
Qatar Islamic Finance Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Financial Institution Type, Application, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar Islamic Finance Market Summary:
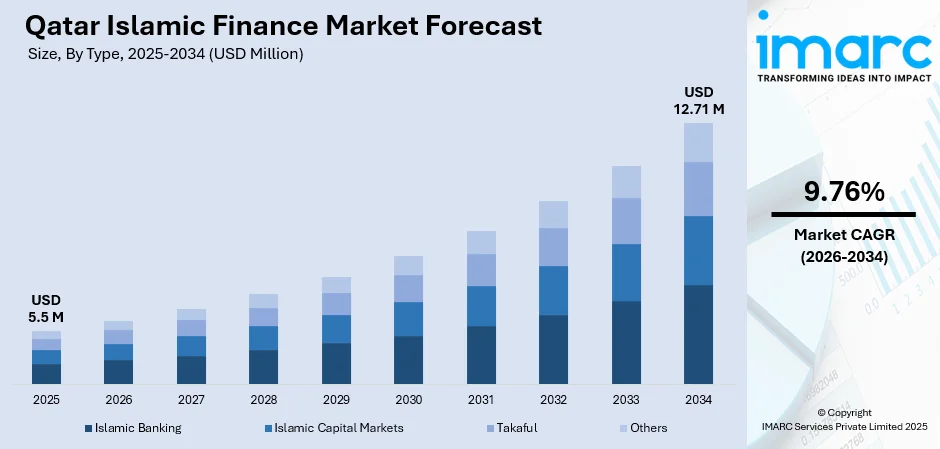
The Qatar Islamic finance market size was valued at USD 5.50 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 12.71 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 9.76% from 2026-2034.
The Qatar Islamic finance market is experiencing robust expansion driven by strong government support, progressive regulatory frameworks, and increasing demand for Sharia-compliant financial products. Strategic initiatives under Qatar National Vision 2030 are accelerating digital transformation and innovation within the sector. Growing consumer preference for ethical financial solutions and expansion of Islamic banking networks are strengthening market penetration and positioning Qatar as a regional Islamic finance hub.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Type: Islamic banking dominates the market with a share of 48% in 2025, owing to well-established institutional presence, comprehensive regulatory frameworks, and deep integration with national economic development strategies. Robust deposit growth and expanding financing portfolios are driving sustained momentum across the segment.
- By Financial Institution Type: Islamic banks lead the market with a share of 50% in 2025. This dominance is driven by strong capital positions, extensive branch networks, diversified product offerings, and strategic focus on digital transformation that enhances customer engagement and operational efficiency across retail and corporate banking segments.
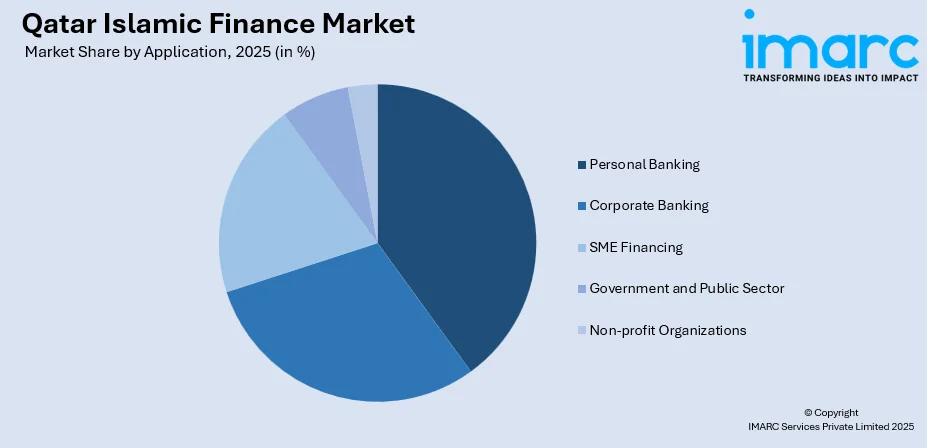
- By Application: Personal banking holds the largest segment with a market share of 33% in 2025, reflecting strong consumer preference for Sharia-compliant savings accounts, home financing, and personal loans. Rising disposable incomes and expanding digital banking platforms are fueling adoption among individual customers.
