
Saudi Arabia Agritech Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Application and Region, 2026-2034
Saudi Arabia Agritech Market Overview:
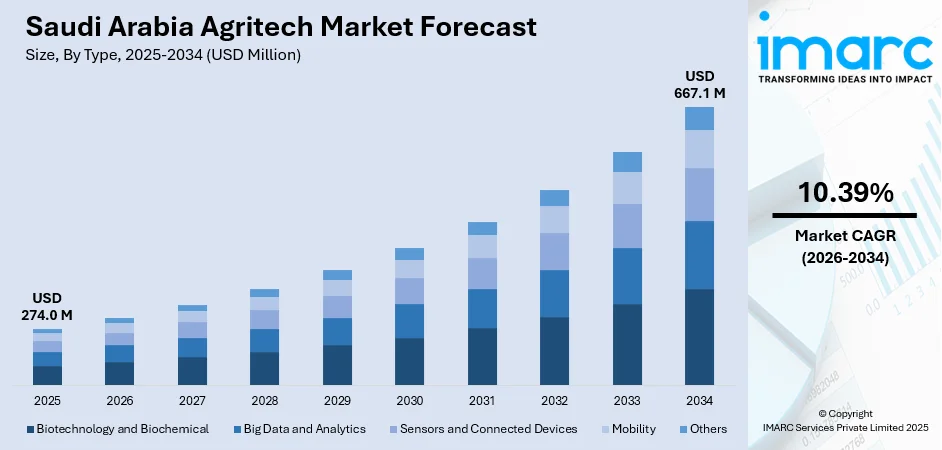
The Saudi Arabia Agritech Market size reached USD 274.0 Million in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 667.1 Million by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 10.39% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by substantial investments in cutting-edge agricultural technologies like hydroponics, vertical farming, and controlled-environment agriculture to enhance food security and reduce dependence on imports. The development of a collaborative environment by the government through funding startups and bringing academia and the private sector together into partnerships is further increasing the Saudi Arabia agritech market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 274.0 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 667.1 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 10.39% |
Saudi Arabia Agritech Market Trends:
Water-efficient and Controlled-environment Agriculture
Saudi Arabia’s agriculture sector is adopting water-efficient techniques and controlled-environment farming to address scarce freshwater resources and improve yields. Technologies, such as drip irrigation, precision water scheduling, hydroponics, and vertical farming, reduce water consumption while enabling higher productivity on limited arable land. As per the IMARC Group, the Saudi Arabia hydroponics market size reached USD 132.6 Million in 2024. Controlled-environment systems allow year-round production with optimal resource use and reduced dependence on unpredictable rainfall. These approaches also enable cultivation closer to urban centers, shortening supply chains and lowering transportation losses. The ability to produce high-value vegetables, herbs, and specialty crops using significantly less water attracts both public and private investment. As desalination and treated wastewater are becoming integrated into irrigation schemes, water-efficient agritech is gaining popularity.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Growing Adoption of Digital Farming
Digital farming tools, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, satellite imagery, and data analytics are transforming decision-making in Saudi agriculture by enabling precision planting, fertilization, and irrigation. The International Data Corporation (IDC) estimated that Saudi Arabia’s IoT market is set to hit USD 2.9 Billion by 2025, growing at an annual rate of 12.8%. Farmers can track soil moisture, nutrient content, and crop condition remotely, applying inputs only where needed to reduce waste and costs. Mobile platforms and farm management software improve traceability, compliance, and market linkages while enabling predictive maintenance for equipment. Remote sensing combined with machine learning (ML) helps identify stress early, optimize harvest timing, and enhance yield forecasting. These technologies also support financial inclusion through improved credit assessments and insurance models based on verifiable production data.
Climate-resilient Crops and Greenhouse Expansion
To cope with extreme heat, aridity, and climate variability, Saudi growers are investing in climate-resilient crop varieties and protective cultivation like greenhouses and shade houses. In December 2024, Topian, NEOM’s food business, launched its inaugural advanced greenhouse in Oxagon, the industrial center situated along Saudi Arabia’s Red Sea shoreline. The facility, spanning four hectares in Oxagon Innovation Bay, aimed to test sustainable and localized food production through cutting-edge agricultural technologies. Improved seed varieties bred for heat tolerance, salinity resistance, and shorter growing cycles enable reliable harvests in challenging environments. Greenhouse technologies, often paired with cooling, misting, and controlled lighting, extend cultivation seasons and safeguard crops from harsh external conditions. These protective systems also limit pest pressures and minimize pesticide use, aligning with sustainability goals.
Key Growth Drivers of Saudi Arabia Agritech Market:
Government Focus on Food Security and Policy Support
Food security ranks high on Saudi national priorities, leading to government policies that support agricultural modernization, local production, and technology adoption. Strategic initiatives include incentives for local farming projects, subsidies, technical assistance, and partnerships with international research institutes. Programs aiming to diversify food sources emphasize self-sufficiency in key commodities and reducing reliance on imports, creating market opportunities for agritech solutions that increase productivity and resource efficiency. Public funding for demonstration farms, pilot projects, and knowledge transfer accelerates farmer uptake of innovative practices. Furthermore, regulatory measures that streamline land use approvals and support investment in protected cultivation encourage private sector participation. By aligning national policy with technological modernization, government actions are minimizing barriers to scaling agritech and catalyzing the demand for irrigation systems and digital platforms.
