
Qatar LNG-to-Power Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Project Type, Ownership, Power Capacity Range, Technology, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar LNG-to-Power Market Summary:
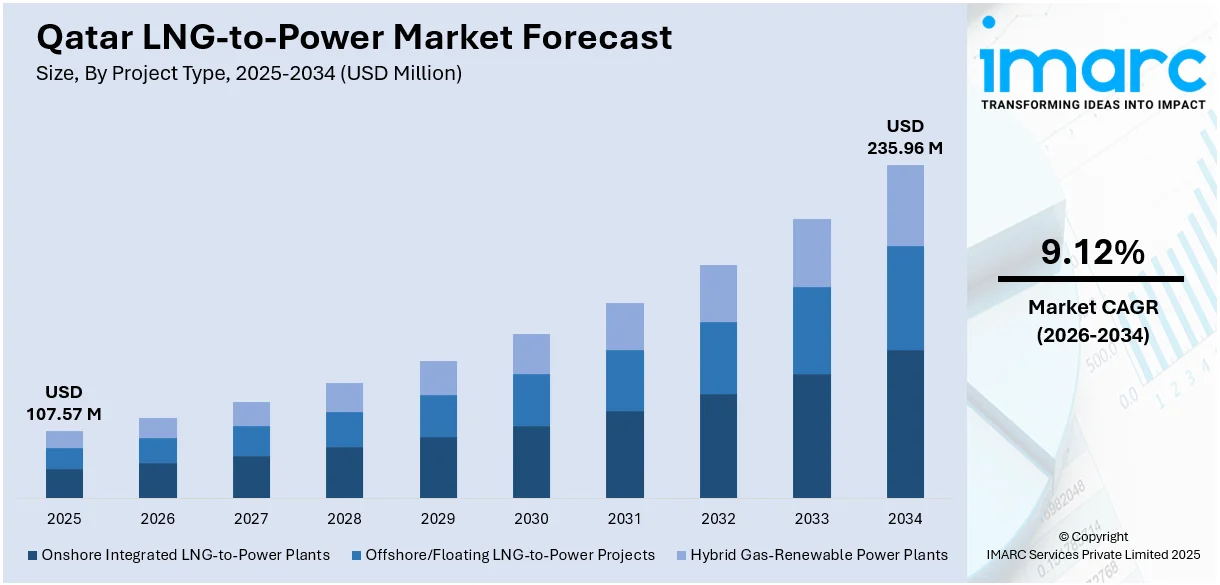
The Qatar LNG-to-power market size reached USD 107.57 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 235.96 Million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 9.12% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by aggressive LNG production expansion requiring substantial integrated power infrastructure, rapid solar energy integration to diversify the power mix and support sustainability goals, and the adoption of Independent Power Producer models with public-private partnerships to foster innovation and attract investment. Additionally, the increasing emphasis on carbon capture and storage technologies alongside power generation projects is expanding the Qatar LNG-to-power market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 107.57 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 235.96 Million |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 9.12% |
| Key Segments | Project Type (Onshore Integrated LNG-to-Power Plants, Offshore/Floating LNG-to-Power Projects, Hybrid Gas-Renewable Power Plants), Ownership (Government-owned Projects, Public–private Partnerships (PPPs), Independent Power Producers (IPPs)), Power Capacity Range (Small-scale (<500 MW), Medium (500–1000 MW), Large-scale (>1000 MW)), Technology (Combined-cycle Gas Turbines (CCGT), Open-cycle Gas Turbines (OCGT), Floating Storage and Regasification Units (FSRU), Hybrid LNG-renewable Systems), End User (Domestic Power Generation Sector, Industrial and Desalination Sector) |
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
Qatar LNG-to-Power Market Outlook (2026-2034):
The Qatar LNG-to-power market is positioned for robust growth throughout the forecast period, driven by the country's strategic expansion of LNG production capacity and corresponding infrastructure requirements. Qatar's ambitious plan to increase annual LNG production from 77 million metric tons to 142 million metric tons by 2030 necessitates substantial investments in reliable, high-efficiency power generation systems. The government's commitment to integrating carbon capture and storage technologies with new power facilities, combined with the transition toward the Independent Power Producer model, will create significant opportunities for international partnerships and technological innovation. Furthermore, the increasing integration of renewable energy sources, particularly solar power targeting 4 GW capacity by 2030, will drive demand for hybrid power solutions and advanced grid management systems to support Qatar's balanced energy transition strategy.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Impact of AI:
Artificial intelligence is transforming Qatar's LNG-to-power sector by optimizing operational efficiency across the entire value chain. AI-driven predictive maintenance systems are minimizing downtime at LNG facilities and power plants, while machine learning algorithms enhance grid management and load balancing capabilities. Smart energy management platforms utilizing AI are achieving significant efficiency gains, with projects like Qatar Solar Technologies demonstrating 20% improvements in solar panel performance through predictive analytics. Additionally, AI applications in demand forecasting, emissions monitoring, and real-time optimization of integrated water and power plants are enabling Qatar to manage the complex interdependencies between electricity generation, desalination operations, and industrial requirements more effectively, supporting the country's sustainability objectives while maintaining operational excellence.
