
Qatar Personalized Medicine Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product, End Use, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar Personalized Medicine Market Summary:
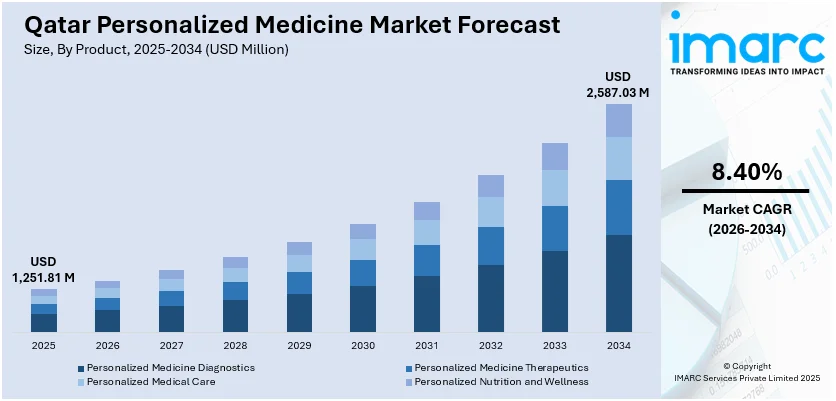
The Qatar personalized medicine market size reached USD 1,251.81 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 2,587.03 Million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 8.40% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by national genomic programs and precision health infrastructure expansion through initiatives like the Qatar Precision Health Institute, advanced digital health and telemedicine integration leveraging artificial intelligence for diagnostic accuracy, and substantial government investment aligned with Qatar National Vision 2030's healthcare transformation agenda. These strategic initiatives, combined with growing emphasis on pharmacogenomics implementation and population-based biobanking, are collectively expanding the Qatar personalized medicine market share.
|
Particulars |
Details |
|
Market Size (2025) |
USD 1,251.81 Million |
|
Forecast (2034) |
USD 2,587.03 Million |
|
CAGR (2026-2034) |
8.40% |
|
Key Segments |
Product (Personalized Medicine Diagnostics, Personalized Medicine Therapeutics, Personalized Medical Care, Personalized Nutrition and Wellness), End Use (Hospitals, Diagnostic Centers, Research and Academic Institutes, Others) |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
Qatar Personalized Medicine Market Outlook (2026-2034):
The Qatar personalized medicine market is poised for robust growth throughout the forecast period, propelled by the country's comprehensive precision health infrastructure initiatives and technological innovation. The Qatar Precision Health Institute's genomic sequencing programs, targeting 100,000 genomes by 2025, will provide critical data foundations for therapeutic development and disease prevention strategies. Meanwhile, artificial intelligence integration across diagnostic platforms and telemedicine services continues expanding care accessibility while reducing healthcare delivery costs. Government funding commitments under the 2024-2030 Health Strategy, coupled with international collaborations and educational initiatives embedding pharmacogenomics into university curricula and healthcare provider training, will further strengthen the market's upward trajectory throughout the forecast period.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Impact of AI:
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally transforming Qatar's personalized medicine landscape by enabling unprecedented diagnostic accuracy and predictive capabilities. AI-powered diagnostic tools currently achieve 95% accuracy rates for complex conditions including cancer and cardiovascular diseases, while machine learning algorithms rapidly analyze massive genomic datasets to identify disease-causing genetic variations within seconds. AI-driven platforms facilitate personalized treatment recommendations by recognizing subtle patterns in genetic data, thereby reducing adverse drug reactions and improving therapeutic outcomes. Furthermore, AI integration with digital twin technology and remote monitoring systems enhances chronic disease management, supports pharmacogenomics implementation, and enables predictive health modeling that positions Qatar at the forefront of precision medicine innovation in the Middle East region.
