
South Korea Space Launch Services Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Payload, Launch Platform, Service Type, Orbit, Launch Vehicle, End User, and Region, 2025-2033
South Korea Space Launch Services Market Overview:
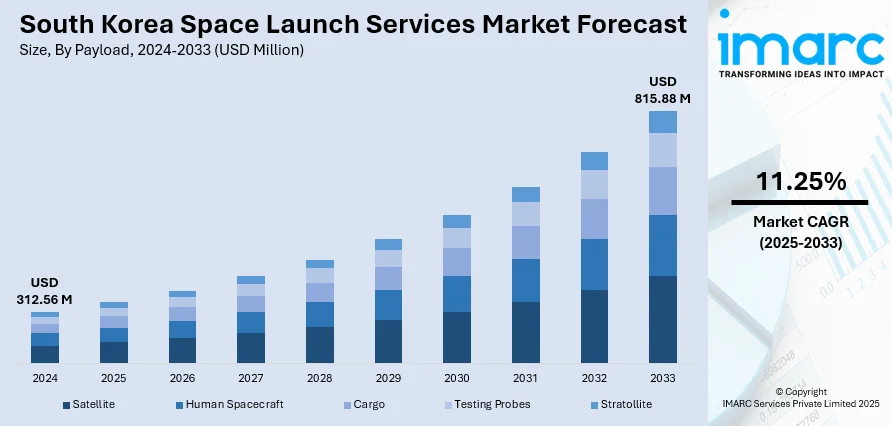
The South Korea space launch services market size reached USD 312.56 Million in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 815.88 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 11.25% during 2025-2033. The space launch market is driven by strong government investment aligned with national goals, emphasizing technological independence and global competitiveness. Rising commercial demand encourages private sector participation, boosted by regulatory support and incentives, fostering innovation, competition, and contributing to the expansion of the South Korea space launch services market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 312.56 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 815.88 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 11.25% |
South Korea Space Launch Services Market Trends:
Government Investment and Strategic National Goals
The market for space launch services in South Korea is heavily influenced by significant government funding and a focused effort to enhance national space capabilities. Acknowledging that space exploration and satellite launch are essential for national security, technological independence, and global competitiveness, the governing body is focusing on cultivating domestic launch vehicles, improving infrastructure, and building collaborations with prominent research institutions. These initiatives closely match South Korea’s enduring aim of decreasing reliance on international launch services and positioning itself as a significant competitor in the worldwide space sector. In 2024, South Korea reached a significant milestone by revealing an ambitious initiative to raise its governmental space budget to 1.5 trillion won (around $1.1 billion) by 2027. Under the guidance of Minister Lee Jong-ho and a newly established space agency, this initiative marked a significant effort to surpass former technological constraints and enhance South Korea's status among top spacefaring countries. Alongside this financial investment, there are policies that promote public-private collaborations, creating a favorable environment where innovation can thrive and the commercialization of space technologies can speed up. This unified strategy guarantees steady financing, efficient regulatory assistance, and intersectoral cooperation, all of which are crucial for maintaining and growing the nation’s launch services industry. The government’s robust support not only accelerates technological progress but also establishes a basis for South Korea’s long-term goals in space exploration and industry dominance.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Rising Commercial Demand and Private Sector Involvement
The increasing commercial need for satellite-based services like telecommunications, earth observation, and navigation is a major factor supporting the South Korea space launch services market growth. With the growing reliance of companies on satellite technology for information, connectivity, and operational strategy, the demand for dependable and affordable launch solutions is rising. This request is motivating private firms in South Korea to engage more actively in the development of launch vehicles, space platforms, and necessary infrastructure. In 2025, Samsung took a major step by revealing intentions to venture into the space sector, emphasizing the creation of space infrastructure and components, which includes partnering with Seoul National University to research rocket launch pads. This strategic shift underscores how large companies are acknowledging space infrastructure as a potential, largely overlooked market with fresh business prospects that go beyond conventional areas. Samsung’s involvement exemplifies the wider movement of diversification in the private sector. Regulatory changes and government incentives are reducing entry barriers, promoting a more dynamic private space industry. The increasing participation of private firms is fostering a more varied and robust space economy in South Korea, enhancing competition, speeding up innovation, and broadening the nation’s position as a supplier of space launch services on both regional and international levels. This active commercial involvement is crucial for maintaining long-term expansion in the space launch industry.