Market Dynamics:
Key Market Trends & Growth Drivers:
Massive LNG Expansion Requiring Integrated Power Infrastructure
Qatar is pursuing one of the most ambitious energy expansion programs globally, aimed at significantly increasing its LNG production and reinforcing its leadership in the global energy market. The large-scale North Field Expansion project forms the core of this initiative, driving strong demand for advanced, high-efficiency power generation infrastructure to support LNG liquefaction, compression, and related industrial operations across Ras Laffan and Mesaieed Industrial Cities. Qatar’s integrated energy framework requires sophisticated combined cycle power plants capable of supplying both electricity and process heat for LNG operations while integrating advanced emissions control systems. The nation’s extensive investments position it to play a pivotal role in shaping future global LNG supply dynamics. In line with this growth, major infrastructure projects such as the Facility E Desalination and Combined Cycle Power Project, developed by leading international engineering and construction firms for Kahramaa, underscore Qatar’s commitment to expanding its power and water generation capabilities. Once operational, the project is expected to make a substantial contribution to the country’s total electricity and desalinated water supply, further strengthening the resilience and sustainability of Qatar’s energy ecosystem. The continuous stream of major infrastructure projects demonstrates the sustained Qatar LNG-to-power market growth driven by the fundamental requirement to match power generation capacity with expanding hydrocarbon production capabilities while meeting increasingly stringent environmental standards.
Accelerated Solar Energy Integration Supporting Sustainability Goals
Qatar is rapidly advancing its solar power development as a key pillar of its National Renewable Energy Strategy, aiming to make solar energy a major contributor to the country’s electricity generation and overall decarbonization goals. This focus reflects Qatar’s strong commitment to diversifying its energy mix beyond natural gas while capitalizing on its abundant solar resources and favorable climatic conditions. The national renewable energy agenda includes both large-scale utility projects and distributed generation initiatives, led by QatarEnergy’s development of world-class solar facilities that demonstrate growing self-sufficiency in energy project execution. The integration of solar capacity into Qatar’s predominantly gas-based power system is driving demand for hybrid power solutions that combine renewable energy with conventional LNG-to-power infrastructure to ensure grid reliability and efficiency. Advanced technologies being adopted include high-performance solar modules with tracking and automated cleaning systems suited to desert conditions, alongside smart grid networks for managing renewable variability. The recent inauguration of major solar power plants marked a milestone in Qatar’s transition toward sustainable energy, underscoring a shift from dependence on foreign expertise to the use of national capabilities. This ongoing solar expansion also opens pathways for innovative projects blending renewable generation, energy storage, and intelligent management systems to optimize the interaction between clean and conventional power sources.
Independent Power Producer Model Adoption Attracting International Investment
Qatar is transitioning from a traditionally state-controlled power sector to an Independent Power Producer (IPP) model, aligning with the Qatar National Vision 2030 goal of promoting innovation, efficiency, and international investment in its expanding electricity generation landscape. This shift allows greater private sector participation through public-private partnerships and build-own-operate arrangements, while Kahramaa continues to oversee transmission and distribution to maintain reliability and coordinated planning. The IPP framework supports Qatar’s ambitious integrated water and power development plans, which require advanced technology, strong financing, and operational excellence that global consortia can deliver through long-term agreements. Leading international companies are actively participating in this transformation, introducing next-generation combined cycle gas turbines, carbon capture solutions, and proven project management expertise. Qatar’s transparent regulatory environment, well-structured tendering processes, and stable offtake agreements make it an attractive market for large-scale power investments, particularly those integrating conventional and renewable generation. The successful award of the Facility E Independent Water and Power Project to a consortium of international and Qatari partners exemplifies the effective implementation of the IPP model for strategic infrastructure. The growing adoption of IPP projects is fostering competition, technological innovation, and efficiency gains while enabling Qatar to expand its energy capacity sustainably without overextending public finances.
