
United States Chronic Disease Management Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by type, disease type, deployment type, and end user., and Region, 2026-2034
United States Chronic Disease Management Market Size and Share:
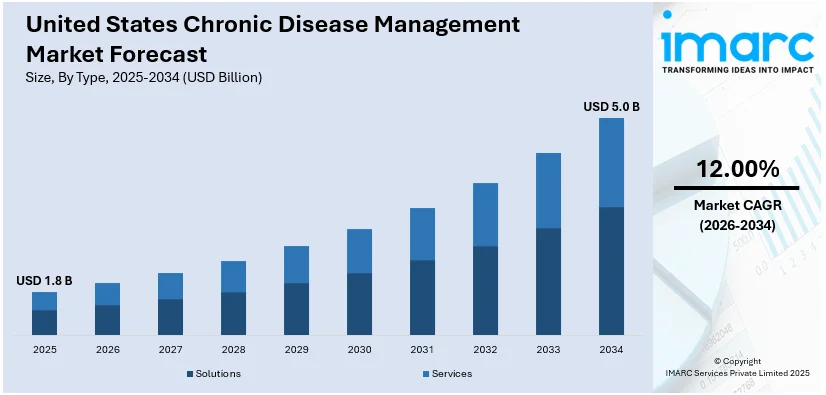
The United States chronic disease management market size was valued at USD 1.8 Billion in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 5.0 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.00% from 2026-2034. The rising demand for remote patient monitoring (RPM) is significantly factor driving growth in the market. RPM enables real-time tracking of patient health outside clinical settings, improving early intervention and reducing hospital visits. Simultaneously, healthcare providers are prioritizing personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs, enhancing care effectiveness and patient engagement. Together, these trends are fostering a shift toward proactive, data-driven care models that improve outcomes and efficiency, thereby accelerating the United States chronic disease management market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.8 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 5.0 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate (2026-2034) | 12.00% |
Chronic conditions demand ongoing care instead of episodic treatment, and thus a transformation toward preventive, long-term care systems. Patients are helped by continuous monitoring, lifestyle advice, and individualized care plans that are adapted to comprehensive, multi-condition requirements. Acute care paradigms prove inadequate to tackle chronic illness, and therefore healthcare systems embrace multidisciplinary care teams and proactive outreach. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is central to this change, with 78% of providers indicating enhanced patient engagement and 60% of physicians consistently incorporating RPM in practice. This increased emphasis on coordination among providers and digital tools is fueling the use of chronic care programs that improve outcomes, avoid complications, and decrease the total cost of healthcare.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Digital health technologies are revolutionizing chronic disease management through remote monitoring, telehealth, and data-based care. Wearables, mobile applications, and AI-driven tools deliver real-time insights, making it possible to intervene early and treat on an individual basis. These technologies give patients the ability to take control of their conditions and enable providers to identify risks and tweak care plans effectively. Interestingly, about 60% of mobile health apps are chronically focused, echoing high adoption among patients and providers alike. The smooth integration of these resources into clinical workflows streamlines communication and care coordination. As demand increases for scalable, accessible solutions, digital health is a key facilitator of proactive, patient-centered care—enhancing outcomes, minimizing complications, and driving long-term efficiency in the delivery of chronic care.
United States Chronic Disease Management Market Trends:
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Conditions and Aging Population
In 2023, 76.4% of U.S. adults reported at least one chronic condition, rising to 93% among older adults—highlighting the clear link between aging and chronic disease prevalence. This growing population living with conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and respiratory disorders is a major driver of the United States chronic disease management market trends. As chronic illnesses become more widespread, especially in older age groups, healthcare systems face increased pressure to provide continuous, long-term care and regular monitoring. Traditional, episodic care models are insufficient for managing these persistent health issues. In response, providers are adopting integrated, proactive approaches, including coordinated care teams, lifestyle interventions, and personalized treatment plans that extend beyond clinical settings. The aging population also increases demand for managing comorbidities, rehabilitation, and supportive services. These trends are fueling investments in infrastructure, technology, and workforce to meet the ongoing needs of chronic disease care.