Market Dynamics:
Key Market Trends & Growth Drivers:
National Genomic Programs and Precision Health Infrastructure Expansion
Qatar has established comprehensive national genomic initiatives that are fundamentally reshaping the personalized medicine landscape through coordinated institutional efforts and substantial resource allocation. The focal point of this change is the Qatar Precision Health Institute, which was created by the strategic union of Qatar Biobank and Qatar Genome Program. It uses more than ten years of useful genomic and multi-omics data collection to develop individualized methods for illness prevention and treatment. The program's ambitious goal of sequencing 100,000 genomes will give researchers and medical professionals previously unheard-of insights into the genetic makeup of the Arab and Qatari populations, which have hitherto been underrepresented in international genomic databases. This population-based biobanking initiative, which began recruiting participants in 2011 and aims to enroll more than 60,000 Qatari nationals and long-term residents, serves as a central research platform supporting biomedical research and facilitating the translation of genomic discoveries into impactful preventive, diagnostic, and therapeutic practices. Following the merger of Qatar Biobank and Qatar Genome Program, the Qatar Precision Health Institute was formally established in November 2024, marking a strategic shift from supporting precision medicine at the basic research level to clinical implementation and positioning Qatar as a major hub for precision health throughout the Middle East. The development of the Qatar gene chip or Q-chip, containing gene variants specific to the Qatari population identified through extensive sequencing and genetic screening, exemplifies the practical applications of this genomic infrastructure, enabling more accurate diagnoses tailored to local genetic profiles compared to international laboratory results or gene assays developed using data from other populations.
Advanced Digital Health and Telemedicine Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence, telemedicine platforms, and electronic health records into Qatar's healthcare ecosystem is accelerating the Qatar personalized medicine market growth through enhanced diagnostic capabilities and improved patient accessibility. Under the Qatar National Vision 2030 framework, healthcare authorities have implemented comprehensive digital transformation strategies focusing on precision medicine, telemedicine, and genomic research, with AI-powered diagnostic tools achieving remarkable 95% accuracy rates for conditions including cancer and cardiovascular diseases. This technological advancement is complemented by widespread telemedicine adoption, which significantly reduces patient travel time while expanding care access particularly for remote and underserved populations. The deployment of centralized electronic health record systems covering approximately 80% of healthcare providers enables seamless data integration and interoperability, ensuring healthcare professionals have unified access to patient records for more informed clinical decision-making. Blockchain technology exploration for data security enhancement and claims processing streamlining further demonstrates the sophisticated approach to digital health infrastructure development. In January 2025, reporting revealed that telemedicine platforms facilitated 1.5 million virtual consultations in 2024 while AI-powered diagnostic tools achieved 95% accuracy for cancer and cardiovascular disease detection, demonstrating substantial progress in digital health integration under Qatar's healthcare innovation strategy. Companies like DxWELL are combining AI and wearable technology to deliver real-time monitoring solutions supporting Qatar's precision medicine and chronic disease management initiatives, while the integration of AI imaging into approximately 75% of diagnostic tools by 2025 represents a fundamental shift in clinical practice. This technological ecosystem, supported by onshore hyperscaler cloud regions and local data centers ensuring low latency and data residency compliance, creates an optimal environment for personalized medicine applications ranging from pharmacogenomics-guided prescribing to predictive health modeling.
Government Investment and Strategic Healthcare Transformation
Qatar's substantial government commitment to healthcare modernization through the Qatar National Vision 2030 and the newly launched 2024-2030 Health Strategy provides a robust foundation for sustained personalized medicine market expansion through dedicated funding, regulatory support, and institutional capacity building. The government has allocated significant resources specifically for digital health initiatives, with Qatar's healthcare expenditure projected to reach substantial levels reflecting commitment to improving health services and implementing advanced technologies for patient care optimization. The Ministry of Public Health's strategic focus encompasses developing digital health platforms, implementing telemedicine initiatives, and fostering precision medicine research programs that emphasize pharmacogenomics, genetic counseling, and personalized therapeutic approaches. These initiatives are supported by world-class medical institutions including Hamad Medical Corporation, which established a Precision Medicine Committee comprising representatives from cardiology, oncology, and other specialties to oversee precision medicine integration into clinical decision-making processes. Educational initiatives further strengthen this ecosystem, with pharmacogenomics and precision medicine concepts integrated into university curricula at institutions like Qatar University and Hamad Bin Khalifa University, alongside healthcare provider training programs and annual precision medicine conferences that facilitate knowledge exchange and international collaboration. The regulatory framework continues evolving to support innovation while ensuring patient safety, with guidelines governing stem cell research, genetic testing protocols, and data privacy considerations. With its diverse immigrant population, cutting-edge healthcare system, and extensive national genome program, Qatar is positioned as an exemplar case study for precision medicine implementation in the Middle East region. International collaborations with organizations like Genomics England enable cross-analysis with national datasets, contributing to a broader understanding of genetic variations across populations.
