
South East Asia Food Service Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Sector, Systems, Types of Restaurants, and Country, 2026-2034
South East Asia Food Service Market Summary:
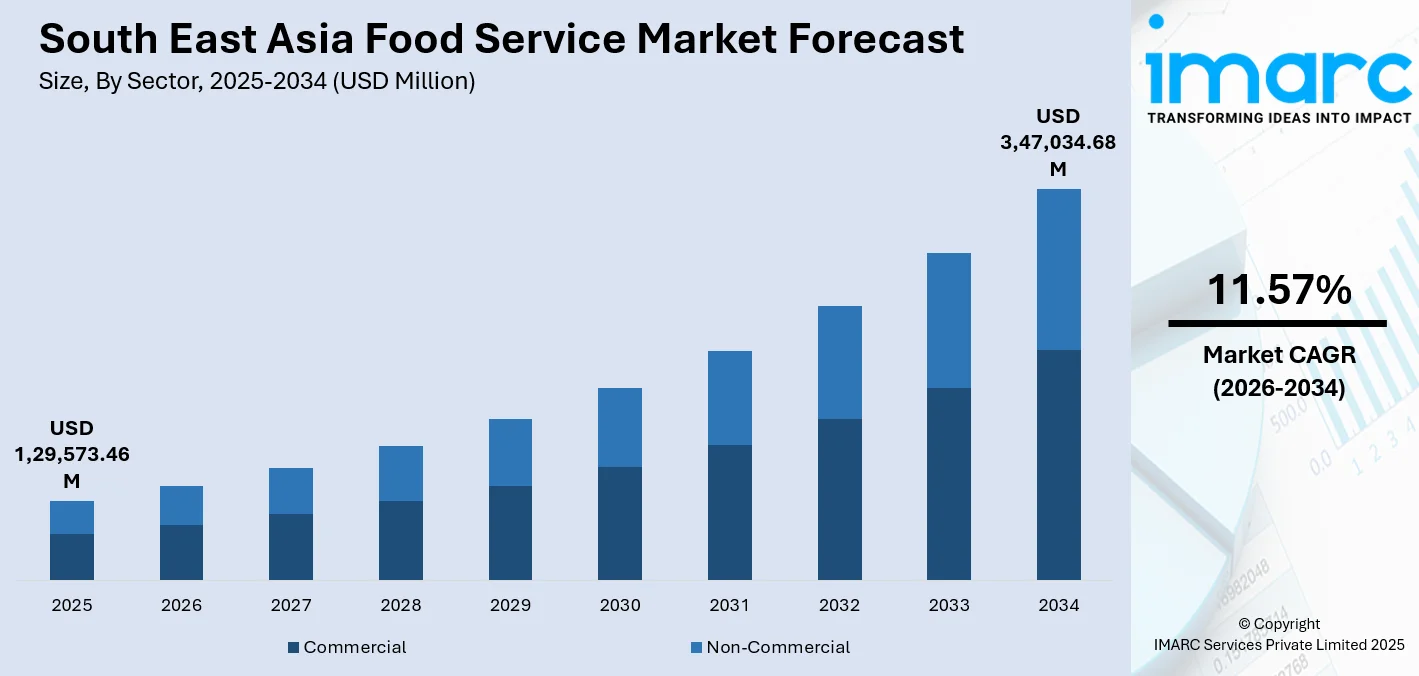
The South East Asia food service market size was valued at USD 1,29,573.46 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 3,47,034.68 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 11.57% from 2026-2034.
The South East Asia food service market is experiencing robust expansion driven by rapid urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and an increasingly youthful population seeking diverse culinary experiences. The region's dynamic economic growth, coupled with evolving consumer preferences toward convenient dining options, is reshaping the foodservice landscape across key markets including Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines. Digital transformation has fundamentally altered how consumers access food services. The proliferation of quick-service restaurants, cloud kitchens, and tech-enabled ordering systems is accelerating market penetration while meeting demands for speed and affordability. Tourism recovery, growing middle-class populations, and increased female workforce participation are creating sustained demand for out-of-home dining options. Strategic investments in supply chain infrastructure, menu innovation, and digital capabilities are positioning operators to capture emerging opportunities in the South East Asia food service market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Sector: Commercial dominates the market with a share of 65% in 2025, owing to widespread urbanization driving demand for quick-service restaurants, full-service dining establishments, and cafeterias serving office complexes. Rising dual-income households and extended working hours are accelerating commercial foodservice adoption across metropolitan areas.