- By End User: Individuals exhibit a clear dominance in the market with 41% share in 2025, driven by growing awareness of Islamic financial principles, convenient digital access channels, and competitive profit-sharing arrangements offered by Islamic banks compared to conventional alternatives.
- By Region: Ad Dawhah represents the largest region with 49% share in 2025, driven by its position as Qatar's financial center housing major Islamic bank headquarters, concentration of corporate clients, higher population density, and presence of key regulatory bodies including Qatar Central Bank and Qatar Financial Centre.
- Key Players: Key players drive the Qatar Islamic finance market by expanding Sharia-compliant product portfolios, investing in digital transformation initiatives, strengthening sukuk issuances, and forming strategic partnerships to enhance market presence and customer accessibility.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Qatar Islamic finance market is advancing rapidly as the nation strengthens its position as a regional hub for Sharia-compliant financial services. The Qatar Central Bank's Third Financial Sector Strategic Plan, launched in 2023, places strong emphasis on Islamic finance development across banking, insurance, digital finance, and capital markets. Regulatory reforms are enhancing governance standards and attracting international investment. In November 2024, Qatar Development Bank announced a strategic investment in Wahed, a global Shariah-compliant fintech managing over USD 1 Billion in assets with more than 400,000 clients worldwide, demonstrating Qatar's commitment to fostering innovation within Islamic finance. The market benefits from increasing adoption of sustainable sukuk instruments and growing integration of financial technology solutions. Qatar's well-developed infrastructure, competitive tax policies, and strategic geographic location continue attracting Islamic financial institutions seeking regional expansion. Strong economic fundamentals supported by hydrocarbon revenues provide stability for continued sector growth and diversification.
Qatar Islamic Finance Market Trends:
Accelerating Digital Transformation and Islamic Fintech Innovation
Qatar's Islamic finance sector is witnessing rapid digital transformation as institutions embrace advanced technologies to enhance service delivery and customer experience. The Qatar Central Bank launched its Fintech Strategy, establishing regulatory sandboxes and digital asset frameworks that encourage innovation. Islamic fintech transaction volumes have grown substantially, demonstrating strong adoption of digital banking platforms and mobile payment solutions. The QFC Digital Assets Lab is fostering innovation in blockchain-based Sharia-compliant solutions, tokenization initiatives, and smart contract applications, supporting Qatar Islamic finance market growth.
Expansion of Sustainable and Green Sukuk Instruments
The sukuk market is experiencing significant expansion with growing emphasis on sustainable finance instruments aligned with environmental and social governance principles. According to the industry report, Sukuk issuance by Qatari entities tripled from QAR 9.2 Billion in 2020 to QAR 30.4 Billion in 2024. Qatar International Islamic Bank became the first Qatari bank to issue sustainable sukuk in January 2024, establishing a dedicated framework for sustainable financing. This trend reflects increasing alignment between Islamic finance principles and global sustainability objectives.
Rising Takaful Insurance Penetration and Product Diversification
The takaful insurance segment is experiencing steady growth driven by increasing demand for Sharia-compliant insurance coverage and product innovation. Gross written premiums in the takaful industry rose to QAR 1.9 Billion in 2024, with market share nearly doubling from 6% to 11% between 2020 and 2024. Digital takaful regulations introduced in April 2024 are accelerating service accessibility through online platforms. Growing awareness of ethical insurance solutions among consumers and businesses is supporting continued expansion across motor, health, and family takaful products.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Qatar Islamic finance market outlook remains positive, supported by robust regulatory frameworks, strategic government initiatives, and accelerating digital innovation. Continued implementation of the Third Financial Sector Strategic Plan will strengthen institutional capabilities and attract international investment. Expansion of Islamic fintech solutions, growing sukuk market depth, and increasing takaful penetration will drive sustained growth. Qatar's strategic positioning as a regional financial hub, combined with strong economic fundamentals supported by hydrocarbon revenues, creates favorable conditions for continued sector development and diversification. The market generated a revenue of USD 5.50 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 12.71 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 9.76% from 2026-2034.