Shift Toward Value-Based Care and Preventive Health Focus
The U.S. healthcare system is increasingly shifting toward value-based care, in which providers are incentivized for enhancing health outcomes over the volume of services provided. The model promotes a more proactive and holistic management of chronic diseases. Preventive care, including lifestyle guidance, early diagnosis, and regular monitoring, is prioritized to limit complications and prevent emergency interventions at high cost. Healthcare professionals are prioritizing long-term patient engagement and multidisciplinary care to provide more customized and coordinated services. Policy reforms and reimbursement reforms also facilitate this shift by rewarding quality-enhancing and efficiency-improving practices. Therefore, organizations are investing in chronic care management programs, care coordination services, and patient education platforms. The intersection of economic incentives and improved health outcomes provides a robust pressure for chronic disease care solutions that are sustainable and scalable.
Advancements in Digital Health and AI-Driven Technologies
Innovations in digital health are revolutionizing how chronic diseases are monitored, managed, and treated. Telehealth platforms, wearable devices, and mobile health applications enable real-time monitoring and remote consultations, allowing patients to stay connected with care providers beyond traditional settings. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) further enhance clinical decision-making by predicting disease progression and supporting personalized care plans. As of 2024, 66% of U.S. physicians use AI tools, nearly doubling from the previous year—demonstrating rapid adoption for improving care planning and patient outcomes. These technologies also assist with alerts, trend analysis, and adherence tracking, which are essential for long-term disease control are aiding the United States chronic disease management market demand. When integrated into electronic health records and care workflows, digital tools improve coordination, reduce delays, and enable more efficient interventions. Additionally, they empower patients to take an active role in their health. Overall, digital innovation is reshaping chronic care into a more connected and patient-centered system.
United States Chronic Disease Management Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the United States chronic disease management market, along with forecast at the regional and country levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on type, disease type, deployment type, and end user.
Analysis by Type:
- Solutions
- Services
Chronic disease management solutions are software platforms, digital solutions, and remote monitoring technology intended to aid diagnosis, monitoring, and tailored care. The solutions facilitate data integration, real-time monitoring of health, and decision-making based on analytics, enhancing the care coordination, efficiency, and outcomes for patients and providers alike.
In addition to this, services include clinical support, care coordination, patient education, and consulting by healthcare professionals or third-party providers. These services guarantee continuous involvement, treatment compliance, and tailored care delivery. Services tend to augment digital products, optimizing their efficacy by offering on-site assistance, interpretation of health information, and customized interventions in the management of chronic disease.
Analysis by Disease Type:
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Diabetes
- Cancer
- Asthma
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders
- Others
Based on the United States chronic disease management market forecast, the cardiovascular diseases represent the majority of shares of 29.1% owing to their high prevalence and significant impact on public health. These conditions, including hypertension, heart failure, and coronary artery disease, require continuous monitoring, lifestyle management, and long-term medication adherence. As a result, they demand comprehensive care coordination and regular patient engagement, making them a key focus area for chronic disease management programs. The complexity and cost associated with cardiovascular conditions drive healthcare providers to adopt digital tools, remote monitoring, and personalized treatment strategies. Additionally, government initiatives and reimbursement support for managing heart-related illnesses further encourage the adoption of targeted care solutions, solidifying cardiovascular diseases as the leading segment in chronic disease management efforts.
Analysis by Deployment Type:
- On-premises
- Cloud-based
- Web-based
On-Premises dominate the market with a share of 49.8% driven by the demand for greater control, security, and customization of patient data and care systems. Many healthcare organizations prefer on-premises infrastructure to maintain compliance with strict data privacy regulations such as HIPAA, as it allows them to manage sensitive patient information internally. Additionally, on-premises setups offer more reliable performance in environments with limited internet connectivity and allow full integration with existing hospital information systems. Large healthcare institutions often invest in tailored, in-house solutions to meet specific workflow needs and ensure system interoperability. This approach also supports real-time data access and customization, making on-premises systems a preferred choice for organizations seeking robust, secure, and fully integrated chronic care management platforms.
