
Qatar Utility-Scale Solar Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Application, Installation Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Qatar Utility-Scale Solar Market Summary:
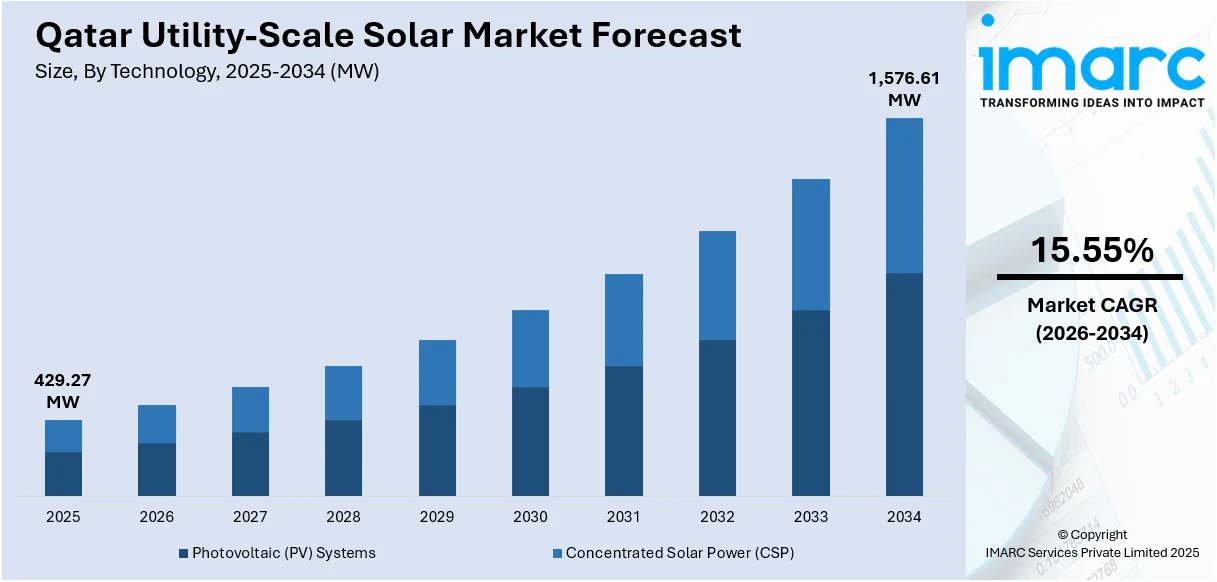
The Qatar utility-scale solar market size reached at a volume of 429.27 MW in 2025. The market is projected to reach a volume of 1,576.61 MW by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 15.55% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by the government's ambitious renewable energy strategy targeting 18 percent solar power generation by 2030, massive infrastructure investments in gigawatt-scale solar facilities across industrial cities, and strategic international partnerships facilitating technology transfer and operational excellence. Additionally, the expanding Qatar utility-scale solar market share reflects the nation's commitment to environmental sustainability and economic diversification.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2025 | 429.27 MW |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | 1,576.61 MW |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 15.55% |
| Key Segments | Technology (Photovoltaic (PV) Systems, Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)), Application (Power Generation, Energy Storage), Installation Type (Ground-mounted Systems, Rooftop Solar) |
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
Qatar Utility-Scale Solar Market Outlook (2026-2034):
The Qatar utility-scale solar market is well-placed for rapid growth, driven by government mandates under the Qatar National Vision 2030 and aggressive capacity expansion targets. Major projects being completed, such as the 2,000-megawatt Dukhan Solar Power Plant by 2029, will catapult the country to a much higher level of renewable energy penetration. Furthermore, the development of bifacial solar modules, single-axis tracking systems, and AI-enabled smart grid integration will further enhance operational efficiency and reliability. Strategic collaborations with international engineering companies and declining levelized costs of solar electricity further support this market trajectory.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Impact of AI:
Artificial intelligence is reshaping the utility-scale solar industry in Qatar with predictive maintenance systems that use sensor data of solar panels and other inverters to predict equipment failures, smart grid solutions that optimize active distribution of electricity and balancing the supply with fluctuations in demand and AI-based monitoring systems that maximize the energy output by adjusting the system parameters in accordance with the weather patterns and environmental factors. These technologies will play a critical role in ensuring that the efficiency and reliability of the growing solar infrastructure in Qatar are maximized and that the grid can adequately withstand the growing levels of renewable energy penetration.
