
United States Forage Seed Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast Report by Product, Livestock, Species, and Region, 2025-2033
United States Forage Seed Market Size and Share:
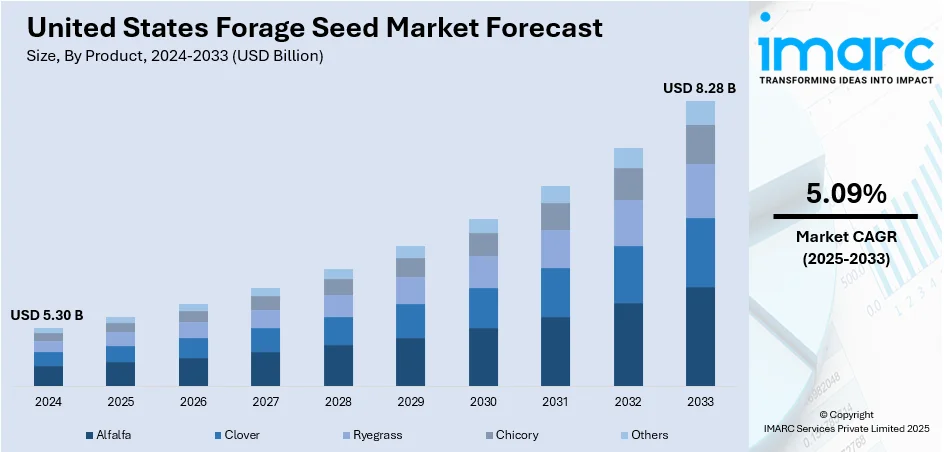
The United States forage seed market size was valued at USD 5.30 Billion in 2024. The market is expected to reach USD 8.28 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 5.09% during 2025-2033. The market is driven by rising demand for high-quality forage to support the expanding livestock industry, where dairy and beef producers prioritize nutritional efficiency. Moreover, growth in organic and sustainable farming practices also stimulates the adoption of certified forage seeds, as producers seek environmentally friendly and resilient crop options. Apart from this, the implementation of government initiatives promoting feed security and improved pasture management further enhance seed utilization, thereby augmenting the United States forage seed market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 5.30 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 8.28 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 5.09% |
The market is influenced by rising livestock production across the country boosts the need for high-quality forage to meet nutritional requirements, while the expansion of dairy and beef industries creates consistent demand for improved seed varieties. According to industry reports, in 2024, total red meat and poultry production increased by nearly 1 percent to reach 107.6 Billion pounds, marking a return to growth following the overall production decline recorded in 2023. Moreover, the growing awareness among farmers about the benefits of using certified forage seeds for enhancing yield and soil health has encouraged wider adoption. Furthermore, the push for sustainable farming practices has increased interest in forage crops, as they improve soil fertility, prevent erosion, and support crop rotation systems.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
In addition to this, the implementation of government initiatives and subsidies promoting modern agricultural practices is accelerating the use of forage seeds among small and medium-scale farmers. Besides this, advancements in seed technology, including genetically improved and pest-resistant varieties, are making forage cultivation more efficient and reliable. Also, increasing consumer demand for organic and natural livestock products is fueling the requirement for nutrient-rich forage, which is providing a boost to United States forage seed market growth. In October, a combination of elevated temperatures and dry conditions across much of the United States led to unprecedented drought coverage. At its peak, 45.3% of the contiguous 48 states were affected by drought, while 73.2% experienced Abnormally Dry (D0) conditions or were classified as being in drought. Every state, with the exceptions of Alaska and Kentucky, reported some level of drought. The changing climatic conditions and the need for drought-resistant varieties have made forage seeds a critical part of resilience strategies in U.S. agriculture.
United States Forage Seed Market Trends:
Rising Demand for Animal Feed
The growing livestock industry in the U.S. acts as a major driver for the market. As more people demand for meat, dairy products, and other animal-related items, there is also a demand for superior animal feed products that will meet their healthy lifestyles. According to industry reports, total red meat and poultry production reached a record 107.5 Billion pounds in 2022. Moreover, per year per capita consumption of poultry in the United States reached 53.03 kg in 2022, while that of beef and pork reached 37.65 kg and 29.58 kg, respectively, as per industry reports. Forage seeds comprise alfalfa, clover, and ryegrass, each forming an important aspect in developing nutritional hay and silage, providing nutritional requirements for cattle, sheep, and other livestock. High-protein forage crops raise milk production in dairy cattle and allow for better growth rates in beef cattle. Due to this fact, farmers are beginning to invest in high-quality forage seeds to ensure a steady and nutritional feed supply for their animals. Such United States forage seed market trends are more likely to continue with the rise in demand for animal protein both nationally and globally, driving growth further in the forage seed market.
