
Qatar Polymers Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Process, End Use, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar Polymers Market Summary:
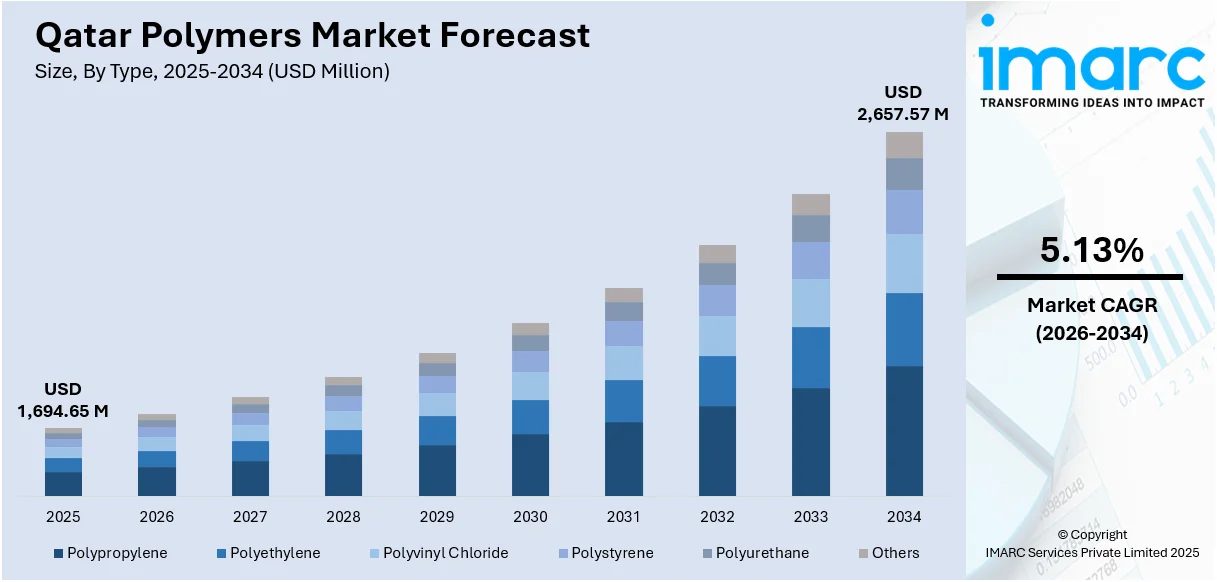
The Qatar polymers market size reached USD 1,694.65 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 2,657.57 Million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 5.13% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by government-led economic diversification initiatives emphasizing plastics as a strategic manufacturing sector, massive petrochemical infrastructure expansion through landmark international partnerships including the USD 6 billion Ras Laffan Petrochemical Complex, and aggressive circular economy adoption with enhanced recycling infrastructure across industrial zones. These transformative developments, combined with robust demand from construction, packaging, and automotive sectors, are significantly expanding the Qatar polymers market share.
|
Particulars |
Details |
|
Market Size 2025 |
USD 1,694.65 Million |
|
Forecast 2034 |
USD 2,657.57 Million |
|
CAGR (2026-2034) |
5.13% |
|
Key Segments |
Type (Polypropylene, Polyethylene, Polyvinyl Chloride, Polystyrene, Polyurethane, Others), Process (Injection Molding, Extrusion, Others), End Use (Packaging, Building and Construction, Automotive, Electrical and Electronic, Agriculture, Medical/Healthcare, Others) |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
Qatar Polymers Market Outlook (2026-2034):
The deliberate government investments in downstream petrochemical expansion and manufacturing diversification have positioned the Qatari polymers market for long-term growth. Plastics are a key industry in the Qatar National Manufacturing Strategy 2024–2030, which aims to boost production capacity and export competitiveness. Major infrastructure projects, including the Ras Laffan Petrochemical Complex expected to commence operations in late 2026, will substantially boost domestic production capabilities. Additionally, growing emphasis on circular economy principles, supported by expanding recycling infrastructure in designated industrial zones, will create new revenue streams while addressing sustainability imperatives throughout the forecast period.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Impact of AI:
Artificial intelligence technologies are beginning to influence Qatar's polymer manufacturing sector through optimization of production processes and supply chain management. To improve material recovery efficiency and operational effectiveness, smart waste management systems with blockchain-based traceability, real-time tracking, and AI-powered sorting technologies are being implemented. In manufacturing facilities, AI-driven quality control systems are improving consistency in polymer production while predictive maintenance algorithms reduce downtime. As these technologies mature, AI is expected to play an increasingly important role in demand forecasting, inventory management, and process optimization across Qatar's polymer value chain.
