
South Korea Agricultural Films Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
South Korea Agricultural Films Market Summary:
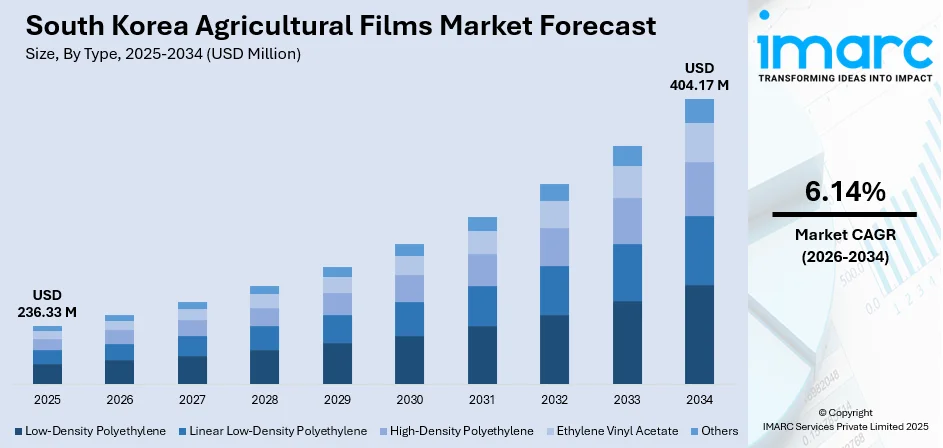
The South Korea agricultural films market size was valued at USD 236.33 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 404.17 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.14% from 2026-2034.
The South Korea agricultural films market is experiencing steady expansion driven by the nation's increasing adoption of protected cultivation practices and precision agriculture technologies. Rising demand for high-quality crop production, coupled with limited arable land availability and climate variability challenges, is accelerating the deployment of greenhouse and mulching film solutions across the country. Government initiatives supporting smart farming infrastructure, combined with growing environmental awareness promoting sustainable agricultural practices, are contributing to the expanding South Korea agricultural films market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Type: Linear Low-Density Polyethylene dominates the market with a share of 49.72% in 2025, attributed to its superior tensile strength, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness for mulching and greenhouse applications.
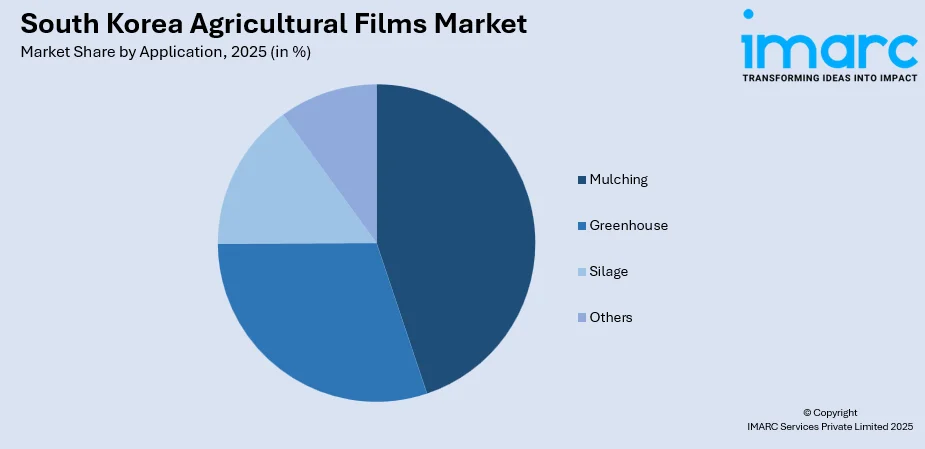
- By Application: Mulching leads the market with a share of 44.74% in 2025, driven by widespread adoption for soil moisture retention, weed suppression, and temperature regulation in vegetable and fruit cultivation.
- Key Players: The South Korea agricultural films market features a moderately competitive landscape characterized by the presence of multinational polymer manufacturers alongside regional film converters. Market participants compete through product innovation, sustainable material development, and strategic partnerships with agricultural cooperatives and government-backed smart farming initiatives.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
The South Korea agricultural films market represents one of the most technologically advanced segments within the Asia-Pacific region, reflecting the nation's commitment to agricultural modernization and food security enhancement. South Korea's agricultural sector faces structural challenges including an aging farming population, limited cultivable land comprising only about seventeen percent of total territory, and increasing climate unpredictability. These factors have driven accelerated adoption of protected cultivation methods and precision farming technologies.