Market Dynamics:
Key Market Trends & Growth Drivers:
Government-Led National Renewable Energy Strategy Driving Market Expansion
Qatar’s utility-scale solar market is being driven by the government’s renewed focus on expanding clean energy under the Qatar National Renewable Energy Strategy, introduced by Kahramaa in April 2024. This strategy outlines clear ambitions to significantly scale up solar power generation by 2030 through both large-scale projects and distributed rooftop systems. It places photovoltaic technology at the center of national energy planning, leveraging Qatar’s strong solar resource potential. Aligned with Qatar National Vision 2030, the initiative seeks to balance economic growth with environmental protection by increasing the share of renewable energy in the overall power mix. Beyond setting targets, the government is providing strong institutional and financial support, including streamlined approvals, coordinated efforts across energy-sector stakeholders, and mechanisms to encourage private participation. Key elements of the strategy include developing net billing schemes to promote small-scale solar adoption, working with banks to introduce appealing financing options, and simplifying the permitting process for utility-scale projects. The recommended energy mix is also expected to lower overall power generation costs and strengthen energy security by diversifying supply sources. Together, these measures create a robust foundation for the rapid expansion of Qatar’s solar power market.
Unprecedented Infrastructure Investments in Gigawatt-Scale Solar Facilities
Qatar is executing one of the most aggressive utility-scale solar deployment programs in the Gulf Cooperation Council region, characterized by multi-billion-dollar investments in state-of-the-art photovoltaic facilities strategically located to power industrial cities and contribute to national electricity grids. The infrastructure development initiative encompasses multiple flagship projects at various stages of completion, including the operational 800-megawatt Al Kharsaah Solar PV Power Plant commissioned in 2022, which supplies approximately 10 percent of Qatar's peak electricity demand. The momentum accelerated significantly with capital deployments exceeding several billion dollars across concurrent projects designed to transform Qatar's energy landscape. These facilities incorporate advanced technologies including high-efficiency bifacial solar modules that capture sunlight on both sides, single-axis tracking systems that follow the sun's movement throughout the day, and automated cleaning robots that operate daily to minimize soiling losses from desert dust accumulation. The projects are strategically positioned within Qatar's major industrial zones, Ras Laffan Industrial City in the northeast and Mesaieed Industrial City in the southeast, enabling direct power supply to energy-intensive liquefied natural gas facilities and petrochemical operations while simultaneously feeding the national grid. In April 2025, His Highness Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani inaugurated the Ras Laffan and Mesaieed solar photovoltaic power plants with a combined capacity of 875 megawatts, more than doubling Qatar's solar energy production to 1,675 megawatts of renewable energy. These fully owned QatarEnergy projects are expected to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 4.7 million tons annually and supply around 15 percent of Qatar's total peak electricity demand, with this percentage projected to rise to 30 percent following the completion of additional planned facilities.
Strategic International Partnerships Accelerating Technology Transfer and Operational Excellence
The Qatar utility-scale solar market growth is significantly bolstered by strategic collaborations with leading global engineering, procurement, and construction firms, as well as technology providers and international energy companies. These partnerships serve multiple critical functions, including access to cutting-edge solar technologies, transfer of operational expertise, risk-sharing in large capital-intensive projects, and positioning Qatar as a regional hub for renewable energy development. QatarEnergy has established long-term relationships with major international corporations, including TotalEnergies, Marubeni Corporation, and Samsung C&T, leveraging their technical capabilities and project management experience to execute world-class solar facilities. The collaborative model extends beyond domestic projects to encompass international ventures that export Qatar's capital and renewable energy expertise to neighboring countries. The partnership framework encompasses joint ventures for project ownership, knowledge transfer programs for developing local technical capabilities, and supply chain collaborations ensuring access to high-quality components including solar modules, inverters, and tracking systems. Minister of State for Energy Affairs Saad Sherida Al-Kaabi has emphasized Qatar's evolution from reliance on foreign expertise toward implementation using national capabilities, reflecting successful technology and knowledge transfer. In September 2025, QatarEnergy signed an engineering, procurement, and construction agreement with Samsung C&T's Engineering & Construction Group for the construction of the 2,000-megawatt Dukhan Solar Power Plant, located approximately 80 kilometers west of Doha. The project, valued at KRW 1.46 trillion and covering 27 square kilometers, will be equipped with 2.74 million solar panels and developed in two phases with full capacity expected by mid-2029. This contract builds on Samsung C&T's successful delivery of the Ras Laffan and Mesaieed facilities, positioning the company to account for nearly 80 percent of Qatar's total solar power generation capacity upon project completion.
