
Qatar Microfinance Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Provider Type, Purpose, Tenure, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar Microfinance Market Summary:
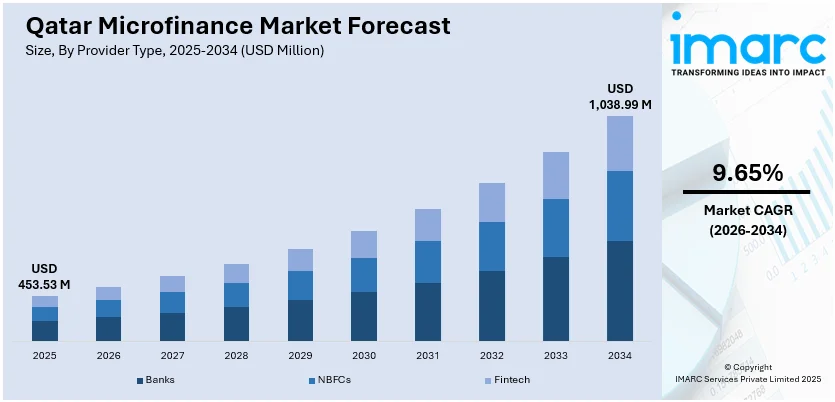
The Qatar microfinance market size was valued at USD 453.53 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 1,038.99 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 9.65% from 2026-2034.
The market is driven by government initiatives supporting financial inclusion, expanding small and medium enterprise financing requirements, and growing adoption of Islamic financing principles among underserved populations. Rising digital banking penetration and fintech innovation are accelerating accessibility to microfinance services across the nation. Additionally, economic diversification efforts under Qatar National Vision are creating sustained demand for entrepreneurial credit facilities, contributing to overall Qatar microfinance market share expansion.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Provider Type: Banks dominates the market with a share of 58% in 2025, driven by strong infrastructure, regulatory compliance, extensive branches, capital strength, customer trust, and diverse products meeting varied borrower needs.
-
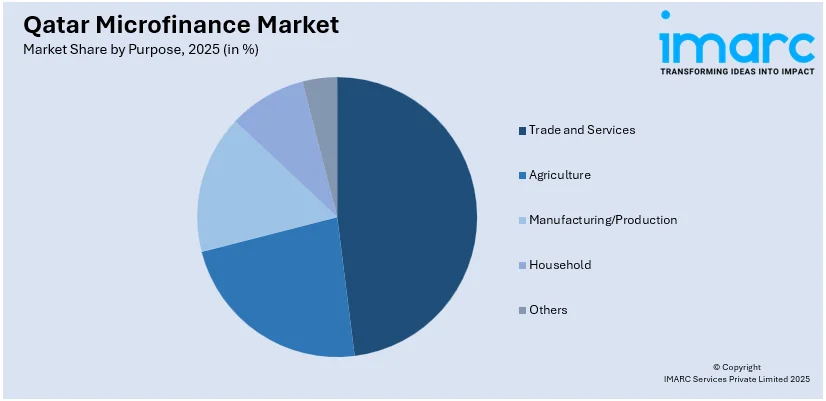
By Purpose: Trade and services lead the market with a share of 48% in 2025, owing to Qatar’s commercial sector growth, entrepreneurial expansion, government support, rising consumer spending, and alignment with non-hydrocarbon economic goals.
-
By Tenure: Less than 1 year represents the largest segment with a market share of 43% in 2025, driven by small enterprises’ working capital needs, seasonal financing, inventory cycles, short-term interest advantages, and flexible repayment enabling faster business turnaround.
-
Key Players: The Qatar microfinance market exhibits a consolidated competitive structure, with established banking institutions maintaining significant presence alongside emerging fintech providers. Market participants differentiate through Sharia-compliant product offerings, digital lending platforms, and specialized enterprise financing solutions tailored to local business requirements.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Qatar microfinance market is witnessing significant growth, driven by extensive government initiatives aimed at promoting financial inclusion and supporting small and medium-sized enterprise development. According to reports, Qatar Development Bank reported QR1.5 Billion in direct financing to SMEs during 2024, reflecting a 33% year-on-year increase, underscoring strengthened government support for private sector development. Moreover, under the Qatar National Vision framework, the country’s focus on economic diversification has created a conducive environment for expanding access to credit for underserved populations, including emerging entrepreneurs and start-ups. Investments in digital infrastructure are enhancing the efficiency and reach of microfinance services, with mobile banking applications and online lending platforms enabling convenient and timely financial transactions. In parallel, the increasing importance of Islamic finance has encouraged market participants to introduce Sharia-compliant microcredit products, aligning with local cultural and religious expectations. These developments collectively strengthen the market’s competitiveness, foster wider participation, and reinforce the sustainability of microfinance as a critical tool for economic growth and entrepreneurial empowerment in Qatar.