Government Support and Incentives
Government policies and benefits create a good demand for the U.S. forage seed market. Many federal and state programs are promoting cover crops and forage planting as part of conservation programs to improve soil health, reduce runoff, and boost biodiversity on farmlands. Programs such as EQIP and CRP provide incentives in monetary form to farmers who adopt practices that include the production of forage crops. In 2023, the United States Department of Agriculture invested more than USD 1.77 Billion in agricultural producers and landowners through its Conservation Reserve Program. This longstanding program is one of many USDA tools helping to build an environment-friendly future on working lands. These incentives make it more financially feasible for farmers to invest in high-quality forage seeds, boosting their adoption across the country. This, in turn, is enhancing the United States forage seed market outlook. Continued government support is expected to sustain the demand for forage seeds, particularly as environmental and agricultural policies evolve to address climate change and sustainability goals.
United States Forage Seed Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the United States forage seed market, along with forecasts at the regional and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on product, livestock, and species.
Analysis by Product:
- Alfalfa
- Clover
- Ryegrass
- Chicory
- Others
Alfalfa leads the market as it is widely known for its high protein and digestibility. Farmers rely on its dense root system to pull nutrients from deep soil layers, promoting soil health through reduced erosion and improved structure. As a perennial that reblooms multiple times per season, it offers dependable yields and strong livestock performance. Its widespread adoption makes it a benchmark for seed pricing and quality, driving innovation in disease-resistant and drought-tolerant cultivars. In short, alfalfa anchors the forage seed sector, shaping market dynamics and breeding priorities with its economic and agronomic weight.
Clover holds a niche yet significant role in the market, especially as a companion to grasses in mixed pastures or standalone cover crops. Its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen reduces fertilizer needs and boosts overall pasture productivity. White and red clovers supply adaptable, high-quality forage across diverse climates, from the cool Northeast to the South. Their shorter maturation time allows flexibility in grazing rotation, while their resilience under stress helps maintain fodder supply. Though less dominant than alfalfa, clover fuels sustainable intensification and soil-building practices, making it a strategic choice for environmentally conscious producers and seed innovators.
Ryegrass, in its perennial and annual forms, offers rapid establishment and vigorous regrowth, making it a staple in rotational grazing and overseeding systems. Perennial ryegrass is valued in temperate regions for its fine texture, high palatability, and steady growth through spring and fall. Annual ryegrass is often used to fill gaps between major forage cycles or to extend grazing seasons. Seed producers emphasize performance traits—like disease resistance, digestibility, and dry matter yield—in their breeding programs. Its adaptability and quick productivity make ryegrass a versatile and responsive tool in managing forage supply, influencing seed-market trends in speed, yield, and quality.
Chicory stands out as a niche but growing segment in the market, known for its deep taproots, high mineral content, and strong summer production. Often included in pasture mixes to diversify forage options, chicory remains green and productive during heat and drought when grasses slow down. It improves animal intake and average daily gains, especially in lambs and dairy cows. Its inclusion can reduce problems like internal parasites in grazing animals. Despite its smaller market share, chicory’s unique benefits, nutrition, resilience, and animal health spark interest from progressive seed developers and pasture managers aiming for more resilient, high-performance forage blends.
Analysis by Livestock:
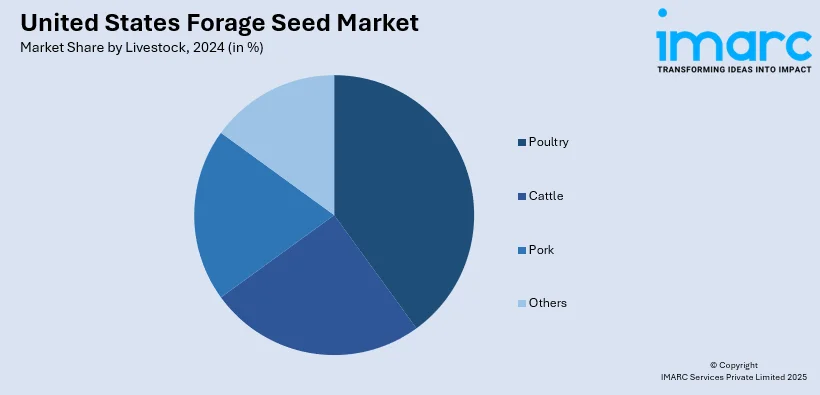
- Poultry
- Cattle
- Pork
- Others
Poultry’s link with the market centers on the role forages play in raising quality feed for egg- and meat-producing birds. Whether in smallholder settings or more integrated systems, forage such as alfalfa, clover, and chicory can augment diets, lowering reliance on expensive grains. Their use supports bird growth, immunity, and digestive health while enhancing sustainability. Forage patches help reduce feed transport costs and can partially offset grain market shocks. As backyard and niche poultry producers grow, demand for regionally adapted forage seeds reflects a premium placed on natural, local feed production, spotlighting poultry’s role in niche forage-seed demand dynamics.
