
Qatar Green Mobility Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Vehicle Type, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar Green Mobility Market Summary:
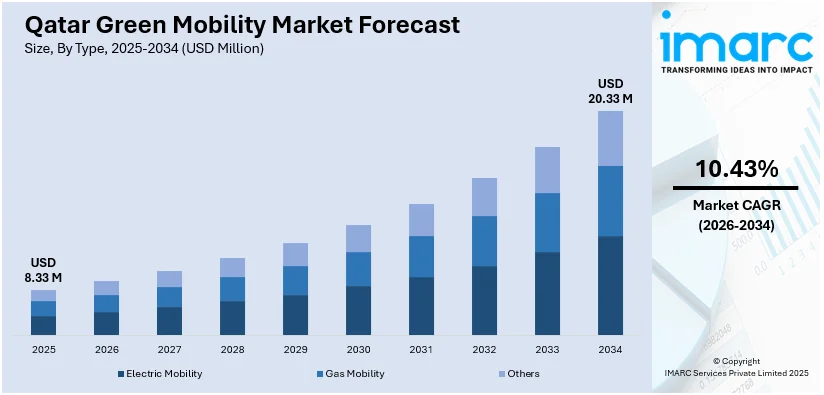
The Qatar green mobility market size reached USD 8.33 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 20.33 Million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.43% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by ambitious government policy frameworks and public transport electrification initiatives, rapid expansion of charging infrastructure with smart grid integration, and the development of domestic EV manufacturing capabilities through localization strategies. These drivers are positioning Qatar as a regional leader in sustainable transportation, and the expanding Qatar green mobility market share is supported by comprehensive national strategies aligned with Qatar National Vision 2030.
|
Particulars |
Details |
|
Market Size (2025) |
USD 8.33 Million |
|
Forecast (2034) |
USD 20.33 Million |
|
CAGR (2026-2034) |
10.43% |
|
Key Segments |
Type (Electric Mobility, Gas Mobility, Others), Vehicle Type (Commercial Vehicles, Passengers Vehicles, Two and Three Wheelers), Application (Urban Logistics, Mass Transit Infrastructure, Others) |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
Qatar Green Mobility Market Outlook (2026-2034):
The Qatar green mobility market is poised for robust expansion driven by the government's commitment to electrifying 35 percent of the national vehicle fleet and 100 percent of public buses by 2030. The nation will be able to fully meet the demand for EV charging using clean energy sources thanks to strategic investments in renewable energy infrastructure, with solar capacity predicted to reach 5 gigawatts by 2035. A favorable environment for sustained market growth throughout the forecast period is created by the development of local manufacturing capabilities through partnerships with foreign OEMs, appealing green financing options, and a projected annual economic growth rate of 4.1 percent between 2025 and 2029.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Impact of AI:
Artificial intelligence is transforming Qatar's green mobility ecosystem by optimizing traffic management, fleet operations, and smart infrastructure integration. AI-powered platforms developed by the Qatar Mobility Innovation Center enable intelligent transportation systems including predictive maintenance, route optimization, and real-time traffic flow management. These technologies support the deployment of autonomous vehicles, smart intersections, digital parking systems, and vehicle counting applications that enhance operational efficiency. AI integration with charging infrastructure through cloud-based monitoring systems using over 400 parameters maximizes uptime and ensures reliable operations. As Qatar advances toward its smart city goals, AI will play an increasingly critical role in coordinating integrated mobility solutions and supporting data-driven decision-making across the transportation network.