Qatar Islamic Finance Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Type |
Islamic Banking |
48% |
|
Financial Institution Type |
Islamic Banks |
50% |
|
Application |
Personal Banking |
33% |
|
End User |
Individuals |
41% |
|
Region |
Ad Dawhah |
49% |
Type Insights:
- Islamic Banking
- Islamic Capital Markets
- Takaful
- Others
Islamic banking dominates with a market share of 48% of the total Qatar Islamic finance market in 2025.
Islamic banking represents the cornerstone of Qatar's Islamic finance sector, commanding significant market share through comprehensive Sharia-compliant financial services. The segment benefits from strong institutional infrastructure, established regulatory frameworks, and growing consumer preference for ethical banking solutions. Qatar is home to several major Islamic banks that have built extensive branch networks and diversified product portfolios serving retail, corporate, and government clients. The strong deposit base and diversified financing portfolios continue driving sustained growth across the segment.
The Islamic banking segment is experiencing continued expansion driven by digital transformation initiatives and product innovation. Leading institutions have successfully issued sukuk with strong investor demand and significant oversubscription, demonstrating sustained international confidence in Qatar's Islamic banking sector. Banks are investing in mobile banking applications, artificial intelligence integration, and seamless digital onboarding processes to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency across retail and corporate segments, positioning Qatar as a regional leader in Islamic financial services.
Financial Institution Type Insights:
- Islamic Banks
- Investment Firms
- Takaful Companies
- Asset Management Firms
- Others
Islamic banks lead with a share of 50% of the total Qatar Islamic finance market in 2025.
Islamic banks in Qatar have established themselves as the dominant financial institutions within the Sharia-compliant ecosystem, commanding significant market share through extensive branch networks and comprehensive product offerings. The segment benefits from strong capital positions, diversified financing portfolios, and strategic digital transformation initiatives. These institutions have consistently outperformed conventional banking counterparts in asset growth, demonstrating robust demand for Sharia-compliant banking services and strong consumer confidence in ethical financial solutions across Qatar's growing economy.
The Islamic banking segment continues strengthening its position through strategic initiatives and innovative product development. Qatar's Islamic banks are expanding their international presence through sukuk issuances and cross-border partnerships with global financial institutions. Leading institutions have achieved strong credit growth and profitability improvements, outpacing industry benchmarks. These banks are investing heavily in fintech integration, mobile banking solutions, and sustainable finance frameworks to maintain competitive advantages and attract new customer segments across retail and corporate markets.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Personal Banking
- Corporate Banking
- SME Financing
- Government and Public Sector
- Non-profit Organizations
Personal banking holds the largest share with 33% of the total Qatar Islamic finance market in 2025.
Personal banking represents a critical growth segment within Qatar's Islamic finance market, driven by increasing consumer demand for Sharia-compliant financial products and services. The segment encompasses savings accounts, home financing, auto loans, credit cards, and investment products tailored for individual customers. Qatar Islamic Bank pioneered fully-digital personal financing through its One Click Financing platform, driving 52% of retail sales through digital channels and demonstrating successful integration of technology with Islamic banking principles.
The personal banking segment continues expanding through enhanced digital accessibility and competitive product offerings. Rising disposable incomes, growing awareness of Islamic financial principles, and convenient mobile banking applications are fueling adoption rates. The segment benefits from strong digital account creation trends and increasing numbers of retail customers becoming digitally active. Banks are introducing innovative savings products with attractive profit-sharing arrangements and expanding personal financing options to capture market share among Qatar's diverse population including both nationals and expatriate residents.
End User Insights:
- Individuals
- Businesses
- Government Bodies
- Non-profit Organizations
Individuals represent the leading segment with a 41% share of the total Qatar Islamic finance market in 2025.
Individual customers represent the largest end-user segment within Qatar's Islamic finance market, driven by strong cultural affinity for Sharia-compliant financial solutions and growing awareness of ethical banking principles. The segment benefits from increasing financial literacy, rising income levels, and expanded accessibility through digital banking platforms. Individual deposits constitute a significant portion of Islamic bank funding bases, with private sector deposits representing the majority of total deposits and providing stable liquidity for financing operations across retail and corporate segments.
The individual segment is experiencing accelerated growth through innovative product offerings and enhanced digital service delivery. Islamic banks are targeting retail customers with competitive savings products, home financing solutions, and investment opportunities aligned with Sharia principles. The introduction of mobile applications, simplified onboarding processes, and personalized financial services are improving customer engagement. Growing expatriate population and increasing preference for ethical financial solutions among younger demographics are creating additional growth opportunities within this segment.