Cattle drive a vast share of forage-seed consumption across the U.S., with grazing operations and feedlots alike tapping forage species for maintenance and growth. Alfalfa, ryegrass, clover, chicory, and mixtures all serve to meet the protein and fiber requirements of beef and dairy herds. Dairy systems especially depend on high-yield, nutrient-rich forages to fuel milk production, shaping seed breeding and marketing priorities. Forage performance here is vital under variable weather; deep-rooted chicory helps fill summer feed gaps. Even with high demand, producers weigh persistency, palatability, yield, and cost, making cattle a central force in shaping forage-seed varietal strategy and overall market direction.
Pork production relies on forages differently compared to poultry or cattle, but foraging blends, or cover-crop forages in rotational systems, can support soil health and reduce feed cost pressures. Farrow-to-finish operations may use forage cover crops during downtime to build soil nutrients and limit erosion, indirectly supporting grain-based feed systems. Occasional use of forage in the diet can reduce waste and improve the digestive welfare of pigs. While not a primary driver of seed demand, pork’s connection to forage emerges in integrated systems valuing sustainable feed cycles. This subtle role influences forage-seed markets by highlighting cover-crop uses and by-product feed opportunities, especially in diversified and pasture-based pork systems.
Chicory’s growing presence in the market is increasingly tied to livestock performance and system resilience, with each livestock type drawing different benefits. For poultry, chicory adds nutritional value; for cattle, it boosts summer productivity and animal health; for pigs, it enriches rotational forage mixes that support broader feed ecosystems. Chicory appeals to producers open to integrating deep-rooted, nutrient-dense forages into blends that fill seasonal gaps or enhance pasture mixes. Its niche status reflects a reputation for drought-tolerance and value-added qualities. As livestock systems diversify and seek forage solutions that reduce risk, chicory’s role in the seed market gains visibility beyond its small share.
Analysis by Species:
- Legumes
- Grasses
Legumes bring rich, protein-dense forage to U.S. pastures and hayfields, playing a vital role in livestock nutrition and soil fertility. Their nitrogen-fixing ability benefits companion grasses or succeeding crops, minimizing synthetic fertilizer use. In mixed stands, legumes enhance forage quality and promote palatability, supporting milk yield in dairy cows or growth rates in beef cattle. Producers often choose legumes like clover or alfalfa for their resilience and multi-cut potential. This dual value, feed and fertility, drives breeders to focus on improving traits like drought tolerance, pest resistance, and persistency, ensuring legumes remain a cornerstone of the forage-seed market.
Grasses form the backbone of the market, with their fast establishment and versatile uses across grazing, hay, and silage systems. Species such as ryegrass, fescue, orchardgrass, and timothy support year-round productivity and ground coverage, helping manage erosion and soil moisture. They offer bulk and fiber in livestock diets, anchoring mixed swards and providing stable yields. Grass breeding prioritizes dry-matter output, disease resistance, and environmental adaptability. As foundational components, grasses sustain the forage-seed trade by meeting wide-ranging demands—from high-altitude pastures to low-input operations, making them indispensable to producers and seed marketers alike.
Regional Analysis:
- Northeast
- Midwest
- South
- West
The Northeast is characterized by humid summers and cold winters, which necessitate hardy and fast-maturing forage varieties. The region relies heavily on grass–legume mixtures that establish quickly and remain resilient under frequent rainfall and fluctuating temperatures. Winter survival, digestibility, and disease resistance are critical factors driving seed selection. Demand in this region emphasizes perennial forages that provide flexibility and support for dairy, beef, and diversified livestock operations. Breeding efforts focus on developing varieties suited to the Northeast’s condensed growing season. Consequently, the market in this region is defined by the need for adaptability, cold tolerance, and consistent growth performance.
In the Midwest, agricultural production is divided between extensive row-cropping and forage cultivation, with corn silage and hay serving as the primary outputs. The forage-seed market emphasizes high-yielding grasses and legumes that integrate seamlessly with mechanized farming systems. Producers typically rely on large-scale, dependable species such as alfalfa and bromegrass to ensure a stable supply for dairy and beef operations. Broad acreage translates into substantial seed demand, encouraging suppliers to operate at scale. Market priorities include productivity, ease of harvest, and compatibility with intensive crop rotations. Robust perennial species capable of withstanding seasonal variability remain central to regional seed selection.