Market Dynamics:
Key Market Trends & Growth Drivers:
Ambitious Government Policy Framework and Public Transport Electrification
Under Qatar National Vision 2030 and the Third National Development Strategy, Qatar has implemented a comprehensive three-phase Electric Vehicle Strategy that extends through 2030. This strategy demonstrates a holistic vision that integrates infrastructure development, technological innovation, and policy transformation. These government-led initiatives represent one of the most ambitious transportation electrification programs in the Middle East, with policies specifically designed to accelerate adoption through favorable regulations, tax benefits reducing EV purchase costs by up to 30 percent, mandatory EV parking requirements in new developments, and green building standards that mandate charging infrastructure. The Electric Vehicle Strategy 2021 established specific goals, such as attaining 10% of all vehicle sales by 2030 and quickly implementing EV infrastructure to enable a future of zero-emission mobility. Under Mowasalat, Qatar successfully installed more than 900 electric buses in 2024–2025, making up roughly 73–74% of the fleet of public transportation vehicles and allowing for a 43 million kilogram reduction in carbon emissions. With more than 1,000 e-buses transporting spectators and guests, the 2022 FIFA World Cup acted as a historic catalyst and was the first FIFA World Cup to be held in the Middle East with such a strong emphasis on electric mobility. These strategic policy interventions, combined with substantial R&D investments in setting up EV manufacturing facilities and the country's strategic location and resources, are propelling the Qatar green mobility market growth at an accelerated pace throughout the forecast period.
Rapid Expansion of Charging Infrastructure and Smart Grid Integration
Qatar is investing heavily in deploying comprehensive EV charging infrastructure across the country as a cornerstone of its sustainable mobility transformation. The government's infrastructure strategy focuses on installing over 1,000 charging stations by 2030 and expanding to 4,000 stations by 2035 to support projected EV adoption rates. The first phase covering 2024-2025 prioritizes installing 600 charging stations while implementing smart grid integration technologies to create a robust technological framework capable of supporting large-scale electric vehicle adoption without compromising grid stability. Through its National Programme for Conservation and Energy Efficiency (Tarsheed), the General Electricity and Water Corporation (KAHRAMAA) has introduced comprehensive Charging Units Infrastructure Guidelines that encourage the use of fast chargers in key locations, such as shopping centres, government buildings, residential areas, metro stations, and major transportation corridors. ABB won a significant contract in July 2021 to design and provide high-power charging infrastructure for Qatar's fleet of electric buses. This infrastructure will include 89 opportunity chargers spread across four bus depots, eight bus stations, and twelve metro stations, as well as over 125 megawatts of charging capacity and 1,300 connectors for destination charging. The charging infrastructure is integrated with the ABB Ability cloud for 24/7 fleet optimization and remote monitoring using more than 400 parameters, ensuring maximum uptime, efficiency, and reliable infrastructure operations. Notable developments include the Lusail Electric Bus Depot, recognized as the world's largest electric bus depot housing 478 e-buses and equipped with over 25,000 square meters of solar panels generating 4 megawatts of clean power for bus charging. With solar capacity expected to reach 5 gigawatts and green energy generation predicted to reach 8.5 terawatt-hours by 2035, Qatar's growing renewable energy sector puts the country in a position to power its EV ecosystem entirely through sustainable sources, fostering a synergy between clean power generation and green mobility.
