
South Korea Smart Agriculture Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Agriculture Type, Offering, Farm Size, and Region, 2025-2033
South Korea Smart Agriculture Market Overview:
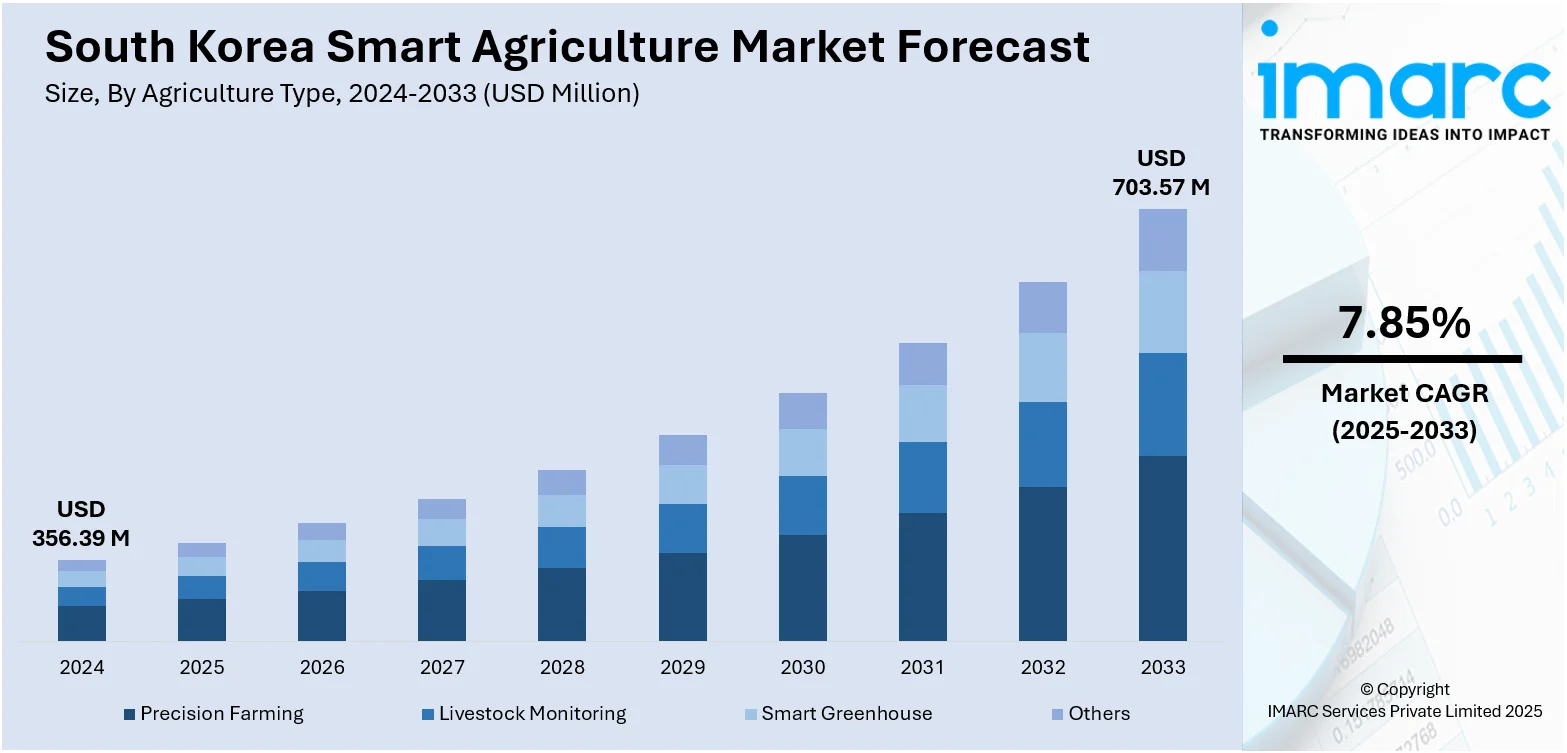
The South Korea smart agriculture market size reached USD 356.39 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 703.57 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 7.85% during 2025-2033. The market is growing steadily, driven by the adoption of advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and automation to improve crop productivity and resource efficiency. Government initiatives, labor shortages, and rising food demand are accelerating this shift toward digital farming practices, contributing significantly to the expanding South Korea smart agriculture market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 356.39 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 703.57 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 7.85% |
South Korea Smart Agriculture Market Trends:
Robust Government Initiatives and Policy Backing
The South Korean government plays a central role in accelerating smart agriculture through strategic planning, subsidies, and infrastructure development. Large-scale projects, such as the so-called Smart Farm Innovation Valley, provide farmers with training opportunities, research, and pilot technologies that promote their implementation throughout the country. Policies mainly centered where the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) and the Ministry of Science and ICT are based on the integration of digital with IoT, AI and big data. Both the smallholders and large-scale farmers are being driven to modernize operations by financial offers, such as grants and low-interest loans for smart equipment. These efforts not only boost productivity and sustainability but also create a supportive ecosystem for startups and agri-tech innovation, positioning policy support as a key driver of the South Korea smart agriculture market growth.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Aging Rural Workforce and Labor Shortages