Key Market Challenges:
Rapidly Escalating Electricity Demand Straining Infrastructure Capacity
Qatar faces mounting challenges in meeting rapidly increasing electricity demand driven by expanding water desalination needs, heavy air conditioning usage in extreme climatic conditions, and ongoing industrial growth in petrochemicals and manufacturing. The nation’s energy consumption pattern reflects strong sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, with even small increases leading to disproportionately higher power usage during summer months. This dynamic significantly strains generation and distribution infrastructure, demanding continuous capacity expansion to maintain grid reliability and prevent supply shortfalls during peak load periods. The country’s integrated water-power systems further intensify the challenge, as higher water demand directly translates into greater electricity generation requirements. Substantial investments are therefore essential not only in conventional and renewable generation capacity but also in expanding and modernizing transmission and distribution networks. Coordination between power infrastructure, urban development, and industrial zones remains critical to ensuring capacity availability aligns with regional demand growth. Sustaining such an energy-intensive ecosystem while maintaining reliability and efficiency underscores the urgency of strategic planning, technology adoption, and diversification in Qatar’s power infrastructure to meet long-term national development goals.
Grid Integration Complexities for Large-Scale Renewable Energy
Integrating large-scale solar power into Qatar’s predominantly gas-based grid introduces complex technical and operational challenges related to managing intermittency, ensuring stability, and modernizing transmission systems for variable and bidirectional power flows. The country’s renewable energy expansion goals demand substantial upgrades to legacy infrastructure and grid management protocols historically optimized for predictable gas-fired generation. Solar photovoltaic output varies considerably with weather conditions, dust accumulation, and the natural day-night cycle, requiring grid operators to adopt advanced balancing mechanisms and flexible generation assets. Investment in battery storage, AI-driven forecasting tools, and intelligent grid automation is critical to maintaining stability and minimizing curtailment. Kahramaa’s deployment of smart grid technologies, including advanced metering infrastructure, automated load balancing, and real-time monitoring, marks a major step toward enabling renewable integration. However, significant capital investment and workforce capability development are needed to reinforce networks connecting remote solar farms with high-demand centers. Coordinated planning across generation, transmission, and distribution segments is essential to ensure system reliability, optimize energy dispatch, and integrate renewables efficiently while transitioning toward a diversified and sustainable power mix that strengthens Qatar’s long-term energy security.
Water-Energy Nexus Complexity Affecting System Planning
Qatar’s power sector operates under a uniquely intertwined water-energy framework where electricity generation and desalination are co-located within integrated water and power plants. This configuration has historically delivered efficiency advantages by using waste heat from gas-fired power plants to drive thermal desalination processes such as Multi-Stage Flash and Multi-Effect Distillation. However, the shift toward renewable energy, particularly solar photovoltaics, challenges this synergy as clean power sources lack the thermal output needed for conventional desalination. The transition necessitates greater reliance on reverse osmosis and other electricity-dependent desalination methods, potentially increasing overall energy consumption for water production. As desalination capacity continues to expand to meet population and industrial growth, planners must carefully balance efficiency, flexibility, and sustainability across both sectors. Future system design will depend on innovative desalination technologies capable of operating directly on renewable electricity, along with hybrid solutions integrating solar and conventional power. This evolution requires significant research investment, pilot-scale demonstrations, and coordinated infrastructure planning to maintain water security while decarbonizing the power sector. Successfully managing this water-energy nexus is central to achieving Qatar’s dual objectives of sustainability and resilience in a resource-constrained environment.
Qatar LNG-to-Power Market Report Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Qatar LNG-to-power market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on project type, ownership, power capacity range, technology, and end user.
