
UK Renewable Energy Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
UK Renewable Energy Market Summary:
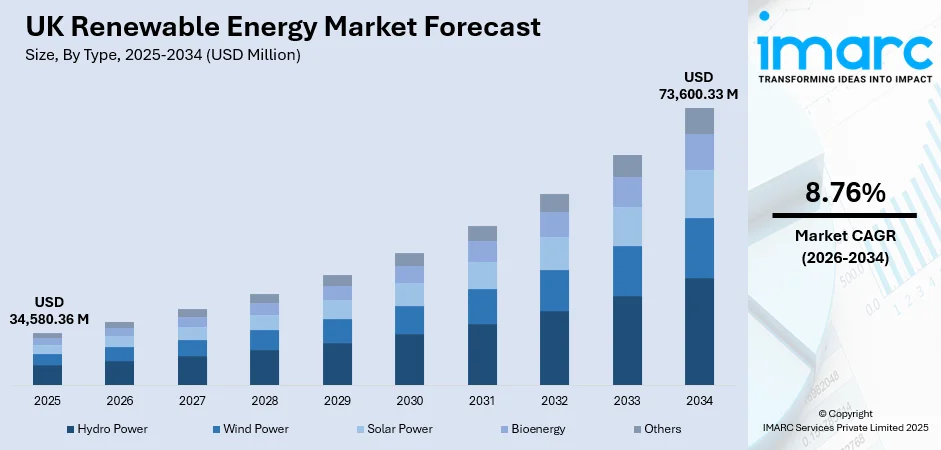
The UK renewable energy market size was valued at USD 34,580.36 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 73,600.33 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.76% from 2026-2034.
The market is driven by the government's ambitious net-zero emissions targets and supportive policy frameworks that encourage clean energy adoption. The declining costs of wind and solar technologies, coupled with the country's exceptional offshore wind resources, have accelerated renewable capacity expansion. Rising consumer awareness and corporate sustainability commitments further strengthen demand for green energy solutions. Additionally, grid modernisation initiatives and energy storage advancements support the integration of variable renewable sources, reinforcing the sector's momentum and expanding the UK renewable energy market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Type: Wind power dominates the market with a share of 33% in 2025, driven by the nation's world-leading offshore wind infrastructure, favourable coastal wind conditions, and substantial government investment in large-scale wind farm developments.
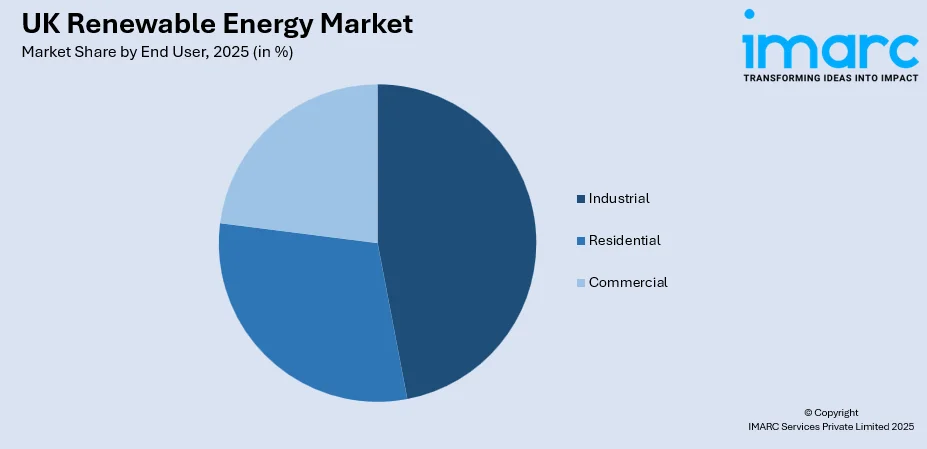
- By End User: Industrial leads the market with a share of 47% in 2025, owing to corporate sustainability mandates, long-term power purchase agreements, and the manufacturing sector's transition towards cleaner energy sources to reduce operational carbon footprints.
- Key Players: The market exhibits a moderately concentrated competitive landscape, with established utility companies and international energy developers competing across offshore wind, solar, and energy storage segments through strategic partnerships and technology investments.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The UK renewable energy market is experiencing robust expansion, propelled by a combination of regulatory mandates, technological innovation, and shifting consumer preferences towards sustainable energy sources. The government's legally binding commitment to achieve net-zero carbon emissions has catalysed significant public and private investment in clean energy infrastructure. Offshore wind development continues to anchor the market, supported by favourable auction mechanisms and seabed leasing programmes. According to sources, in August 2024, the UK increased its sixth CfD renewable energy auction budget by 51.7% to £1.555 billion, allocating £1.1 billion for offshore wind, £185 million for established technologies, and £270 million for emerging projects. Solar photovoltaic installations are gaining traction across residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications, benefiting from declining module costs and improved efficiency ratings. Furthermore, the emergence of green hydrogen initiatives and advanced battery storage technologies is creating new growth avenues, enabling greater grid flexibility and energy independence.
