
Turkey Electric Vehicle Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Charging Type, Propulsion Type, Vehicle Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Turkey Electric Vehicle Market Summary:
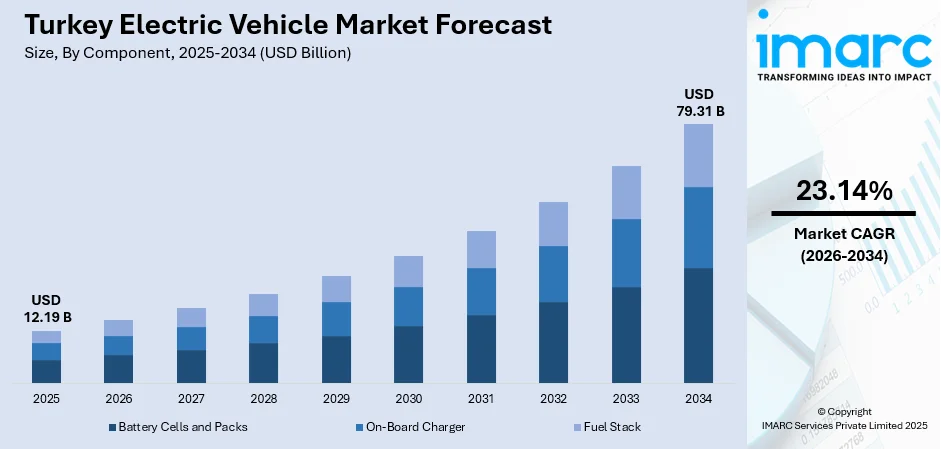
The Turkey electric vehicle market size was valued at USD 12.19 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 79.31 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 23.14% from 2026-2034.
The market growth is driven by aggressive government tax incentives favoring locally produced vehicles and strategic foreign manufacturing investments positioning Turkey as a European export hub. Moreover, the accelerated charging infrastructure deployment across urban centers is collectively transforming the nation into one of the most dynamic electrification markets. Apart from this, the rise in eco-consciousness among the masses is expanding the Turkey electric vehicle market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Propulsion Type: Battery electric vehicle (BEV) represents the largest segment with a market share of 48.01% in 2025, supported by expanding fast-charging networks and competitive pricing structures that outpace plug-in hybrid adoption despite infrastructure constraints.
-
By Vehicle Type: Passenger vehicles dominate the market with a share of 55.03% in 2025, driven by consumer preference for efficient models offering practical urban mobility solutions alongside government incentives targeting personal transportation electrification.
-
By Region: Marmara leads the market with a share of 26% in 2025, capitalizing on Istanbul's concentration of charging infrastructure, higher disposable incomes, and proximity to manufacturing hubs that facilitate rapid model availability.
-
Key Players: Key market players in Turkey's electric vehicle sector are enhancing local production, expanding charging infrastructure, launching new models, and forming strategic partnerships for technology and battery innovation. They are also adjusting pricing to attract customers and exploring export opportunities.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Turkey electric vehicle (EV) market has experienced transformational growth from a negligible base to becoming Europe's fourth-largest battery electric vehicle market within three years. This remarkable acceleration stems from the convergence of the government implementation of preferential special consumption tax rates that create substantial cost advantages for electric vehicles over conventional alternatives, the emergence of Togg as Turkey's first domestic electric vehicle manufacturer, and strategic geographic positioning within Europe's customs union enabling tariff-free exports. The market's evolution reflects broader national ambitions to establish Turkey as a regional manufacturing hub while reducing fossil fuel dependency. For instance, in 2024, Chinese electric vehicle manufacturer BYD signed a landmark agreement to invest one billion dollars in a Turkish manufacturing facility with an annual production capacity of one hundred fifty thousand vehicles, underscoring international recognition of Turkey's strategic importance in the global electric mobility transition.