Market Dynamics:
Key Market Trends & Growth Drivers:
Government-Led Economic Diversification and Strategic Manufacturing Investments
The Qatar government has positioned polymers and plastics as strategic pillars for economic diversification beyond hydrocarbon dependence, driving substantial market growth through comprehensive policy frameworks and targeted investments. Under the theme "Achieving Sustainable Economic Growth," Qatar introduced the Ministry of Commerce and Industry Strategy and Qatar National Manufacturing Strategy 2024-2030 in January 2025. Plastics was identified as one of seven strategic manufacturing sub-sectors, along with polymers, aluminum, additive manufacturing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and extreme environment services. To improve Qatar's standing on the Competitive Industrial Performance Index and place it among the top 40 nations in the world by 2030, the strategy consists of 15 major initiatives and 60 projects that are intended to increase manufacturing competitiveness. Specific goals include growing the manufacturing sector's value addition to QAR 70.5 billion, increasing the percentage of Qatari manufacturers using circular economy techniques to 35%, and increasing non-hydrocarbon exports to roughly QAR 49.1 billion at a 2.5% annual growth rate. Along with luring QAR 2.75 billion in yearly industrial investments, the strategy also aims to raise the proportion of highly trained personnel to 26.5% of the population. These comprehensive initiatives create a favorable ecosystem for polymer manufacturers, providing incentives for capacity expansion, technological upgrading, and integration with global value chains. The emphasis on leveraging Qatar's competitive advantages in petrochemical feedstock availability, combined with systematic efforts to develop downstream manufacturing capabilities, positions the polymer sector as a key contributor to the nation's economic transformation agenda aligned with Qatar National Vision 2030.
Massive Petrochemical Infrastructure Expansion Through International Partnerships
Qatar is undertaking unprecedented capacity expansion in polymer production through landmark joint ventures with leading global petrochemical companies, fundamentally transforming the market landscape and establishing the nation as a major regional producer. The most significant development is the Ras Laffan Petrochemical Complex, a USD 6 billion integrated polymers facility jointly developed by QatarEnergy (70% equity) and Chevron Phillips Chemical (30% equity). Senior leaders from QatarEnergy and Chevron Phillips Chemical attended the groundbreaking event in February 2024 when His Highness Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani, Amir of Qatar, lay the foundation stone for this facility. The 435-acre complex has two high-density polyethylene units with a combined production capacity of 1.68 million tons annually and an ethane cracker with an annual capacity of 2.08 million tons, making it the largest in the Middle East and among the largest worldwide. By starting operations in late 2026, this enormous infrastructure project is anticipated to raise Qatar's total petrochemical production capacity to over 14 million tons annually, an 82% increase in total production capacity and more than double ethylene output capacities. By using ethane feedstock and cutting-edge, energy-efficient equipment, the facility will produce substantially fewer greenhouse gas emissions than comparable operations throughout the world. Beyond this flagship project, Qatar's petrochemical sector benefits from established production facilities operated by Qatar Petrochemical Company (QAPCO), which currently produces 780,000 tons annually of low-density polyethylene and 840,000 tons of ethylene, alongside joint ventures including Qatofin producing 570,000 tons of linear low-density polyethylene. These strategic partnerships leverage Qatar's abundant natural gas reserves and competitive feedstock advantages while bringing world-class technology, operational expertise, and access to international markets, substantially enhancing the Qatar polymers market growth and export competitiveness.