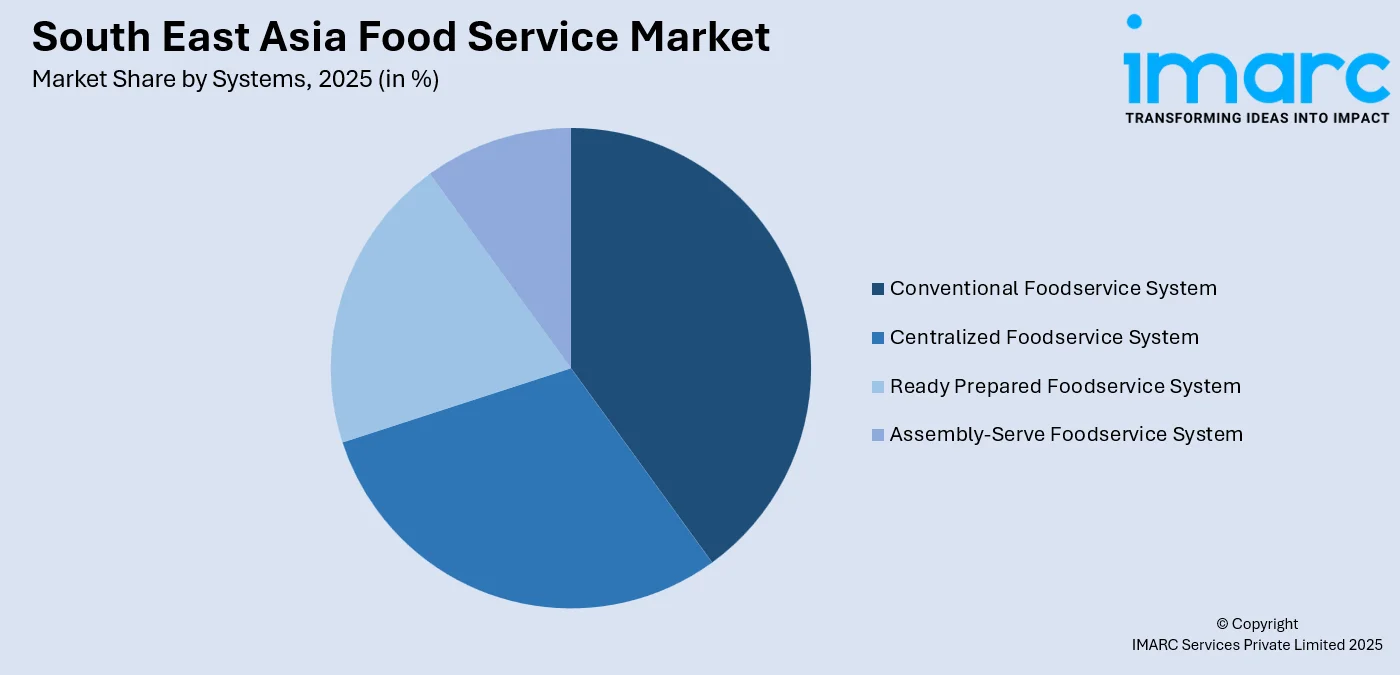
- By Systems: Conventional foodservice system leads the market with a share of 40% in 2025. This dominance reflects the region's preference for freshly prepared meals and traditional cooking methods that accommodate diverse local cuisines. Independent restaurants and family-owned establishments primarily utilize conventional systems to maintain authenticity.
- By Types of Restaurants: Fast food restaurants represent the biggest segment with a market share of 36% in 2025, driven by affordability, convenience, and aggressive expansion by international chains and regional players. Younger demographics seeking quick, accessible meal options are fueling sustained growth across urban centers.
- By Country: Indonesia is the largest country with 25% share in 2025, reflecting the nation's vast population base, expanding middle class, and vibrant food culture. Growing urbanization and increasing smartphone penetration are accelerating foodservice market development across major Indonesian cities.
- Key Players: Key players drive the South East Asia food service market by expanding restaurant networks, investing in digital ordering platforms, and enhancing delivery infrastructure. Their focus on menu localization, franchise development, and strategic partnerships with delivery aggregators strengthens market positioning while improving accessibility across diverse consumer segments. Some of the key players operating in the market include Jollibee Foods Corporation, Marrybrown Sdn. Bhd., McDonald's Corporation, Minor International, Secret Recipe Cakes & Café Sdn Bhd, and Tung Lok Restaurants (2000) Ltd.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
South East Asia Food Service Market Trends:
Digital Transformation Reshaping Consumer Engagement
The foodservice sector across South East Asia is undergoing significant digital transformation as operators embrace technology-driven solutions to enhance customer experiences. Online ordering platforms, mobile payment systems, and artificial intelligence-powered inventory management are becoming integral components of restaurant operations. This technological shift enables operators to streamline processes, reduce operational inefficiencies, and deliver personalized dining experiences. Growing internet penetration and smartphone adoption across the region are accelerating consumer engagement with digital food platforms, demonstrating widespread readiness for tech-enabled dining solutions that support South East Asia food service market growth.