Turkey Electric Vehicle Market Trends:
Domestic Manufacturing Emergence Reshaping Competitive Dynamics
Turkey's EV landscape has undergone fundamental transformation through the introduction of indigenous manufacturing capabilities, fundamentally altering market structure and consumer perceptions. The establishment of locally-produced vehicles has created new competitive parameters beyond traditional price and feature comparisons, introducing considerations of national identity and economic contribution into purchasing decisions. Based on information from the Association of Automobile Distributors (ODMD), during the initial eleven months of 2025, the nation reported 166,665 transactions of fully electric vehicles, surpassing twice the amount for the equivalent timeframe in 2024. This shift manifests most visibly through government policies explicitly designed to support domestic production, including tax advantages and preferential procurement programs that create distinct market advantages for locally-manufactured vehicles. The domestic manufacturing trend extends beyond passenger vehicles into component production, with battery manufacturing facilities and supplier networks emerging to support the broader ecosystem.
Tax Policy Innovation Driving Rapid Market Expansion
Turkey's EV market growth has been fundamentally shaped by innovative special consumption tax structures that create unprecedented cost differentials between electric and conventional vehicles. The government's implementation of dramatically reduced tax rates for battery electric vehicles compared to internal combustion alternatives has effectively rewritten the economic calculus for vehicle purchases, making electric options financially compelling across multiple price segments. EVs receive significant tax cuts like 10% for models under 160 kW and a base price below 1.65 million Turkish lira (approximately €47,000), and as much as 60% for those exceeding these limits. Even in the least favorable scenario, an electric vehicle remains more appealing from a tax perspective than its internal combustion counterpart. This tax architecture extends beyond simple rate differentiation to include power output thresholds and price brackets that influence both consumer choices and manufacturer product strategies. The policy's effectiveness is evidenced by observable buyer behavior patterns, particularly surge purchasing patterns before announced policy adjustments.
Infrastructure Network Expansion Enabling Market Maturation
Turkey has witnessed unprecedented charging infrastructure deployment that transforms fundamental market dynamics by addressing the primary barrier to electric vehicle adoption. In June 2025, Turkey reported 31,433 public charging stations, as per the Energy Market Regulatory Authority (EPDK), up from only 6,500 in March 2023. The charging network's expansion demonstrates coordinated efforts across public and private sectors, with government licensing frameworks compelling operators to establish minimum geographic coverage requirements while private investment pursues profitable urban corridors. Infrastructure development exhibits distinct characteristics including concentration in major metropolitan areas with gradually expanding coverage into secondary markets, emergence of multiple competing charging networks with varying access models and pricing structures, and integration of fast-charging capabilities that reduce charging times to levels approaching conventional refueling experiences. The infrastructure buildout strategy reflects both market realities and policy priorities, balancing immediate urban demand with longer-term national coverage objectives. This infrastructure foundation creates enabling conditions for sustained market growth while simultaneously revealing ongoing challenges in achieving comprehensive geographic coverage that would fully eliminate range anxiety concerns across all use cases.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Turkey electric vehicle market is positioned for sustained robust expansion through the forecast period, driven by maturing infrastructure networks, increasing model availability across price segments, and continued government commitment to electrification objectives despite potential policy adjustments. The market generated a revenue of USD 12.19 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 79.31 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 23.14% from 2026-2034. Market development will be characterized by increasing competition as domestic production scales alongside foreign manufacturer investments, gradual infrastructure extension into underserved regions addressing current geographic limitations, and evolving consumer acceptance as EVs transition from early adopter novelty to mainstream transportation option.
Turkey Electric Vehicle Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Propulsion Type |
Battery Electric Vehicle |
48.01% |
|
Vehicle Type |
Passenger Vehicles |
55.03% |
|
Region |
Marmara |
26% |
Component Insights:
- Battery Cells and Packs
- On-Board Charger
- Fuel Stack
Battery cells and packs represent the highest-value component in electric vehicles, commanding substantial cost share while determining range capabilities and performance characteristics. Turkey's market features growing domestic battery production through Siro's Gemlik facility supporting Togg vehicles, alongside imported cells from established Asian suppliers. Component localization strategies increasingly prioritize battery manufacturing to reduce import dependency, capture value addition, and support domestic electric vehicle production competitiveness.
