
United States Autocatalyst Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Material, Catalyst Type, Distribution Channel, Vehicle Type, Fuel Type, and Region, 2026-2034
United States Autocatalyst Market Size and Share:
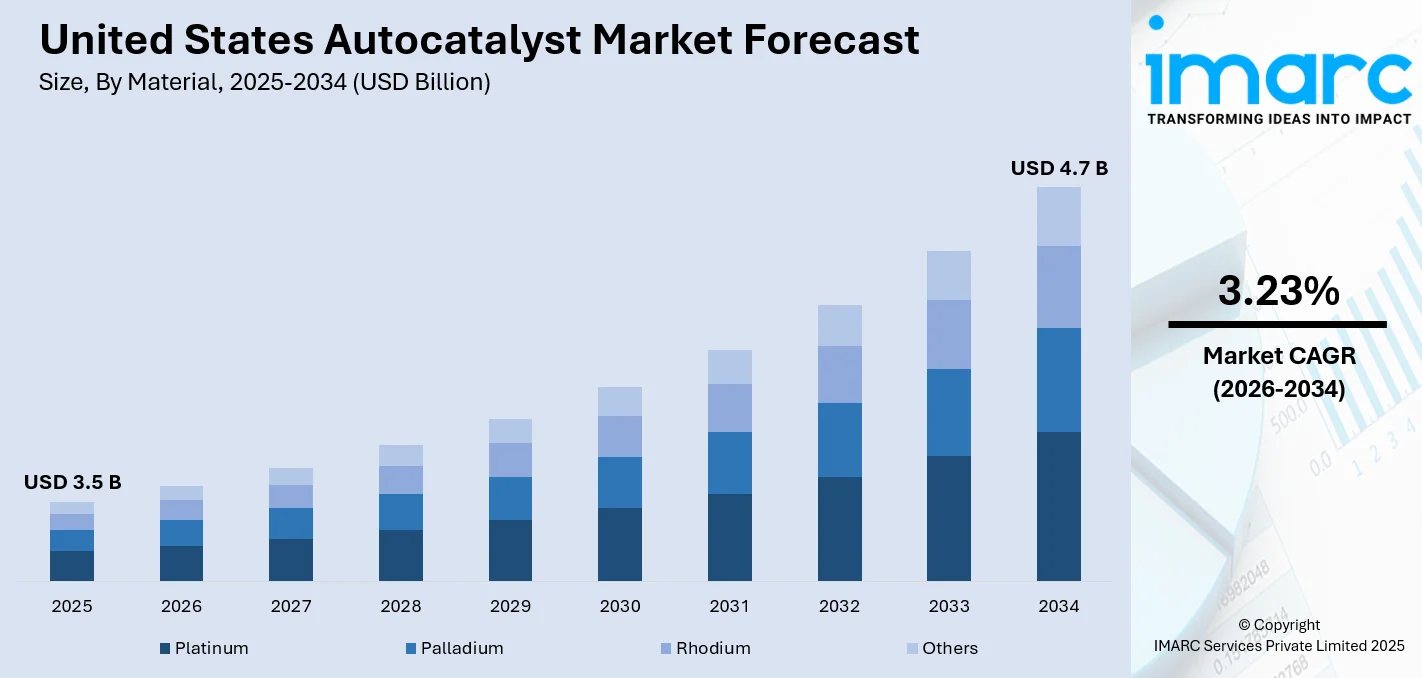
The United States autocatalyst market size was valued at USD 3.5 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 4.7 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 3.23% during 2026-2034. The market is driven by the increasing enforcement of emission control regulations across the automotive sector, compelling manufacturers to adopt advanced catalytic solutions. The rising demand for cleaner internal combustion engines, coupled with the integration of platinum group metals in emission-reducing technologies, is accelerating product deployment. These trends, alongside sustained innovations in catalyst design and recycling practices, are expected to further augment the United States autocatalyst market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 3.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 4.7 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 3.23% |
The market in the United States is primarily driven by the rising focus on reducing vehicular emissions to meet stringent environmental norms. In line with this, the growing adoption of advanced exhaust treatment systems in gasoline and diesel engines is also providing an impetus to the market. For instance, in May 2025, Tata AutoComp Systems and Katcon Global launched a joint venture in Mexico to manufacture advanced composites, including for gasoline and diesel engine applications, for the North American market with a focus on the U.S. The venture focuses on lightweight components for emission systems in passenger, commercial, and off-road vehicles, supporting stricter U.S. emissions standards. Moreover, the increasing integration of platinum group metals in catalyst formulations is also acting as a significant factor for the United States autocatalyst market growth. In addition to this, the surging demand for fuel-efficient and low-emission vehicles is resulting in a higher investment in next-generation catalytic converters.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Besides this, the escalating need to comply with federal emission standards is creating lucrative opportunities in the market. Also, the steady rise in automotive production volumes and the aftermarket replacement of catalytic systems is impacting the market positively. In July 2025, BASF launched BASF Environmental Catalyst and Metal Solutions (ECMS) as a standalone entity focused on emissions catalysts and PGM services, headquartered in New Jersey. ECMS is the world’s largest recycler of PGMs from spent automotive catalysts, achieving 97% lower CO₂ emissions than primary refining. The company will expand its role in autocatalyst production and recycling, aligned with tightening emissions standards. The market is further driven by the implementation of nationwide regulatory policies aimed at curbing air pollution from mobile sources. Apart from this, robust distribution networks and supply chains across key states are propelling the market. Some of the other factors contributing to the market include advancements in nanotechnology-based catalyst coatings, the push toward cleaner mobility solutions, and continuous innovation by key manufacturers in the sector.
