
Qatar Hospital Infrastructure Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Infrastructure Type, Hospital Type, Service Line, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar Hospital Infrastructure Market Summary:
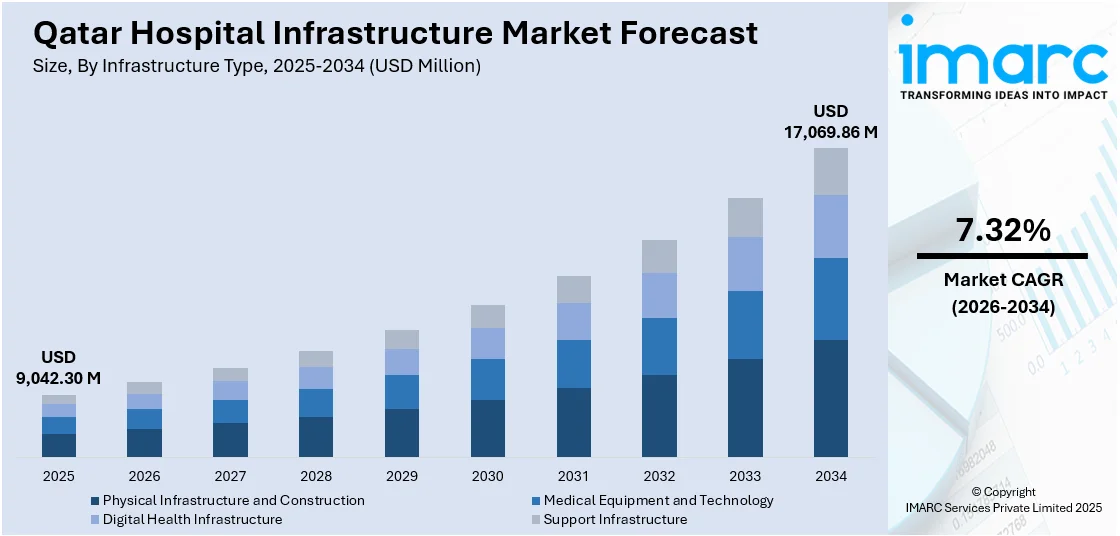
The Qatar hospital infrastructure market size reached USD 9,042.30 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 17,069.86 Million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 7.32% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by substantial government investment in healthcare facilities aligned with the National Health Strategy 2024-2030, accelerating digital health transformation through AI integration and telemedicine platforms, and expanding private sector participation through strategic public-private partnerships. Additionally, the increasing focus on medical tourism and specialty care centers is contributing to the Qatar hospital infrastructure market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 9,042.30 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 17,069.86 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 7.32% |
Qatar Hospital Infrastructure Market Outlook (2026-2034):
The Qatar hospital infrastructure market is positioned for robust expansion through 2034, underpinned by the government's allocation of QAR 22 billion to healthcare in 2025 and the implementation of the National Health Strategy 2024-2030. The ongoing construction of state-of-the-art medical facilities, modernization of existing hospitals, and integration of advanced medical technologies will enhance healthcare capacity across all regions. Furthermore, the rising prevalence of non-communicable diseases, growing medical tourism initiatives, and increasing emphasis on specialized tertiary and quaternary care facilities will create sustained demand for comprehensive hospital infrastructure development throughout the forecast period.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Impact of AI:
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing Qatar's hospital infrastructure by enabling predictive healthcare analytics, AI-powered diagnostic imaging systems, and automated patient management workflows. The TASMU Smart Qatar Programme integrates AI with big data and electronic health records to optimize resource allocation and reduce operational bottlenecks across healthcare facilities. Qatar's pioneering implementation of AI-powered breast cancer screening through the Lunit partnership demonstrates the nation's commitment to technology-driven healthcare excellence. As AI capabilities mature, intelligent hospital design, robotic surgery infrastructure, and AI-enhanced emergency response systems will become integral components of Qatar's next-generation medical facilities.