On-board chargers facilitate alternating current conversion enabling home and workplace charging accessibility that proves essential for consumer adoption. Turkish market dynamics favor vehicles equipped with higher-capacity on-board chargers supporting faster Level 2 charging, addressing consumer convenience preferences and infrastructure compatibility requirements. Component specifications increasingly influence purchase decisions as charging speed consciousness grows among informed buyers evaluating practical ownership experiences.
Fuel stack components remain nascent in Turkey's electric vehicle market given overwhelming battery electric vehicle dominance and minimal hydrogen infrastructure development. Technology adoption faces substantial barriers including absent refueling network, hydrogen production cost economics, and policy frameworks exclusively favoring battery electric solutions. Commercial vehicle applications represent potential future fuel cell opportunities if hydrogen infrastructure development accelerates supporting long-haul transportation requiring extended range capabilities.
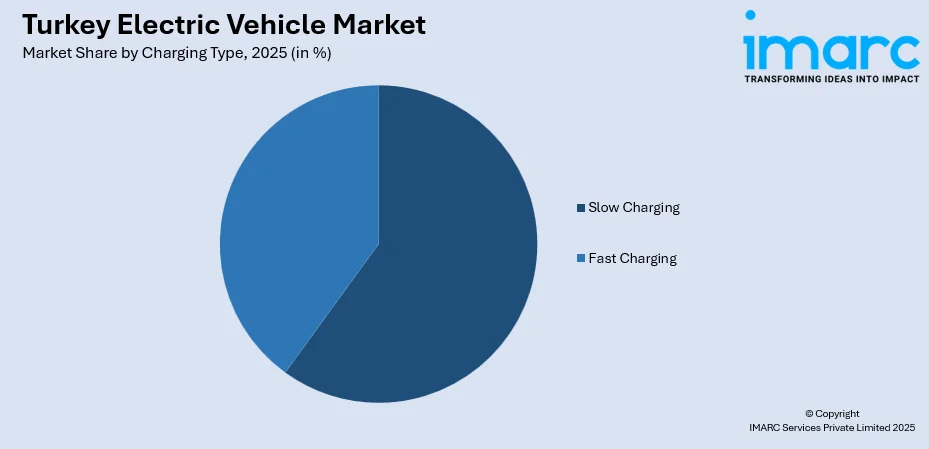
Charging Type Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Slow Charging
- Fast Charging
Slow charging infrastructure dominates Turkey's network deployment through residential installations and workplace charging facilities that accommodate overnight charging patterns aligned with typical vehicle usage. Home charging solutions prove particularly attractive for Turkish consumers offering maximum convenience and lowest electricity costs through off-peak residential tariffs. Slow charging's market position benefits from lower installation costs enabling widespread deployment across residential complexes and commercial properties supporting daily charging needs.
Fast charging infrastructure has expanded rapidly across urban corridors and intercity routes addressing range anxiety concerns and enabling long-distance travel confidence. Turkish market demonstrates growing fast charging adoption driven by declining charging times approaching conventional refueling experiences, strategic highway corridor deployment connecting major metropolitan centers, and competitive pricing structures making public fast charging economically viable. Technology evolution toward ultra-fast charging capabilities exceeding one hundred kilowatts promises further adoption acceleration.
Propulsion Type Insights:
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
- Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
Battery electric vehicle (BEV) exhibits a clear dominance with a 48.01% share of the total Turkey electric vehicle market in 2025.
Battery electric vehicles have established clear market leadership within Turkey's electrified powertrain landscape through their maximization of both tax advantages and operating cost benefits that create compelling total ownership propositions. Pure electric powertrains receive the most favorable treatment under Turkey's special consumption tax structure, creating substantial purchase price advantages over plug-in hybrid alternatives that retain conventional engines and associated tax burdens. This tax differential proves particularly impactful in the mid-range price segment where consumption patterns concentrate, effectively steering mainstream consumers toward battery electric rather than hybrid solutions.