United States Autocatalyst Market Trends:
Regulatory Push and Public Investment Driving Emission Control Technologies
The United States autocatalyst market is seeing a clear surge due to increasing regulatory efforts aimed at reducing vehicle-related emissions. Federal and state-level mandates have been pressuring automakers to adopt more effective emission control technologies, particularly in the commercial and public transit sectors. Autocatalysts are central to helping automakers comply with carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxide, and hydrocarbon limits. The rise of stricter EPA regulations and California's evolving standards further reinforce this as one of the major United States autocatalyst market trends. In July 2024, the Biden-Harris Administration invested USD 1.5 Billion to modernize U.S. transit with cleaner buses, supporting 117 projects in 47 states, augmenting American manufacturing, reducing emissions, and training transit workers. This level of investment underscores the government’s role in reshaping transport infrastructure to include cleaner and more sustainable solutions. As these public transit upgrades scale, the demand for advanced autocatalyst systems is projected to rise sharply, particularly in buses and municipal fleets, making the regulatory push a core market driver.
Electric Vehicle Growth and Autocatalyst Integration
While electric vehicles (EVs) are often seen as competitors to traditional engine components, hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), which combine combustion engines with electric powertrains, continue to rely on autocatalysts. This intersection is fueling demand for more efficient, compact, and high-performance catalyst systems. In urban areas, especially, where low-emission zones are expanding, even partial reliance on internal combustion engines requires robust exhaust treatment technologies. According to 2022 statistics report, 91.7% of U.S. households own at least one vehicle. In Q2 2024, electric vehicle sales in the U.S. rose by 11.3% compared to Q2 2023 and were 23% higher than in Q1 2024. This increase in EV sales includes hybrids that still require autocatalysts to meet emissions compliance. As hybrid and plug-in hybrid models continue to scale, autocatalyst systems will remain relevant, especially those optimized for cold-start emissions and high-efficiency operation under low-load conditions. Market participants are also developing novel materials to support this shifting demand pattern, creating a positive United States autocatalyst market outlook.
Automotive Manufacturing Expansion and Innovation in Catalyst Design
The momentum behind domestic auto manufacturing expansion is directly benefiting the autocatalyst industry, particularly as OEMs localize supply chains and invest in greener technologies. New vehicle platforms are being designed with more stringent emissions limits in mind, requiring advanced materials that can meet evolving regulatory thresholds. In March 2025, Hyundai Motor Group invested USD 21 Billion in the U.S. by 2028 to expand car production, localize parts, expand R&D in robotics, AI, autonomous driving, and strengthen energy infrastructure. This investment reflects a broader industry trend: integrating sustainability into production while reducing dependence on overseas supply chains. Autocatalyst producers are responding with innovations in washcoat formulations, lightweight substrate design, and recycling processes for precious metals like platinum and palladium. These developments not only support environmental goals but also reduce production costs and improve vehicle performance. With major automakers committing to U.S.-based development, the innovation cycle in emission control technologies is set to accelerate through 2030 and beyond.
United States Autocatalyst Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the United States autocatalyst market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on material, catalyst type, distribution channel, vehicle type, and fuel type.
Analysis by Material:
- Platinum
- Palladium
- Rhodium
- Others
Platinum remains a key material in diesel autocatalysts, valued for its strong resistance to catalyst poisoning and outstanding oxidation efficiency. It performs reliably across a wide temperature range, making it well-suited for diesel engines that operate under demanding thermal conditions. Its effectiveness in converting harmful carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into cleaner emissions supports compliance with strict environmental standards. With growing emphasis on material sustainability, platinum recovery from spent converters plays an important role in stabilizing supply and supporting long-term cost efficiency.
