
South Korea Telehealth Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Communication Technology, Hosting Type, Application, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
South Korea Telehealth Market Summary:
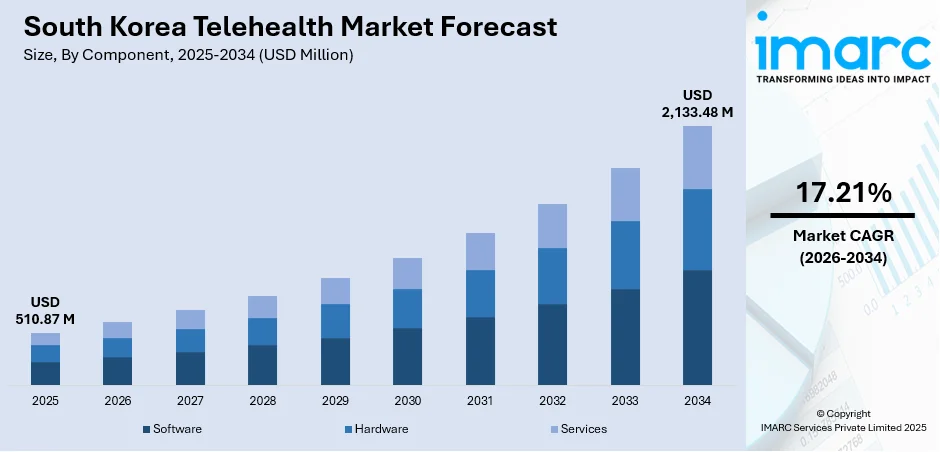
The South Korea telehealth market size was valued at USD 510.87 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 2,133.48 Million by 2034, expanding at a compound annual growth rate of 17.21% from 2026-2034.
The market is propelled by the nation's rapidly aging population and escalating chronic disease burden, which necessitate innovative healthcare delivery solutions that transcend traditional clinical boundaries. South Korea's world-class information and communication technology infrastructure, featuring extensive 5G coverage and near-universal smartphone adoption, creates a robust foundation for telehealth expansion. Government initiatives supporting digital healthcare transformation are accelerating the market penetration.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Component: Software dominates the market with a share of 58% in 2025, driven by the proliferation of artificial intelligence (AI)-powered diagnostic solutions, electronic medical record (EMR) management platforms, and digital therapeutic applications that enable remote patient monitoring and clinical decision support.
- By Communication Technology: mHealth solutions lead the market with a share of 45% in 2025, owing to South Korea's exceptionally high smartphone penetration and advanced 5G network deployment that supports seamless mobile health application functionality.
- By Hosting Type: Cloud-based and web-based represent the largest segment with a market share of 70% in 2025, attributed to government-mandated EMR digitization initiatives, data storage regulations supporting cloud adoption, and the operational efficiency benefits of scalable infrastructure.
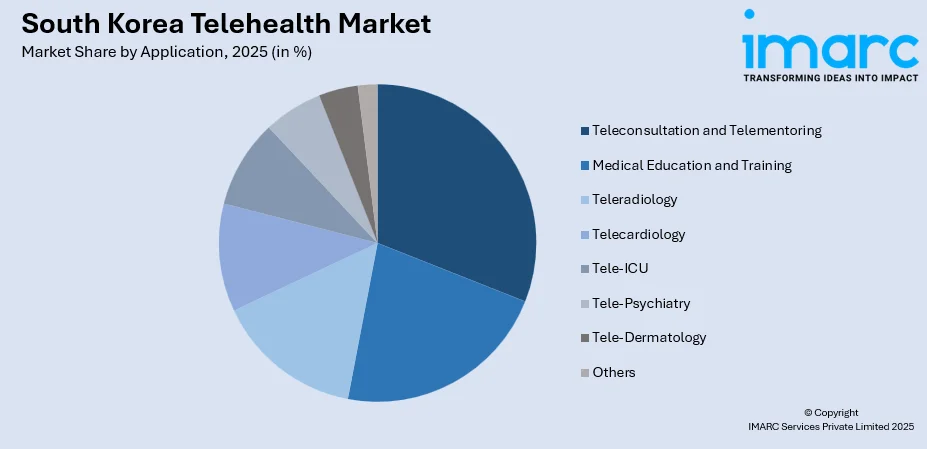
- By Application: Teleconsultation and telementoring prevail the market with a share of 25% in 2025, driven by expanded pilot programs enabling remote physician-patient consultations and the growing demand for specialist access in underserved regions.