Regional Insights:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
Ad Dawhah exhibits a clear dominance with a 49% share of the total Qatar Islamic finance market in 2025.
Ad Dawhah dominates the Qatar Islamic finance market as the nation's capital and primary financial center. The region houses headquarters of major Islamic banks, Qatar Central Bank, Qatar Financial Centre, and key regulatory bodies overseeing the financial sector. The concentration of corporate offices, government institutions, and high-net-worth individuals creates substantial demand for Sharia-compliant financial services. World-class infrastructure, strategic positioning as a regional business hub, and presence of international financial institutions further strengthen Ad Dawhah's leadership position within Qatar's Islamic finance ecosystem.
The region continues attracting Islamic financial institutions and fintech companies through competitive regulatory frameworks and strategic infrastructure. Ad Dawhah serves as the hub for sukuk issuances, investment banking activities, and innovation initiatives within Qatar's Islamic finance sector. The presence of specialized institutions, training centers, and professional services supporting the industry reinforces the region's dominant position. Ongoing development of West Bay financial district and expansion of the Qatar Financial Centre platform are strengthening Ad Dawhah's status as a regional Islamic finance hub.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Qatar Islamic Finance Market Growing?
Strong Regulatory Framework and Government Support
The Qatar Islamic finance market benefits significantly from robust regulatory frameworks and strategic government initiatives aimed at positioning the nation as a leading regional financial hub. The Qatar Central Bank's Third Financial Sector Strategic Plan, launched in 2023, places strong emphasis on Islamic finance development across its four central pillars: banking, insurance, digital finance, and capital markets. This comprehensive approach ensures coordinated advancement of Sharia-compliant financial services throughout the ecosystem. The Islamic Banking Business Prudential Amendment Rules 2024 introduced updated capital adequacy ratios and enhanced credit risk regulations aligned with international standards. These regulatory enhancements strengthen governance, improve transparency, and build investor confidence. Qatar National Vision 2030 provides overarching strategic direction for economic diversification with financial sector development as a key priority. Government support extends through favorable tax policies, streamlined licensing procedures, and investment in digital infrastructure. The Qatar Financial Centre continues expanding its platform, offering Islamic financial institutions 100% foreign ownership and profit repatriation capabilities that attract international participation.
Accelerating Digital Innovation and Fintech Integration
Digital transformation represents a fundamental growth driver for Qatar's Islamic finance market as institutions embrace advanced technologies to enhance service delivery and customer engagement. The Qatar Central Bank launched its comprehensive Fintech Strategy in 2023, establishing regulatory sandboxes and dedicated frameworks for digital innovation within the financial sector. Key initiatives include the QFC Digital Assets Lab fostering innovation in blockchain-based Sharia-compliant solutions and development of central bank digital currency infrastructure with pilot programs commencing in 2024. Buy Now Pay Later regulations introduced in 2024 set licensing requirements and consumer protection measures for emerging fintech services. Islamic banks are investing substantially in mobile banking applications, artificial intelligence integration, and digital onboarding processes. Qatar Islamic Bank's One Click Financing platform demonstrates successful technology adoption driving over half of retail sales through digital channels.
Growing Demand for Sharia-Compliant Financial Products
Increasing consumer preference for ethical and Sharia-compliant financial solutions represents a significant growth driver for Qatar's Islamic finance market. Rising awareness about Islamic financial principles, combined with growing disposable incomes and expanding financial literacy, is driving adoption rates across retail and corporate segments. Qatar's diverse population including both nationals and expatriate residents creates varied demand for Sharia-compliant savings, financing, and investment products. Banks are responding with innovative offerings including sustainable sukuk, profit-sharing savings accounts, and home financing solutions aligned with Islamic principles. The takaful insurance segment demonstrates growing penetration with gross written premiums as consumers seek ethical insurance alternatives. Corporate clients are increasingly utilizing Islamic financing structures for infrastructure projects and business expansion, contributing to sustained demand growth across all market segments.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Qatar Islamic Finance Market is Facing?