Palladium plays a key role in gasoline vehicle applications, offering excellent efficiency in oxidizing hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide. Its strong performance and adaptability have made it the preferred choice in three-way catalysts for the dominant gasoline passenger vehicle segment. Despite growing demand influencing prices in recent years, palladium continues to be a dependable material, and its widespread use reflects ongoing industry confidence in its capabilities for meeting emissions standards.
Rhodium, though used in small amounts, delivers unmatched effectiveness in reducing nitrogen oxides (NOx), a critical need in emission control. Its unique catalytic properties make it essential for three-way catalysts, helping automakers meet stringent Tier 3 and CARB requirements. With increasing attention on sustainability and resource optimization, rhodium recycling is gaining traction, supporting a more efficient and resilient supply chain while maintaining high performance in emissions treatment.
Analysis by Catalyst Type:
- Two-Way
- Three-Way
- Four-Way
Two-way autocatalysts serve as a reliable solution for reducing carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbon (HC) emissions, particularly in simpler engine configurations. While three-way catalysts are now more common, two-way systems remain effective in specific applications, especially in legacy vehicles and low-power equipment where NOx control is not a primary requirement. Their continued use in targeted markets reflects their proven functionality and suitability for engines operating under less complex emission demands.
Three-way autocatalysts are the industry standard in the United States for gasoline-powered vehicles. They simultaneously reduce CO, HC, and NOx, aligning with the stringent emission targets set by the EPA and CARB. Three-way catalysts require precise air-fuel ratio control to function effectively and are integrated with engine management systems. The widespread usage of gasoline engines in the U.S. market ensures that three-way catalysts remain the most significant segment in terms of volume and value.
Four-way autocatalysts are advanced systems that incorporate particulate filters in addition to standard three-way catalyst functions, enabling control of fine particulate matter (PM) along with CO, HC, and NOx. They are increasingly relevant for hybrid vehicles and engines with direct injection, where particulate emissions can be higher. Four-way catalysts are also part of emerging solutions for achieving zero-impact emission targets in urban environments, and their adoption is expected to grow as emission limits tighten further.
Analysis by Distribution Channel:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- OEM
- Aftermarket
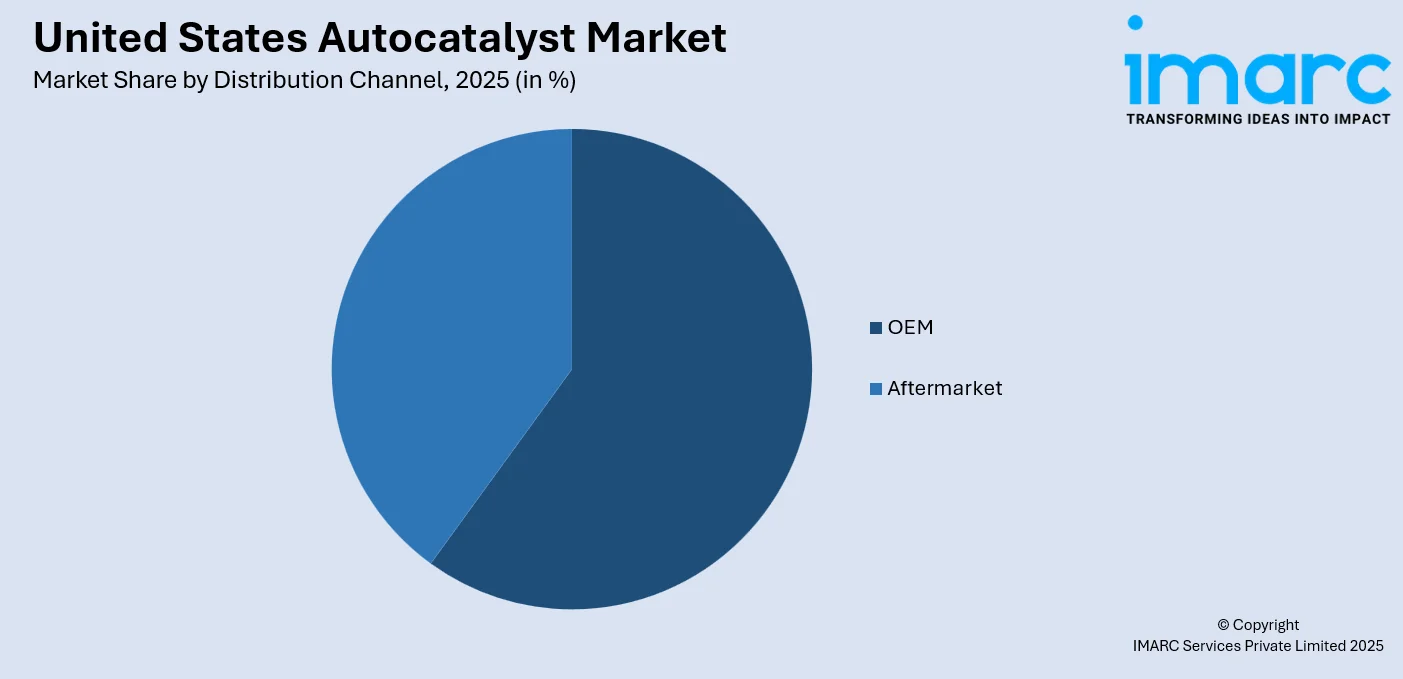
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) channel represents catalysts supplied directly to automakers for use in new vehicles. This segment is driven by regulatory requirements, product design integration, and long-term supply contracts. OEM demand is tightly linked to vehicle production volumes and shifts in powertrain technology. As the U.S. automotive industry continues to adopt cleaner engines, OEMs seek catalysts that not only meet emission standards but also offer performance and cost efficiency over the vehicle lifecycle.
