
United States Small Satellite Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Type, Frequency, Application, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
United States Small Satellite Market Overview:
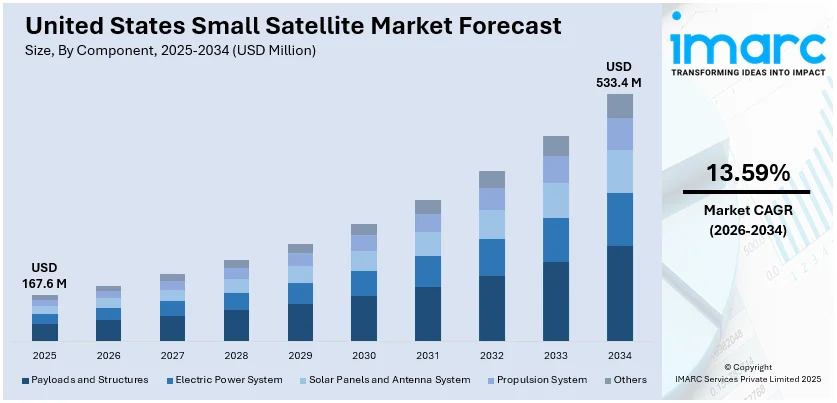
The United States small satellite market size was valued at USD 167.6 Million in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 533.4 Million by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 13.59% from 2026-2034. The market is driven by mounting demand for low-cost space missions, defense spending, and technological innovation in satellites. These satellites are being utilized more and more for communications, navigation, and Earth observation in government, military, and commercial applications. The need for quick deployment and growing space accessibility is also fueling adoption. With powerful backing by federal programs and the amplified development of flexible smallest applications, the market has the potential to develop steadily, propelling the United States small satellite market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
|
Market Size in 2025
|
USD 167.6 Million |
|
Market Forecast in 2034
|
USD 533.4 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 13.59% |
The integration of small satellites in environmental and climate monitoring is one of the prime drivers of the United States small satellite market. These small satellites provide high-resolution imagery and accurate data regarding atmospheric variations, deforestation, the water cycle, and ocean temperature, which are critical to climate science and natural resource management. They can make frequent observations of regions of interest, making them useful for monitoring quick environmental changes. Policymakers, environmental organizations, and research institutions are highly using this space-based information to guide climate policies and disaster preparedness strategies. With heightened awareness of environmental concerns by the population and a national focus on sustainability, small satellites are invaluable tools for well-informed decision-making. They are also cost-effective, making them easily accessible to regional governments and non-governmental organizations. With amplified demand for timely, accurate, and localized environmental information, small satellites are being used more extensively, increasingly enhancing United States small satellite market growth in scientific and ecological applications. As per the reports, in June 2024, bluShift Aerospace of Maine revealed that it will start launching small satellites in 2025, seeking to provide faster, lower-cost orbital access and enhance the regional presence for commercial nanosatellite deployment.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Another crucial impetus for the development of the U.S. small satellite market is the development of data-intensive industries that need geospatial intelligence in real-time. According to the sources, in December 2024, Muon Space of the United States was awarded a $2.9 million U.S. Space Force contract to evaluate its small satellites for military weather imaging, supporting the United States Small Satellite market's dual-use potential. Moreover, industries like precision agriculture, insurance, logistics, and city planning are embracing satellite-based tools to improve operational effectiveness and strategic decision-making. Small satellites help through the provision of near-real-time imagery and analytics that facilitate quick, localized decision-making. For example, crop health monitoring, traffic regulation, and infrastructure planning all take significant advantage of these dynamic data streams. With greater deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models to satellite data, the utility of small satellites in commercial analytics is also growing. In addition, with wider digital transformation initiatives across sectors, the need for trusted space-based data collection platforms is expanding rapidly. Small satellites offer a flexible and scalable answer to these changing demands, enabling industries to tailor data gathering to their specific requirements. This integration of digital innovation and space-based intelligence is powerfully driving the local market.
United States Small Satellite Market Trends:
Increased Need for Economical Space Missions
The United States is experiencing a quick expansion in using small satellites because they are affordable and readily accessible in comparison to conventional big satellites. These small satellites are allowing different groups such as private firms, universities, and nongovernmental organizations to make space missions without financial hurdles. Their appropriateness for low Earth orbit missions makes them perfect for targeted short term goals. In November 2024, it was reported that 475 small satellites were deployed with 55 missions, with some missions sending over 100 satellites into space. This trend illustrates how small satellites are slowly but surely becoming indispensable to commercial space ventures. Their compact nature and reduced cost of production make them appealing for quick development and innovation. The higher number of companies that join the space business and look for cost-effective solutions means that demand for small satellites will continue to be steady and redefine the course of space exploration in the nation.