Development of Domestic EV Manufacturing Capabilities and Localization Strategy
Qatar is actively fostering indigenous electric vehicle production capabilities and establishing local manufacturing ecosystems to reduce import dependence, create employment opportunities, and develop export capabilities to neighboring markets. The country's localization strategy emphasizes promoting domestic intellectual property development, assembly operations, and establishing Qatar as a regional eMobility hub with integrated infrastructure and end-to-end supply chain development for EVs and green energy technologies. This approach aligns with economic diversification objectives under Qatar National Vision 2030 while building technological sovereignty and reducing long-term costs associated with imported vehicles. In June 2023, EcoTranzit unveiled prototypes of VIM, Qatar's first electric vehicle brand incorporating exclusive Qatari intellectual property rights developed in collaboration with international partners including Beijing Automotive Works. The company showcased three electric vehicle models during the launch ceremony attended by senior government officials: the VIM VX 50, a five-door five-seater SUV with 72 kilowatt-hour battery, the VIM VS 30 Sedan, a four-door five-seater vehicle, and the VIM P 100 van offering seven-to-nine seats. EcoTranzit has begun investing in assembly plants and preliminary production lines with plans to design and manufacture its own electric vehicles in the near future while establishing the inaugural regional center dedicated to certifying EVs according to worldwide specifications and Gulf standards. Furthermore, a strategic partnership between Mowasalat (Karwa) and Chinese manufacturer Yutong resulted in the establishment of an e-bus assembly plant in the Um Al Houl Free Zone, with a framework agreement to assemble 1,500 electric buses within seven years for domestic deployment and export to markets in the Middle East, Europe, South America, and Africa. Through huge investments in important international businesses like SK On, the fifth-largest EV battery producer in the world, the Qatar Investment Authority has positioned Qatar among important worldwide participants in the EV battery manufacturing sector. These localization efforts are creating a thorough domestic value chain that will sustain market growth and technological advancement over the course of the forecast, especially when combined with Qatar's favorable market conditions attracting interest from foreign EV manufacturers like Volkswagen, Porsche, and Gaussin.
Key Market Challenges:
Inadequate Charging Infrastructure Coverage and Grid Capacity Constraints
Despite significant progress in deploying charging infrastructure, Qatar faces challenges in achieving sufficient charging station density and geographic distribution to support projected EV demand growth and provide convenience comparable to conventional fueling stations. The country currently operates around 200-250 fast chargers as of early 2024, substantially below the requirement for over 4,000 additional public charging points by 2035 to accommodate projected vehicle electrification targets. The geographic concentration of existing charging infrastructure primarily in Doha and Lusail creates accessibility gaps in residential neighborhoods, rural areas, and along intercity corridors, contributing to range anxiety concerns among potential EV adopters. High-density urban zones face grid infrastructure bottlenecks including limitations in substation capacity, transformer points, and grid connections that may constrain further rapid expansion if infrastructure upgrades lag behind charging demand growth. The technical infrastructure hurdles become particularly acute during peak charging periods when multiple high-power chargers operate simultaneously, potentially straining local grid capacity. Qatar's 2024 real GDP of USD 176 billion and modest GDP growth rate of approximately 2-3 percent annually reflect economic stability and underscores pressure on existing electrical infrastructure to serve new high-power charging loads estimated to reach 125 megawatts for public transport alone. Addressing these infrastructure challenges requires substantial capital investments estimated at hundreds of millions of dollars for grid reinforcement, strategic placement of charging stations in high-traffic corridors, deployment of distributed generation including solar installations at charging sites, and implementation of smart charging technologies that optimize load distribution across the network. The collaboration between government authorities, utility providers, and private sector stakeholders becomes essential to accelerate infrastructure development, ensure adequate coverage, and maintain grid stability while supporting the ambitious vehicle electrification timeline through 2030.
High Upfront Costs and Limited EV Model Availability
Electric vehicles currently carry significantly higher purchase prices compared to internal combustion engine vehicles, presenting a substantial financial barrier that limits widespread consumer adoption despite Qatar's high GDP per capita of approximately USD 85,000. The premium pricing stems from expensive battery technology, specialized components, and limited economies of scale in EV manufacturing compared to mature conventional vehicle production. Over 90 percent of vehicles sold in Qatar remain traditional ICE models, indicating limited market penetration with EVs comprising only 1.1 percent of new vehicle sales in 2024 and total EV registrations reaching approximately 5,624 vehicles. The total cost of ownership for private EV ownership remains higher than conventional vehicles when considering purchase price, insurance, maintenance, and depreciation factors, though commercial fleets have approached cost parity with battery electric vehicles demonstrating only 0.8 percent higher total cost of ownership compared to ICE vehicles in commercial use scenarios. Limited availability of affordable EV models suited to diverse consumer preferences and use cases further constrains market expansion, with most available options concentrated in premium and luxury segments that target high-income buyers rather than mass-market consumers. The absence of strong financial incentives comparable to European or North American markets, where governments provide substantial purchase subsidies and tax credits, reduces the economic attractiveness of EV adoption for cost-conscious buyers. Addressing these economic barriers requires comprehensive policy interventions including direct purchase subsidies, enhanced tax benefits, reduced registration fees, preferential financing rates through green lending programs, and incentivizing international manufacturers to introduce more affordable EV models into the Qatari market. Expanding domestic assembly and manufacturing capabilities through initiatives like EcoTranzit's VIM brand and the Yutong collaboration will gradually reduce costs through localization and economies of scale, improving affordability and accelerating market penetration throughout the forecast period.