Analysis by Project Type:
- Onshore Integrated LNG-to-Power Plants
- Offshore/Floating LNG-to-Power Projects
- Hybrid Gas-Renewable Power Plants
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the project type. This includes onshore integrated LNG-to-power plants, offshore/floating LNG-to-power projects, and hybrid gas-renewable power plants.
Analysis by Ownership:
- Government-owned Projects
- Public–private Partnerships (PPPs)
- Independent Power Producers (IPPs)
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the ownership have also been provided in the report. This includes government-owned projects, public–private partnerships (PPPs), and independent power producers (IPPs).
Analysis by Power Capacity Range:
- Small-scale (<500 MW)
- Medium (500–1000 MW)
- Large-scale (>1000 MW)
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the power capacity range. This includes small-scale (<500 MW), medium (500–1000 MW), and large-scale (>1000 MW).
Analysis by Technology:
- Combined-cycle Gas Turbines (CCGT)
- Open-cycle Gas Turbines (OCGT)
- Floating Storage and Regasification Units (FSRU)
- Hybrid LNG-renewable Systems
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology have also been provided in the report. This includes combined-cycle gas turbines (CCGT), open-cycle gas turbines (OCGT), floating storage and regasification units (FSRU), and hybrid LNG-renewable systems.
Analysis by End User:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Domestic Power Generation Sector
- Industrial and Desalination Sector
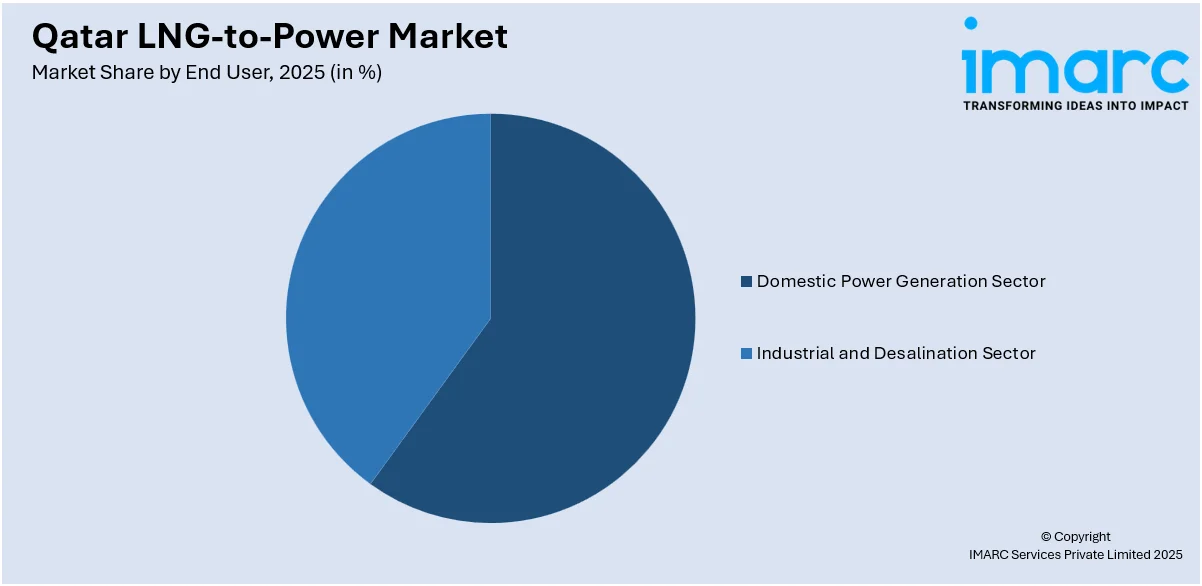
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user. This includes domestic power generation sector and industrial and desalination sector.