Strategic Military Investment in Satellite Communications
The defense industry is taking a leading position in the development of the US small satellite market. Military organizations are spending significantly on satellite communications as part of an overarching strategy to enhance surveillance and communication networks. The FY2025 budget includes over 400 million dollars in Army satellite procurement, over 200 million for the Navy, and over 300 million total for defense agency space research including at DARPA and the Missile Defense Agency. Also, over 400 million has gone to assist in the operations of the United States Space Command. These investments illustrate how little satellites are now viewed as strategic assets in defense at the national level. They enable faster deployment and improved data gathering in remote or disputed regions. The military's emphasis on responsive and adaptable satellite systems is likely to fuel future innovation and enhance the small-satellite market.
Market Democratization and Versatility in Applications
Small satellites are applied in a broad number of fields in America, and they are among the most adaptable devices in contemporary space technology. Small satellites find their applications in communication, navigation, meteorology, scientific studies, and earth observation. These roles play a critical function in industries like agriculture, environment control, disaster relief, and transportation logistics. The need for real time information and quicker decision making is growing the significance of small satellites. With lower prices and quicker production times, even small enterprises and academic institutions are able to take part in space missions. This has created a more open and competitive market that promotes innovation. With huge and small organizations now investing in satellite technologies, the sky of space exploration is changing. The simplicity of launching small satellites and their capacity to perform certain roles are making space more accessible and are likely to continue driving market growth in the future.
United States Small Satellite Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the United States small satellite market, along with forecasts at the regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on component, type, frequency, application, and end user.
Analysis by Component:
- Payloads and Structures
- Electric Power System
- Solar Panels and Antenna System
- Propulsion System
- Others
Payloads and structures claimed 39.1% of the U.S. small satellite market share in 2025, which positions them as the dominant category by components. This supremacy mirrors the spurring need for advanced onboard hardware that can facilitate complicated space missions like communication, Earth observation, and science studies. Miniaturization of the payload, the use of light structural material, and higher modularity are the essential drivers for this trend. As the performance expectations and versatility continue to grow, satellite structures are designed to be cost-efficient as well as light in weight. Standardized architectures with rapid integration features are also increasingly driving adoption, especially in commercial and government markets with the need for rapid deployment. Buildings with better thermal control, radiation protection, and strength-to-weight ratios also lead to boosted functionality and robustness. This percentage reflects the central position of hardware innovation in influencing mission performance, especially in small satellites. With payload capabilities accelerating, their percentage is likely to rise with new applications across industries.
Analysis by Type:
- Mini Satellite
- Micro Satellite
- Nano Satellite
- Others
Micro satellites achieved the largest market share by type in 2025, at 40.6% of the U.S. small satellite market. These satellites usually range from 10 to 100 kilograms and provide an excellent balance between payload capability and affordability, rendering them extremely desirable for a broad variety of missions. They are most favored due to heightened application in remote sensing, communication, and space-based research. The segment is advantaged through technological advances in miniaturized equipment, better propulsion systems, and lower launch prices. In governmental and business use, micro satellites facilitate more responsive and versatile mission planning, making constellations available for permanent coverage and expedited data acquisition. Multipurpose payloads and real-time delivery are facilitated by their versatile design. Micro satellites find widespread use in military surveillance, weather monitoring, and broadband rollouts owing to their rapid turnaround and reusability. Their dominance is indicative of their versatility in end-use scenarios and cost of operations benefits.
Analysis by Frequency:
- L-Band
- S-Band
- C-Band
- X-Band
- Ku-Band
- Ka-Band
- Q/V-Band
- HF/VHF/UHF-Band
- Others
Ku-band frequency had a dominant share of 23.0% in 2025 in the United States small satellite market outlook because of its vast application in satellite communications. Ku-band, varying from 12–18 GHz, is preferred to provide high-bandwidth, low-latency data transmission, especially in remote and underserved areas. It facilitates services like video broadcasting, broadband internet, and mobile communication, so it is as much needed for commercial use as for defense. Small satellite systems based on Ku-band provide better beam focus and reduced ground equipment requirements, lowering infrastructure cost. The band is compatible with fixed and mobile services, making it as widely used as it is in aviation, maritime, and emergency response applications. Its strength across diverse weather conditions, coupled with technological improvements in satellite payload development, further positions it as part of U.S. satellite launches. With satellite internet and defense-class connectivity on the rise, Ku-band frequencies will continue to be an indispensable part of U.S. satellite equipment.