Market Dynamics:
Key Market Trends & Growth Drivers:
Government-Led Infrastructure Expansion and Strategic Healthcare Investment
Qatar's hospital infrastructure development is fundamentally driven by unprecedented government commitment to healthcare excellence as articulated in the National Health Strategy 2024-2030 and Qatar National Vision 2030. The government allocated QAR 22 billion (approximately USD 6 billion) to healthcare in the 2025 national budget, representing 10.5% of total government expenditure and marking a 4.6% increase from 2024. These substantial allocations are specifically earmarked for completing construction of new hospitals and developing existing facilities for Hamad Medical Corporation and the Primary Health Care Corporation. Major infrastructure projects include the comprehensive modernization of Hamad General Hospital with a three-year renovation program commencing in 2025, the expansion of Hamad Bin Khalifa Medical City with specialized facilities, and the development of satellite hospitals in rapidly growing municipalities. The government's strategy emphasizes optimizing existing infrastructure while attracting private investment to create a sustainable healthcare ecosystem. In September 2024, Qatar's Ministry of Public Health launched the National Health Strategy 2024-2030 as part of the Third National Development Strategy, with the budget specifically earmarking funds for completing construction of new hospitals and developing existing facilities for Hamad Medical Corporation and the Primary Health Care Corporation, demonstrating sustained commitment to healthcare infrastructure development aligned with Qatar National Vision 2030. The strategy aims to increase average life expectancy to 82.6 years and reduce non-communicable disease mortality by 36% by 2030, objectives that necessitate continued infrastructure investment and capacity expansion across the healthcare network.
Digital Health Infrastructure and Artificial Intelligence Integration
The Qatar hospital infrastructure market growth is significantly propelled by the nation's ambitious digital transformation agenda, positioning the country as a regional leader in smart healthcare solutions. The government-backed TASMU Smart Qatar Program serves as the technological backbone for integrating advanced digital health infrastructure, including AI-powered diagnostic systems, telemedicine platforms, electronic health records, and remote patient monitoring solutions across the healthcare network. The government's Digital Agenda 2030 prioritizes comprehensive digitization of healthcare services, with 60% of healthcare providers now offering telemedicine services including virtual consultations and remote patient monitoring through wearable devices and mobile applications. In July 2024, Qatar's Primary Health Care Corporation partnered with Lunit to implement the Lunit INSIGHT MMG artificial intelligence-powered breast cancer detection solution across Qatar's national Screen for Life program, making Qatar the first country in the Middle East to implement AI technology at a national level for breast cancer screening, with two radiologists reading each mammogram while referring to the AI system's results to enhance early detection and reduce missed diagnoses. The integration of AI extends beyond diagnostics to include intelligent hospital management systems, automated patient flow optimization, predictive analytics for resource allocation, and AI-enhanced medical imaging interpretation. Infrastructure investments now incorporate smart building technologies, IoT-enabled medical equipment, 5G connectivity for real-time data transmission, and integrated platforms that facilitate seamless information exchange between primary care centers, specialty hospitals, and emergency services, fundamentally transforming healthcare delivery models and operational efficiency.
Private Sector Expansion Through Public-Private Partnerships and Medical Tourism Development
Qatar is witnessing rapid expansion in private hospital infrastructure, fueled by strategic public-private partnerships and strong government initiatives to position the nation as a leading medical tourism hub in the Gulf region. The Ministry of Public Health continues to encourage private sector participation, recognizing its pivotal role in enhancing healthcare capacity, introducing specialized medical services, and fostering a culture of excellence that raises overall care standards. Private healthcare providers are investing in high-end medical facilities that blend advanced clinical capabilities with luxury amenities, appealing to both local patients seeking premium services and international visitors pursuing medical treatment. These hospitals feature cutting-edge surgical suites, advanced diagnostic and imaging technologies, and specialized departments catering to a wide range of medical needs. Recent facility inaugurations underscore growing private sector confidence in Qatar’s healthcare potential and highlight strong government backing for diversified healthcare delivery models. Collaborative arrangements between Hamad Medical Corporation and major private hospitals allow seamless patient referrals from public to private institutions, ensuring timely access to care and efficient utilization of system capacity. Supportive government measures, such as streamlined administrative processes, international accreditations, and targeted global promotion, continue to strengthen Qatar’s reputation as a destination for world-class medical and wellness services.
Key Market Challenges:
Healthcare Workforce Shortages and Dependence on Expatriate Medical Professionals
Qatar’s hospital infrastructure expansion continues to face major challenges due to persistent shortages of qualified healthcare professionals, particularly specialist doctors and nursing staff, which constrain the operational capacity of both new and existing facilities. While the nation has invested heavily in building advanced healthcare infrastructure, workforce limitations remain the primary bottleneck affecting service delivery and utilization across the network. Staffing gaps in key specialties hinder the activation of new hospital beds and the rollout of specialized services, even in fully constructed facilities. The healthcare system’s heavy reliance on expatriate professionals adds further complexity, as high turnover rates, global competition for medical talent, and challenges in adapting to local regulations and cultural contexts create instability in staffing levels. Expatriate workers often face hurdles related to language proficiency, licensing procedures, and integration into Qatar’s healthcare framework, contributing to recruitment and retention difficulties. Additionally, as new hospitals and specialty centers open, competition for limited skilled personnel intensifies, sometimes drawing staff away from existing institutions. Addressing these challenges will require a comprehensive strategy encompassing investment in local medical education and training, stronger retention incentives for international professionals, simplified licensing processes, and the adoption of innovative staffing and technological solutions to enhance workforce efficiency and long-term sustainability.