- By End User: Providers hold the largest market share of 55% in 2025, reflecting substantial investments by tertiary hospitals and healthcare institutions in telehealth platforms to enhance service delivery capabilities and operational efficiency.
- Key Players: The South Korea telehealth market demonstrates a moderately consolidated competitive structure, with domestic technology innovators and healthcare institutions collaborating alongside global digital health solution providers to develop integrated platforms addressing the nation's unique regulatory and healthcare delivery requirements.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
South Korea's telehealth ecosystem benefits from the convergence of world-leading digital infrastructure and pressing healthcare demands. The telehealth market is driven by an aging population, a tech-savvy smartphone-first culture, and high chronic-disease prevalence. The Ministry of Health and Welfare unveiled an extensive five-year strategy to drive research and development (R&D) in AI for healthcare, extending to 2028, highlighting the nation's wider goal to utilize advanced technology to improve public health. Hospitals and clinics are exploring digital platforms to improve patient access and reduce overcrowding. Wearable devices and mobile health applications are also contributing by enabling real-time health monitoring and virtual follow-ups. While regulatory frameworks may continue to evolve, the growing acceptance of technology-based healthcare is encouraging investments in telemedicine platforms.
South Korea Telehealth Market Trends:
Integration of AI in Diagnostic and Treatment Solutions
South Korea is witnessing accelerated integration of AI across telehealth platforms, transforming diagnostic accuracy and treatment personalization. VUNO, the prominent South Korean medical AI company, reported profit in Q3 2025, with cumulative revenue for the first three quarters reaching KRW 27.6 Billion, exceeding the full-year 2024 total and achieving the company's annual growth target ahead of schedule. Domestic AI healthcare firms are developing sophisticated algorithms for medical image analysis, predictive analytics, and clinical decision support, enhancing telehealth service quality and diagnostic capabilities.
Expansion of 5G-Enabled Smart Hospital Infrastructure
Healthcare institutions across South Korea are deploying 5G-powered smart hospital systems that enable advanced telehealth functionalities, including real-time remote consultations and continuous patient monitoring. At a demonstration kickoff ceremony in July 2025, the field deployment of Korea's first mobile smart hospital was officially initiated, featuring seven connected trailers equipped with diagnostic devices equivalent to secondary hospitals and 5G-based AI diagnosis systems. These infrastructure investments support immersive telemedicine experiences and enable emergency medical response capabilities.
Growth of Digital Therapeutics and Regulatory Evolution
The digital therapeutics segment is experiencing significant growth, as regulatory pathways are maturing and reimbursement frameworks are evolving. The Digital Medical Products Act, enacted on January 23, 2024, came into effect on January 24, 2025, establishing comprehensive regulatory frameworks for digital medical devices and convergence products. This regulatory clarity is encouraging investments in software-based therapeutic interventions.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The South Korea telehealth market is positioned for substantial revenue expansion, as demographic pressures are intensifying and digital healthcare adoption is accelerating. The market generated a revenue of USD 510.87 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 2,133.48 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 17.21% from 2026-2034. The market is driven by government investments in healthcare AI research, expanding telemedicine pilot programs, and increasing consumer acceptance of remote care services. The transition towards permanent telehealth legalization and insurance reimbursement frameworks will catalyze mainstream adoption, while continued technology innovations in AI diagnostics, remote monitoring, and digital therapeutics will enhance service capabilities and market penetration across all segments.
South Korea Telehealth Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Component | Software | 58% |
| Communication Technology | mHealth Solutions | 45% |
| Hosting Type | Cloud-Based and Web-Based | 70% |
| Application | Teleconsultation and Telementoring | 25% |
| End User | Providers | 55% |
Component Insights:
- Software
- Hardware
- Services
Software dominates with a market share of 58% of the total South Korea telehealth market in 2025.