South Korea Agricultural Films Market Trends:
Accelerating Adoption of Smart Greenhouse Technologies
South Korean farmers are rapidly embracing smart greenhouse systems that integrate agricultural films with advanced environmental monitoring and control technologies. The government's smart farming initiatives aim to convert over sixty percent of conventional farms to technology-enabled operations by 2025. In February 2025, the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs announced its comprehensive five-year master plan allocating substantial funding for smart farm infrastructure development, including specialized smart-farming fostering zones in four cities and counties across the country. These integrated systems combine high-performance greenhouse films with IoT sensors for real-time climate monitoring, enabling precise control over temperature, humidity, and light exposure, which is contributing to the South Korea agricultural films market growth.
Rising Focus on Biodegradable and Sustainable Film Solutions
Environmental sustainability is becoming a central consideration in South Korea's agricultural sector, driving innovation in biodegradable and eco-friendly film alternatives. Research institutions including Kyung Hee University have received substantial funding from the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy for developing biodegradable polymers using high-performance enzyme activation technologies. These initiatives reflect growing recognition that conventional polyethylene films contribute to soil contamination and microplastic pollution, prompting farmers and policymakers to seek decomposable alternatives that maintain agricultural performance while reducing environmental impact.
Advanced Film Technologies Enhancing Crop Protection and Yield
Continuous innovation in agricultural film formulations is driving market evolution with enhanced UV protection, thermal stability, and light management capabilities. Modern films incorporate specialized additives that extend product lifespan while improving crop growing conditions. In July 2024, BASF introduced Tinuvin NOR 211 AR, a high-performance heat and light stabilizer designed specifically for agricultural plastics requiring resistance to intense UV radiation, thermal stress, and inorganic chemicals commonly used in crop management. Such technological advancements enable thinner film applications without compromising durability, supporting industry trends toward material efficiency and resource conservation while delivering superior plant protection and yield enhancement across diverse climatic conditions.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The South Korea agricultural films market demonstrates robust growth potential throughout the forecast period, underpinned by structural shifts toward protected agriculture and precision farming practices. Government commitments to agricultural modernization, including substantial allocations through the Smart-Farming General Fund and expanded vocational education programs, are creating sustained demand for advanced film solutions. The market generated a revenue of USD 236.33 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 404.17 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.14% from 2026-2034.
South Korea Agricultural Films Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Linear Low-Density Polyethylene | 49.72% |
| Application | Mulching | 44.74% |
Type Insights:
- Low-Density Polyethylene
- Linear Low-Density Polyethylene
- High-Density Polyethylene
- Ethylene Vinyl Acetate
- Others
Linear low-density polyethylene leads the market with a share of 49.72% of the total South Korea agricultural films market in 2025.
Linear low-density polyethylene has established market leadership in South Korea's agricultural films sector due to its exceptional combination of mechanical properties, processing versatility, and cost efficiency. LLDPE films offer superior tensile strength, puncture resistance, and flexibility compared to conventional low-density polyethylene, enabling the production of thinner yet more durable films that reduce material consumption while maintaining excellent performance characteristics. These attributes make LLDPE particularly suitable for demanding agricultural applications including mulching, greenhouse covering, and silage protection where durability and environmental resistance are critical requirements.
The segment's dominance reflects South Korean farmers' preference for high-performance materials that deliver consistent protection across variable weather conditions. LLDPE agricultural films demonstrate excellent UV resistance and thermal stability, extending product lifespan across multiple growing seasons and reducing replacement frequency. The material's adaptability to both greenhouse and open-field applications, combined with its compatibility with modern film extrusion technologies, has positioned LLDPE as the preferred polymer choice for film manufacturers serving the Korean agricultural market. Major global suppliers including Dow, ExxonMobil, and regional producers have developed specialized LLDPE grades optimized for agricultural film applications, ensuring reliable supply chains and competitive pricing for Korean agricultural operations.
Application Insights:
Access the Comprehensive Market Breakdown, Request Sample
- Greenhouse
- Silage
- Mulching
- Others
Mulching dominates the market with a share of 44.74% of the total South Korea agricultural films market in 2025.
Mulching films have achieved market leadership in South Korea driven by their essential role in intensive vegetable and fruit cultivation practices that characterize Korean agriculture. These films provide critical benefits including soil moisture conservation, weed suppression, soil temperature regulation, and prevention of soil erosion, enabling farmers to optimize growing conditions while reducing labor requirements and chemical inputs. South Korea's limited arable land necessitates maximizing productivity per hectare, making mulching films indispensable tools for achieving consistent crop quality and yield enhancement across diverse agricultural operations.