Beyond taxation considerations, battery electric vehicles offer operational advantages including lower maintenance requirements due to simpler mechanical configurations with fewer components subject to wear, reduced fueling costs that become increasingly attractive as gasoline prices rise relative to electricity rates, and superior urban performance characteristics through instant torque delivery and regenerative braking benefits in stop-and-go traffic. The segment's growth has been enabled by simultaneous charging infrastructure expansion that addresses range anxiety concerns, with network buildout focused initially on urban corridors where battery electric vehicles concentrate.
Vehicle Type Insights:
- Passenger Vehicles
- Commercial Vehicles
- Others
Passenger vehicles lead with a share of 55.03% of the total Turkey electric vehicle market in 2025.
Passenger vehicles dominate Turkey's EV market through their alignment with government incentive structures primarily targeting individual ownership and urban transportation patterns. The segment's leadership reflects several converging factors including the availability of diverse models spanning utility vehicles to sedans that address varied preferences, competitive total cost of ownership calculations that favor electric powertrains over conventional alternatives particularly in urban driving conditions characterized by frequent acceleration cycles, and social signaling dynamics where vehicle ownership represents status and technological progressiveness. In 2025, Hyundai Motor Türkiye has made a notable advancement in enhancing its production capability and sustainability initiatives by planning to produce EVs in Türkey. This action strengthens the company's dedication to minimizing its carbon footprint while bolstering the local economy and aiding the worldwide shift towards green mobility
The domestic manufacturer Togg's strategic focus on passenger vehicles through its SUV and sedan offerings has accelerated segment growth by providing locally-produced alternatives that benefit from preferential taxation while resonating with national pride sentiments. Market research indicates that passenger vehicle purchasers prioritize practical considerations including charging convenience, operating cost savings, and technology features over performance characteristics, creating product development parameters distinct from international markets. The passenger vehicle segment's continued dominance appears sustainable through the forecast period as charging infrastructure expansion primarily serves personal vehicle use cases and manufacturer product strategies concentrate investment in this highest-volume segment.
Regional Insights:
- Marmara
- Central Anatolia
- Mediterranean
- Aegean
- Southeastern Anatolia
- Black Sea
- Eastern Anatolia
Marmara exhibits a clear dominance with a 26% share of the total Turkey electric vehicle market in 2025.
The Marmara region's market dominance reflects fundamental geographic and economic realities that concentrate both electric vehicle demand and enabling infrastructure within Turkey's most economically developed territory. Istanbul's status as Turkey's largest metropolis and economic center creates density advantages for charging infrastructure deployment where station utilization rates justify investment, higher average disposable incomes that overcome electric vehicle price premiums, and greater exposure to environmental concerns that motivate sustainable transportation adoption.
The region benefits from proximity to automotive manufacturing facilities including domestic producer Togg's plant that facilitates model availability and service network density, port facilities enabling efficient import of international electric vehicle models, and technology sector concentration that correlates with early adopter demographics most receptive to EV technology. Charging infrastructure data demonstrates Marmara's advantage with Istanbul alone accounting for over three thousand charging stations representing disproportionate national share, supporting convenient daily charging access that proves critical for consumer adoption decisions. The region's EV ecosystem exhibits network effects where growing vehicle populations justify further infrastructure investment creating positive feedback loops that sustain leadership. However, Marmara's dominance also reveals broader market challenges, as its infrastructure and adoption concentration highlights the substantial development gap facing other regions that must be addressed for comprehensive national electrification.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Turkey Electric Vehicle Market Growing?