Circular Economy Adoption and Enhanced Recycling Infrastructure
Qatar is aggressively implementing circular economy principles through systematic expansion of recycling infrastructure and waste management capabilities, creating new opportunities for recycled polymer production while addressing environmental sustainability imperatives. Through the Waste Recycling and Treatment Department at the Ministry of Municipality, Qatar made major progress toward its circular economy agenda in 2024. Five new recycling factories were opened in the Al-Afjah Industrial Area, bringing the total number of operational facilities to 21. Nine more are currently under construction, and 21 more projects are planned across 50 designated plots set aside specifically for recycling industries. The Ministry allocated these plots strategically in the Mesaieed Industrial Area, approximately 40 kilometers south of Doha, developing Al-Afjah as a comprehensive hub for the recycling industry to meet Qatar's ambitious sustainability goals. Over 835,000 tons of waste were processed in 2024 at the Mesaieed Waste Treatment Center, one of the biggest specialized waste management facilities in the Middle East. This produced over 250,834 megawatts of clean energy, 27,000 tons of organic fertilizer, and 277,000 tons of recyclable materials, including 12,555 tons of plastic, 14,433 tons of ferrous metals, and 4,222 tons of non-ferrous metals. The Ministry's 2024-2030 strategy implements the National Integrated Solid Waste Program, incorporating waste segregation at source through containerized collection systems being rolled out in phases across all municipalities, aiming to increase the percentage of recycled materials substantially. These initiatives align with Qatar National Vision 2030 objectives and support the Third National Development Strategy's emphasis on environmental sustainability. For polymer manufacturers, this expanding recycling infrastructure provides access to recycled feedstock materials, reduces dependence on virgin petrochemical inputs, and enables development of sustainable product lines meeting international environmental standards, while simultaneously creating downstream opportunities in recycled polymer processing and applications.
Key Market Challenges:
Raw Material Price Volatility and Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
The Qatar polymers market faces significant challenges from fluctuating petrochemical feedstock prices and global supply chain instabilities that directly impact production economics and operational predictability. Despite Qatar's advantageous position as a major natural gas producer with access to competitively priced ethane feedstock, the polymer industry remains exposed to global commodity price fluctuations, particularly for specialized raw materials and additives that must be imported. Polyethylene prices are projected to fluctuate between USD 1,200 and USD 1,500 per ton, influenced by global supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions in key production regions, and demand volatility from major consuming markets. This price volatility creates substantial challenges for manufacturers in maintaining stable profit margins, as production costs can vary significantly within short timeframes while sales contracts often operate on longer-term pricing structures. The volatility is exacerbated by Qatar's heavy reliance on petrochemical derivatives whose prices are correlated with crude oil and natural gas markets, making the sector susceptible to energy market dynamics beyond local control. Additionally, global supply chain disruptions—whether from pandemic-related logistics challenges, geopolitical conflicts affecting shipping routes, or natural disasters impacting major production centers—can create shortages in specialized materials, catalysts, and processing additives essential for polymer production. These supply vulnerabilities can force production adjustments, delay projects, or necessitate costly procurement from alternative suppliers at premium prices. For smaller manufacturers and downstream processors with limited financial buffers, such volatility can threaten operational viability and constrain investment in capacity expansion or technology upgrades. Managing these risks requires sophisticated hedging strategies, diversified supplier networks, and flexible production capabilities that many regional players are still developing, creating ongoing challenges for market stability and growth predictability.
Stricter Environmental Regulations and Rising Compliance Costs
Qatar's polymer manufacturers face mounting challenges from progressively stringent environmental regulations requiring substantial investments in compliance infrastructure and operational modifications that impact cost structures and competitive positioning. The Qatari government has implemented comprehensive environmental frameworks including Ministerial Decision No. 143 of 2023 on the Regulation of Plastic Products, which mandates strict compliance with environmental standards encompassing plastic waste reduction targets, mandatory use of recyclable materials in manufacturing processes, and implementation of comprehensive recycling initiatives throughout product lifecycles. These regulations require manufacturers to maintain operational licenses contingent on demonstrating environmental compliance through regular audits, documentation, and performance metrics. Over the course of the forecast period, compliance expenses are predicted to increase by around 20%, which will have a substantial impact on operating budgets, especially for small and medium-sized businesses with limited financial resources. Companies must invest in advanced waste treatment systems, emissions control technologies, and monitoring equipment to meet evolving air quality and effluent discharge standards. The Qatar Construction Specifications mandate compliance with international standards for materials used in public infrastructure projects, requiring manufacturers to obtain certifications demonstrating thermal performance, fire safety, and environmental criteria, adding layers of testing and documentation expenses. Furthermore, the government's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 25% by 2030 under Qatar National Vision 2030 necessitates energy efficiency improvements and potential transitions to lower-carbon production processes, requiring substantial capital expenditures. For manufacturers accustomed to traditional production methods, these regulatory shifts demand organizational changes, workforce training, and technology adoption that strain existing capabilities. Failure to comply can result in significant fines exceeding USD 1.5 million for serious violations, operational shutdowns, and reputational damage that impedes market access and customer relationships, creating existential risks for non-compliant operators and raising barriers to entry for new market participants.