Qatar Microfinance Market Trends:
Digital Transformation and Mobile Banking Integration
The Qatar microfinance sector is witnessing accelerated digital transformation as institutions prioritize mobile-first lending solutions and automated loan processing systems. Financial service providers are deploying sophisticated digital platforms that enable remote account opening, instant credit assessment, and seamless fund disbursement through smartphone applications. As per the sources, in 2024, the Qatar Central Bank launched the FAWRAN instant payment service, enabling 24/7 real-time bank transfers via mobile applications using aliases or mobile numbers, supporting Qatar’s transition toward a cashless digital economy. Moreover, this technological shift is particularly significant given Qatar's exceptionally high internet penetration and smartphone adoption rates, creating fertile ground for digital microfinance expansion. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities is enhancing credit scoring accuracy while reducing processing timelines, ultimately improving customer experience and operational efficiency across the microfinance value chain.
Islamic Microfinance Product Innovation
Islamic microfinance solutions are gaining substantial traction within Qatar's financial ecosystem as institutions develop innovative Sharia-compliant lending instruments. Providers are introducing specialized products based on murabaha, musharaka, and qard hassan principles that align with religious requirements while meeting diverse financing needs. According to reports, in November 2024, Qatar Development Bank strategically invested in Wahed, a Sharia-compliant FinTech, expanding digital Islamic finance solutions and supporting financial inclusion across ethical microfinance products. Further, this trend reflects broader regional movement toward ethical banking alternatives that emphasize risk-sharing partnerships rather than conventional interest-based lending relationships. The expansion of Islamic microfinance offerings is attracting previously underbanked populations who sought alternatives to conventional credit products, thereby contributing to enhanced financial inclusion across demographic segments.
Women Entrepreneurship and Financial Inclusion Focus
Microfinance institutions in Qatar are increasingly prioritizing women entrepreneurs through dedicated lending programs and customized financial literacy initiatives. As per sources, in February 2024, the Qatari Businesswomen Association partnered with Qatar Islamic Bank to empower female entrepreneurs through tailored financial products, services, and advisory support, advancing women’s economic participation. This strategic focus aligns with national objectives promoting gender economic participation and female-led enterprise development within the private sector. Financial service providers are designing specialized microcredit products that address unique challenges faced by women business owners, including flexible repayment schedules and reduced collateral requirements. The emphasis on women's financial inclusion is generating positive socioeconomic outcomes while expanding the addressable market for microfinance services, as female entrepreneurs represent a growing segment of Qatar's small business landscape.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Qatar microfinance market revenue is projected to experience sustained growth throughout the forecast period, underpinned by continued government commitment to financial inclusion and private sector development initiatives. Revenue expansion will be driven by increasing adoption of digital lending platforms, growing small enterprise financing requirements, and expanding Sharia-compliant product portfolios. The market outlook remains favorable as institutions invest in technological capabilities and develop innovative credit solutions addressing evolving borrower preferences, positioning Qatar as a regional leader in accessible financial services. The market generated a revenue of USD 453.53 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 1,038.99 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 9.65% from 2026-2034.
Qatar Microfinance Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Provider Type | Banks | 58% |
| Purpose | Trade and Services | 48% |
| Tenure | Less than 1 year | 43% |
Provider Type Insights:
- Banks
- NBFCs
- Fintech
Banks dominates with a market share of 58% of the total Qatar microfinance market in 2025.
Banks maintain commanding presence within Qatar's microfinance landscape owing to their established regulatory compliance frameworks, extensive physical and digital distribution networks, and substantial capital reserves enabling diversified lending activities. These institutions leverage long-standing customer relationships and brand recognition to attract microfinance borrowers seeking reliable credit partnerships with transparent terms and competitive interest structures. Their deep understanding of local market dynamics and comprehensive borrower profile assessments further enhances lending precision and portfolio quality management across diverse customer segments.
The dominance of banks is further reinforced by comprehensive product ecosystems that bundle microcredit facilities with ancillary services including savings accounts, insurance products, and dedicated financial advisory support. Banks continue investing significantly in digital infrastructure upgrades and mobile lending platforms to enhance accessibility and streamline application processes, thereby strengthening competitive positioning against emerging non-bank providers. As per sources, in February 2024, QNB launched a digital onboarding service through its mobile app, allowing new customers to remotely open accounts, complete verification, activate virtual cards, and access banking services without visiting branches. Additionally, their established ability to offer preferential interest rates and flexible repayment terms attract borrowers seeking cost-effective and reliable financing solutions.