Improved Supply Chains and Logistics
Enhancements in supply chain infrastructure, cold chain logistics, and processing capacity are increasing the commercial viability of local agricultural production. Modern packhouses, refrigerated transport, and storage facilities diminish post-harvest wastage and prolong the longevity of perishable goods, linking farmers to urban markets and export channels. Investments in traceability systems and quality assurance improve buyer confidence and open higher-value market opportunities. Aggregation platforms and contract farming models help coordinate production volumes, ensure consistent quality, and lower transaction costs for smallholders. Improved logistics also enable seasonal produce to reach markets quickly, ensuring price stability and decreasing dependence on distant imports. As agritech solutions are being integrated with logistics and processing investments, the entire value chain is becoming more efficient, encouraging further production and expenditure.
Labor Challenges and Automation Adoption
Chronic labor shortages, rising labor costs, and changing workforce dynamics are leading Saudi farmers towards mechanization and automation. Robotic harvesters, automated transplanting systems, and mechanized greenhouse operations reduce dependence on seasonal and migrant labor while improving the timeliness and consistency of farm tasks. Automation also helps address labor productivity constraints by performing repetitive, labor-intensive activities with higher precision and speed. For high-value crops where labor availability can make or break harvest windows, mechanization ensures marketable quality and reduces losses. Meanwhile, training programs and vocational initiatives are building local capacity to operate and maintain advanced machinery, creating skilled jobs and reducing reliance on external labor pools. The twin pressures of labor scarcity and the need for consistent quality are accelerating investments in robotics and automated systems.
Saudi Arabia Agritech Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on type and application.
Type Insights:
- Biotechnology and Biochemical
- Big Data and Analytics
- Sensors and Connected Devices
- Mobility
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes biotechnology and biochemical, big data and analytics, sensors and connected devices, mobility, and others.
Application Insights:
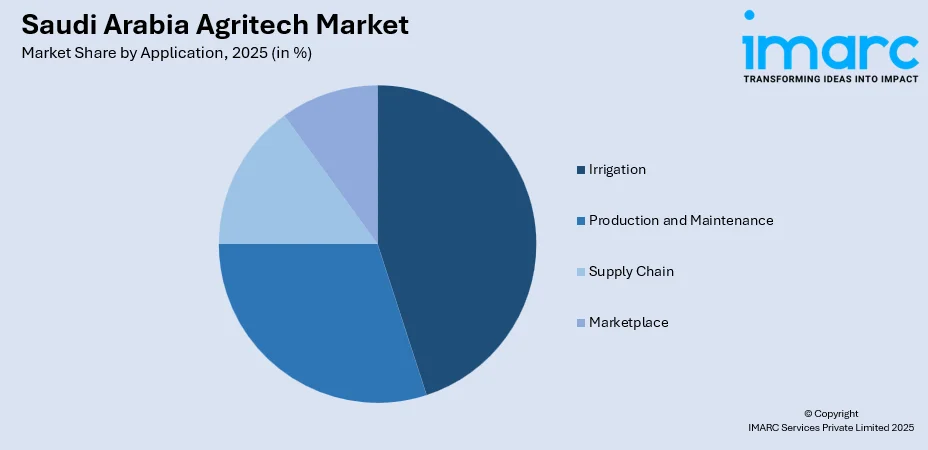
- Irrigation
- Production and Maintenance
- Supply Chain
- Marketplace
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the application. This includes irrigation, production and maintenance, supply chain, and marketplace.
Regional Insights:
- Northern and Central Region
- Western Region
- Eastern Region
- Southern Region
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include the Northern and Central Region, Western Region, Eastern Region, and Southern Region.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Saudi Arabia Agritech Market News:
- May 2025: Saudi Arabia and South Korea initiated a joint effort to advance modern agriculture by launching a smart farming facility in Riyadh. The new plant represented Saudi Arabia's agricultural ambitions to bolster the farming industry while improving food security and production capabilities. According to Al Mushaiti, the project originated from collaborative endeavors focused on enhancing innovations and meeting the rising food demands in the region.
- February 2025: Saudi Arabia finalized its biggest indoor vertical farming initiative in Riyadh, signaling a crucial advancement in the nation’s agricultural industry. The project was a collaborative endeavor involving Vertical Farms Company (VFCo), Mowreq Specialized Agriculture, and YesHealth Group, showcasing global collaboration in agritech. The farm had a 20,000-square-meter cultivation area, featuring automated and AI-based monitoring technologies.
- January 2025: The Saudi Arabian agritech startup Arable announced that it successfully finished a USD 2.55 Million seed funding round. The investment round attracted attention from both private and institutional firms, with 90% of the capital coming from overseas supporters. The funds would be allocated in Saudi Arabia to foster the development of the country's agricultural sector.
Saudi Arabia Agritech Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Biotechnology and Biochemical, Big Data and Analytics, Sensors and Connected Devices, Mobility, Others |
| Applications Covered | Irrigation, Production and Maintenance, Supply Chain, Marketplace |
| Regions Covered | Northern and Central Region, Western Region, Eastern Region, Southern Region |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Saudi Arabia agritech market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Saudi Arabia agritech market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Saudi Arabia agritech industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The agritech market in Saudi Arabia was valued at USD 274.0 Million in 2025.
The Saudi Arabia agritech market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 10.39% during 2026-2034, reaching a value of USD 667.1 Million by 2034.
With rising population and food demand, the government is actively promoting modern farming solutions like hydroponics, vertical farming, smart irrigation, and precision agriculture. Technology adoption is also being driven by water scarcity challenges, encouraging the use of sensors and drones for efficient resource management. Vision 2030 initiatives are aiming to boost local food production, reduce import dependency, and attract private investments into agriculture technology startups.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












