
South Korea Smart Water Management Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Application, and Region, 2026-2034
South Korea Smart Water Management Market Summary:
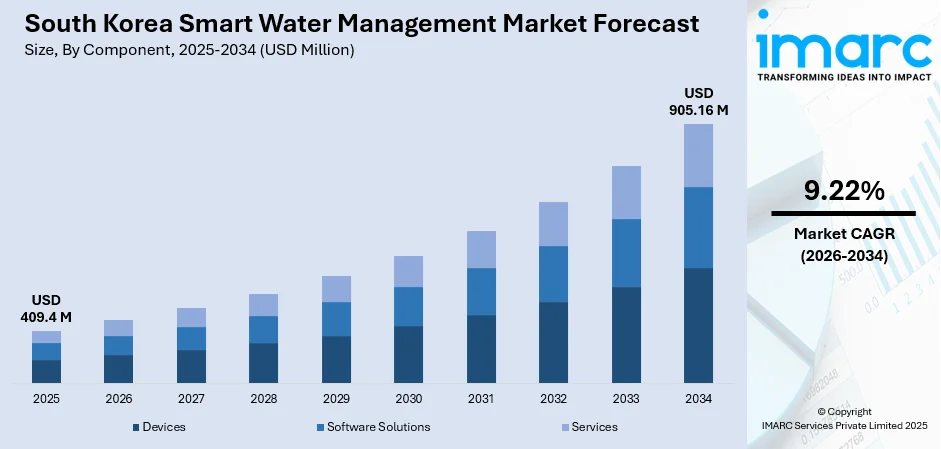
The South Korea smart water management market size was valued at USD 409.4 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 905.16 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 9.22% from 2026-2034.
The market expansion is primarily propelled by intensifying climate change impacts creating water scarcity concerns across the peninsula, coupled with substantial government investments in digital infrastructure modernization. The national framework for integrated water management has positioned smart technologies as central to addressing both water quality and quantity challenges. Additionally, the government's commitment to carbon neutrality in water management and the deployment of artificial intelligence (AI)-driven solutions across treatment facilities are strengthening the market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Component: Devices dominate the market with a share of 48% in 2025, driven by the nationwide deployment of advanced smart meters and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, enabling real-time water flow monitoring, pressure optimization, and automated leak detection across municipal and industrial water networks.
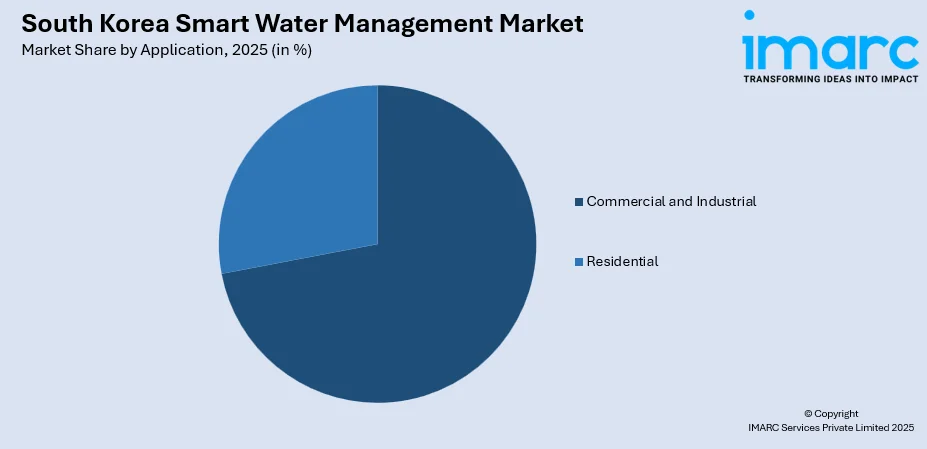
- By Application: Commercial and Industrial lead the market with a share of 72% in 2025, owing to semiconductor manufacturing facilities requiring ultra-pure water systems, expanding industrial complexes in regions experiencing water scarcity, and stringent process water quality requirements across heavy industries.