Expansion of Cloud Kitchen and Delivery-Only Models
Cloud kitchens are emerging as transformative business models enabling foodservice operators to expand reach without traditional dine-in infrastructure investments. These delivery-only facilities allow brands to test new concepts with substantially lower capital requirements compared to conventional restaurant setups. The model provides operators with operational flexibility, enabling rapid menu adjustments and geographic expansion through optimized kitchen networks. Strategic integration with food delivery platforms enhances order volumes while reducing customer acquisition costs, positioning cloud kitchens as essential components of modern foodservice strategies across emerging Southeast Asian markets.
Rising Demand for Health-Conscious and Sustainable Dining Options
Consumer preferences across South East Asia are increasingly shifting toward healthier menu options and environmentally sustainable dining practices. Foodservice operators are responding by introducing plant-based alternatives, reduced-sodium offerings, and locally sourced ingredients that appeal to health-conscious demographics. Sustainability initiatives including eco-friendly packaging, food waste reduction programs, and energy-efficient kitchen equipment are gaining prominence as consumers prioritize brands demonstrating environmental responsibility. This trend reflects broader lifestyle changes among younger consumers who seek dining experiences aligned with their wellness and environmental values.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The South East Asia food service market demonstrates promising growth trajectory underpinned by favorable demographic trends, technological advancement, and sustained economic development across the region. Urbanization continues accelerating, creating expanded consumer bases seeking convenient out-of-home dining solutions. The market generated a revenue of USD 1,29,573.46 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 3,47,034.68 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 11.57% from 2026-2034. Tourism recovery, rising middle-class populations, and increasing digital platform adoption are strengthening demand drivers. Quick-service restaurants, cloud kitchens, and hybrid dining formats are positioned for accelerated expansion as operators leverage technology and strategic partnerships to capture emerging market opportunities across diverse consumer segments.
South East Asia Food Service Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Sector | Commercial | 65% |
| Systems | Conventional Foodservice System | 40% |
| Types of Restaurants | Fast Food Restaurants | 36% |
| Country | Indonesia | 25% |
Sector Insights:
- Commercial
- Non-Commercial
Commercial dominates with a market share of 65% of the total South East Asia food service market in 2025.
The commercial sector encompasses restaurants, cafes, bars, quick-service establishments, and hospitality-related foodservice operations that serve paying customers seeking dining experiences outside their homes. This segment benefits from widespread urbanization patterns across South East Asia, where metropolitan populations increasingly prefer convenient dining options that accommodate busy professional lifestyles. Full-service restaurants, casual dining establishments, and premium fine-dining venues collectively serve diverse consumer preferences ranging from affordable daily meals to experiential gastronomy. Rising dual-income households and extended working hours further amplify demand for commercial foodservice solutions that provide quality meals without home preparation requirements.
The commercial foodservice segment continues strengthening as tourism recovers and business travel resumes across major regional hubs. Expanding hospitality infrastructure drives substantial demand for restaurant and hotel dining services catering to international visitors and domestic travelers. Quick-service restaurants and cafes serving office workers, students, and urban residents demonstrate sustained growth as time-constrained consumers prioritize accessibility and convenience over home-prepared meals. Social dining culture and increasing preference for experiential gastronomy reinforce commercial segment dominance across the regional market.
Systems Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Conventional Foodservice System
- Centralized Foodservice System
- Ready Prepared Foodservice System
- Assembly-Serve Foodservice System
Conventional foodservice system leads with a share of 40% of the total South East Asia food service market in 2025.
The conventional foodservice system involves on-site food preparation where ingredients are cooked and served fresh within the same establishment, maintaining direct quality control throughout the production process. This system predominates across South East Asia due to cultural preferences for freshly prepared meals and the region's rich culinary traditions emphasizing authentic cooking techniques. Independent restaurants, family-owned establishments, and traditional eateries primarily operate using conventional systems that allow customization and freshness valued by local consumers. The hands-on approach enables chefs to adjust flavors and presentation according to individual customer preferences and seasonal ingredient availability.
