters of online transactions due to superior logistics infrastructure, high population density, and concentrated delivery networks, reaching customers in peripheral regions such as Al Wakrah, Al Khor, and rural areas presents substantial cost and complexity challenges. Limited delivery network coverage in these areas necessitates longer transit times and higher per-delivery costs, eroding profitability margins for e-retailers. Urban congestion within Doha itself creates bottlenecks during peak traffic hours, hindering timely deliveries and increasing fuel consumption and vehicle operating costs. The persistent preference for cash-on-delivery (COD) payment methods compounds these challenges, as COD transactions require delivery personnel to handle cash, verify payment authenticity, and manage complex reconciliation processes. Cash-on-delivery shipments experience return rates 1.7 times higher than prepaid orders, adding cost and inventory distortion to operations. The physical return of products requires reverse logistics capabilities that many e-retailers struggle to implement efficiently, involving product inspection, restocking, and potential inventory write-offs for damaged goods. Temperature-controlled logistics for groceries and perishable items adds another layer of complexity, requiring specialized cold-chain infrastructure and expedited delivery schedules. Although same-day delivery coverage now spans nearly all central Doha districts and hyper-local delivery networks are compressing order-to-delivery times to under 45 minutes for certain categories, extending these capabilities nationwide requires substantial capital investment in distribution centers, delivery fleet expansion, and route optimization technology. The fragmented nature of Qatar's residential development patterns, with villas and low-rise compounds interspersed across suburban areas, further complicates route planning and reduces delivery density, ultimately impacting service quality and customer satisfaction.
Digital Skills Gap and Talent Shortage Constraining Market Growth
The rapid evolution of Qatar's e-retail market has created unprecedented demand for specialized digital talent across multiple functional areas, exposing a significant skills gap that constrains market growth and innovation. E-retailers require professionals with expertise in e-commerce platform management, data analytics, digital marketing, user experience design, cybersecurity, mobile application development, and artificial intelligence implementation. However, the supply of locally available talent with these competencies falls substantially short of market demand, forcing companies to compete aggressively for a limited pool of qualified candidates or rely on expensive expatriate talent. The shortage is particularly acute in emerging technology domains such as machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing, and blockchain, which are increasingly relevant for implementing advanced e-retail features including personalized recommendations, chatbots, visual search, and secure payment processing. Small and medium-sized e-retail businesses face especially severe constraints, as they lack the financial resources and employer brand recognition to attract top talent, putting them at a competitive disadvantage relative to established players and international platforms. The skills deficit extends beyond technical roles to encompass digital marketing specialists who can effectively leverage social media, search engine optimization, influencer partnerships, and programmatic advertising to drive customer acquisition. The difficulty is exacerbated by the speed at which technology is changing, necessitating ongoing retraining and upskilling of current workforces in order to stay relevant. While the Qatar government has responded with initiatives including the National Cyber Security Academy established in 2024 and various training programs targeting 50,000 individuals by 2025 on advanced digital skills, the immediate shortage persists and will take years to fully address through education pipeline development. The talent gap limits e-retailers' ability to fully capitalize on market opportunities, slows the implementation of strategic initiatives, increases recruitment and retention costs, and ultimately moderates the pace of innovation and competitive differentiation.
