
Seed Industry in India Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Crop Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Markey Overview:
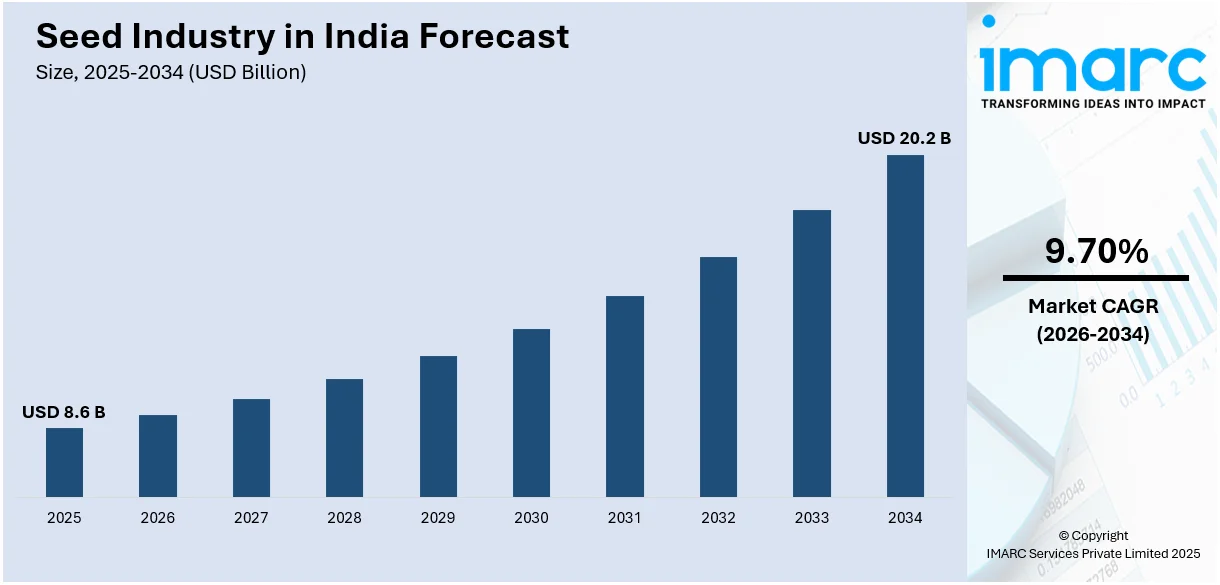
The size of the seed industry in India reached USD 8.6 Billion in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 20.2 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 9.70% during 2026-2034. The market growth is attributed to the growing population, commercialization of agriculture, advancements in seed technology, active collaboration between the public and private sectors, and increasing government support for farmers and breeders.
Market Insights:
- Based on region, Uttar Pradesh is the largest region for seed production in India, driven by its agricultural activities, particularly in paddy cultivation.
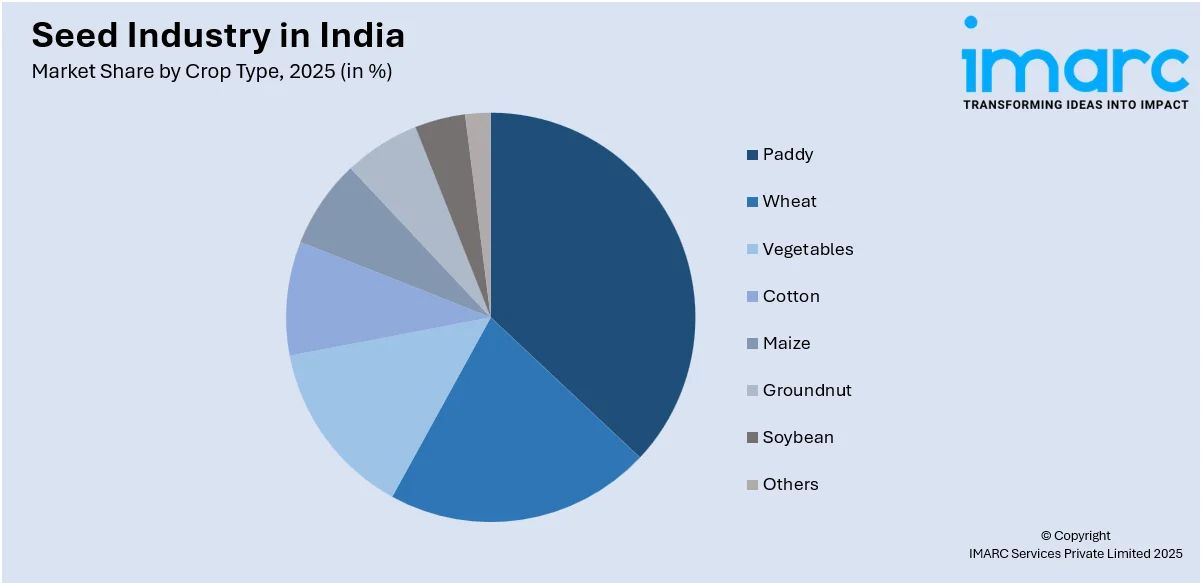
- Based on crop type, paddy leads the seed industry in India due to its importance as a staple food crop and government support.