The aftermarket channel involves the replacement of worn-out or stolen catalytic converters. It is influenced by vehicle age, miles driven, and emission inspection policies. In states like California, which enforce strict Smog Check programs, aftermarket catalyst demand is high. Additionally, the surge in catalytic converter thefts, driven by high PGM prices, has increased replacement volumes. This segment is also sensitive to price and certification standards like EPA and CARB-compliant replacement units.
Analysis by Vehicle Type:
- Passenger Car
- Light Commercial Vehicle
- Heavy Commercial Vehicle
- Others
Passenger car is the one of the largest vehicle categories in the autocatalyst market, representing the majority of U.S. vehicles. Passenger cars typically use three-way catalysts and are subject to tight emissions controls. As the average age of cars on the road increases, both OEM and aftermarket demand for catalytic converters remains strong. Fuel efficiency and emissions compliance are critical, driving innovations in catalyst formulations specifically for this segment.
Light commercial vehicles (LCVs) such as vans and pickups have gained prominence due to urban delivery and logistics expansion. These vehicles operate in dense traffic and variable load conditions, requiring catalysts with durable and rapid light-off performance. Emission systems must handle higher engine loads and varying fuel qualities, especially in fleet applications. The segment’s continued growth in e-commerce logistics will sustain demand for reliable and long-life exhaust treatment systems.
Heavy commercial vehicle (HCV) includes trucks and buses, which typically use diesel engines and require complex after-treatment systems including DOCs (diesel oxidation catalysts), DPFs (diesel particulate filters), and SCR (selective catalytic reduction). These systems are more expensive and must meet stricter NOx and PM emission targets. HCVs contribute significantly to emissions despite being fewer in number, making this a priority area for emissions control innovations and regulatory focus.
Analysis by Fuel Type:
- Gasoline
- Diesel
- Hybrid Fuels
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell
A majority of U.S. light vehicles are gasoline-powered and use three-way catalysts extensively. As emission norms tighten, especially for cold-start and urban driving conditions, gasoline vehicles require advanced catalysts with rapid activation and long durability. This segment is expected to remain one of the dominant segments in the near term, despite the gradual rise of electric vehicles, ensuring steady demand for palladium-heavy catalyst formulations.
Diesel vehicles, mostly in commercial and off-road applications, use multi-stage after-treatment systems to manage NOx and particulates. The U.S. diesel catalyst market is influenced by EPA regulations for commercial fleets, off-road equipment, and marine engines. Diesel catalysts are costlier and more complex, but essential for meeting emission standards in logistics, agriculture, and construction. Their maintenance and performance remain key issues in fleet management and environmental compliance.
Vehicles powered by hybrid fuel systems (gasoline-electric or diesel-electric) require special catalyst configurations that can handle frequent cold starts and varying engine loads. Since the internal combustion engine in hybrids runs intermittently, the catalyst must be designed to remain active despite engine cycling. Hybrid catalysts must balance performance, weight, and thermal stability, and are increasingly important as hybrid adoption grows in the U.S. market.
While still a niche in the U.S., hydrogen fuel cell vehicles may use small catalytic systems to purify intake air or manage trace emissions. As per the United States autocatalyst market forecast, the relevance of this segment will increase as hydrogen infrastructure expands and fuel cell vehicle production scales up. The use of PGMs like platinum in fuel cell stacks also intersects with the autocatalyst supply chain, making this segment strategically important for future resource planning.