Complex Regulatory Compliance and Cross-Border Trade Requirements
E-retailers operating in Qatar must navigate an increasingly complex regulatory environment that spans multiple domains including data privacy, consumer protection, payment security, import controls, and tax compliance. The Personal Data Protection Law sets strict guidelines for the gathering, storing, processing, and transfer of consumer data, requiring strong cybersecurity protections, explicit permission procedures, and data localization concerns. Investments in legal knowledge, compliance management systems, and frequent audits are necessary because non-compliance can lead to significant financial penalties and reputational harm. Consumer protection regulations govern various aspects of e-retail operations including product descriptions, pricing transparency, return policies, delivery timeframes, and dispute resolution mechanisms, requiring careful attention to terms and conditions and customer service protocols. Payment security standards, particularly those related to card-not-present transactions, demand implementation of secure payment gateways, fraud detection systems, and adherence to international payment card industry standards. For e-retailers engaged in cross-border trade, additional layers of complexity emerge from import regulations, customs duties, and value-added tax considerations. The de minimis duty exemption threshold of QR 1,000 (USD 275) for imported shipments provides some relief but requires accurate customs declarations and documentation. Intricate currency exchange processes, variable exchange rates, and cross-border payment settlement mechanisms introduce operational complexity and financial risk. Product-specific regulations governing categories such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food supplements, and electronics require specialized knowledge and may necessitate registration, certification, or approval from relevant authorities before products can be marketed and sold. The Ministry of Commerce and Industry's ongoing efforts to digitize services and streamline processes, including plans to launch 38 new e-services in 2025, represent positive developments, yet the fundamental complexity of regulatory compliance remains a barrier to entry for new market participants and an ongoing operational burden for established players, particularly those operating across multiple GCC markets with divergent regulatory frameworks.
Qatar E-Retail Market Report Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Qatar e-retail market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on product category, sales channel, customer type, and payment method.
Analysis by Product Category:
- Electronics
- Fashion
- Home Goods
- Beauty Products
- Groceries
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the product category. This includes electronics, fashion, home goods, beauty products, and groceries.
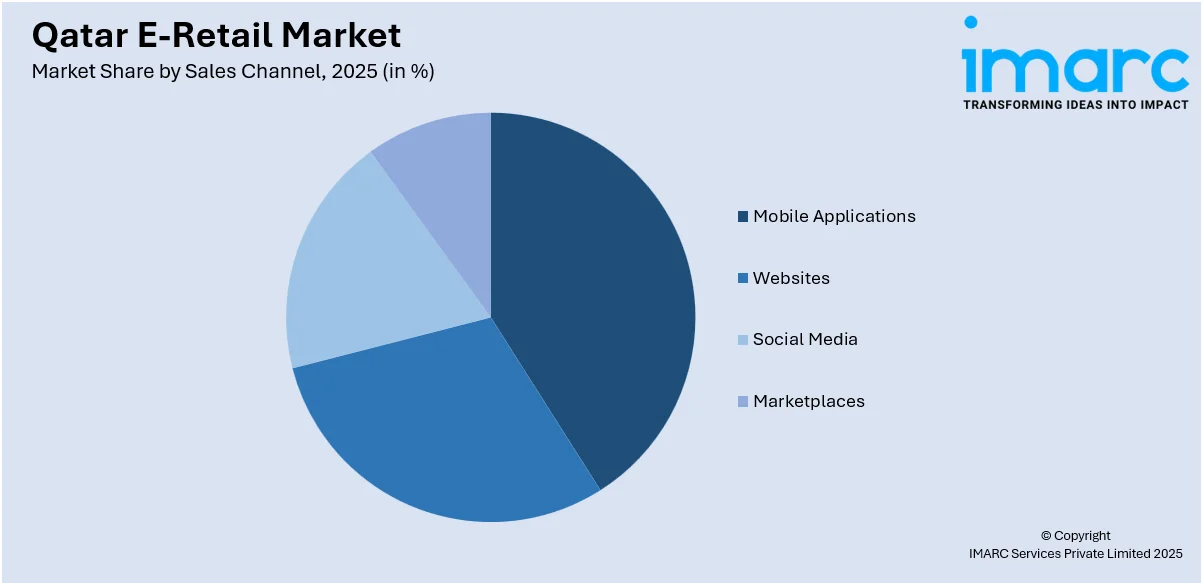
Analysis by Sales Channel:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Mobile Applications
- Websites
- Social Media
- Marketplaces
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the sales channel have also been provided in the report. This includes mobile applications, websites, social media, and marketplaces.
Analysis by Customer Type:
- Individual Consumers
- Business Consumers
- Bulk Buyers
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the customer type. This includes individual consumers, business consumers, and bulk buyers.