The segment benefits from South Korea's extensive cultivation of high-value horticultural crops including strawberries, tomatoes, peppers, and leafy vegetables that require precise soil management for optimal production. Black mulch films dominate this segment due to their superior weed control capabilities achieved by blocking sunlight penetration, while clear and colored variants serve specialized applications requiring different thermal characteristics. Korean farmers increasingly adopt advanced mulching practices incorporating drip irrigation integration and reflective film technologies that enhance light distribution within crop canopies. The growing emphasis on sustainable agriculture is also driving interest in biodegradable mulching films that decompose naturally in soil after crop harvest, eliminating collection and disposal requirements while reducing environmental impact.
Regional Insights:
- Seoul Capital Area
- Yeongnam (Southeastern Region)
- Honam (Southwestern Region)
- Hoseo (Central Region)
- Others
The Seoul Capital Area represents a significant consumer base for agricultural films, driven by substantial peri-urban farming operations and advanced greenhouse cultivation facilities serving the metropolitan population. Yeongnam in the southeastern region maintains strong demand supported by extensive vegetable and fruit production across Gyeongsang provinces, while Honam in the southwest contributes substantially through its established rice cultivation and horticultural operations. Hoseo in the central region benefits from proximity to major distribution networks and growing adoption of smart farming technologies. Regional market dynamics reflect local agricultural specializations, climate conditions, and government support programs promoting protected cultivation across different provincial administrations.
The Yeongnam (Southeastern Region) constitutes South Korea's primary agricultural heartland with fertile plains along the Nakdong River supporting intensive cultivation. Agricultural films in this region support diverse applications including greenhouse production of vegetables, fruit orchards, and mulching for strawberries, tomatoes, and peppers cultivated across the region's extensive protected cultivation infrastructure.
The Honam (Southwestern Region) represents South Korea's traditional rice cultivation heartland with historically favorable climatic conditions dating back to ancient Korean dynasties. Haenam in South Jeolla Province produces premium rice renowned for sushi preparation, receiving multiple awards from the Korea Consumer Organization Council. The region hosts the Youngsan River reclaimed lands designated for large-scale agricultural complex development, with significant paprika production for export markets. Agricultural films support extensive greenhouse horticulture and mulching applications across the region's diverse crop portfolio including rice, vegetables, and specialty horticultural products destined for domestic and international markets.
The Hoseo (Central Region) serves as a critical agricultural production hub supplying the capital region's substantial food demands. South Chungcheong Province specializes in strawberry, tomato, melon, and watermelon cultivation, operating the dedicated Nonsan Strawberry Experiment Station for variety development and disease management. The region's Chungcheongnam-do Agricultural Research and Extension Services supports ginseng, medicinal plant, and flower cultivation including chrysanthemums, lilies, and orchids. North Chungcheong Province is developing rental smart farms with 4.3 hectares of smart greenhouses in Yeongdong-gun, driving agricultural film demand for protected cultivation and advanced greenhouse facilities.
The others category encompasses Gangwon Province, Jeju Province, and remaining regions characterized by distinctive agricultural conditions. Jeju Province and southern coastal areas increasingly cultivate subtropical fruits including bananas, mangoes, lemons, and passion fruit primarily within heated greenhouse environments. These regions collectively demonstrate growing agricultural film requirements for specialty crop protection, subtropical fruit greenhouses, and expanding protected cultivation facilities adapting to shifting climatic conditions and diversifying production portfolios across specialty agricultural segments.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the South Korea Agricultural Films Market Growing?
Government Initiatives Accelerating Smart Farming Adoption
The South Korean government is actively promoting agricultural modernization through comprehensive policy frameworks and substantial financial support that directly benefit agricultural films adoption. The Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs established the First Five-Year Master Plan for Promotion of the Growth of the Smart-Farming Industry for 2025-2029, targeting conversion of thirty-five percent of the nation's greenhouse facilities into technology-enabled smart farms. This initiative includes expansion of the Smart-Farming General Fund providing low-interest loans for farmers investing in modern cultivation infrastructure including advanced film technologies. The government has designated smart-farming fostering zones in four cities and counties in 2025, bringing together young farmers, agritech companies, and research institutions to accelerate technology adoption. Additionally, the number of specialized vocational education institutes offering smart farming training programs doubled from two in 2024 to four in 2025, ensuring adequate skilled workforce availability for operating sophisticated protected cultivation systems.