Regional Analysis:
- Northeast
- Midwest
- South
- West
In the Northeast, including states like New York and Massachusetts, strict emissions policies aligned with CARB standards have created a reliable environment for autocatalyst demand. High vehicle density, combined with a significant number of aging vehicles on the road, drives a strong aftermarket for replacement catalytic converters. Urban pollution controls and frequent cold-weather driving conditions make catalyst performance especially important, as low temperatures can affect emissions control systems. Regular state inspection programs and consistent regulatory enforcement help maintain steady turnover in catalytic components, supporting both service markets and emissions compliance efforts.
The Midwest plays a central role in the U.S. automotive industry, with a strong base of OEM manufacturing alongside diverse driving environments. Long-distance travel and seasonal variations in road conditions increase wear on catalytic systems, contributing to healthy aftermarket demand. The region also sees consistent activity in diesel applications, particularly among fleets in industrial and agricultural sectors. This supports steady uptake of diesel oxidation catalysts (DOCs) and diesel particulate filters (DPFs).
Southern states like Texas and Florida are experiencing steady population growth, leading to more vehicles on the road and an expanding aftermarket for emission control systems. Many of these states have less stringent emissions testing, but the sheer size of the vehicle population ensures continued demand for catalytic converters, especially as older vehicles remain in use. Urban sprawl and longer commutes increase fuel use, raising the importance of well-functioning emissions systems. Growth in hybrid vehicle ownership is also contributing to demand for specialized catalyst systems designed to handle frequent engine cycling and variable load conditions typical in hybrid applications.
The West, and especially California, leads the country in emissions regulation, setting the standard for both OEM vehicle certifications and aftermarket replacement requirements through CARB. This has made the region a consistent driver of innovation in catalyst design, especially for systems that must meet low emissions thresholds under a wide range of operating conditions. While electric vehicle adoption is high, the region still maintains a large population of combustion-engine vehicles that must comply with advanced emissions standards. As a result, manufacturers often test and roll out new catalytic technologies here first, making the West a proving ground for next-generation after-treatment systems such as close-coupled catalysts, SCR systems, and advanced substrate coatings.
Competitive Landscape:
Key players in the US autocatalyst market are focusing on product innovations, regional expansion, and strategic partnerships to support market growth. They are investing in advanced catalyst formulations that meet tightening emissions standards, especially in states with CARB-aligned regulations. Many are strengthening domestic supply chains to ensure reliable access to critical materials like platinum group metals. Companies are also collaborating with OEMs and regulatory agencies to align catalyst designs with upcoming vehicle certification requirements. In the aftermarket, they are expanding distribution networks and offering fitment-optimized products for aging vehicle fleets. Additionally, some players are investing in hybrid and low-emission vehicle technologies, including catalysts designed for start-stop engines and hybrid systems, to meet the evolving needs of a diversifying vehicle base.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the United States autocatalyst market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- May 2025, Honeywell announced it will acquire Johnson Matthey’s Catalyst Technologies for GBP 1.8 Billion to expand its catalyst manufacturing, refining, petrochemical, and renewable fuels portfolio. The deal strengthens Honeywell’s process technologies, supports low-emission fuel production, and is expected to boost earnings and deliver synergies by 1H 2026.
- September 2024, BMW announced plans to launch its first hydrogen-powered car in 2028, using fuel cell technology co-developed with Toyota. This fuel cell uses a catalyst to split hydrogen, producing electricity. BMW expects improved hydrogen infrastructure by then to support quick refueling and extended driving ranges.
United States Autocatalyst Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Materials Covered | Platinum, Palladium, Rhodium, Others |
| Catalyst Types Covered | Two-Way, Three-Way, Four-Way |
| Distribution Channels Covered | OEM, Aftermarket |
| Vehicle Types Covered | Passenger Car, Light Commercial Vehicle, Heavy Commercial Vehicle, Others |
| Fuel Types Covered | Gasoline, Diesel, Hybrid Fuels, Hydrogen Fuel Cell |
| Regions Covered | Northeast, Midwest, South, and West |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the (Region) United States autocatalyst market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the United States autocatalyst market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the United States autocatalyst industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The market in the U.S. was valued at USD 3.5 Billion in 2025.
The United States autocatalyst market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 3.23% during 2026-2034, reaching a value of USD 4.7 Billion by 2034.
The market is driven by stringent emission regulations, growing demand for low-emission and fuel-efficient vehicles, increasing integration of platinum group metals, and advancements in catalytic converter design and recycling. Additional factors include federal investments in cleaner transportation, rising hybrid vehicle adoption, and ongoing OEM innovations in emission control technologies.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