Software holds prominence due to the rapid proliferation of AI-powered diagnostic platforms, electronic health record (EHR) systems, and patient management solutions. South Korean technology companies have developed sophisticated medical software, incorporating machine learning (ML) algorithms for image analysis, clinical decision support, and predictive health monitoring.
The government's push for healthcare digitization and the high EMR adoption rate across medical institutions further accelerate software deployment. Compared to hardware, software is easier to scale, customize, and update, allowing hospitals to adopt new features without major infrastructure changes. Subscription-based models also make software financially attractive for providers, encouraging faster adoption. In addition, software enables interoperability between different healthcare systems, improving data sharing and continuity of care. As telehealth is expanding beyond simple video calls into full digital care ecosystems, software remains the most dynamic and value-generating component of the South Korea telehealth market.
Communication Technology Insights:
- Video Conferencing
- mHealth Solutions
- Others
mHealth solutions lead with a share of 45% of the total South Korea telehealth market in 2025.
The mHealth solutions dominate the market segment, benefiting from South Korea's exceptional mobile technology ecosystem and consumer digital literacy. As per industry reports, in 2024, smartphone reliance in South Korea hit 75.3%. Smartphone-based healthcare access fits naturally into the country’s highly connected digital lifestyle.
Patients prefer mobile apps for booking appointments, consulting doctors, accessing prescriptions, and tracking health data, making mHealth the most convenient telehealth channel. High smartphone usage allows healthcare providers to reach patients instantly through notifications, reminders, and health alerts. Wearable device integration further strengthens mHealth adoption by enabling real-time health tracking and data sharing with doctors. Compared to web-based platforms, mobile solutions offer greater flexibility and on-the-go healthcare access. mHealth also supports chronic disease management by allowing continuous monitoring and follow-up without frequent hospital visits. Its user-friendly design increases patient engagement and treatment adherence.
Hosting Type Insights:
- Cloud-Based and Web-Based
- On-Premises
Cloud-based and web-based exhibit a clear dominance with a 70% share of the total South Korea telehealth market in 2025.
Cloud-based and web-based hosting leads the market because it allows healthcare providers to access patient data anytime, from any location. These platforms support quick deployment, low infrastructure investment, and real-time updates. Hospitals prefer flexible systems that scale easily with rising patient volumes.
Cloud and web platforms also enable seamless data sharing between doctors, labs, and patients, improving treatment continuity and clinical decision-making. Automatic data backups and disaster recovery features increase reliability and reduce the risk of service disruption. Healthcare organizations benefit from subscription-based pricing, making advanced telehealth technology more affordable. Web-based systems are easier to integrate with existing hospital software, reducing operational complexity. As hospitals are expanding virtual services and mobile healthcare access, cloud infrastructure is becoming essential for managing large data volumes and high user demand efficiently. In November 2024, Newbase, a pioneer in medical education platforms within the metaverse, unveiled 'Medicrew,' a platform aimed at delivering personalized virtual reality (VR) education aligned with the clinical skills of healthcare workers. The platform was extensively utilized by prominent nursing colleges and elite hospitals in South Korea, including the Seoul Asan Medical Center. A customizable VR platform incorporated AI-driven virtual patients along with a three-stage learning approach to improve clinical skills, lower nurse turnover, and broaden global training options beginning in 2025.
Application Insights:
Access the Comprehensive Market Breakdown Request Sample
- Teleconsultation and Telementoring
- Medical Education and Training
- Teleradiology
- Telecardiology
- Tele-ICU
- Tele-Psychiatry
- Tele-Dermatology
- Others
Teleconsultation and telementoring represent the leading segment with a 25% share of the total South Korea telehealth market in 2025.
Teleconsultation and telementoring applications dominate the market, enabling remote patient-physician interactions and specialist consultations. Starting February 23, 2024, telemedicine was made accessible in all healthcare facilities in South Korea, including hospitals, due to regulatory modifications that broadened access beyond just clinic-level sites.
Patients avoid travel and waiting time, while doctors extend services beyond hospital walls. Real-time advice and specialist access make virtual care highly practical and widely accepted. Telementoring supports skill development by allowing experienced specialists to guide junior doctors remotely, improving treatment quality in smaller facilities. This reduces dependence on physical presence and expands access to specialist knowledge. Teleconsultation also improves hospital capacity by filtering non-emergency cases through virtual visits. For patients, digital consultations reduce healthcare costs and stress. For hospitals, they increase service reach without major infrastructure expansions.