Analysis by Payment Method:
- Credit Card
- Digital Wallet
- Bank Transfer
- Cash on Delivery
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the payment method have also been provided in the report. This includes credit card, digital wallet, bank transfer, and cash on delivery.
Analysis by Region:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar e-retail market exhibits moderate competition characterized by the presence of both international e-commerce giants and locally rooted platforms vying for market share. International players leverage their technological capabilities, extensive product catalogs, vast logistics networks, and established brand recognition to capture significant transaction volumes, particularly in categories such as electronics, fashion, and cross-border purchases. These platforms benefit from economies of scale that enable competitive pricing and sophisticated features including advanced search algorithms, personalized recommendations, and seamless omnichannel experiences. Local and regional e-retail platforms differentiate themselves through deep understanding of Qatari consumer preferences, Arabic language support, culturally relevant marketing campaigns, and stronger relationships with local merchants and suppliers. Competition increasingly centers on delivery speed and convenience, with platforms investing heavily in logistics infrastructure including warehouses, fulfillment centers, and last-mile delivery capabilities to offer same-day or even faster delivery options. Customer loyalty programs, cashback incentives, and exclusive deals represent additional competitive battlegrounds as platforms seek to increase customer lifetime value and reduce churn. The market also witnesses growing specialization, with category-focused platforms emerging in verticals such as groceries, beauty products, and electronics, leveraging deep domain expertise to provide superior curation and customer service within their niches.
Qatar E-Retail Industry Latest Developments:
- March 2025: Al Jisr for Commercial Representation, a division of Al Khalaf Group, and My Q Trading & Advertising announced the launch of an integrated e-commerce platform scheduled for April 2025. In line with Qatar's national digitization objectives and supporting the expansion of the digital economy, the platform, which is designed to smoothly integrate in-store and online inventory, seeks to increase customer engagement through exclusive products, immersive experiences, and cutting-edge digital solutions.
- November 2024: Talabat Holding PLC completed its initial public offering on the Dubai Financial Market, raising approximately USD 2 billion in what became the largest global technology IPO of 2024. The company, which operates on-demand delivery services across eight markets including Qatar, attracted substantial investor interest including USD 250 million in cornerstone commitments, with proceeds earmarked for fintech expansion, customer loyalty program enhancements, and strategic growth initiatives across its regional footprint.
- October 2023: Amazon.ae announced the launch of its international shopping experience in Qatar, allowing local consumers to peruse and buy hundreds of thousands of qualifying items in over 30 categories, such as toys, home and kitchen appliances, electronics, fashion, beauty, books, and health. Amazon handles cross-border customs clearance on behalf of customers, and products are dispatched from the UAE with explicit pricing, delivery schedules, and shipping charges that include import taxes.
Qatar E-Retail Market Report Coverage:
|
Report Features |
Details |
|
Base Year of the Analysis |
2025 |
|
Historical Period |
2020-2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
|
Units |
Million USD |
|
Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
|
Product Categories Covered |
Electronics, Fashion, Home Goods, Beauty Products, Groceries |
|
Sales Channels Covered |
Mobile Applications, Websites, Social Media, Marketplaces |
|
Customer Types Covered |
Individual Consumers, Business Consumers, Bulk Buyers |
|
Payment Methods Covered |
Credit Card, Digital Wallet, Bank Transfer, Cash on Delivery |
|
Regions Covered |
Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
|
Customization Scope |
10% Free Customization |
|
Post-Sale Analyst Support |
10-12 Weeks |
|
Delivery Format |
PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Qatar e-retail market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar e-retail market on the basis of product category?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar e-retail market on the basis of sales channel?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar e-retail market on the basis of customer type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar e-retail market on the basis of payment method?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar e-retail market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Qatar e-retail market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Qatar e-retail market?
- What is the structure of the Qatar e-retail market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Qatar e-retail market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC's industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Qatar e-retail market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Qatar e-retail market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Qatar e-retail industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