South Korea Space Launch Services Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on payload, launch platform, service type, orbit, launch vehicle, and end user.
Payload Insights:
- Satellite
- Small Satellite (Less Than 1000 Kg)
- Large Satellite (Above 1000 Kg)
- Human Spacecraft
- Cargo
- Testing Probes
- Stratollite
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the payload. This includes satellite (small satellite (less than 1000 kg) and large satellite (above 1000 kg)), human spacecraft, cargo, testing probes, and stratollite.
Launch Platform Insights:
- Land
- Air
- Sea
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the launch platform have also been provided in the report. This includes land, air, and sea.
Service Type Insights:
- Pre-Launch
- Post-Launch
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the service type. This includes pre-launch and post-launch.
Orbit Insights:
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO)
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
- Geosynchronous Orbit
- Polar Orbit
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the orbit have also been provided in the report. This includes low earth orbit (LEO), medium earth orbit (MEO), geosynchronous orbit, and polar orbit.
Launch Vehicle Insights:
- Small Launch Vehicle
- Heavy Launch Vehicle
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the launch vehicle. This includes small launch vehicle and heavy launch vehicle.
End User Insights:
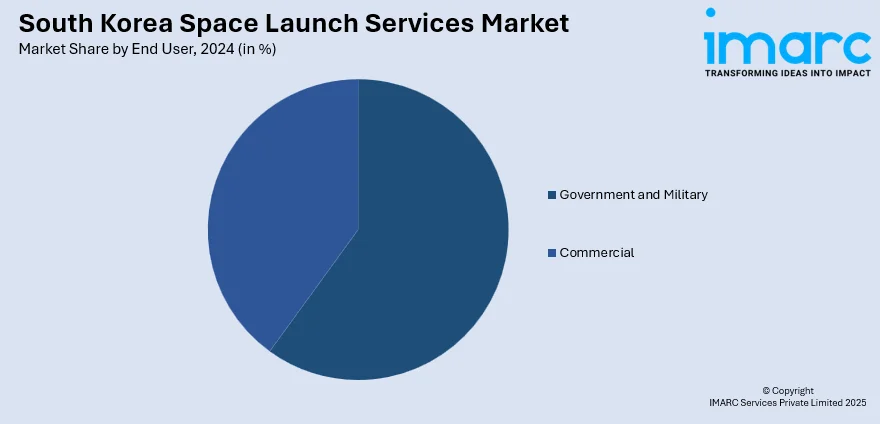
- Government and Military
- Commercial
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user have also been provided in the report. This includes government and military and commercial.
Regional Insights:
- Seoul Capital Area
- Yeongnam (Southeastern Region)
- Honam (Southwestern Region)
- Hoseo (Central Region)
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
South Korea Space Launch Services Market News:
- In May 2025, South Korea’s INNOSPACE and US-based Saturn Satellite Networks signed a strategic MOU to jointly develop next-generation LEO satellites and expand launch services. Their collaboration includes the Caelsat satellite and the Skycel 5G Non-Terrestrial Network project with 120 planned satellites. This partnership aims to offer cost-effective, integrated satellite and launch solutions.
- In February 2025, South Korea approved strategic space plans focusing on reusable launch vehicles, advanced satellites, and lunar exploration to become a top-five space power. The Korea Aerospace Administration aims to develop reusable KSLV-III rockets by 2035 and support private sector innovation.
South Korea Space Launch Services Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Payloads Covered |
|
| Launch Platforms Covered | Land, Air, Sea |
| Service Types Covered | Pre-Launch, Post-Launch |
| Orbits Covered | Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), Geosynchronous Orbit, Polar Orbit |
| Launch Vehicles Covered | Small Launch Vehicle, Heavy Launch Vehicle |
| End Users Covered | Government and Military, Commercial |
| Regions Covered | Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the South Korea space launch services market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea space launch services market on the basis of payload?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea space launch services market on the basis of launch platform?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea space launch services market on the basis of service type?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea space launch services market on the basis of orbit?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea space launch services market on the basis of launch vehicle?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea space launch services market on the basis of end user?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea space launch services market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the South Korea space launch services market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the South Korea space launch services market?
- What is the structure of the South Korea space launch services market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the South Korea space launch services market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the South Korea space launch services market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the South Korea space launch services market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the South Korea space launch services industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