- Key Players: The South Korea smart water management market demonstrates collaborative competition between domestic technology providers and the state-owned K-water corporation, which serves as both infrastructure operator and innovation catalyst supporting water technology startups.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The South Korea smart water management market is expected to grow steadily, as utilities and municipalities are focusing on efficiency, sustainability, and digital control of water resources. Rising urban population and industrial activities are increasing the need for real-time monitoring of water quality, pressure, and leakage. Smart sensors and data analytics help reduce water loss and improve supply reliability. Utilities are adopting automated metering systems to improve billing accuracy and customer transparency. Government support for smart infrastructure is encouraging investments in intelligent water networks. Integration of AI and IoT technologies improves predictive maintenance and asset management. As per IMARC Group, the South Korea AI market size was valued at USD 3.12 Billion in 2024. Commercial and residential buildings increasingly install smart systems to track consumption.
South Korea Smart Water Management Market Trends:
Integration of Digital Twin Technology for Predictive Water Management
South Korea is advancing smart integrated water management through digital twin platforms equipped with real-time monitoring, analysis, and prediction functions based on 3D virtual environments. K-water's Digital GARAM+ technology, showcased at World Water Forum in May 2024, leveraged digital twin technology that creates virtual replicas of real-world water systems, enabling real-time monitoring and simulation of water management scenarios, including floods, droughts, and water quality issues, to support optimal decision-making.
Expansion of AI-Powered Smart Water Cities
The broadening of AI-powered smart water cities is driving the market growth by enabling real-time monitoring, prediction, and automation across water networks. AI systems detect leaks, forecast demand, and optimize pressure control, reducing water loss and improving efficiency. Cities integrate water systems with broader smart infrastructure for better planning and emergency response. K-water declared its plan to adopt an AI-first approach in June 2025, aiming to integrate AI throughout the complete water management strategy. It handled up to 7.4 Billion data items each day. Automated analytics improve water quality tracking and maintenance scheduling.
Government-Driven Smart Sewerage and Treatment Facility Modernization
Government-driven modernization of sewerage and treatment facilities is accelerating the market growth by promoting automation, monitoring, and efficiency across wastewater infrastructure. Upgraded plants use sensors and remote systems to track flow, detect faults, and optimize treatment processes. Digital monitoring improves compliance with environmental standards and reduces operational costs. Smart controls also enhance emergency response and maintenance planning. As public investments are increasing, utilities are adopting intelligent technologies to improve resource management and service reliability, driving nationwide demand for smart water management solutions. In September 2025, Finance Minister of South Korea, Koo Yun-cheol, announced that the government aimed to infuse another 7 Trillion Won (USD 5.03 Billion) by year’s end to encourage investments from public institutions, as part of strategies to rejuvenate the economy during an extended downturn.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The market growth trajectory is underpinned by the national strategic commitment to establish smart water management systems across seven major metropolitan areas by 2030, supported by continued public-private partnerships driving technology commercialization. The market generated a revenue of USD 409.4 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 905.16 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 9.22% from 2026-2034. The market will benefit from expanding deployment of advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) infrastructure, increasing adoption of predictive analytics for leak detection and maintenance, and government initiatives promoting water technology exports alongside domestic infrastructure modernization.
South Korea Smart Water Management Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Component | Devices | 48% |
| Application | Commercial and Industrial | 72% |
Component Insights:
- Devices
- Advanced Water Meters
- Meter Read Technology
- Software Solutions
- Asset Management
- Distribution Network Monitoring
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
- Meter Data Management (MDM)
- Advance Analytics
- Others
- Services
- Managed Services
- Professional Services
Devices (advanced water meters and meter read technology) dominate with a market share of 48% of the total South Korea smart water management market in 2025.
The devices segment maintains market leadership, driven by accelerating deployment of smart water meters, facilitating automated data collection and real-time monitoring capabilities across municipal and industrial applications. The smart devices provide hourly water usage data updates, enabling early detection of indoor water leakage and collaboration through social safety networks, representing a fundamental shift from billing-focused metering to comprehensive water service management.
Devices also represent the highest initial investment compared to software and services, making them the largest revenue contributor. Advanced sensors improve accuracy and system visibility, helping reduce water loss. As cities are modernizing infrastructure, large-scale deployment of hardware is required across pipelines, treatment plants, and consumer endpoints. Continuous replacement cycles, maintenance needs, and technology upgrades further sustain demand. This makes devices the most dominant and essential component in South Korea’s smart water management market.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Residential
- Commercial and Industrial
Commercial and industrial lead with a share of 72% of the total South Korea smart water management market in 2025.