Key Market Challenges:
Complex Regulatory and Data Integration Barriers
The Qatar personalized medicine market confronts substantial regulatory complexity and data management challenges that can significantly delay innovation and market entry for novel diagnostic tests and therapeutic products. The regulatory landscape requires extensive documentation and clinical validation, with approval processes for clinical trials and new biomarker tests often extending up to 18 months, creating considerable uncertainty for companies seeking to develop and commercialize personalized medicine solutions including DNA-encoded libraries, multiplex assays, and pharmacogenomics-based diagnostic products. The Ministry of Public Health maintains stringent compliance standards aligned with international best practices, which, while ensuring patient safety and product efficacy, can complicate logistics operations and increase costs for distributors navigating these complex compliance landscapes. Beyond regulatory hurdles, establishing comprehensive databases of genetic and clinical information required for effective personalized medicine implementation presents formidable technical and operational challenges regarding data collection, storage, security, and accessibility. The integration of pharmacogenomics data into electronic health records remains incomplete, with limited availability of regulated clinical pharmacogenomics testing and technical obstacles hindering seamless information flow across healthcare institutions. Translating the vast amounts of genetic and clinical data collected through initiatives like Qatar Biobank into clinically relevant, actionable information for individual patient care demands sophisticated analytical tools and methodologies to interpret complex genetic variations and their clinical implications. Furthermore, ensuring interoperability across diverse healthcare information systems while maintaining robust cybersecurity protocols and compliance with data privacy regulations adds additional layers of complexity. These data integration barriers, combined with the need for standardization of genetic testing methodologies and interpretation guidelines, can slow the pace at which genomic insights translate into routine clinical practice, thereby limiting the near-term realization of personalized medicine's full potential despite substantial investments in genomic infrastructure and research capabilities.
Limited Clinical Literacy and Workforce Readiness
One of the most significant obstacles to widespread personalized medicine adoption in Qatar is the limited knowledge, awareness, and expertise regarding pharmacogenomics and genetic testing among both healthcare providers and patients, creating substantial gaps between technological capabilities and practical clinical implementation. Many healthcare professionals lack familiarity with genetic testing technologies, interpretation of genetic results, and how to effectively integrate genomic information into treatment decision-making processes, as pharmacogenomics education may not have been included in the medical school curricula or clinical training programs, that senior physicians completed decades ago. This literacy gap manifests in multiple ways: clinicians may be uncertain about when to order genetic tests, how to interpret complex genetic reports, which pharmacogenomics guidelines to follow, and how to communicate genetic risk information effectively to patients. The challenge extends beyond physicians to encompass nurses, pharmacists, genetic counselors, and laboratory professionals who all play critical roles in the personalized medicine care pathway but may lack adequate training in genomics and precision medicine concepts. Patient awareness and understanding of genetic testing also remains limited, with many individuals unfamiliar with the potential benefits, limitations, and implications of genomic information for their healthcare. This knowledge deficit can reduce patient willingness to participate in genetic testing programs or genomic research initiatives, thereby limiting the data available for developing population-specific implementation strategies and evidence-based clinical guidelines. Educational institutions and healthcare organizations are working to address these gaps through curriculum development, continuing medical education programs, and precision medicine conferences, but transforming the knowledge and capabilities of the entire healthcare workforce requires sustained, long-term investment in education and training infrastructure. Until healthcare providers develop confidence and competence in utilizing genetic information for clinical decision-making, and patients become more informed and engaged participants in genomic medicine, the translation of Qatar's substantial investments in genomic infrastructure into widespread clinical impact will remain constrained, potentially slowing market growth and limiting the population-level health benefits that personalized medicine promises to deliver.