UK Renewable Energy Market Trends:
Accelerating Offshore Wind Deployment and Floating Technology Advancement
The offshore wind sector continues to dominate capacity additions, with floating wind technology emerging as a transformative development enabling access to deeper water locations with stronger wind resources. Floating foundations are expanding the viable development areas beyond traditional fixed-bottom installations, unlocking substantial untapped potential in Scottish and Celtic Sea waters. According to reports, in March 2025, the UK government awarded over £55 million to expand Scotland’s Port of Cromarty Firth, and establishing the first UK port producing floating offshore wind turbines at scale. This technological evolution is attracting significant investment from major energy developers seeking to establish early-mover advantages in next-generation wind projects, while supporting domestic supply chain development and port infrastructure upgrades.
Integration of Battery Storage with Renewable Generation Assets
Co-location of battery energy storage systems with wind and solar installations is becoming increasingly prevalent as developers seek to maximise asset utilisation and grid connection efficiency. This trend addresses intermittency challenges inherent to renewable generation while enabling participation in frequency response and capacity markets. In December 2025, RWE approved its Pembroke Battery Storage project in Wales, a 350 MW / 700 MWh facility, enhancing renewable energy integration and grid stability, with construction scheduled to start in the first half of 2026. Further, energy storage integration enhances project economics by capturing revenue from multiple market streams, including wholesale price arbitrage and ancillary services. The growing pipeline of hybrid renewable-storage projects reflects the maturation of the market toward more sophisticated and grid-supportive configurations.
Corporate Power Purchase Agreements Driving Commercial Renewable Procurement
Corporate power purchase agreements have emerged as a significant demand driver, with major technology companies, retailers, and industrial consumers securing long-term renewable electricity contracts to meet sustainability commitments. In April 2025, RWE signed a 10-year corporate PPA to supply 53 GWh/year of renewable electricity to over 400 UK retail locations, supporting corporate sustainability goals. Moreover, these agreements provide revenue certainty for developers while enabling corporate buyers to demonstrate tangible progress toward carbon reduction targets. The expanding corporate PPA market is stimulating investment in new renewable capacity beyond government-supported auction mechanisms, creating additional pathways for project development and diversifying the commercial landscape for green energy procurement.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The UK renewable energy market is positioned for sustained revenue growth throughout the forecast period, underpinned by ambitious clean power targets and accelerating infrastructure investment. Offshore wind capacity expansion will remain the primary growth engine, complemented by increasing solar deployment and emerging marine energy technologies. Energy storage and grid modernisation investments will support higher renewable penetration levels. Revenue generation is expected to benefit from favourable policy continuity, declining technology costs, and strengthening corporate demand for verified green electricity supply. The market generated a revenue of USD 34,580.36 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 73,600.33 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 8.76% from 2026-2034.
UK Renewable Energy Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Wind Power | 33% |
| End User | Industrial | 47% |
Type Insights:
- Hydro Power
- Wind Power
- Solar Power
- Bioenergy
- Others
Wind power dominates with a market share of 33% of the total UK renewable energy market in 2025.
Wind power has established itself as the cornerstone of the UK's renewable energy portfolio, benefiting from the nation's exceptional wind resources and extensive coastline suitable for offshore development. As per sources, in 2024, renewables generated a record 50.8% of the UK’s electricity, surpassing 50% for the first time, with wind contributing 29.5%. Further, the offshore segment has witnessed particularly rapid expansion, with large-scale wind farms situated in shallow North Sea waters generating substantial electricity volumes. Government-backed contract mechanisms have provided long-term revenue stability, encouraging investment in increasingly large turbine installations that maximise generation efficiency.
Onshore wind development has also experienced renewed momentum following the removal of previous planning restrictions, with new projects advancing across Scotland, Wales, and northern England. Technological improvements in turbine design have enhanced capacity factors and reduced levelised costs, strengthening wind power's competitive position against conventional generation sources. The continued scaling of wind installations supports the broader energy transition while creating employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance activities.
End User Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Industrial
- Residential
- Commercial
Industrial leads with a share of 47% of the total UK renewable energy market in 2025.
The industrial sector represents the dominant end-user segment for renewable energy consumption, reflecting the substantial electricity requirements of manufacturing operations and heavy industries. Corporate sustainability mandates and regulatory pressures have accelerated industrial adoption of renewable power procurement through direct contracts and green tariff arrangements. Energy-intensive industries including chemicals, metals processing, and food manufacturing are increasingly prioritising renewable supply to reduce Scope 2 emissions.