The commercial and industrial segment commands substantial market share, driven by heavy manufacturing industries requiring precise water quality control and efficient resource utilization. K-water was set to build the biggest desalination plant in South Korea to provide water for heavy industries in the Daesan Industrial Complex, which produced 40% of South Korea's petrochemicals, tackling water shortages due to severe droughts and dependence on external water sources.
Factories, power plants, office complexes, and commercial facilities rely on smart systems to monitor consumption, detect leaks, and manage treatment processes efficiently. For industries, water quality directly affects production outcomes, making real-time monitoring essential. Smart systems also help businesses meet environmental regulations and reduce operating costs through water optimization. Commercial buildings use intelligent meters to improve billing accuracy and resource planning. Compared to residential users, commercial and industrial entities have larger budgets for infrastructure upgrades and faster return on investment from efficiency gains.
Regional Insights:
- Seoul Capital Area
- Yeongnam (Southeastern Region)
- Honam (Southwestern Region)
- Hoseo (Central Region)
- Others
The Seoul Capital Area holds prominence due to high population density and complex water networks. Utilities invest heavily in sensors, automated metering, and leak detection to ensure reliable supply and minimize losses across residential, commercial, and industrial areas.
In Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), industrial base and port cities drive the demand for smart water systems. Factories and municipalities use advanced monitoring to manage consumption, wastewater treatment, and pollution control efficiently.
Honam (Southwestern Region) focuses on improving water quality and agricultural efficiency. Smart irrigation, treatment monitoring, and rural water management systems support sustainable water usage and minimize wastage.
Hoseo (Central Region) benefits from growing industrial zones and technology institutions. Utilities adopt digital water platforms to enhance operational control and support expansion of urban infrastructure networks.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the South Korea Smart Water Management Market Growing?
Intensifying Climate Change Impacts and Water Scarcity Challenges
Intensifying climate change and increasing water scarcity are major drivers of the market growth. Extreme weather events, irregular rainfall, and rising temperatures strain existing water resources, making efficient monitoring and distribution critical. According to the annual climate report from the Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA) published on April 1, 2025, South Korea’s national average temperature reached 14.5 deg C in 2024, marking the hottest year since 1973. Smart sensors and IoT systems help detect leaks, optimize water pressure, and forecast demand, reducing wastage and improving resilience. Advanced analytics enable utilities to plan for droughts and floods, protecting urban supply and agricultural needs. Real-time monitoring ensures water quality remains safe under changing environmental conditions. These climate-driven pressures increase public and private investment in smart infrastructure. Municipalities adopt AI-powered management to enhance resource allocation, minimize losses, and maintain sustainable supply. Overall, environmental challenges accelerate the deployment of intelligent water networks as part of South Korea’s long-term strategy for water security.
Strong Government Smart City and Digital Infrastructure Initiatives
Government-led smart city and digital infrastructure programs are fueling the market growth. Public policies prioritize urban modernization, energy efficiency, and resource sustainability, encouraging municipalities to deploy intelligent water networks. South Korea implemented the Smart City Act in 2024, signifying an important policy transition towards data-informed and citizen-focused urban innovation with legal and organizational frameworks for smart city progress. Investments in sensors, automated metering, and connected platforms support centralized monitoring, leak detection, and predictive maintenance. Government pilot projects demonstrate cost savings, improve regulatory compliance, and showcase technological benefits, boosting confidence in smart water adoption. Integration with broader smart city systems, including traffic, energy, and public safety networks, enhances operational efficiency. Financial incentives, regulatory frameworks, and standardization policies facilitate large-scale implementation. These initiatives also stimulate collaboration between technology vendors, utilities, and local governments. As digital urban infrastructure is expanding nationwide, government support remains a central force accelerating smart water system deployment across cities and industrial zones.