Ethical and Cultural Concerns Regarding Genetic Testing
Addressing the complex ethical, legal, and cultural considerations surrounding genetic testing, data sharing, and informed consent poses ongoing challenges for personalized medicine implementation in Qatar's diverse and culturally sensitive society. Patients' acceptance and willingness to participate in pharmacogenomics programs and genomic research initiatives are greatly influenced by cultural beliefs, religious perspectives, and privacy concerns. Public engagement is impacted by worries about medical ethics, genetic record confidentiality, and potential misuse or discrimination based on genetic information. Research indicates that approximately 60% of the population has expressed concerns regarding the ethical implications of stem cell and genetic research, which can lead to stricter regulations, reduced research participation rates, and deterrence of potential investors in the personalized medicine sector. Precision medicine adoption may be slowed by public policy discussions on social and political barriers, such as data ownership, genetic discrimination in employment or insurance contexts, and the proper use of genetic information by governmental or commercial entities. Religious and cultural considerations regarding genetic manipulation, embryonic research, and the interpretation of genetic predisposition to disease add additional complexity to informed consent processes and program design. Furthermore, genetic testing programs must navigate a variety of cultural perspectives and belief systems regarding health, disease, family, and medical intervention due to Qatar's diverse population composition, which includes a large immigrant population from various cultural backgrounds in addition to a small native Qatari population. The challenge extends to ensuring equitable access to personalized medicine benefits across different population segments while respecting cultural preferences and values. Developing regulatory frameworks that adequately address ethical considerations encompassing patient consent, data privacy, and cultural perceptions regarding genetic testing and personalized medicine requires ongoing dialogue among policymakers, healthcare providers, ethicists, religious scholars, and community representatives. Until these ethical and cultural concerns are comprehensively addressed through transparent policies, community engagement, education initiatives, and robust privacy protections, public trust and participation in personalized medicine programs may remain suboptimal, potentially limiting the scale and impact of genomic initiatives and constraining market growth despite favorable technological and infrastructure conditions.
Qatar Personalized Medicine Market Report Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Qatar personalized medicine market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on product and end use.
Analysis by Product:
- Personalized Medicine Diagnostics
- Genetic Testing
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Diagnostics
- Esoteric Lab Services
- Esoteric Lab Tests
- Personalized Medicine Therapeutics
- Pharmaceutical
- Genomic Medicine
- Medical Device
- Personalized Medical Care
- Telemedicine
- Health Information Technology
- Personalized Nutrition and Wellness
- Retail Nutrition
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the product. This includes personalized medicine diagnostics (genetic testing, direct-to-consumer (DTC) diagnostics, esoteric lab services, and esoteric lab tests), personalized medicine therapeutics (pharmaceutical, genomic medicine, and medical device), personalized medical care (telemedicine and health information technology), and personalized nutrition and wellness (retail nutrition and complementary and alternative medicine).
Analysis by End Use:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Centers
- Research and Academic Institutes
- Others
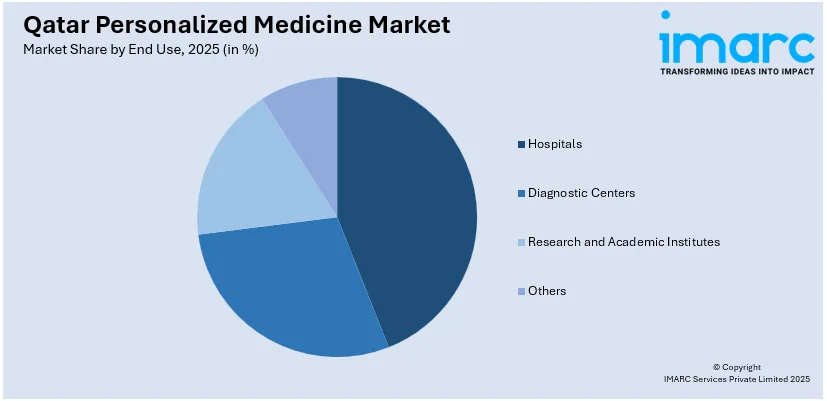
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end use have also been provided in the report. This includes hospitals, diagnostic centers, research and academic institutes, and others.