Full-service restaurants represent substantial channels within regional consumer foodservice sectors, demonstrating strong preference for conventional preparation methods that preserve culinary authenticity. The system enables operators to accommodate diverse regional cuisines including Indonesian, Thai, Vietnamese, and Malaysian specialties that require traditional cooking approaches and specialized techniques. While centralized and assembly-serve systems gain traction among chain operators seeking operational efficiency and cost optimization, conventional systems maintain dominance through quality differentiation, authentic dining experiences, and cultural resonance with local consumer expectations.
Types of Restaurants Insights:
- Fast Food Restaurants
- Full-Service Restaurants
- Limited Service Restaurants
- Special Food Services Restaurants
Fast food restaurants exhibit a clear dominance with 36% share of the total South East Asia food service market in 2025.
Fast food restaurants deliver quick, affordable, and consistent dining experiences through standardized menus, efficient service models, and convenient locations targeting time-constrained consumers. The segment thrives due to alignment with accelerating urban lifestyles where consumers prioritize speed, value, and accessibility over extended dining experiences. Major international chains alongside regional operators have established extensive networks across shopping centers, transportation hubs, and high-traffic commercial areas throughout the region. Menu localization strategies enable operators to balance global brand consistency with regional taste preferences, attracting diverse consumer demographics.
The fast food segment demonstrates strong expansion momentum driven by aggressive franchising strategies and digital transformation initiatives. Jollibee Foods Corporation achieved 27.8% systemwide sales growth across its Southeast Asia operations in early 2025, opening 51 new stores including its landmark 200th outlet in Vietnam during 2024. Integration with delivery platforms, mobile ordering applications, and loyalty programs enhances customer engagement while drive-through and express formats capture commuter traffic across expanding metropolitan areas. Competitive pricing strategies, promotional bundling, and value meal offerings attract price-sensitive consumers seeking affordable dining solutions without compromising convenience or quality expectations.
Country Insights:
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Singapore
- Philippines
- Vietnam
- Malaysia
- Others
Indonesia represents the leading country with a 25% share of the total South East Asia food service market in 2025.
Indonesia represents the largest foodservice market within South East Asia, benefiting from the region's most populous consumer base, expanding middle-class demographics, and vibrant culinary traditions spanning diverse regional cuisines. The archipelago's young population demonstrates strong appetite for both traditional Indonesian fare and international dining concepts, driving market diversification and segment expansion. Major urban centers including Jakarta, Surabaya, and Bandung serve as primary growth hubs where restaurant density and consumer spending continue accelerating alongside infrastructure development.
The Indonesian foodservice industry was valued at USD 29.2 Billion in 2024, growing at 9.6% annually since 2020. Local coffee chains including Kopi Kenangan with over 900 outlets and Tomoro Coffee operating approximately 600 stores demonstrate remarkable scalability in the cafe segment. Food delivery platforms have revolutionized consumer access, enabling widespread adoption of online ordering throughout the Indonesian market. Independent restaurants, quick-service chains, and casual dining establishments collectively benefit from favorable demographic trends, increasing urbanization rates, and evolving consumer preferences toward convenient and experiential dining options.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the South East Asia Food Service Market Growing?
Rapid Urbanization and Expanding Middle-Class Population
Urbanization across South East Asia is accelerating at unprecedented rates, creating concentrated consumer populations seeking convenient foodservice options that complement fast-paced metropolitan lifestyles. The expansion of urban centers drives demand for quick-service restaurants, cafes, and casual dining establishments positioned within commercial districts, transportation corridors, and residential communities. Rising disposable incomes enable consumers to allocate greater household budgets toward out-of-home dining experiences, transitioning from necessity-based food consumption toward experiential gastronomy. Middle-class growth creates demand for premium dining options, international cuisines, and quality-focused establishments that reflect aspiring consumer preferences and enhanced purchasing power.
Digital Platform Integration and Technology Adoption
Digital transformation is fundamentally reshaping foodservice operations and consumer engagement across South East Asia through integrated ordering platforms, mobile payment systems, and data-driven business intelligence. Food delivery aggregators have created accessible channels connecting restaurants with consumers, eliminating geographic barriers and expanding market reach beyond traditional dine-in limitations. Technology adoption enhances operational efficiency through automated inventory management, predictive demand forecasting, and streamlined kitchen workflows that reduce waste while improving service consistency. Restaurant operators leveraging digital tools achieve competitive advantages through personalized marketing, loyalty programs, and seamless omnichannel experiences that strengthen customer relationships and drive repeat transactions.