Limited Domestic Recycling Infrastructure Despite Growth Initiatives
Despite substantial government investment in recycling infrastructure expansion, Qatar's polymer recycling capabilities remain significantly underdeveloped relative to market generation of plastic waste and circular economy ambitions, constraining sustainable material availability and increasing environmental pressures. According to official data, only about 12% of municipal solid waste is currently diverted through recycling and waste-to-energy processes, 9% is processed through the Domestic Solid Waste Management Center via recycling, anaerobic digestion, and waste-to-energy, and 3% is handled by private-sector recyclers. More specifically, only about 10% of plastic waste is actually recycled as reported by the Ministry of Municipality and Environment, leaving the vast majority directed to landfills or waste-to-energy incineration, representing substantial loss of potential feedstock for recycled polymer production. This limited recycling rate reflects multiple underlying challenges including insufficient segregation at source despite ongoing containerization programs, inadequate collection logistics covering dispersed residential and commercial areas, and technological limitations in sorting and processing mixed plastic waste streams into usable feedstock grades. The absence of comprehensive multi-bin segregation requirements in current regulations limits the quality and purity of collected recyclables, as contamination significantly reduces material value and processing efficiency. Additionally, Qatar's recycling industry faces economic viability challenges, as the relatively small domestic market and high costs of collection, sorting, and processing can make recycled materials less economically attractive compared to competitively priced virgin petrochemical feedstocks from local production facilities. This situation is further complicated by fluctuating global markets for recycled materials, where demand and pricing can vary substantially based on international commodity cycles and policy changes in major consuming markets. For polymer manufacturers seeking to incorporate recycled content to meet sustainability targets or regulatory requirements, the limited availability of consistent, high-quality recycled feedstock constrains product development and forces continued reliance on virgin materials, undermining circular economy objectives and potentially limiting export competitiveness as international markets increasingly demand recycled content credentials.
Qatar Polymers Market Report Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Qatar polymers market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on type, process, and end use.
Analysis by Type:
- Polypropylene
- Polyethylene
- HDPE
- LDPE
- LLDPE
- Others
- Polyvinyl Chloride
- Polystyrene
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)
- Polyurethane
- Flexible Polyurethane Foam
- Rigid Polyurethane Foam
- Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU)
- Others
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes polypropylene, polyethylene (HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE, and others), polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene (expanded polystyrene (EPS) and extruded polystyrene (XPS)), polyurethane (flexible polyurethane foam, rigid polyurethane foam, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), and others), and others.
Analysis by Process:
- Injection Molding
- Extrusion
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the process have also been provided in the report. This includes injection molding, extrusion, and others.
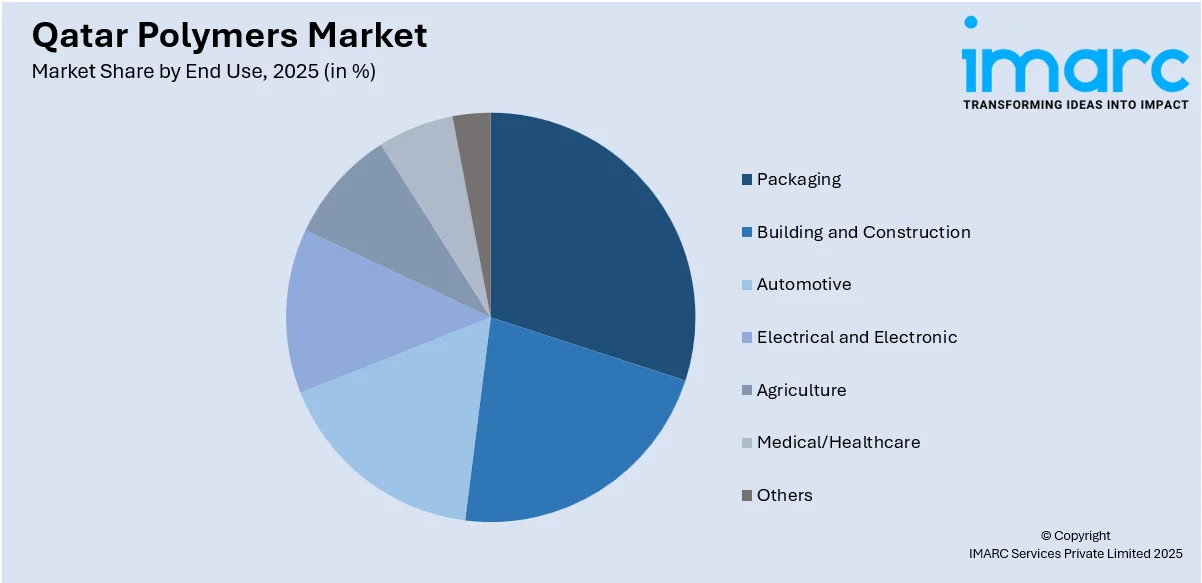
Analysis by End Use:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Packaging
- Rigid
- Flexible
- Building and Construction
- Roofing
- Windows
- Flooring
- Others
- Automotive
- Engine
- Tires
- Body Panel
- Others
- Electrical and Electronic
- Agriculture
- Medical/Healthcare
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the market based on the end use. This includes packaging (rigid and flexible), building and construction (roofing, windows, flooring, and others), automotive (engine, tires, body panel, and others), electrical and electronic, agriculture, medical/healthcare, and others.