Operating Cost Advantages and Favorable Energy Economics
Turkey's EV adoption is being propelled by compelling operational cost advantages that create substantial total ownership benefits compared to conventional vehicles, driven by the country's unique energy pricing dynamics where electricity costs remain significantly lower than gasoline prices. Turkish consumers recognize that EVs deliver dramatically reduced per-kilometer operating costs through electricity charging that costs substantially less than gasoline refueling for equivalent distances, enabling meaningful monthly savings that accumulate to significant amounts over vehicle ownership periods. By July 2025, the crude oil index fell to 83.10, whereas Turkey’s gasoline index rose to 113.85. These economic advantages prove particularly impactful in Turkey's context where fuel prices have risen substantially in recent years while residential electricity tariffs remain relatively stable, creating widening cost differentials that strengthen electric vehicles' value proposition.
Customs Union Integration Enabling European Export Hub Positioning
Turkey's strategic positioning within the European Union customs union creates unique advantages that drive both domestic market development and international manufacturer investment decisions, establishing Turkey as an increasingly attractive EV production hub serving multiple regional markets simultaneously. The customs union framework enables Turkish-manufactured vehicles to enter European Union markets without facing the substantial tariffs imposed on vehicles produced in non-member countries, providing Turkish production facilities with preferential access to Europe's massive automotive market. This tariff advantage proves particularly significant given recent European Union decisions to impose additional duties on Chinese electric vehicle imports, creating strong incentives for Asian manufacturers to establish Turkish production that circumvents these trade barriers while accessing European customers. The combination of European market access and geographic positioning has attracted substantial foreign direct investment including BYD's commitment to establish one hundred fifty thousand unit annual capacity production that will primarily serve export markets rather than solely domestic demand. Hyundai is set to start manufacturing its recently revealed Concept THREE in Türkiye in 2026, signifying the automaker's initial electric vehicle (EV) production in Europe and establishing it as the first foreign car manufacturer to produce battery-powered vehicles in the nation. Hyundai's inaugural compact EV concept within the IONIQ sub-brand, the Concept THREE, premiered globally at this week's IAA Mobility, Europe's largest auto exhibition, in Munich.
Mature Automotive Manufacturing Ecosystem Supporting Industry Transition
Turkey's EV market benefits from the country's well-established automotive manufacturing ecosystem that provides essential foundations for successful industry transition including skilled workforce availability, sophisticated supplier networks, and proven production capabilities. The Turkish automotive sector encompasses a large number of component manufacturers with production facilities serving both domestic assembly and international exports, creating comprehensive supply chain capabilities that can be adapted to support EV production requirements including specialized components for battery systems, electric powertrains, and charging infrastructure. This existing industrial base provides significant advantages over markets attempting to build automotive capabilities from scratch, enabling faster production ramp-up through established manufacturing expertise, reduced investment requirements by leveraging existing facilities and workforce skills, and greater technology absorption capacity facilitating knowledge transfer from international partners. The industry's transition toward EVs is being supported by targeted skills development programs that retrain existing workforce in electric powertrain technologies. The mass manufacturing of Türkiye’s second homemade electric vehicle Very is anticipated to commence in 2025. The four-passenger vehicle, weighing 400 kilograms, can travel between 300 and 350 kilometers on a full charge. The firm intends to introduce three additional models, which will include a pick-up and a convertible.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Turkey Electric Vehicle Market is Facing?
High Upfront Vehicle Costs Constraining Market Accessibility
Despite substantial government tax incentives that reduce relative electric vehicle pricing, absolute upfront costs remain significantly elevated compared to conventional alternatives, creating persistent adoption barriers particularly for price-sensitive consumer segments that comprise substantial portions of Turkey's automotive market. EV pricing reflects fundamental manufacturing economics where battery costs continue representing substantial vehicle value components despite declining trends, creating inherent cost floors that prevent pricing parity with mature conventional vehicle production that benefits from decades of manufacturing optimization and economies of scale. This pricing dynamic proves particularly challenging in Turkey's economic context characterized by lower average incomes compared to Western European markets, currency volatility that periodically increases imported vehicle costs, and inflation pressures that constrain discretionary purchasing power across consumer segments.