Extreme Climate Conditions Affecting Battery Performance and Thermal Management
Qatar's extreme desert climate characterized by summer temperatures regularly exceeding 45-50 degrees Celsius, high humidity levels along coastal areas, frequent dust storms, and intense solar radiation poses significant technical challenges for electric vehicle battery performance, thermal management, and overall system reliability. High ambient temperatures accelerate battery degradation through increased internal resistance and electrolyte breakdown, reducing battery lifespan and requiring more frequent replacements that increase total cost of ownership. Elevated temperatures negatively impact charging efficiency and speed, with batteries requiring extended cooling periods before accepting rapid charging, thus reducing convenience and increasing charging times during peak summer months when temperatures are highest. Vehicle range decreases substantially in hot conditions as battery capacity diminishes and air conditioning systems draw significant power to maintain cabin comfort, creating range anxiety concerns for drivers undertaking longer journeys. Thermal management systems must work continuously to maintain optimal battery operating temperatures between 20-35 degrees Celsius, consuming additional energy and reducing overall vehicle efficiency. The harsh environment necessitates specialized cooling technologies including liquid cooling systems, advanced thermal insulation, and heat-resistant materials that add complexity and cost to vehicle design and manufacturing. Dust and sand infiltration can damage electrical components, charging ports, and cooling systems if not adequately protected through robust sealing and filtration systems. Addressing these climate-related challenges requires continued battery innovation focusing on heat-resistant chemistries such as lithium iron phosphate that demonstrate better thermal stability, deployment of adaptive thermal management systems with sophisticated cooling algorithms, installation of shaded charging infrastructure with solar canopies that simultaneously generate clean power while protecting vehicles, and consumer education regarding optimal charging practices and vehicle care in extreme conditions. The development of climate-adapted EV models specifically designed for Gulf region conditions becomes critical for ensuring reliable year-round performance and building consumer confidence in electric vehicle technology throughout Qatar's challenging environmental context.
Qatar Green Mobility Market Report Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Qatar green mobility market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on type, vehicle type, and application.
Analysis by Type:
- Electric Mobility
- Battery Electric Vehicle
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- Gas Mobility
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes electric mobility (battery electric vehicle, hybrid electric vehicle, fuel cell electric vehicle, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicle), gas mobility, and others.
Analysis by Vehicle Type:
- Commercial Vehicles
- Medium and Heavy Commercial Vehicles
- Light Commercial Vehicles
- Passengers Vehicles
- Two and Three Wheelers
- E-scooters
- E-bikes
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the vehicle type have also been provided in the report. This includes commercial vehicles (medium and heavy commercial vehicles, and light commercial vehicles), passengers vehicles, and two and three wheelers (e-scooters, e-bikes, and others).