Market Size and Forecast:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 8.6 Billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 20.2 Billion
- CAGR (2026-2034): 9.70%
- Uttar Pradesh: Largest Market in 2025
Seeds are small embryonic plants enclosed in a protective cover with a food reserve. They are found inside fruits and develop into new plants when grown under optimum environmental conditions. They consist of undeveloped miniature plants, endosperm, and seed coats and are formed from the fertilization of an ovule after pollination. They are good sources of fiber, healthy monounsaturated fats, polyunsaturated fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Their regular consumption help reduce blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure. They are consequently utilized for growing fruits, vegetables, cereals, and lentils and obtaining oils for cooking, margarine production, lubrication, cooking, and painting. At present, seeds are available in varied colors, shapes, sizes, weights, and specific gravity across India.
To get more information of this market Request Sample
The growing population and the availability of rich arable lands and various agro-climatic zones in India represent one of the key factors positively influencing the Indian seed market size. In addition, the commercialization of agriculture and the active collaboration of private and public sectors are propelling the growth of the seed industry in the country. Apart from this, leading seed breeders are increasingly introducing advanced digital technologies to help farmers overcome the negative impacts of pests, climate, and other environmental factors. This, in turn, is contributing to the market growth. Additionally, the integration of data science, artificial intelligence (AI) tools, advanced phenomics, and genomics in the agricultural sector is augmenting the seed industry in India share. Along with this, various opportunities provided by the Government of India (GoI) to encourage farmers and breeders are creating a positive outlook for the market. It is also launching various programs, such as Integrated Scheme for Oilseeds, Pulses, Oil Palm, and Maize (ISOPOM), and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana, which, in turn, is providing continuous support and offering lucrative growth opportunities to farmers and seed breeders. Moreover, increasing investments by research institutes in research and development (R&D) activities to enhance crop production, supply chain management, and quality assurance is expected to drive the seed industry in India.
Seed Industry in India Market Trends:
Government Support and Growth Drivers for the Seed Industry in India
The government plays a significant role in supporting the Indian seed industry, providing subsidies, seed certification, and facilitating research and development (R&D) for high-yielding, pest-resistant, and climate-resilient seed varieties. Initiatives like the National Mission on Agricultural Extension and Technology (NMAET) have helped improve seed production techniques, ensuring quality and uniformity across regions. Additionally, favorable policies and investment in agricultural infrastructure drive the adoption of advanced farming practices, encouraging the use of hybrid and genetically modified (GM) seeds. These growth drivers are amplified by the increasing demand for superior seeds that cater to changing environmental conditions, enhance yield, and improve food security. As per the seed industry in India analysis, India is focused on modernizing its agriculture, where the industry benefits from technological advancements, better distribution networks, and expanded export markets, propelling the sector toward greater efficiency and sustainability.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Seed Industry in India
The Indian seed industry faces several challenges that, while hindering its full potential, also create opportunities for innovation and growth. Issues like inconsistent seed quality, counterfeit seeds, and limited access to high-quality seed varieties in rural areas can undermine trust and reduce productivity. Additionally, the unpredictability of climate conditions and insufficient cold storage and supply chain infrastructure complicate the timely delivery of seeds. However, these challenges open avenues for seed industry in India growth as well. The need for climate-resilient seeds and better-quality control systems has led to innovations in seed technology, such as genetically modified and organic varieties designed to withstand extreme weather and pests. The increasing demand for sustainable agriculture, particularly organic farming, presents further opportunities to address both the challenges and the evolving needs of the agricultural sector, fostering long-term growth in the seed industry.
Key Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each sub-segment of the seed industry in India, along with forecasts at the country and state level from 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on crop type.