Analysis by Region:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the region have also been provided in the report. This includes Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar polymers market is characterized by a dynamic mix of state-owned enterprises, joint ventures with international petrochemical majors, and regional private sector players spanning upstream production to downstream processing. Market concentration is relatively high in primary polymer production, dominated by established producers with substantial capital investments and integrated feedstock access, while downstream segments including conversion, compounding, and finished products exhibit greater fragmentation with numerous small and medium enterprises. Competition centers on production scale, technological capabilities, product quality consistency, and access to competitively priced ethane and other petrochemical feedstocks. Major producers leverage vertical integration from ethylene crackers through polyethylene production to maintain cost advantages and supply reliability. The market is witnessing increased competitive intensity from upcoming mega-projects including the Ras Laffan Petrochemical Complex, which will substantially expand domestic capacity and potentially shift competitive dynamics. International joint ventures bring advanced technologies, operational excellence practices, and global market access, while local players compete through proximity to end-users, customized service offerings, and government procurement preferences supporting Qatari businesses. Sustainability credentials, recycled content capabilities, and circular economy compliance are emerging competitive differentiators as environmental regulations tighten and customer preferences evolve toward sustainable sourcing.
Qatar Polymers Industry Latest Developments:
- September 2024: Mesaieed Petrochemical Holding Company, Qatar Industrial Manufacturing Company, and Atlas Yatirim Planlama of Turkey have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to form Qatar Salt Products Company (QSalt) through a strategic partnership. The Qatar Petrochemical Company (QAPCO) and Qatar Vinyl Company (QVC) will run the QAR 1 billion salt production plant in the Um Al Houl area, which will produce industrial salts necessary for the petrochemical industry as well as bromine, potassium chloride, and demineralized water to support downstream polymer manufacturing. The plant will have an annual capacity of one million tons.
- January 2025: Plastics is one of seven strategic manufacturing subsectors that are essential for economic diversification, according to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry's officially released Qatar National Manufacturing Strategy 2024–2030. With 60 projects and 15 major initiatives, the comprehensive strategy aims to increase the value addition of the manufacturing sector to QAR 70.5 billion, boost non-hydrocarbon exports to about QAR 49.1 billion with an annual growth rate of 2.5%, and increase the proportion of Qatari factories using circular economy practices to 35% by 2030.
Qatar Polymers Market Report Coverage:
|
Report Features |
Details |
|
Base Year of the Analysis |
2025 |
|
Historical Period |
2020-2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
|
Units |
Million USD |
|
Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
|
Types Covered |
|
|
Processes Covered |
Injection Molding, Extrusion, Others |
|
End Uses Covered |
|
|
Regions Covered |
Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
|
Customization Scope |
10% Free Customization |
|
Post-Sale Analyst Support |
10-12 Weeks |
|
Delivery Format |
PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Qatar polymers market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar polymers market on the basis of type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar polymers market on the basis of process?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar polymers market on the basis of end use?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar polymers market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Qatar polymers market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Qatar polymers market?
- What is the structure of the Qatar polymers market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Qatar polymers market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC's industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Qatar polymers market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Qatar polymers market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Qatar polymers industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