Analysis by End User:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Healthcare Providers
- Healthcare Payers
- Others
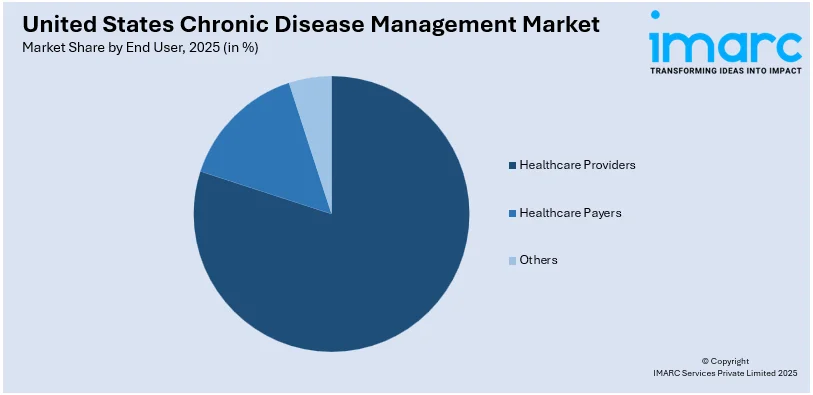
Healthcare Providers account for the majority of shares with a 78.2% owing to their central role in care delivery and patient engagement. They serve as the primary point of contact for individuals with chronic conditions, managing diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing monitoring. Their established infrastructure, including hospitals, clinics, and care networks, allows them to implement integrated care models and remote monitoring systems effectively. Providers also have access to patient health records, enabling them to develop personalized treatment plans and ensure continuity of care. Additionally, value-based care initiatives and reimbursement models increasingly reward providers for long-term outcomes, making them key players in adopting chronic care solutions. Their direct interaction with patients positions them as leaders in United States chronic disease management market analysis driving care coordination and improved health management.
Breakup by Region:
- Northeast
- Midwest
- South
- West
The Northeast region benefits from a high concentration of advanced healthcare facilities and academic medical centers, driving the adoption of chronic disease management programs. Strong policy support, high insurance coverage, and an aging population contribute to increased demand for integrated care, digital health solutions, and personalized treatment services.
Additionally, in the Midwest, chronic disease management is driven by a mix of urban and rural healthcare needs. The region faces challenges like limited access in remote areas, encouraging the use of telehealth and remote patient monitoring. Regional healthcare systems are increasingly investing in scalable, value-based care models to improve chronic condition outcomes.
Besides this, the South experiences a high burden of chronic illnesses due to lifestyle and socioeconomic factors. This drives strong demand for disease management solutions, especially in underserved communities. Healthcare providers are focusing on preventive care, remote monitoring, and education services to address disparities and improve long-term health outcomes across diverse populations.
Furthermore, the West region leads in digital health adoption, driven by a strong tech ecosystem and innovation hubs. Chronic disease management programs here emphasize advanced analytics, AI-driven care models, and patient engagement platforms. The region also sees active collaboration between technology companies and healthcare providers, accelerating the shift toward proactive care delivery.