Industrial consumers benefit from economies of scale in renewable procurement, with large electricity volumes enabling favourable pricing through corporate power purchase agreements. In January 2024, Statkraft signed a ten-year CPPA with Workspace for its 20 MW Beavor Grange Solar Farm in Devon, supplying two-thirds of Workspace’s electricity demand. Furthermore, on-site renewable installations, particularly rooftop and ground-mounted solar arrays, provide additional supply diversification while demonstrating environmental leadership. The industrial segment's renewable transition supports broader decarbonisation objectives while enhancing energy cost predictability and reducing exposure to volatile fossil fuel markets.
Regional Insights:
- London
- South East
- North West
- East of England
- South West
- Scotland
- West Midlands
- Yorkshire and The Humber
- East Midlands
- Others
London renewable energy landscape is characterised by innovative urban deployment strategies, maximising commercial rooftop solar installations across the capital's dense built environment. The metropolitan area demonstrates strong adoption of decentralised generation solutions, with solar photovoltaic systems installed on public buildings, commercial properties, and residential developments contributing to local clean energy supply.
The South East region benefits from favourable solar irradiance levels, supporting substantial photovoltaic capacity deployment across residential and commercial applications. The region hosts numerous large-scale solar farms alongside distributed generation installations, while proximity to major demand centres enhances grid connectivity and transmission efficiency for renewable electricity supply.
The North West region demonstrates growing renewable capacity with particular strength in onshore wind development across elevated terrain and coastal areas. The region's industrial heritage supports energy transition initiatives, with manufacturing facilities increasingly incorporating on-site renewable generation to meet sustainability targets and reduce operational energy costs.
East of England holds a prominent position in the renewable energy landscape, benefiting from excellent solar resources and proximity to major offshore wind developments in the North Sea. The region hosts significant solar farm capacity alongside supporting infrastructure for offshore wind operations, establishing itself as a key renewable energy hub.
The South West leads in renewable installation density, with Cornwall and Devon hosting the highest concentrations of renewable energy sites nationally. The region demonstrates particular strength in solar deployment, benefiting from above-average sunshine hours, while marine energy development opportunities along the coastline present emerging growth potential.
Scotland represents the dominant renewable energy region, generating substantially more clean electricity than domestic consumption requires. The nation leads in onshore wind capacity with exceptional resources across the Highlands and Islands, while offshore wind development in Scottish waters continues expanding with floating technology advancing into deeper locations.
The West Midlands region is advancing renewable capacity through targeted investment programmes supporting solar installations and energy efficiency initiatives. Urban regeneration projects incorporate renewable energy systems, while industrial facilities across the region transition toward cleaner electricity supply to meet manufacturing sector decarbonisation requirements.
Yorkshire and The Humber demonstrates strong renewable growth, hosting major offshore wind developments connected through Humber ports and significant bioenergy capacity. The region benefits from diverse renewable resources including wind, solar, and biomass, while energy park developments combine multiple technologies to maximise clean generation potential.
The East Midlands region contributes growing renewable capacity with expanding solar farm developments across agricultural land. The region's central location supports grid integration while emerging energy storage projects complement variable renewable generation, enhancing supply reliability and enabling participation in flexibility markets.
Other regions including Wales, Northern Ireland, and the North East contribute important renewable capacity through diverse technology deployments. These areas host significant onshore wind resources, emerging tidal stream projects, and expanding solar installations, collectively supporting the national transition toward clean electricity generation.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the UK Renewable Energy Market Growing?
Government Policy Support and Net-Zero Commitments
The UK government's legally binding commitment to achieve net-zero carbon emissions has established a comprehensive policy framework supporting renewable energy deployment. Clean power initiatives prioritise decarbonising the electricity system through accelerated renewable capacity additions and grid infrastructure modernisation. Competitive auction mechanisms provide long-term revenue certainty for wind and solar projects, enabling investment decisions based on predictable income streams. Regulatory reforms streamline planning processes and reduce development timelines, while public financing institutions provide catalytic capital for innovative technologies. These coordinated policy interventions create favourable market conditions that attract domestic and international investment into the renewable sector. In June 2025, the UK government announced an additional £700 million for Great British Energy to invest in domestic clean energy supply chains, boosting jobs and infrastructure across industrial and coastal regions.