Purpose Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Agriculture
- Manufacturing/Production
- Trade and Services
- Household
- Others
Trade and services lead with a share of 48% of the total Qatar microfinance market in 2025.
Trade and services leadership reflects Qatar's dynamic commercial ecosystem characterized by thriving retail, hospitality, and professional services sectors requiring consistent working capital financing solutions. Small business owners operating within these diverse industries demonstrate strong demand for microloans supporting inventory acquisition, equipment procurement, and operational expansion activities aligned with national economic diversification priorities. According to sources, in 2024, Global Finance recognized Qatar Development Bank as Qatar’s Best SME Bank and Trade Finance Provider, highlighting its support for SMEs, trade financing, and digital solutions for entrepreneurs. Moreover, the segment also benefits significantly from increasing consumer spending patterns and rising tourism activities that collectively drive sustained commercial enterprise growth throughout the nation.
The segment benefits from government initiatives actively promoting entrepreneurship and private sector growth, creating highly favorable conditions for trade-focused microfinance expansion across various municipalities. Lenders have developed specialized credit products addressing unique requirements of service-oriented enterprises, including seasonal financing arrangements and revenue-linked repayment structures that accommodate variable business cash flows common within commercial trading activities. Furthermore, the increasing number of small enterprises entering retail and hospitality sectors continues driving sustained demand for accessible and affordable microfinance solutions.
Tenure Insights:
- Less than 1 year
- 1-2 years
- More than 2 years
Less than 1 year exhibits a clear dominance with a 43% share of the total Qatar microfinance market in 2025.
Less than 1 year dominates Qatar microfinance market as borrowers prioritize flexible financing arrangements with reduced long-term commitment obligations and lower overall interest payment burdens. Small enterprises typically require rapid capital infusion for immediate operational needs including inventory replenishment, seasonal demand fulfillment, and short-cycle business opportunities that align naturally with sub-annual loan durations. According to reports, in October 2024, Qatar Development Bank launched zero-profit short-term financing for companies that fully repaid National Response Guarantee Program loans, supporting working capital needs and continued business operations. Further, this preference is particularly evident among retail and service sector businesses where working capital requirements fluctuate based on prevailing market conditions and consumer demand patterns.
The prevalence of Less than 1 year reflects prudent risk management preferences among both institutional lenders and borrowers within Qatar's dynamic financial ecosystem. Institutions benefit significantly from accelerated capital turnover and reduced exposure periods, while entrepreneurs appreciate lower total interest costs and faster debt resolution timelines enabling subsequent borrowing flexibility for emerging business requirements. Additionally, short-term loan structures allow businesses to quickly adapt their financing strategies based on changing market conditions and evolving operational priorities throughout the calendar year.
Regional Insights:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
Ad Dawhah represents the dominant regional market for microfinance services as Qatar's capital and primary commercial hub housing the majority of financial institutions and small enterprise activities. The municipality benefits from concentrated banking infrastructure, advanced digital connectivity, and substantial entrepreneurial populations driving sustained microcredit demand across trade, services, and professional sectors.
Al Rayyan constitutes a significant microfinance market supported by its status as Qatar's education and residential growth corridor experiencing substantial commercial development. The municipality's expanding retail, agricultural, and service sectors generate consistent microloan requirements, while proximity to Doha metropolitan area ensures access to established lending institutions and emerging fintech providers.
Al Wakrah demonstrates growing microfinance market potential driven by industrial development, maritime commercial activities, and expanding residential communities requiring localized financial services. The municipality's economic diversification initiatives and small business growth create favorable conditions for microfinance penetration, particularly among trade and manufacturing-oriented enterprises.
Others in Qatar municipalities including Al Khor, Al Shahaniya, and Umm Salal contribute collectively to Qatar's microfinance landscape through agricultural financing, community-based lending initiatives, and decentralized commercial activities. These regions present emerging opportunities for microfinance expansion as infrastructure development and population growth stimulate local entrepreneurial ecosystems.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Qatar Microfinance Market Growing?
Government Financial Inclusion Initiatives and Policy Support
Qatar's government has prioritized financial inclusion as a cornerstone of national development strategy, implementing comprehensive programs supporting microfinance sector expansion and accessibility enhancement. The Qatar Central Bank's Financial Sector Strategic Plan establishes clear frameworks encouraging institutions to develop innovative credit products serving underbanked populations and small enterprises. Regulatory sandboxes enable fintech experimentation while maintaining consumer protection standards, creating balanced environments for microfinance innovation. As per sources, in May 2024, Qatar Central Bank launched the Express Sandbox, enabling fintech firms faster market entry with streamlined regulatory assessment, promoting innovation and financial inclusion in the Qatari financial ecosystem. Moreover, development agencies provide complementary support through entrepreneurship training programs, business incubation services, and credit guarantee schemes reducing lender risk exposure.