Aging Water Infrastructure and Non-Revenue Water (NRW) Reduction Imperatives
Aging water infrastructure and the need to reduce NRW are key drivers of the market expansion. Many urban pipelines and treatment facilities are decades old, prone to leaks, and inefficient, leading to significant water loss. Utilities adopt smart meters, sensors, and automated monitoring systems to detect leaks, optimize pressure, and improve maintenance planning. Real-time data allows operators to prioritize repairs and minimize operational disruptions. Reducing NRW not only improves water availability but also cuts energy consumption and operational costs. Upgrading old infrastructure with intelligent systems ensures compliance with regulatory standards and enhances service reliability. The combination of infrastructure modernization needs and efficiency imperatives accelerates investment in digital water solutions, positioning smart water technologies as essential tools for sustainable water management in South Korea.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the South Korea Smart Water Management Market is Facing?
High Initial Investment and Budget Constraints
Smart water systems require heavy upfront investment in sensors, meters, network equipment, and software. Municipalities and utilities must allocate large budgets for upgrading aging infrastructure, which slows adoption in smaller cities. Installation costs, training expenses, and system integration further increase financial pressure. Although smart water solutions generate long-term savings, limited short-term funding often delays projects. This financial barrier reduces the speed of modernization, especially in regions with lower infrastructure investment capacity compared to major urban centers.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection Risks
Smart water networks rely on connected devices, remote monitoring, and cloud platforms, exposing systems to cyber threats. Hacking, data breaches, and system manipulation can disrupt water supply operations and compromise safety. Utilities hesitate to expand digital networks without guaranteed cybersecurity frameworks. Fear of data misuse also affects public trust. Securing thousands of devices and data channels requires specialized expertise, increasing operational complexity and cost. Inadequate protection mechanisms remain a critical challenge for large-scale implementation.
Skill Shortage and Technical Expertise Gaps
Operating smart water systems requires knowledge of IoT, analytics, cybersecurity, and automation. Many utilities lack trained staff to manage advanced digital platforms. Recruiting skilled professionals is costly and time-consuming. Without proper training, organizations underutilize system capabilities, reducing expected benefits. This skills gap slows adoption and affects system outcomes. Dependence on external vendors for system maintenance also raises long-term costs and operational risks for utility providers.
Competitive Landscape:
The South Korea smart water management market features a distinctive ecosystem where K-water, the state-owned water resources corporation, serves as both infrastructure operator and technology catalyst supporting domestic innovation. Differentiation is achieved through system reliability, scalability, real-time monitoring capabilities, and seamless integration with existing infrastructure. Strategic partnerships with municipalities, industrial clients, and utilities are critical to securing large-scale projects. Vendors also compete on energy efficiency solutions, predictive maintenance tools, and cybersecurity features to meet regulatory and operational requirements. Continuous innovation, product customization, and after-sales support are key competitive levers. Market players invest heavily in research and development (R&D) to improve automation, reduce operational costs, and enhance water quality monitoring. As public and private investments in smart water infrastructure are increasing, competition is intensifying, making technological superiority and local adaptation essential for market leadership.
Recent Developments:
- In January 2025, K-water took part in CES 2025 presenting three main advanced water management technologies, leading to more than 800 consultations on exports and investments estimated at around 51 Billion Won (USD 35 Million), culminating in five memoranda of understanding (MoU) signed with global partners.
South Korea Smart Water Management Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered |
|
| Applications Covered | Residential, Commercial and Industrial |
| Regions Covered | Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The South Korea smart water management market size was valued at USD 409.4 Million in 2025.
The South Korea smart water management market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 9.22% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 905.16 Million by 2034.
Devices dominate the market with 48% share, driven by nationwide deployment of advanced smart meters and IoT sensors enabling real-time water monitoring, automated leak detection, and pressure optimization across municipal and industrial networks.
Key factors driving the South Korea smart water management market include intensifying climate change impacts creating water scarcity challenges, substantial government investments, aging water infrastructure requiring modernization, and non-revenue water reduction imperatives targeting significant annual financial losses from water leakage.
Major challenges include high initial investment costs for smart infrastructure implementation, complexity of integrating new technologies with legacy water distribution systems, cybersecurity vulnerabilities in IoT-connected water networks, shortage of digitally skilled workforce, and data privacy concerns affecting citizen acceptance of smart water monitoring solutions.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