Declining Technology Costs and Improved Generation Efficiency
Substantial reductions in wind turbine and solar photovoltaic costs have transformed renewable energy from premium alternatives into economically competitive generation sources. In June 2025, UK small-scale solar installation costs fell roughly 20% in the 2024–25 financial year, driven by technology improvements and increased supply, with 203,185 installations recorded. Technological advances in turbine design have increased capacity factors and energy yields, while solar module efficiency improvements enable greater output from equivalent installation areas. Manufacturing scale economies and supply chain optimisation continue driving cost reductions across renewable technologies. Battery storage costs have declined significantly, enabling cost-effective integration solutions that address intermittency concerns. These technology improvements enhance project economics and returns, stimulating deployment across utility-scale and distributed generation applications.
Corporate Sustainability Mandates and Green Procurement Requirements
Growing corporate commitment to environmental sustainability is driving substantial demand for verified renewable electricity supply. Major corporations across technology, retail, and manufacturing sectors have established ambitious carbon reduction targets requiring transition to clean energy procurement. Power purchase agreements provide mechanisms for corporate buyers to secure long-term renewable supply while supporting new project development. According to sources, in April 2024, RWE signed its first UK Solar Power Purchase Agreement with Kerry Group, committing over 10 years of clean electricity from Cotmoor and Copse Lodge solar farms. Further, stakeholder pressure from investors, customers, and employees reinforces corporate sustainability priorities, while regulatory reporting requirements increase transparency around emissions performance. This corporate demand creates additional revenue pathways for renewable developers beyond government-supported mechanisms, diversifying market opportunities.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the UK Renewable Energy Market is Facing?
Grid Infrastructure Constraints and Connection Delays
The UK’s existing transmission and distribution infrastructure faces capacity limitations that hinder the prompt connection of new renewable energy projects. Connection queues have lengthened, causing multi-year delays that disrupt project schedules and financing arrangements. Upgrading grid infrastructure involves substantial reinforcement costs and technical complexities, which add financial and operational burdens to developers while slowing the pace of renewable energy deployment across regions seeking low-carbon generation expansion.
Supply Chain Pressures and Component Availability
Global demand for renewable energy components exerts pressure on supply chains, affecting project timelines and costs. Turbine and solar module manufacturers experience production constraints, while fluctuating international trade conditions influence availability. Additionally, shortages of skilled personnel for installation and maintenance further restrict sector growth. These supply chain dynamics introduce uncertainty into project delivery schedules, increase procurement costs, and may delay commissioning of renewable infrastructure across multiple markets.
Intermittency Management and System Balancing Requirements
Variable output from renewable energy sources presents challenges for system operators, requiring sophisticated balancing solutions and backup capacity. During periods of excess generation, curtailment reduces asset utilisation and diminishes project returns. Integrating renewables demands investment in operational technologies and grid management strategies to address intermittency, ensure reliability, and maintain system stability, adding ongoing costs and operational complexity for both developers and network operators seeking efficient renewable deployment.
Competitive Landscape:
The UK renewable energy market demonstrates a moderately concentrated competitive structure, characterised by established utility companies and international energy developers competing across technology segments. Major market participants maintain diversified generation portfolios spanning offshore wind, onshore wind, solar, and emerging storage technologies. Competitive dynamics are shaped by auction success in government-backed contract mechanisms, with bidding strategies balancing volume growth against pricing discipline. Strategic partnerships between developers, equipment suppliers, and financial investors enable large-scale project execution. Technology differentiation increasingly influences competitive positioning, with floating wind capabilities, hydrogen production expertise, and digital optimisation creating value beyond raw capacity. Market entry barriers remain significant for utility-scale developments, while distributed generation segments offer opportunities for smaller participants.
Recent Developments:
-
In November 2024, NextPower UK ESG acquired its eleventh UK utility-scale solar project, Locks Solar Farm, raising its portfolio to 515.5 MW. The 18.5 MW Hampshire project secured a Contract-for-Difference, providing stable long-term revenue while supporting the UK’s renewable energy expansion and Net Zero transition.
UK Renewable Energy Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Hydro Power, Wind Power, Solar Power, Bioenergy, Others |
| End Users Covered | Industrial, Residential, Commercial |
| Regions Covered | London, South East, North West, East of England, South West, Scotland, West Midlands, Yorkshire and The Humber, East Midlands, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The UK renewable energy market size was valued at USD 34,580.36 Million in 2025.
The UK renewable energy market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 8.76% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 73,600.33 Million by 2034.
Wind Power dominated the market with approximately 33% revenue share, driven by the nation's exceptional offshore wind infrastructure, favourable coastal conditions, and substantial government investment in large-scale wind developments.
Key factors driving the UK renewable energy market include government net-zero commitments, declining technology costs, supportive policy frameworks, corporate sustainability mandates, grid modernisation investments, and growing consumer demand for clean energy.
Major challenges include grid infrastructure constraints, connection queue delays, supply chain pressures, skilled labour shortages, intermittency management requirements, and substantial capital investment needs for transmission upgrades.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