Structural Shift Toward Protected Cultivation Practices
South Korea's agricultural sector is experiencing fundamental transformation toward controlled environment agriculture driven by multiple converging factors that necessitate expanded use of agricultural films. Limited arable land comprising only seventeen percent of national territory, combined with an aging farming population and intensifying climate variability, requires maximizing productivity through protected cultivation methods. Korea maintains an active greenhouse farming culture accounting for approximately twelve percent of agricultural output by value, reflecting significant existing infrastructure for film-based cultivation. Over sixty percent of South Korean farms are projected to adopt smart greenhouse systems by 2025, incorporating advanced films for temperature regulation, humidity control, and light management. The nation's Smart Farm Innovation Valleys provide comprehensive training and pilot technologies that facilitate broader implementation of protected agriculture techniques across the country.
Rising Demand for High-Quality Agricultural Production
Consumer preferences for premium agricultural products are driving farmers to adopt sophisticated cultivation technologies that deliver consistent quality and extended availability. South Korean consumers demonstrate strong preferences for fresh, domestically produced vegetables and fruits, creating market incentives for year-round protected cultivation. Agricultural films enable farmers to create optimized growing environments that reduce pest pressure, minimize crop damage from adverse weather, and improve uniformity of harvested products meeting stringent quality standards. Export-oriented cultivation operations require precise environmental control to achieve consistent specifications for international markets. The hybrid farm systems gaining traction in South Korea combine vertical farming elements with greenhouse structures, exemplified by facilities generating approximately seven and a half million dollars in annual sales through integrated production systems. These developments reflect broader industry recognition that agricultural films represent essential infrastructure investments for competitive commercial farming operations.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the South Korea Agricultural Films Market is Facing?
Environmental Concerns Over Plastic Waste Accumulation
The persistence of polyethylene-based agricultural films in soil ecosystems creates significant environmental challenges that attract regulatory scrutiny and public concern. Plastic film residues accumulate over years of cultivation, potentially disrupting soil structure, hindering nutrient cycling, and contributing to microplastic pollution. The Korean government has established stringent waste management frameworks and is actively pursuing strategies to reduce agricultural plastic pollution through improved collection systems and biodegradable alternatives development.
High Initial Investment Costs for Advanced Film Systems
The substantial capital requirements for implementing comprehensive protected cultivation systems incorporating advanced agricultural films present barriers for smaller farming operations. Smart greenhouse infrastructure combining specialized films with environmental monitoring and control technologies requires significant upfront investment that may exceed the financial capacity of traditional farmers. Although government loan programs provide support, adoption rates remain constrained by economic considerations particularly among aging farmer populations hesitant to undertake major capital expenditures.
Limited Availability of Cost-Effective Biodegradable Alternatives
Despite growing demand for environmentally sustainable film options, biodegradable agricultural films remain more expensive than conventional polyethylene products and may offer inferior mechanical performance or inconsistent degradation characteristics. The technological maturity of biodegradable materials has not yet achieved cost parity with established petroleum-based polymers, limiting widespread adoption among price-sensitive agricultural operations. Research initiatives continue advancing formulations, but commercial-scale availability of competitive biodegradable films remains constrained.
Competitive Landscape:
The South Korea agricultural films market exhibits moderate competitive intensity characterized by the participation of multinational polymer manufacturers, regional film converters, and specialized agricultural materials suppliers. Market dynamics reflect strategic positioning across performance tiers ranging from premium innovation-driven products emphasizing advanced properties to value-oriented offerings targeting cost-conscious agricultural operations. Competition increasingly centers on sustainability credentials, technical support capabilities, and integration with smart farming ecosystems. Key players are strengthening market presence through product innovation addressing specific crop requirements, partnerships with agricultural cooperatives, and participation in government-sponsored modernization programs promoting advanced cultivation technologies.
South Korea Agricultural Films Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Low-Density Polyethylene, Linear Low-Density Polyethylene, High-Density Polyethylene, Ethylene Vinyl Acetate, Others |
| Applications Covered | Greenhouse, Silage, Mulching, Others |
| Regions Covered | Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The South Korea agricultural films market size was valued at USD 236.33 Million in 2025.
The South Korea agricultural films market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.14% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 404.17 Million by 2034.
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene held the largest market share of 49.72%, driven by its superior tensile strength, flexibility, puncture resistance, and cost-effectiveness for mulching and greenhouse applications across Korean agricultural operations.
Key factors driving the South Korea agricultural films market include government initiatives promoting smart farming adoption, structural shifts toward protected cultivation practices, rising demand for high-quality crop production, and increasing focus on sustainable agricultural technologies.
Major challenges include environmental concerns over plastic waste accumulation in agricultural soils, high initial investment costs for advanced protected cultivation systems, limited commercial availability of cost-effective biodegradable film alternatives, and regulatory pressures regarding plastic use and disposal.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