Competitive Landscape:
The U.S. chronic disease management market exhibits an active and dynamic competitive arena fueled by innovation, collaborations, and service differentiation. Participants vary from established healthcare providers and payers to digital health companies and technology platforms, all of whom seek to provide end-to-end, value-based care. Integrated solutions that bring together clinical services, remote monitoring, data analytics, and patient engagement tools are the emphasis. Competition is focused on the capacity to provide individualized, scalable, and affordable care and show enhanced outcomes. Support from regulators, reimbursement incentives, and increasing demand for virtual healthcare drive continued market growth. To stay competitive, organizations focus on innovation, care coordination, and integrated touch across physical and digital touchpoints, setting themselves up for long-term influence in the management of chronic disease.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the United States Chronic Disease Management market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
Latest News and Developments:
- May 2025: The Nutrition Regulatory Science Program was established by the FDA and NIH to target chronic disorders linked to food. The initiative aims to investigate the impact of ultra-processed foods, food additives, and maternal diets on health, supporting evidence-based food policies and promoting transparency to improve Americans' health outcomes.
- May 2025: Sumitomo Corporation acquired full ownership of ActivStyle, a U.S. provider of home medical supplies for chronic conditions. This move expands Sumitomo’s healthcare portfolio and aims to create synergies with Quest, enhancing patient care and optimizing medical costs, while targeting significant U.S. healthcare market investments by 2030.
- April 2025: Longevity Health Holdings announced a merger with 20/20 BioLabs, a leader in chronic disease risk management and early cancer detection. The merger aims to expand revenue, create synergies, and improve healthcare services, with an expected post-merger valuation of $99 million and operational savings in fiscal year 2025.
- February 2025: Owens & Minor launched ByramConnect, a digital health platform powered by the Welldoc App, for Byram Healthcare customers. The platform offers AI-driven coaching, health tracking, and personalized insights for managing diabetes and other chronic conditions, aiming to improve health outcomes and support long-term behavior change.
- February 2025: Biocon Biologics launched YESINTEK (ustekinumab-kfce), a biosimilar to Stelara in the U.S. The product, approved for treating conditions like Crohn’s disease, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis, offers a cost-effective treatment option and will be available with commercial payor coverage and a patient assistance program.
- February 2025: ScienceSoft delivered the MVP of VitalOp Wellness, a chronic disease management platform. The solution enables users to track health data, access personalized content, and manage conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Developed with AWS services, it includes features for health assessments, wellness tracking, and nutrition guidance.
United States Chronic Disease Management Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Solutions, Services |
| Disease Types Covered | Cardiovascular Diseases, Diabetes, Cancer, Asthma, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorders, Others |
| Deployment Types Covered | On-premises, Cloud-based, Web-based |
| End Users Covered | Healthcare Providers, Healthcare Payers, Others |
| Regions Covered | Northeast, Midwest, South, West |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the United States chronic disease management market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the United States chronic disease management market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the United States chronic disease management industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The chronic disease management market in the United States was valued at USD 1.8 Billion in 2025.
The United States chronic disease management market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 12.00% during 2026-2034, reaching a value of USD 5.0 Billion by 2034.
Key factors driving the United States chronic disease management market include the rising prevalence of chronic conditions, an aging population, and the shift toward value-based care. Technological advancements such as remote patient monitoring, telehealth, and AI-driven tools also enhance care delivery, enabling personalized, continuous, and cost-effective management of chronic illnesses.
Cardiovascular diseases represent the majority of shares of 29.1% driven by their high prevalence and need for continuous, long-term management. Conditions like hypertension and heart failure require regular monitoring, medication adherence, and lifestyle changes, making them ideal candidates for chronic care programs that focus on prevention, early intervention, and coordinated treatment strategies.
On-premises dominate the market with a share of 49.8% owing to their enhanced data security, customization, and control over patient information. Healthcare organizations prefer these systems to meet regulatory requirements, ensure seamless integration with existing infrastructure, and maintain reliable performance, especially in environments with strict compliance and limited internet connectivity.
Healthcare providers hold a 78.2% market share due to their central role in delivering, coordinating, and managing chronic care. Their direct access to patients, clinical infrastructure, and integration capabilities allow them to implement long-term treatment plans, monitor progress, and ensure continuity of care, making them key drivers in chronic disease management.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