Breakup by Crop Type:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Wheat
- Paddy
- Vegetables
- Cotton
- Maize
- Groundnut
- Soybean
- Others
Paddy dominates India's seed industry due to its essential role as the country's staple food and its widespread cultivation across multiple states. As one of the most crucial crops for both domestic consumption and export, the demand for paddy seeds remains consistently high. The government’s focus on rice production through support policies, such as minimum support prices and seed subsidies, further fuels this demand. Additionally, advancements in seed technology, such as hybrid varieties that improve yield, disease resistance, and climate adaptability, have contributed significantly to the growth of the paddy seed market. India's position as a leading exporter of rice also drives the demand for superior quality seeds, ensuring that paddy remains the largest crop segment in the seed industry.
Breakup by Region:
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
- West Bengal
- Rajasthan
- Punjab
- Maharashtra
- Andhra Pradesh
- Bihar
- Karnataka
- Others
Uttar Pradesh (UP) stands as the largest region for seed production due to its central role in India’s agricultural landscape. The state’s vast and diverse agricultural activities, particularly paddy cultivation, contribute significantly to the demand for quality seeds. With a large farming population relying on agricultural income, the adoption of high-yielding seed varieties is critical for improving productivity. UP also benefits from robust government initiatives, such as subsidies and loans for seeds, along with a strong infrastructure for agricultural marketing and distribution. This ensures a steady supply of seeds to farmers, further bolstering the region’s importance. Moreover, the state’s contribution to multiple crops, including wheat and sugarcane, broadens the seed market, driving continuous growth in UP.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the market has been analyzed in the report, along with the detailed profiles of the major players operating in the industry. Some of these players are:
- Advanta
- DuPont
- Kaveri Seeds
- Syngenta
- Bayer
- J K Seeds
- Rallis India Limited
Latest News and Developments:
- In July 2025, Advanta Seeds, one of India's leading hybrid seed companies, secured Plant Variety Protection (PVP) for its widely popular hybrid okra variety, Raadhika. This recognition not only solidifies Advanta's position as a leader in agricultural innovation but also ensures that farmers will continue benefiting from superior okra genetics, with enhanced disease resistance and higher yields.
- In July 2025, Bangalore announced it will host the 16th edition of AgriTech India, South Asia's premier agri-food technology event, from August 1-3, 2025, at the Bangalore International Exhibition Centre (BIEC). The exhibition will feature over 250 exhibitors from over 20 countries, showcasing innovations in farm machinery, precision irrigation, smart seeds, agrochemicals, dairy, and post-harvest technologies.
- In May 2025, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approved an increase in the Minimum Support Prices (MSP) for 14 Kharif crops for the Marketing Season 2025-26 to ensure remunerative prices for farmers. This move is in line with the Union Budget 2018-19's goal of fixing MSP at 1.5 times the cost of production, supporting the government's efforts to promote diversified crop cultivation, including pulses and oilseeds.
- In February 2025, the Indian government announced the National Mission on High Yielding Seeds as part of the Union Budget. This initiative aims to strengthen the research ecosystem, develop and propagate seeds with high yield, pest resistance, and climate resilience, while ensuring the commercial availability of over 100 new seed varieties released since July 2024. With a budget allocation of INR 100 Crore (USD 12.1 Million) for the National Mission on Hybrid Seeds, the government is investing in cutting-edge agricultural research.
Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Segment Coverage | Crop Type, State |
| State Covered | Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Rajasthan, Punjab, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Karnataka, Others |
| Companies Covered | Advanta, DuPont, Kaveri Seeds, Syngenta, Bayer, J K Seeds, Rallis India Limited |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The seed industry in India was valued at USD 8.6 Billion in 2025.
Commercialization in the agriculture sector, growing number of public-private collaborations, inflating consumer income levels and introduction of hybrid product variants represent some of the factors driving the seed industry in India.
Sudden outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic had led to the implementation of stringent lockdown regulations resulting in temporary shutdown of numerous supply units of agricultural products across the country. The non-availability of migrant labor has also interrupted the harvesting activities in India.
Based on the crop type, the seed industry in India can be segmented into wheat, paddy, vegetables, cotton, maize, groundnut, soybean, and others. Among these, paddy accounts for the largest market share.
On a regional level, the market has been classified into Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Rajasthan, Punjab, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, and Karnataka, where Uttar Pradesh currently dominates the Indian market.
Some of the major players in the seed industry in India include Advanta, DuPont, Kaveri Seeds, Syngenta, Bayer, J K Seeds and Rallis India Limited.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