Capacity Pressures from Rapid Population Growth and Rising Healthcare Demand
Qatar’s hospital infrastructure is under increasing strain from rapid population growth and rising healthcare utilization, which continue to outpace capacity expansion despite substantial investment efforts. The country’s demographic growth, fueled by economic development and labor migration, has intensified demand for medical services, leading to overcrowding in major hospitals and extended wait times for specialized and elective care. To alleviate these pressures, the government has implemented public-private partnership models to redirect patients to private facilities when public institutions reach capacity. The growing prevalence of chronic non-communicable diseases, particularly diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, and cancer, further heightens the need for specialized diagnostic, treatment, and long-term care infrastructure. These conditions require advanced technologies, skilled medical professionals, and significant capital investment to ensure sustainable service delivery. Additionally, the concentration of tertiary and quaternary care facilities in Doha creates geographic disparities, leaving outlying regions with limited access to specialized care despite new hospitals in Al Wakrah and Al Khor. Future infrastructure planning must integrate long-term demographic, epidemiological, and technological trends, emphasizing flexible facility design, equitable access, and sustainable financing. Anticipating future healthcare needs through data-driven forecasting and scalable infrastructure models will be crucial to maintaining service quality and system resilience in Qatar’s evolving healthcare landscape.
Regulatory Complexity and Extended Licensing Processes
Qatar’s hospital infrastructure development faces considerable challenges stemming from complex regulatory frameworks and lengthy approval processes that extend project timelines and escalate costs. Healthcare developers must comply with rigorous licensing requirements overseen by the Qatar Council for Healthcare Practitioners and the Ministry of Public Health, where evolving standards have made approval procedures increasingly time-consuming. Private sector investors frequently cite unclear guidelines, inconsistent interpretations, and limited regulatory transparency as key barriers to efficient project execution. The approval process for advanced medical equipment, such as imaging systems, radiation therapy units, and surgical robotics, further contributes to procurement and commissioning delays. International healthcare operators also encounter difficulties adapting to Qatar’s distinct partnership models, ownership regulations, and operational licensing procedures, which differ significantly from global norms. Moreover, uncertainty surrounding digital health regulations, including data protection, cybersecurity, telemedicine, and AI-based diagnostics, creates hesitation among providers seeking to adopt innovative technologies. While stringent oversight upholds patient safety and care quality, excessive procedural complexity often undermines efficiency and deters investment. Streamlining regulatory processes through standardized approval pathways, clearer compliance guidance, prioritized reviews for proven technologies, and improved investor support could significantly accelerate healthcare infrastructure development while preserving Qatar’s high standards of safety and clinical excellence.
Qatar Hospital Infrastructure Market Report Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Qatar hospital infrastructure market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on infrastructure type, hospital type, and service line.
Analysis by Infrastructure Type:
- Physical Infrastructure and Construction
- Medical Equipment and Technology
- Digital Health Infrastructure
- Support Infrastructure
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the infrastructure type. This includes physical infrastructure and construction, medical equipment and technology, digital health infrastructure, and support infrastructure.