Regulatory Fragmentation Across International Markets
The Qatar Islamic finance market faces challenges from regulatory fragmentation and licensing complexities when pursuing international expansion. Different jurisdictions maintain varying Sharia interpretations and compliance requirements, creating operational barriers for cross-border activities. While awareness and confidence in Islamic products within Qatar and the broader GCC region remains relatively high, the same does not apply in certain other jurisdictions, potentially constraining demand for Islamic fintech and financial services. Licensing costs and regulatory heterogeneity across developed markets limit efficient cross-border expansion for Qatari Islamic financial institutions.
Limited Consumer Awareness in Non-Traditional Markets
Despite growing global interest in Islamic finance, limited consumer understanding of Sharia-compliant products in non-Muslim majority markets presents expansion challenges. Surveys indicate significant portions of potential customers lack comprehensive understanding of how Islamic finance differs from conventional alternatives. This knowledge gap affects customer engagement and adoption rates in emerging markets targeted for growth. Educational initiatives and marketing investments are required to address awareness limitations. Complex product structures and unfamiliar terminology can deter potential customers from exploring Islamic financial solutions.
Macroeconomic Uncertainties and Oil Price Volatility
Qatar's Islamic finance market remains exposed to macroeconomic uncertainties including oil price volatility, regional geopolitical developments, and global economic fluctuations. As hydrocarbon revenues significantly influence the national economy, price instability can affect government spending, corporate profitability, and consumer confidence. Despite strong fundamentals supported by liquefied natural gas exports, external economic shocks may impact growth trajectories. Evolving regulatory frameworks across competing financial centers and potential fragmentation from policy shifts present additional challenges requiring continued monitoring and strategic adaptation.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar Islamic finance market features a competitive landscape characterized by established institutions investing in innovation, digital transformation, and product diversification to strengthen market positions. Major players are expanding Sharia-compliant product portfolios while enhancing customer experience through advanced technology integration. Competition is intensifying as institutions pursue strategic partnerships, sukuk issuances, and sustainable finance initiatives to differentiate offerings. Banks are investing in mobile banking platforms, artificial intelligence solutions, and blockchain-based services to attract digitally-oriented customers. Takaful companies are expanding coverage options and improving service accessibility through digital channels. The market benefits from regulatory frameworks encouraging competition while maintaining stability and consumer protection standards.
Recent Developments:
- In November 2025, Qatar International Islamic Bank successfully issued a USD 500 Million five-year senior unsecured benchmark sukuk priced at 85 basis points over US Treasuries with a 4.50% coupon. The orderbook closed at USD 1.85 Billion demonstrating strong international investor demand. The sukuk was issued under QIIB's USD 2 Billion Trust Certificate Issuance Programme and listed on the London Stock Exchange's International Securities Market.
- In September 2024, Qatar Islamic Bank successfully issued a USD 750 Million sukuk with a five-year tenor and profit rate of 4.485%, representing the lowest achieved by a GCC bank for senior unsecured issuance in 2024. The orderbook peaked at USD 2.2 Billion representing three times oversubscription, showcasing strong investor confidence in Qatar's Islamic banking sector.
Qatar Islamic Finance Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Islamic Banking, Islamic Capital Markets, Takaful, Others |
| Financial Institution Types Covered | Islamic Banks, Investment Firms, Takaful Companies, Asset Management Firms, Others |
| Applications Covered | Personal Banking, Corporate Banking, SME Financing, Government and Public Sector, Non-profit Organizations |
| End Users Covered | Individuals, Businesses, Government Bodies, Non-profit Organizations |
| Regions Covered | Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Qatar Islamic finance market size was valued at USD 5.50 Million in 2025.
The Qatar Islamic finance market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 9.76% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 12.71 Million by 2034.
Islamic banking dominated the market with a share of 48%, owing to well-established institutional presence, comprehensive regulatory frameworks, and deep integration with national economic development strategies driving sustained growth.
Key factors driving the Qatar Islamic finance market include strong regulatory frameworks, government support through strategic initiatives, accelerating digital transformation, growing consumer demand for Sharia-compliant products, and expanding sukuk market depth.
Major challenges include regulatory fragmentation across international markets, limited consumer awareness in non-traditional markets, complex licensing requirements for cross-border expansion, oil price volatility, and macroeconomic uncertainties affecting growth trajectories.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