Key Market Challenges:
Grid Integration Complexities and Energy Storage Infrastructure Requirements
Integrating utility-scale solar power into Qatar’s existing electricity grid presents substantial technical and operational challenges. The country’s power system was originally designed for centralized fossil fuel-based thermal generation, which provides predictable, dispatchable electricity. Solar photovoltaic (PV) power, however, is intermittent and weather-dependent, requiring advanced management to ensure grid stability. With solar capacity expected to grow from under 100 MW to over 4,000 MW by 2030, significant upgrades are needed in transmission and distribution infrastructure, energy storage deployment, and grid management technologies. Key challenges include maintaining voltage and frequency stability, coordinating dispatch between thermal and solar plants, managing bidirectional power flows from distributed generation, and ensuring sufficient spinning reserves. Sophisticated forecasting tools are necessary to predict solar output and synchronize thermal generation with periods of high and low solar production. Kahramaa and QatarEnergy are investing in enhanced transmission networks, smart grid systems with real-time monitoring, and research into energy storage solutions such as batteries, pumped hydro, and thermal storage coupled with concentrated solar power. Addressing these challenges is critical to achieving Qatar’s renewable energy targets while maintaining high reliability standards for both industrial and residential consumers.
Economic Competitiveness Against Subsidized Fossil Fuel Electricity
Qatar faces economic challenges in scaling utility-scale solar power due to extremely low domestic electricity prices, driven by substantial government subsidies on natural gas. In comparison, electricity prices in countries like Norway, the US, and Saudi Arabia are significantly higher, reflecting market-based energy costs. Low prices reduce private sector incentives to invest in solar projects and diminish the financial appeal of distributed solar for commercial and industrial consumers. Utility-scale projects face difficulty competing with near-zero-cost natural gas feedstock, complicating return-on-investment calculations. Overcoming these barriers requires targeted policy interventions, including gradual subsidy reduction, carbon pricing, renewable energy certificates, feed-in tariffs, and mandates for renewable procurement by large consumers. QatarEnergy’s direct investment in solar infrastructure addresses market limitations by prioritizing strategic and environmental objectives. However, sustainable market growth will require long-term adjustments to price distortions, balancing economic competitiveness with environmental and energy diversification goals.
Technical Challenges from Extreme Climatic Conditions and Environmental Factors
Qatar’s desert environment imposes significant technical constraints on utility-scale solar projects. Extreme summer temperatures often exceed 45°C, combined with intense solar radiation, high humidity, frequent dust storms, and persistent sand accumulation, all of which reduce photovoltaic efficiency. Elevated temperatures degrade solar panel performance, accelerate wear on electronic components, and increase cooling requirements for inverters and other equipment. Dust and sand deposition can lower energy output by 15–30% if panels are not cleaned regularly, necessitating daily automated cleaning systems and frequent inspections. These environmental factors demand specialized equipment, including high-temperature-rated inverters, durable mounting structures capable of withstanding wind and sand abrasion, and solar modules with optimized temperature coefficients. Qatari firms, collaborating with research institutions like the Qatar Environment and Energy Research Institute, have developed innovations such as dust-resistant panels and heat-tolerant components to mitigate these challenges. Effective system design, technology selection, and proactive maintenance protocols are critical to maintaining high availability, reliability, and energy yields. Overcoming climatic and environmental obstacles is essential for ensuring that Qatar’s utility-scale solar facilities meet projected production targets and deliver both economic and sustainability benefits.
Qatar Utility-Scale Solar Market Report Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Qatar utility-scale solar market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on technology, application, and installation type.
Analysis by Technology:
- Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP)
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology. This includes photovoltaic (PV) systems and concentrated solar power (CSP).