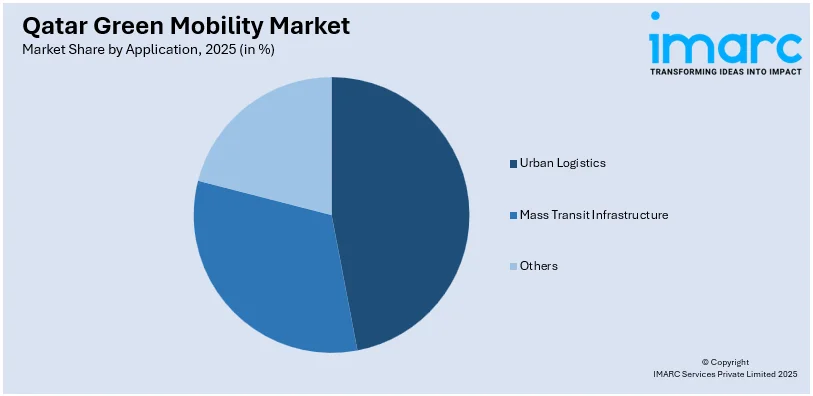
Analysis by Application:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Urban Logistics
- Mass Transit Infrastructure
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application. This includes urban logistics, mass transit infrastructure, and others.
Analysis by Region:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar green mobility market demonstrates moderate competitive intensity characterized by the presence of government-led initiatives, international technology providers, and emerging domestic players collaborating to build a comprehensive sustainable transportation ecosystem. Competition centers on securing government contracts for public transport electrification, establishing charging infrastructure networks, and gaining market share in the nascent private EV segment. Key players focus on differentiation through technological innovation including advanced battery thermal management systems adapted to Qatar's extreme climate, integration of smart charging solutions with fleet management systems, and development of locally manufactured vehicles incorporating Qatari intellectual property. The market structure features strong government influence through entities like the Ministry of Transport, Public Works Authority (Ashghal), and KAHRAMAA driving policy frameworks and infrastructure deployment. International companies including ABB, Yutong, and major automotive OEMs such as Volkswagen, Porsche, Tesla, and Chinese manufacturers are actively engaging in partnerships with local entities to establish manufacturing facilities, service centers, and distribution networks. Emerging domestic players like EcoTranzit are pioneering indigenous EV brands and assembly operations supported by strategic international partnerships. The Qatar Investment Authority's significant investments in global EV battery manufacturers positions Qatar strategically in the international supply chain. As the market matures, competition is expected to intensify with new entrants attracted by Qatar's high per capita income, supportive regulatory environment, and ambitious electrification targets, while existing players strengthen their positions through vertical integration, expanded service offerings, and enhanced consumer experience.
Qatar Green Mobility Industry Latest Developments:
- 2025: In order to develop a cutting-edge service and training facility in the Um Al Houl Free Zone, ABB E-mobility partnered with the Public Works Authority (Ashghal). To support Qatar's shift to sustainable transportation through workforce development and technical capacity building in line with National Vision 2030 objectives, the facility focuses on both theoretical and practical training for EV charging infrastructure.
- January 2025: Doha Municipality launched its first electric vehicle for conducting inspection and control work as part of a comprehensive plan to expand the use of electric vehicles. This initiative aims to transform Doha into a global model for sustainable smart cities, aligning with the goals of sustainable development and the Ministry of Municipality Strategy 2024-2030 and Qatar National Vision 2030 by demonstrating government commitment to green mobility through public sector fleet electrification.
Qatar Green Mobility Market Report Coverage:
|
Report Features |
Details |
|
Base Year of the Analysis |
2025 |
|
Historical Period |
2020-2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
|
Units |
Million USD |
|
Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
|
Types Covered |
|
|
Vehicle Types Covered |
|
|
Applications Covered |
Urban Logistics, Mass Transit Infrastructure, Others |
|
Regions Covered |
Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
|
Customization Scope |
10% Free Customization |
|
Post-Sale Analyst Support |
10-12 Weeks |
|
Delivery Format |
PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Qatar green mobility market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar green mobility market on the basis of type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar green mobility market on the basis of vehicle type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar green mobility market on the basis of application?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar green mobility market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Qatar green mobility market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Qatar green mobility market?
- What is the structure of the Qatar green mobility market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Qatar green mobility market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC's industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Qatar green mobility market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Qatar green mobility market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Qatar green mobility industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