Analysis by Region:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar personalized medicine market is characterized by a dynamic ecosystem combining established international healthcare providers, emerging local biotechnology ventures, and government-backed research institutions collaborating to advance precision health capabilities. Competition centers on technological innovation, quality of genomic data analysis, clinical implementation capabilities, and the ability to navigate Qatar's regulatory environment while addressing population-specific health needs. Key players focus on developing localized genetic testing solutions, integrating pharmacogenomics into clinical workflows, and establishing strategic partnerships with healthcare facilities and research institutions. The market benefits from substantial government support through entities like Qatar Science & Technology Park, Qatar Development Bank, and the Qatar Research, Development, and Innovation Council, which provide funding and infrastructure for health technology startups and research initiatives. While international diagnostic companies and pharmaceutical firms maintain strong presence through distribution networks and partnerships, locally developed digital health platforms leveraging artificial intelligence for chronic disease management and personalized interventions are gaining traction. The competitive landscape emphasizes collaboration over pure competition, with public-private partnerships, academic-industry alliances, and international research collaborations driving innovation and clinical translation of precision medicine technologies.
Qatar Personalized Medicine Industry Latest Developments:
- January 2024: DroobiSmit (later called Lillia) was formed by the merger of Smit.fit, an Indian company, with Droobi Health, a Qatari company, with its headquarters located in Singapore. Supported by an investment of about USD 5 million from Qatar Science & Technology Park, Qatar Development Bank, and M Venture Partners, the merger established the company as the leading provider of digital diabetes solutions in the GCC and South Asia, utilizing digital twin technology for personalized interventions, AI-powered digital therapeutics, and predictive health monitoring to manage chronic diseases.
- February 2025: Lillia (formerly DroobiSmit/Droobi Health) secured USD 1.7 million in funding from the Qatar Research, Development, and Innovation Council to develop a groundbreaking digital twin system designed to monitor, predict, and personalize care for chronic disease patients. The AI-powered tool continuously integrates real-time health data with predictive analytics, supporting the company's expansion across MENA and Southeast Asia regions.
- December 2024: Sidra Medicine, a Qatar Foundation entity, hosted the Precision Medicine and the Future of Genomics 2024 Summit at Qatar National Convention Center from December 3-5, celebrating a decade of progress in precision medicine. The summit featured masterclasses on genome data analysis, generative AI applications, and genetic counseling, while highlighting advancements in newborn genome sequencing, population genomics, and breakthrough precision therapies with participation from international experts including Harvard Medical School faculty.
Qatar Personalized Medicine Market Report Coverage:
|
Report Features |
Details |
|
Base Year of the Analysis |
2025 |
|
Historical Period |
2020-2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
|
Units |
Million USD |
|
Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
|
Products Covered |
|
|
End Uses Covered |
Hospitals, Diagnostic Centers, Research and Academic Institutes, Others |
|
Regions Covered |
Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
|
Customization Scope |
10% Free Customization |
|
Post-Sale Analyst Support |
10-12 Weeks |
|
Delivery Format |
PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Qatar personalized medicine market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar personalized medicine market on the basis of product?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar personalized medicine market on the basis of end use?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar personalized medicine market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Qatar personalized medicine market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Qatar personalized medicine market?
- What is the structure of the Qatar personalized medicine market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Qatar personalized medicine market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC's industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Qatar personalized medicine market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Qatar personalized medicine market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Qatar personalized medicine industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












