
South Korea Waste to Energy Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Technology, Waste Type, and Region, 2025-2033
South Korea Waste to Energy Market Overview:
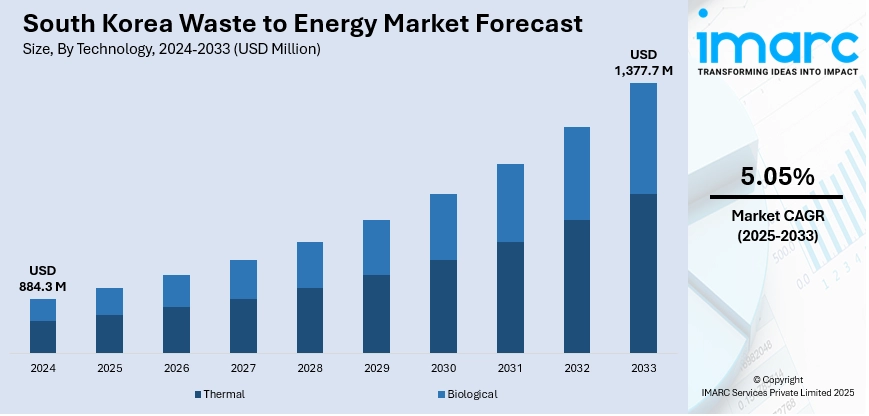
The South Korea waste to energy market size reached USD 884.3 Million in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 1,377.7 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 5.05% during 2025-2033. At present, the strong regulatory environment and government policies towards encouraging sustainable waste management practices. Moreover, Innovations in urban developments and industrial operations in South Korea are resulting in high production of municipal solid waste (MSW). This, along with the technological advancements and infrastructure investments, is expanding the South Korea waste to energy market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 884.3 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 1,377.7 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 5.05% |
South Korea Waste to Energy Market Trends:
Government Policies and Regulatory Support
One of the key drivers of the South Korean waste to energy (WTE) market is the strong regulatory environment and government policies towards encouraging sustainable waste management practices. In 2025, the Seoul Metropolitan Government (SMG) announced plans to transform the city by promoting a circular economy that creates resources from all waste, including waste vinyl, sewing fabrics, and banners. Seoul also aims to cut daily plastic production from the present 2,753 tons to 2,478 tons (a decrease of 10%, or 275 tons) by 2026 and boost the recycling rate from 69% to 79%. These policies aim to minimize the country's dependency on landfills and incineration without energy recovery, thus promoting the use of advanced WTE technologies. In addition, subsidies, tax breaks, and public-private partnerships have been implemented to attract investment in energy recovery facilities. The Green New Deal policy, which formulates a shift towards a low-carbon green economy, also places special emphasis on the growth of renewable energy sources like WTE. These are aligned with the government's strategic vision to become carbon neutral by 2050, creating a favorable climate through support mechanisms in financial and regulatory frameworks.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Urban Developments and Rising Generation of Municipal Solid Waste
Innovations in urban developments and industrial operations in South Korea are resulting in high production of municipal solid waste (MSW), posing both an environmental problem and a potential source of energy recovery. A major part of the country's population lives in urban cities, like the population in Seoul is 10,349,312, and in Busan is 3,678,555, in 2025, according to World Population Review. As a result, the amount and diversity of waste products have increased enormously, causing pressure on conventional waste management. Land shortages compound the issue, rendering landfill enlargement an unsustainable option. Therefore, WTE technologies present a clean way of handling increasing amounts of waste while also producing electricity and heat. South Korea's waste management systems focus on recycling and recovering resources, and WTE plants are a critical element in treating non-recyclable leftovers. The growing energy needs in densely populated urban areas also contribute to the appeal of WTE solutions, which increase energy security at the local level.
Technological Advancements and Infrastructure Development
Rapid technological advancements, along with infrastructure investments, are contributing to the South Korea waste to energy market growth. South Korea has exhibited robust abilities in innovating and adopting thermal and biological WTE processes, such as incineration with energy recovery, anaerobic digestion, and gasification. South Korea's advanced manufacturing industry and research establishments facilitate the upgrading of WTE systems continuously, resulting in increased efficiency, reduced emissions, and higher energy yields. Moreover, the introduction of smart monitoring and control systems has enhanced operating reliability and environmental regulatory compliance. Large-scale urban projects, like district heating systems that are fueled by WTE plants, also illustrate how the nation maximizes energy utilization from waste resources. The feasibility of incorporating WTE plants into already developed urban infrastructure, particularly in larger cities like Seoul and Busan, also underpins market development. For instance, in 2024, PureCycle Technologies, a US-based advanced recycling firm transforming plastic waste, agreed to establish Asia's inaugural recycled polypropylene (PP) plant in Ulsan, South Korea, following a non-binding head of agreement (HOA) with SK Geo Centric (SKGC). The plant boasted an annual capacity of 60,000 tons and was completed by late 2024.
South Korea Waste to Energy Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on technology and waste type.
Technology Insights:
- Thermal
- Biological
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology. This includes thermal and biological.
Waste Type Insights:
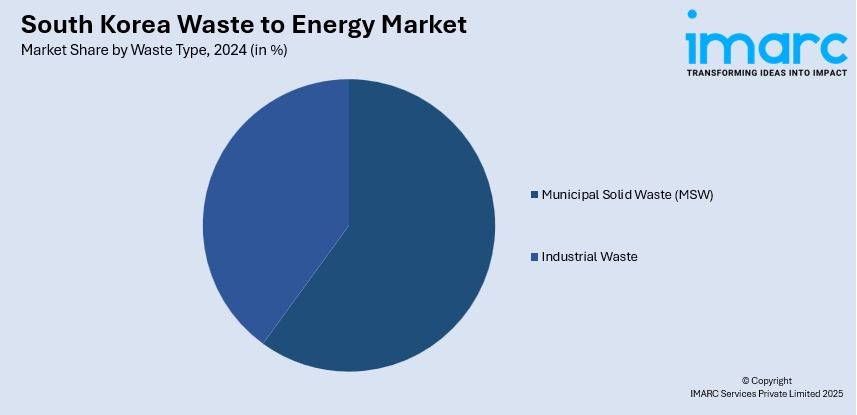
- Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
- Industrial Waste
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the waste type have also been provided in the report. This includes municipal solid waste (MSW) and industrial waste.
Regional Insights:
- Seoul Capital Area
- Yeongnam (Southeastern Region)
- Honam (Southwestern Region)
- Hoseo (Central Region)
- Others
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), and others.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
South Korea Waste to Energy Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Technologies Covered | Thermal, Biochemical |
| Waste Types Covered | Municipal Municipal Solid Waste (MSW), Industrial Waste |
| Regions Covered | Seoul Capital Area, Yeongnam (Southeastern Region), Honam (Southwestern Region), Hoseo (Central Region), Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the South Korea waste to energy market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea waste to energy market on the basis of technology?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea waste to energy market on the basis of waste type?
- What is the breakup of the South Korea waste to energy market on the basis of region?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the South Korea waste to energy market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the South Korea waste to energy market?
- What is the structure of the South Korea waste to energy market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the South Korea waste to energy market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the South Korea waste to energy market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the South Korea waste to energy market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the South Korea waste to energy industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