South Korea faces a serious challenge with its rapidly aging farming population, where a significant portion of farmers are over 65, and younger generations show little interest in traditional agriculture. This labor shortage is accelerating the shift toward automation and digital farming technologies. Smart agriculture solutions like automated irrigation, sensor-driven crop monitoring, drones, and AI-powered machinery reduce reliance on manual labor, making farming more efficient and less physically demanding. These technologies also make agriculture more appealing to younger, tech-savvy entrepreneurs, reversing rural decline. Government-supported education and relocation incentives for new farmers further encourage this transition. Thus, the need to address labor gaps and sustain productivity amidst demographic decline is a major force behind smart agriculture growth.
Advanced Technology and Digital Infrastructure
South Korea’s strong foundation in ICT, AI, and high-speed connectivity gives it a competitive edge in deploying smart farming solutions. The country’s expansive digital infrastructure enables real-time data collection through IoT sensors, satellite imaging, and precision monitoring systems. Farms now leverage AI algorithms to analyze weather patterns, optimize irrigation, detect diseases early, and enhance crop yields. Drones and automated machinery are becoming common in both field and vertical farming setups. Major tech firms like SK Telecom, KT, and Samsung are entering the agri-tech space, accelerating innovation and commercial availability. Combined with integrated data platforms and government-supported research and development (R&D), this ecosystem is transforming agriculture into a high-tech, data-driven sector, making digital innovation a critical growth engine.
South Korea Smart Agriculture Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on agriculture type, offering, and farm size.
Agriculture Type Insights:
- Precision Farming
- Livestock Monitoring
- Smart Greenhouse
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on agriculture type. This includes precision farming, livestock monitoring, smart greenhouse, and others.
Offering Insights:
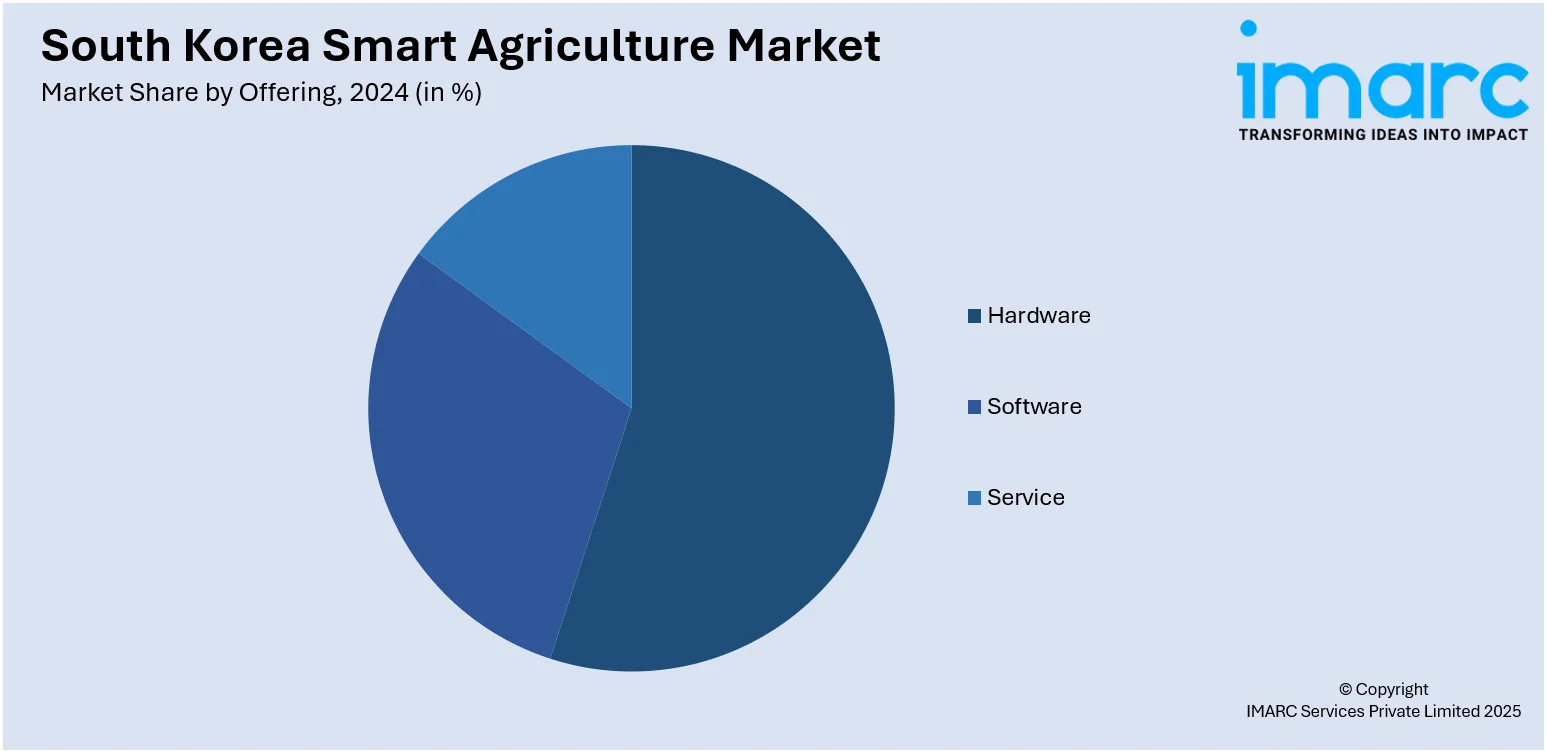
- Hardware
- Software
- Service
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the offerings have also been provided in the report. This includes hardware, software, and service.