End User Insights:
- Providers
- Patients
- Payers
- Others
Providers hold the largest segment with a 55% share of the total South Korea telehealth market in 2025.
Providers lead the market because hospitals and clinics are the primary users and promoters of digital healthcare services. They control service delivery, system adoption, and patient access. Most telehealth interactions originate within healthcare institutions, giving providers greater influence over platform selection and usage patterns.
Healthcare providers are investing heavily in telehealth systems to improve efficiency, reduce workload, and expand patient reach. Large hospitals adopt digital platforms to manage high patient volumes and offer virtual consultations as a standard service. Providers also integrate telehealth into diagnosis, follow-ups, and chronic disease care, making them central to market activity. Training programs and digital readiness among medical staff encourage further adoption. Since providers handle compliance, data management, and clinical responsibility, technology companies rely on hospitals as the main customer base. This makes providers the dominant decision-makers and revenue contributors in South Korea’s telehealth ecosystem.
Regional Insights:
- Seoul Capital Area
- Yeongnam (Southeastern Region)
- Honam (Southwestern Region)
- Hoseo (Central Region)
- Others
The Seoul Capital Area holds prominence due to advanced digital infrastructure, high healthcare density, and tech-savvy population. Hospitals, startups, and digital health platforms drive innovations, while busy urban lifestyles increase demand for quick, remote medical consultations.
Yeongnam (Southeastern Region) shows strong telehealth demand, supported by industrial workforce and major cities. Remote monitoring and occupational healthcare services are preferred. The growing smart hospital investments improve service quality and encourage corporate health partnerships.
In Honam (Southwestern Region), the telehealth market growth is driven by rural healthcare access needs and underserved communities. Teleconsultations reduce travel burdens for patients. Public healthcare outreach programs and digital expansion support wider adoption of virtual healthcare services.
Hoseo (Central Region) benefits from technological research centers and manufacturing hubs. Universities and innovation zones encourage healthcare digitization. Hospitals adopt telehealth for patient management and diagnostics, improving regional healthcare access and efficiency.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the South Korea Telehealth Market Growing?
Rapidly Aging Population Creating Sustained Healthcare Demand
South Korea's demographic transformation represents a fundamental driver of the telehealth market expansion, as the nation is transitioning to a super-aged society requiring innovative healthcare delivery solutions. As per the data released by the Ministry of the Interior and Safety in December 2024, the population of individuals aged 65 and above in South Korea was 10.24 Million, representing 20% of the total population of 51 Million. The country turned into a ‘super-aged’ society where one in five individuals was aged 65 years or older. The elderly population requires more frequent healthcare interactions and chronic disease management, creating substantial demand for remote monitoring, teleconsultation, and home-based care solutions that reduce the burden of physical hospital visits while maintaining care continuity.
Escalating Chronic Disease Burden
The rising incidence of chronic conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases, is driving adoption of telehealth solutions that enable continuous monitoring and management outside traditional clinical settings. As per the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, in 2023, the occurrence of hypertension and diabetes in Koreans aged 70 and older was 68.4% and 27.1% respectively. Remote consultations help patients manage their conditions from home, improving comfort and treatment compliance. Telehealth platforms also enable timely intervention through digital monitoring tools, reducing emergency visits and hospital congestion. For healthcare providers, remote care improves efficiency by allowing the management of larger patient groups. Chronic disease patients benefit from personalized care plans delivered digitally. As chronic conditions are becoming more common, telehealth serves as a practical solution for delivering consistent, cost-effective, and accessible long-term healthcare across South Korea.