Uneven Geographic Infrastructure Distribution Limiting Market Expansion
Turkey's EV charging infrastructure exhibits substantial geographic concentration that constrains market development beyond core metropolitan areas, creating adoption barriers for people residing outside major urban centers and limiting electric vehicles' utility for long-distance travel connecting different regions. Infrastructure deployment naturally concentrates in areas of highest existing electric vehicle density where station utilization rates justify investment economics, creating self-reinforcing patterns where infrastructure availability enables adoption that further supports infrastructure expansion while underserved regions lack both infrastructure and adoption in mutually reinforcing constraint.
Consumer Range Anxiety and Limited Awareness Hampering Adoption
Turkey's electric vehicle market faces persistent consumer psychological barriers rooted in range anxiety concerns and limited awareness regarding electric vehicle capabilities, operational economics, and practical ownership experiences that constrain adoption beyond early adopter demographics. Range anxiety manifests as persistent consumer fears regarding battery depletion during journeys despite infrastructure expansion that objectively addresses many practical concerns, reflecting deeper psychological comfort with familiar conventional vehicle refueling patterns and unfamiliarity with electric vehicle operational characteristics including charging planning requirements and range variation under different conditions. These concerns prove particularly acute for people contemplating EVs as sole household transportation where perceived range limitations create fears of stranded situations despite statistical evidence that typical daily driving patterns fall well within electric vehicle capabilities.
Competitive Landscape:
The Turkey electric vehicle market exhibits intensifying competitive dynamics as domestic manufacturers compete against established global automakers and aggressive Chinese entrants, each pursuing distinct strategic positioning across price segments and powertrain configurations. The competitive landscape reflects Turkey's dual role as both growing domestic market and emerging manufacturing hub, attracting investment from international players seeking European market access while domestic champions pursue national industrial policy objectives. Competition manifests across multiple dimensions including product portfolio breadth where established manufacturers leverage existing model ranges versus focused new entrants, pricing strategies that balance margin objectives against market share ambitions, and distribution network development that determines geographic market coverage and customer access. The market's competitive intensity has accelerated substantially as multiple manufacturers simultaneously increase model availability and marketing investment, creating dynamic environment where first-mover advantages prove fleeting and sustained differentiation requires continuous innovation.
Turkey Electric Vehicle Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Battery Cells And Packs, On- Board Charger, Fuel Stack |
| Charging Types Covered | Slow Charging, Fast Charging |
| Propulsion Types Covered | Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV), Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV), Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV), Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) |
| Vehicle Types Covered | Passenger Vehicles, Commercial Vehicles, Others |
| Regions Covered | Marmara, Central Anatolia, Mediterranean, Aegean, Southeastern Anatolia, Black Sea, Eastern Anatolia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Turkey electric vehicle market size was valued at USD 12.19 Billion in 2025.
The Turkey electric vehicle market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 23.14% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 79.31 Billion by 2034.
Passenger vehicles held the largest market share at 55.03% in the 2025, driven by heightened preference for personal mobility solutions and government incentives primarily targeting individual vehicle ownership.
Key factors driving the Turkey electric vehicle market include favorable government special consumption tax structures that create substantial cost advantages for EV over conventional alternatives, strategic foreign manufacturing investments particularly BYD's one billion dollar facility establishing local production capacity, and rapid charging infrastructure deployment that addresses range anxiety concerns through expanding network coverage in urban centers and intercity corridors.
Major challenges include high upfront vehicle costs that remain significantly elevated compared to conventional alternatives despite tax incentives, uneven geographic infrastructure distribution that concentrates charging stations in western metropolitan areas while leaving eastern and rural regions underserved, and persistent consumer range anxiety coupled with limited awareness regarding EV operational characteristics and total cost of ownership benefits that constrain adoption beyond early adopter demographics.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