Farm Size Insights:
- Small
- Medium
- Large
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the farm size have also been provided in the report. This includes small, medium, and large.
Regional Insights:
- Seoul Capital Area
- Yeongnam (Southeastern Region)
- Honam (Southwestern Region)
- Hoseo (Central Region)
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
South Korea Smart Agriculture Market News:
- In April 2025, South Korea and Saudi Arabia partnered to establish a cutting-edge smart farming complex in central Riyadh, in a significant move to advance sustainable agriculture and drive technological progress. This joint venture represents a pivotal step in transforming agricultural practices across the Middle East, addressing both climate-related challenges and growing food security needs.
South Korea Smart Agriculture Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Agriculture Types Covered | Precision Farming, Livestock Monitoring, Smart Greenhouse, Others |
| Offerings Covered | Hardware, Software, Service |
| Farm Sizes Covered | Small, Medium, Large |
| Regions Covered | Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the South Korea smart agriculture market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea smart agriculture market on the basis of agriculture type?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea smart agriculture market on the basis of offering?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea smart agriculture market on the basis of farm size?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea smart agriculture market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the South Korea smart agriculture market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the South Korea smart agriculture market?
- What is the structure of the South Korea smart agriculture market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the South Korea smart agriculture market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the South Korea smart agriculture market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the South Korea smart agriculture market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the South Korea smart agriculture industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