World-Class Digital Infrastructure Enabling Advanced Telehealth Services
World-class digital infrastructure plays a vital role in driving the growth of the market in South Korea by enabling smooth, fast, and reliable digital communication between patients and healthcare providers. High-speed internet networks support uninterrupted video consultations, remote diagnostics, and digital prescriptions. Hospitals efficiently manage EMRs, improving coordination and reducing administrative burden. Patients benefit from faster access to healthcare services through mobile apps and online platforms. 5G deployment enables real-time data transfer, ultra-low latency, and advanced remote monitoring through connected medical devices. As per IMARC Group, the South Korea 5G infrastructure market size reached USD 281.39 Million in 2024. Strong digital systems also support AI-based diagnostics, cloud data storage, and secure information sharing. As technology trust increases, both providers and patients become more comfortable using telemedicine. This infrastructure foundation makes telehealth a dependable, scalable, and efficient healthcare solution across South Korea.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the South Korea Telehealth Market is Facing?
Regulatory Uncertainty and Absence of Permanent Legal Framework
Regulatory uncertainty slows the growth of the telehealth market in South Korea by creating hesitation among healthcare providers and investors. Without clear long-term legal guidelines, hospitals remain cautious about expanding digital services. Frequent policy changes increase compliance risks and planning difficulties. Providers fear penalties or service disruptions, which limit innovation and large-scale deployment. As a result, telehealth adoption remains controlled rather than fully commercialized.
Healthcare Professional Resistance and Stakeholder Opposition
Some healthcare professionals resist telehealth due to concerns about clinical accuracy, patient safety, and reduced doctor–patient interaction. Traditional practitioners often prefer in-person diagnosis and treatment, slowing acceptance of digital care. Medical associations may oppose telemedicine to protect traditional practice models. This resistance reduces trust in virtual consultations and delays hospital-level investments in telehealth platforms.
Data Privacy Concerns and Liability Ambiguity
Concerns around data security and unclear liability discourage telehealth implementation. Patients worry about misuse of sensitive medical data, while providers fear legal issues from data breaches or misdiagnosis through digital platforms. Without defined responsibility structures, service providers adopt telehealth cautiously. Uncertainty over accountability for clinical errors in virtual care limits risk-taking and slows overall market development.
Competitive Landscape:
The South Korea telehealth market exhibits a dynamic competitive environment, characterized by collaboration between domestic technology innovators, established healthcare institutions, and global digital health solution providers. Market participants range from specialized AI healthcare startups developing diagnostic algorithms to major telecommunications companies building smart hospital infrastructure. Healthcare institutions, including tertiary hospitals and university medical centers, serve as both end users and innovation partners, developing proprietary telehealth platforms while integrating third-party solutions. The competitive landscape is shaped by regulatory developments, with participants navigating evolving telemedicine frameworks while positioning for anticipated market liberalization. Strategic partnerships between technology companies and healthcare providers facilitate clinical validation, market access, and integrated solution development.
Recent Developments:
- In June 2025, the Vietnam Ministry of Health, together with the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Korea Foundation for International Healthcare (KOFIH), conducted the Viet Nam – South Korea Telehealth Workshop. The event gathered almost 100 representatives from central agencies, health departments in 10 project provinces, international organizations, and prominent telehealth experts from South Korea and Vietnam.
South Korea Telehealth Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Software, Hardware, Others |
| Communication Technologies Covered | Video Conferencing, mHealth Solutions, Others |
| Hosting Types Covered | Cloud-Based and Web-Based, On-Premises |
| Applications Covered | Teleconsultation and Telementoring, Medical Education and Training, Teleradiology, Telecardiology, Tele-ICU, Tele-Psychiatry, Tele-Dermatology, Others |
| End Users Covered | Providers, Patients, Payers, Others |
| Regions Covered | Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The South Korea telehealth market size was valued at USD 510.87 Million in 2025.
The South Korea telehealth market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 17.21% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 2,133.48 Million by 2034.
Software dominated the component segment with 58% market share, driven by the widespread adoption of AI-powered diagnostic platforms, EHR systems, and digital therapeutic applications across healthcare institutions
Key factors driving the South Korea telehealth market include the rapidly aging population, escalating chronic disease burden requiring remote management solutions, world-class 5G and digital infrastructure enabling advanced services, and government initiatives supporting healthcare digitization and AI integration
Major challenges include regulatory uncertainty due to the absence of permanent telemedicine legislation, healthcare professional resistance and stakeholder opposition to service expansion, data privacy concerns and liability ambiguity in remote care contexts, reimbursement framework limitations, and the need for standardized technology platforms across diverse healthcare settings.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