Economic Diversification and Small Enterprise Development
Qatar's strategic shift toward economic diversification beyond hydrocarbon dependence is generating substantial demand for microfinance services supporting private sector expansion and entrepreneurial ventures. The Qatar National Vision framework explicitly targets small and medium enterprise development as essential for sustainable economic growth and employment generation. This emphasis has stimulated growth across commercial, retail, hospitality, and professional services sectors where microfinance plays critical enabling roles. Aspiring entrepreneurs and established small business owners increasingly seek accessible credit facilities funding startup costs, working capital requirements, and expansion investments. According to reports, in February 2025, the QRDI Council launched the Small Business Innovation Grant at Web Summit Qatar to support early-stage SMEs, accelerating innovation, R&D, and technology commercialization.
Digital Banking Advancement and Fintech Innovation
Rapid advancement in digital banking infrastructure and fintech capabilities is transforming Qatar's microfinance landscape by enabling efficient, accessible, and cost-effective lending services. High internet penetration and smartphone adoption rates create ideal conditions for mobile-based microfinance delivery reaching previously underserved populations. Financial technology companies are introducing innovative credit assessment methodologies utilizing alternative data sources and artificial intelligence algorithms that expand lending possibilities beyond traditional creditworthiness metrics. Established banks are partnering with fintech providers to enhance digital capabilities while maintaining regulatory compliance and customer trust. In July 2025, Qatar Islamic Bank partnered with PayLater to launch the country’s first Shari’a-compliant Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) solution, enhancing digital financial access and inclusion.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Qatar Microfinance Market is Facing?
Regulatory Complexity and Compliance Requirements
Microfinance providers in Qatar navigate complex regulatory frameworks requiring substantial compliance investments and operational adjustments. Stringent licensing requirements, capital adequacy standards, and consumer protection regulations create barriers for new market entrants and smaller institutions with limited resources. The need for continuous regulatory monitoring and adaptation increases operational costs, potentially affecting lending rates and product accessibility for target borrower segments.
Limited Financial Literacy Among Target Populations
Insufficient financial literacy among potential microfinance borrowers constrains market expansion by limiting awareness of available products and appropriate utilization practices. Many prospective clients lack understanding of loan terms, repayment obligations, and credit management principles necessary for successful borrowing experiences. This knowledge gap increases default risks while discouraging institutions from extending credit to underserved populations, thereby restricting inclusive growth objectives.
Credit Risk and Default Management Challenges
Managing credit risk within microfinance portfolios presents ongoing challenges as institutions balance accessibility objectives with prudent lending standards. Limited credit history availability among target borrowers complicates accurate risk assessment, potentially leading to elevated default rates affecting institutional sustainability. Economic volatility and business uncertainties within small enterprise segments further complicate portfolio management, requiring sophisticated monitoring capabilities and provisioning strategies.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar microfinance market features a structured competitive environment characterized by established banking institutions maintaining significant market presence alongside emerging fintech providers and specialized non-bank financial companies. Competition centers on product innovation, digital service capabilities, pricing competitiveness, and customer experience enhancement. Participants differentiate through Sharia-compliant offerings, customized enterprise solutions, and technological integration enabling streamlined lending processes. Strategic partnerships between traditional banks and technology providers are reshaping competitive dynamics, while regulatory frameworks ensure fair market access and consumer protection standards. Market consolidation trends favor institutions demonstrating strong digital capabilities, robust risk management systems, and comprehensive product portfolios addressing diverse borrower requirements across commercial and consumer segments.
Qatar Microfinance Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Provider Types Covered | Banks, NBFCs, Fintech |
| Purposes Covered | Agriculture, Manufacturing/Production, Trade and Services, Household, Others |
| Tenures Covered | Less than 1 year, 1-2 years, More than 2 years |
| Regions Covered | Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Qatar microfinance market size was valued at USD 453.53 Million in 2025.
The Qatar microfinance market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 9.65% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 1,038.99 Million by 2034.
Banks held the largest share in Qatar microfinance market, leveraging their established institutional infrastructure, regulatory compliance, extensive branch networks, strong capitalization, and customer trust, while offering diverse and tailored financial products that effectively meet the varied needs of local borrowers and enterprises.
Key factors driving the Qatar microfinance market include government financial inclusion initiatives, economic diversification programs supporting small enterprise development, digital banking advancement, Islamic finance product innovation, and growing entrepreneurship culture.
Major challenges include regulatory complexity and compliance requirements, limited financial literacy among target populations, credit risk management difficulties, competition from informal lending sources, and technology adoption barriers among underserved demographics.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