Tourism Recovery and Hospitality Sector Expansion
Tourism recovery across South East Asia is generating substantial incremental demand for foodservice operations serving international visitors, business travelers, and domestic tourists exploring regional destinations. The hospitality sector's expansion drives investment in hotel restaurants, resort dining facilities, and tourist-oriented food establishments catering to diverse culinary preferences and premium service expectations. Government initiatives promoting tourism through visa facilitation, destination marketing, and infrastructure development strengthen visitor arrivals that translate into sustained foodservice demand. Airport foodservice, in-flight catering, and travel retail segments benefit from increasing passenger volumes as regional and international air connectivity expands across major gateway cities.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the South East Asia Food Service Market is Facing?
Rising Labor Costs and Workforce Shortages
Labor costs across South East Asia are increasing as economic development elevates wage expectations while workforce availability remains constrained in urban hospitality sectors. Foodservice operators face challenges recruiting and retaining skilled kitchen staff, service personnel, and management talent amid competitive employment markets. High employee turnover rates increase training costs and disrupt service consistency, impacting customer satisfaction and operational profitability across restaurant operations.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Ingredient Price Volatility
Supply chain disruptions and fluctuating ingredient prices create operational challenges for foodservice operators managing cost structures while maintaining menu pricing competitiveness. The region faces a USD 60 Billion investment gap in cold storage and logistics infrastructure, restricting operators from efficiently managing inventory and mitigating perishable supply volatility. Climate variability affecting agricultural production, transportation constraints, and import dependencies expose operators to procurement uncertainties that impact margin sustainability.
Fragmented Regulatory Environment and Compliance Complexity
Diverse regulatory frameworks across South East Asian nations create compliance complexities for foodservice operators seeking regional expansion or standardized operations. Varying food safety standards, licensing requirements, and operational regulations between countries increase administrative burdens and market entry barriers. Inconsistent enforcement practices and evolving policy environments require continuous monitoring and adaptation, consuming management resources and limiting operational scalability.
Competitive Landscape:
The South East Asia food service market features a fragmented competitive landscape comprising international quick-service chains, regional restaurant groups, and numerous independent operators serving diverse consumer segments. Major players compete through brand differentiation, menu innovation, digital platform integration, and franchise network expansion that extends geographic reach across multiple countries. Strategic investments in supply chain capabilities, kitchen automation, and customer relationship management enhance competitive positioning. Local operators leverage cultural authenticity and community connections to maintain market positions against international competitors. Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships facilitate market consolidation while enabling operators to achieve scale efficiencies and accelerate growth trajectories across the dynamic regional market.
Some of the key players include:
- Jollibee Foods Corporation
- Marrybrown Sdn. Bhd.
- McDonald's Corporation
- Minor International
- Secret Recipe Cakes & Café Sdn Bhd
- Tung Lok Restaurants (2000) Ltd
Recent Developments:
- In December 2025, Chick-fil-A opened its first Asian outlet at Bugis+ in Singapore, marking the American QSR giant's entry into the region with a USD 75 Million, 10-year investment plan. The Singapore flagship features a Spicy Chilli Sauce developed exclusively for Singaporean consumers.
South East Asia Food Service Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Sectors Covered | Commercial, Non-Commercial |
| Systems Covered | Conventional Foodservice System, Centralized Foodservice System, Ready Prepared Foodservice System, Assembly-Serve Foodservice System |
| Types of Restaurants Covered | Fast Food Restaurants, Full-Service Restaurants, Limited Service Restaurants, Special Food Services Restaurants |
| Countries Covered | Indonesia, Thailand, Singapore, Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, Others |
| Companies Covered | Jollibee Foods Corporation, Marrybrown Sdn. Bhd., McDonald’s Corporation, Minor International, Secret Recipe Cakes & Café Sdn Bhd, Tung Lok Restaurants (2000) Ltd, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The South East Asia food service market size was valued at USD 1,29,573.46 Million in 2025.
The South East Asia food service market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 11.57% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 3,47,034.68 Million by 2034.
Commercial dominated the market with a share of 65%, driven by widespread urbanization, rising out-of-home dining preferences, and expanding quick-service restaurant networks serving metropolitan populations across the region.
Key factors driving the South East Asia food service market include rapid urbanization, rising disposable incomes, digital platform adoption, tourism recovery, expanding middle-class populations, and increasing consumer preference for convenient dining options.
Major challenges include rising labor costs, supply chain vulnerabilities, ingredient price volatility, fragmented regulatory environments, intense competition, and infrastructure gaps in cold storage and logistics across the region.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