The southern United States benefits from warm climates and extended growing seasons, enabling a wide range of forage strategies that include both tropical grasses and cool-season species for winter grazing. The forage-seed market caters to conditions of heat, humidity, and variable soil quality by promoting species capable of tolerating acidity and drought stress. Perennial grasses such as bermudagrass, alongside selected forage legumes, have gained strong adoption. Demand is shaped by the region’s double-cropping systems and year-round forage cycles, which require species with rapid establishment and continuous regrowth. Breeding efforts focus on developing drought-resistant, disease-tolerant varieties that sustain intensive grazing systems.
The western United States presents diverse environmental challenges, ranging from arid plains to mountainous regions. Forage demand in this area is driven by the need for drought-tolerant species that can withstand extreme temperature fluctuations and limited water availability. Deep-rooted grasses and resilient legumes are particularly valued for their water-use efficiency and capacity to stabilize soils. In irrigated regions such as California’s Central Valley, perennial ryegrass–legume blends are widely utilized, while rangelands in drier intermountain zones rely on hardy species like crested wheatgrass. Breeding initiatives prioritize persistence, adaptability, and dry-matter yield under stress conditions, shaping a market focused on resilience and resource efficiency.
Competitive Landscape:
The market competition is driven by robust regional competitors, broad product lines, and an increasing focus on innovation. Companies compete on seed quality, yield performance, disease resistance, and responsiveness to different climatic conditions. In addition, companies are spending more on research and development (R&D) activities to create high-performance forage seed varieties that enhance livestock nutrition and sustainable agriculture. Apart from this, the industry is also characterized by a high level of consolidation, with bigger companies consolidating distribution networks and smaller manufacturers concentrating on specialized regional needs. In addition, partnerships with farmer cooperatives and seed distributors are an important initiative to increase market access. Also, developments in biotechnology and precision agriculture are inspiring suppliers to create genetically improved seeds with improved durability. As per the United States forage seed market forecast, the increasing need for quality forage among the dairy and beef industries will further exacerbate competition, fueling increased innovation, strategic alliances, and technology integration throughout the industry.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the United States forage seed market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- July 2025: Beck’s, a prominent retail seed business based in Indiana, confirmed plans for the acquisition of Andrews Farm and Seed. This transaction demonstrates Beck's steadfast dedication to providing farmers with the best seed products supported by first-rate customer service and a thorough awareness about regional requirements.
- June 2025: Cibus, Inc. announced the successful completion of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) Plant Biotechnology Consultation Program for its modified lignin alfalfa trait. This trait, developed in collaboration with S&W Seed Company, was designed to alter the lignin profile of alfalfa, potentially enhancing nutrient availability for cattle.
- March 2025: Beck’s successfully completed the acquisition of Gro Alliance’s seed facilities. The acquisition supports Gro Alliance's strategic investments in seed production, germplasm, and agtech innovation while expanding Beck's Superior Hybrid network with seed manufacturing facilities in Indiana and Illinois.
- July 2024: Heartwood Partners announced the addition of Arrow Seed to its platform for seeds and controlling erosion, NativeSeed Group. The acquisition is expected to enhance NativeSeed's product line by adding more warm-season seed varieties, as well as broaden the company's geographic reach into the Midwest.
- July 2024: DLF created a novel seed enhancement called 4Most internally to retain control over research, product development, and continuous efficacy testing. They evaluated each component to guarantee that the ingredients were of good quality and in the proper ratios. The formula contains slow-release nitrogen as well as numerous beneficial bacteria particular to turf and forage, which are intended to improve seedling nutrition. It also includes a biodegradable starch-based super absorbent to keep moisture around the seed and a calcium carbonate layer to promote soil interaction and moisture retention.
United States Forage Seed Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Products Covered | Alfalfa, Clover, Ryegrass, Chicory, Others |
| Livestocks Covered | Poultry, Cattle, Pork, Others |
| Species Covered | Legumes, Grasses |
| Regions Covered | Northeast, Midwest, South, West |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the United States forage seed market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the United States forage seed market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the United States forage seed industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The forage seed market in the United States was valued at USD 5.30 Billion in 2024.
The United States forage seed market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 5.09% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 8.28 Billion by 2033.
The market is driven by the rising demand for high-quality animal feed to support dairy and livestock production, increasing focus on improving pasture productivity, and the adoption of sustainable farming practices. Government support for advanced agricultural techniques, along with growing awareness of livestock nutrition and rising meat and dairy consumption, further fuels market growth.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