Analysis by Application:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
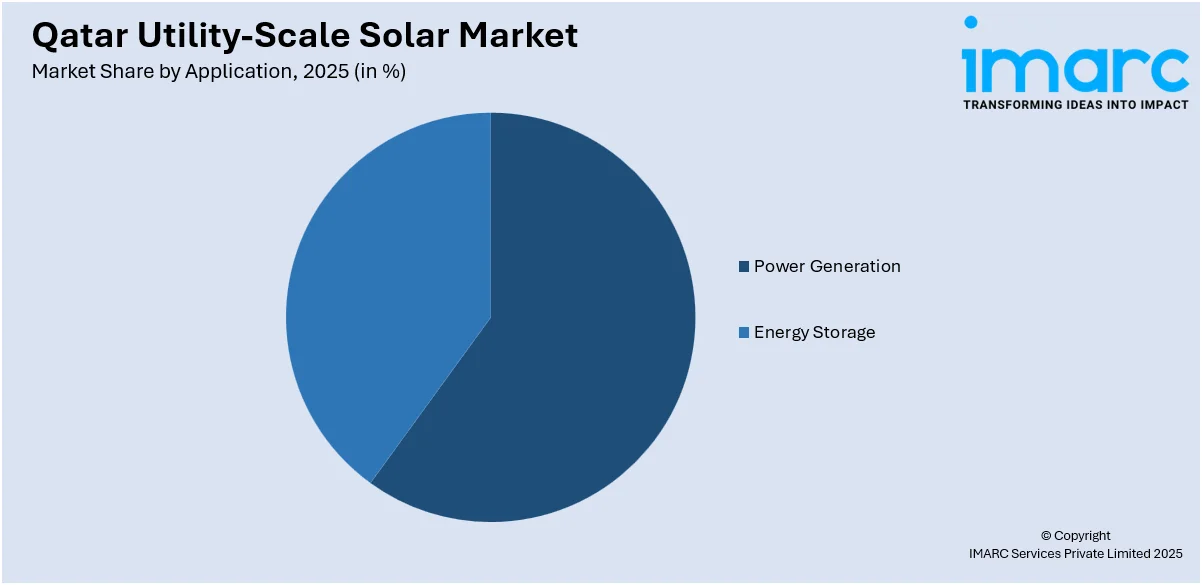
- Power Generation
- Energy Storage
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application have also been provided in the report. This includes power generation and energy storage.
Analysis by Installation Type:
- Ground-mounted Systems
- Rooftop Solar
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the installation type. This includes ground-mounted systems and rooftop solar.
Analysis by Region:
- Ad Dawhah
- Al Rayyan
- Al Wakrah
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The Qatar utility-scale solar market is characterized by significant government involvement through QatarEnergy, the state-owned energy company that owns and operates the majority of large-scale solar facilities. The competitive landscape is shaped by strategic partnerships between QatarEnergy and leading international engineering, procurement, and construction firms including Samsung C&T, TotalEnergies, and Marubeni Corporation. These collaborations leverage global expertise in solar project development while simultaneously building local technical capabilities. The market exhibits high barriers to entry due to substantial capital requirements, complex regulatory frameworks, and the dominance of QatarEnergy in project development and ownership. International contractors compete primarily on technical capabilities, project execution track records, and ability to deliver large-scale facilities under challenging desert conditions within tight timelines and budgets.
Qatar Utility-Scale Solar Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | MW |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Photovoltaic (PV) Systems, Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) |
| Applications Covered | Power Generation, Energy Storage |
| Installation Types Covered | Ground-mounted Systems, Rooftop Solar |
| Regions Covered | Ad Dawhah, Al Rayyan, Al Wakrah, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Qatar utility-scale solar market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar utility-scale solar market on the basis of technology?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar utility-scale solar market on the basis of application?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar utility-scale solar market on the basis of installation type?
- What is the breakup of the Qatar utility-scale solar market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Qatar utility-scale solar market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Qatar utility-scale solar market?
- What is the structure of the Qatar utility-scale solar market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Qatar utility-scale solar market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC's industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Qatar utility-scale solar market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Qatar utility-scale solar market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Qatar utility-scale solar industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