Analysis by Region:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the region have also been provided in the report. This includes Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar LNG-to-power market exhibits a moderately concentrated competitive structure dominated by state-owned entities and major international energy companies operating through public-private partnership arrangements and Independent Power Producer frameworks. Qatar General Electricity and Water Corporation (Kahramaa) maintains monopolistic control over electricity transmission and distribution while serving as the primary offtaker for all power generation through long-term power purchase agreements, effectively functioning as the single buyer in the market. Competition primarily occurs at the project development and operation level, where international consortia comprising engineering firms, equipment suppliers, and financial investors compete for independent power and integrated water-power project awards through competitive tender processes. Major players leverage their technical expertise in combined cycle gas turbine technology, carbon capture integration capabilities, desalination systems, and proven track records of delivering large-scale infrastructure projects on time and within budget. The market is characterized by high barriers to entry due to substantial capital requirements, complex technical specifications, stringent environmental standards, and the need for long-term financing arrangements backed by creditworthy counterparties. Established international firms including Samsung C&T, Sumitomo Corporation, GE, Siemens Energy, Mitsubishi Power, and others maintain strong positions through their technology portfolios, local presence, and established relationships with Qatari entities. The gradual shift toward hybrid projects combining conventional and renewable generation creates opportunities for specialized solar developers and energy storage providers to enter the market through partnerships with established power sector participants, potentially increasing competitive intensity in specific market segments.
Qatar LNG-to-Power Industry Latest Developments:
- April 2025: Qatar inaugurated the Ras Laffan and Mesaieed solar PV power plants with a combined capacity of 875 MW, more than doubling the country's solar energy production to 1,675 MW. The two plants, which cost approximately QAR 2.3 billion and span 10 square kilometers, are expected to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by about 4.7 million tons annually. Minister Saad Sherida Al-Kaabi emphasized that the construction of solar power plants represents one of Qatar's most important initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions, develop sustainability projects, and diversify electricity generation sources, with the plants contributing approximately 15% of total peak electricity demand alongside the existing Al-Kharsaah facility.
- December 2024: Samsung C&T Engineering and Construction Group secured a $2.84 billion EPC contract for the Qatar Facility E Desalination and Combined Cycle Power Project in partnership with Sumitomo Corporation. The project, commissioned by Kahramaa and located in the Ras Abu Fontas area approximately 18 kilometers southeast of Doha, will construct a combined cycle power plant with capacity to generate up to 2,400 MW of electricity and a large-scale desalination facility producing an average of 500,000 tons of water daily. The gas-fired power plant, set to be operational by 2029, will employ high-efficiency gas turbines that consume less gas and emit lower levels of CO2 and other pollutants compared to existing plants, contributing to stable energy supplies and Qatar's decarbonization efforts.
- November 2024: A consortium comprising Sumitomo Corporation, Shikoku Electric Power Co., KOSPO, and KIND was awarded the Facility E independent water and power project by Kahramaa following an international competitive tender. The project involves construction and operation of a natural gas-fired power plant with 2,400 MW capacity and a seawater desalination facility producing 495,000 tons per day on the site of an old power plant in Ras Abu Fontas. The new facility will employ high-efficiency gas turbines designed to reduce gas consumption and emissions, with the Government of Qatar and the project company planning to explore Carbon Capture and Storage plans to further reduce CO2 emissions, as electricity demand is projected to increase by 58% by 2040 compared to 2021 levels.
Qatar LNG-to-Power Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Project Types Covered | Onshore Integrated LNG-to-Power Plants, Offshore/Floating LNG-to-Power Projects, Hybrid Gas-Renewable Power Plants |
| Ownership Covered | Government-owned Projects, Public–private Partnerships (PPPs), Independent Power Producers (IPPs) |
| Power Capacity Ranges Covered | Small-scale (<500 MW), Medium (500–1000 MW), Large-scale (>1000 MW) |
| Technologies Covered | Combined-cycle Gas Turbines (CCGT), Open-cycle Gas Turbines (OCGT), Floating Storage and Regasification Units (FSRU), Hybrid LNG-renewable Systems |
| End Users Covered | Domestic Power Generation Sector, Industrial and Desalination Sector |
| Regions Covered | Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Qatar LNG-to-power market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar LNG-to-power market on the basis of project type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar LNG-to-power market on the basis of ownership?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar LNG-to-power market on the basis of power capacity range?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar LNG-to-power market on the basis of technology?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar LNG-to-power market on the basis of end user?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar LNG-to-power market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Qatar LNG-to-power market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Qatar LNG-to-power market?
- What is the structure of the Qatar LNG-to-power market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Qatar LNG-to-power market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC's industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Qatar LNG-to-power market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Qatar LNG-to-power market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Qatar LNG-to-power industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