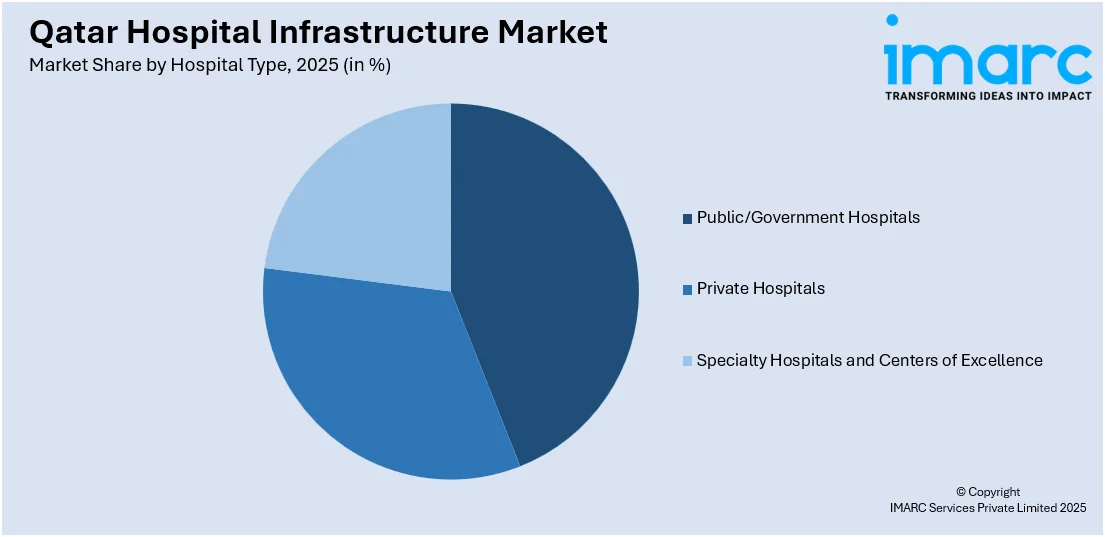
Analysis by Hospital Type:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Public/Government Hospitals
- Private Hospitals
- Specialty Hospitals and Centers of Excellence
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the hospital type have also been provided in the report. This includes public/government hospitals, private hospitals, and specialty hospitals and centers of excellence.
Analysis by Service Line:
- General Acute Care
- Tertiary and Quaternary Care
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the service line. This includes general acute care, tertiary and quaternary care, and ambulatory surgical centers.
Analysis by Region:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar hospital infrastructure market is characterized by strong government dominance through Hamad Medical Corporation, which operates the nation's largest network of public hospitals and specialty centers, establishing quality benchmarks and clinical standards across the healthcare system. Competition primarily revolves around specialized service excellence, technological innovation, international accreditation standards, and patient experience quality rather than pricing, as government subsidies ensure affordable access to public facilities while private hospitals differentiate through premium amenities and reduced wait times. The market is experiencing dynamic evolution as public-private partnerships expand, with leading private hospitals increasingly collaborating with Hamad Medical Corporation to address capacity constraints and enhance service accessibility. International healthcare operators are entering the market through strategic partnerships, bringing global expertise, advanced technologies, and specialized clinical programs that elevate Qatar's position as a regional medical hub. Key competitive strategies include vertical integration of services from primary to quaternary care, investment in cutting-edge medical technologies, recruitment of internationally trained specialists, achievement of prestigious international accreditations like Joint Commission International, and development of niche specialties that attract domestic and international patients seeking advanced treatments.
Qatar Hospital Infrastructure Industry Latest Developments:
- April 2025: Surgi Art Hospital officially opened in Lusail City following its inaugural phase launch in August 2024. The private hospital spans 30,000 square meters with advanced medical and surgical departments, expanding from its original cosmetic surgery focus to become a fully integrated general medical facility offering comprehensive services including pediatrics, gynecology, cardiology, vascular surgery, orthopedics, and general surgery, with 225 parking spaces and state-of-the-art imaging equipment including MRI machines, CT scans, and ultrasound systems.
- October 2024: Hamad Medical Corporation announced a comprehensive three-year modernization program for Hamad General Hospital, with Phase One scheduled to commence in 2025. The renovation will focus on upgrading the two inpatient towers and ground floor facilities, significantly enhancing patient experience while services are relocated to recently opened facilities including Aisha Bint Hamad Al Attiyah Hospital and the Medical Care and Research Center, both opened within the previous two years as part of HMC's network expansion that has added nine new hospitals since 2016.
Qatar Hospital Infrastructure Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Infrastructure Types Covered | Physical Infrastructure and Construction, Medical Equipment and Technology, Digital Health Infrastructure, Support Infrastructure |
| Hospital Types Covered | Public/Government Hospitals, Private Hospitals, Specialty Hospitals and Centers of Excellence |
| Service Lines Covered | General Acute Care, Tertiary and Quaternary Care, Ambulatory Surgical Centers |
| Regions Covered | Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Qatar hospital infrastructure market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar hospital infrastructure market on the basis of infrastructure type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar hospital infrastructure market on the basis of hospital type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar hospital infrastructure market on the basis of service line?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar hospital infrastructure market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Qatar hospital infrastructure market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Qatar hospital infrastructure market?
- What is the structure of the Qatar hospital infrastructure market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Qatar hospital infrastructure market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC's industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Qatar hospital infrastructure market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Qatar hospital infrastructure market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Qatar hospital infrastructure industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