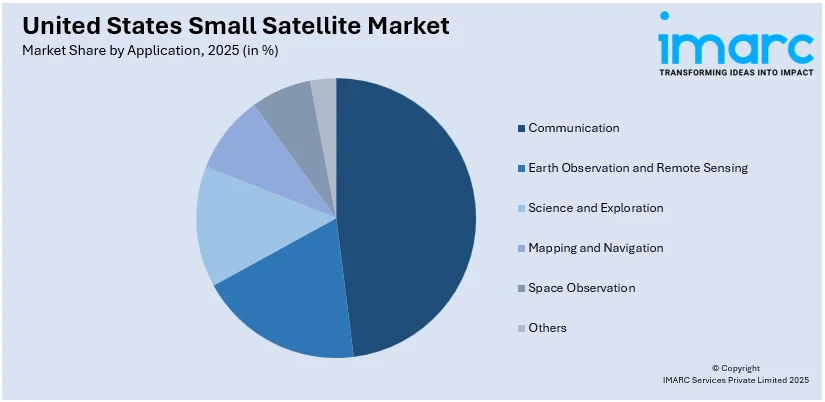
Analysis by Application:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Communication
- Earth Observation and Remote Sensing
- Science and Exploration
- Mapping and Navigation
- Space Observation
- Others
Communication led U.S. small satellite application in 2025, with a dominant 95.4% share. This is the increasing reliance on satellite-based communication networks for broadband, mobile data, and internet-of-things (IoT) services in both urban and rural regions. Small satellites are being launched in constellations to provide global reach, low-latency internet, and secure data channels, and hence they are indispensable to commercial, governmental, and defense communication networks. These systems also enable 5G backhaul, maritime connectivity, and disaster recovery operations. Technological advancements in transponder, bandwidth efficiency, and satellite interlinking are increasing reliability and speed of communication via satellites. The demand for real-time and unbroken transmission of data continues to boost in industries ranging from aviation, energy, and education to public safety. As satellite communication remains at the core of global digital infrastructure and security requirements, small satellites will continue to play an essential role in supporting the country's connectivity ecosystem.
Analysis by End User:
- Commercial
- Academic
- Government and Military
- Others
Government and military organizations were the leaders of the United States small satellite market forecast in 2025 with a 47.7% market share by end-user segment. This leadership is chiefly inspired by increased national security requirements, space surveillance programs, and strategic investments in satellite communications and reconnaissance. U.S. defense initiatives are proactively sponsoring the use of small satellites to aid tactical operations, robust communication networks, and real-time intelligence. Small satellites provide operational flexibility, shorter deployment cycles, and enhanced cost-effectiveness over conventional satellite systems. Small satellites are employed for tracking missile threats, facilitating secure communication in adversarial environments, and monitoring geopolitical trends. Civil agencies are also using small satellites for disaster response, climatic monitoring, and infrastructure monitoring. Expanded coordination among federal agencies and private industry companies is driving innovation and deployment. As government space missions transition toward distributed architectures and multi-orbit concepts, dependence on small satellites will likely increase significantly in the near future.
Regional Analysis:
- Northeast
- Midwest
- South
- West
The Northeast area hosts cutting-edge research centers and aerospace clusters that promote innovation in satellite technology. Demand stems from defense contracts, educational projects, and public-private partnerships for secure communications, Earth observation, and scientific missions, with increased investment in satellite integration plants and launch coordination services fueling regional capabilities.
The Midwestern region experiences consistent growth in satellite production supporting industries due to robust industrial infrastructure and highly skilled labor. Local schools and defense institutions work together on satellite technology development. State-level innovation funds and government funding support development in payload systems, tracking infrastructure, and precision agriculture satellite use.
The South region leads in satellite launches due to proximity to key spaceports and favorable weather. A strong presence of defense operations and aerospace firms contributes to demand for secure and real-time communication networks. Local investment in educational programs and space-related R&D enhances the region’s competitiveness in small satellite deployment.
It is headed by the West region owing to its high concentration of top space technology companies and research facilities. Supportive policy environments, availability of venture capital, and proximity to Pacific launch facilities drive high deployment rates. Startups and tech giants cooperate in Earth imaging, satellite internet, and data analytics, establishing the West as a hub for satellite innovation.
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive dynamics of the United States small satellite industry are characterized by a mix of veteran aerospace companies, universities, and growing numbers of flexible startups emphasizing quick innovation. Industry players are aggressively working on improving satellite miniaturization, propulsion systems, and payload integration to improve mission adaptability and affordability. Strategic partnerships with universities and federal agencies are prevalent, facilitating ongoing technological optimization and deployment readiness. Launch optimization, such as rideshare missions and reusable launch platforms, is also being invested in by companies to minimize deployment costs and enhance access to space. Domestic companies are placing more emphasis on proprietary satellite design and software-defined payloads that enable in-orbit reprogramming, reflecting changing mission objectives. The industry also indicates vertical integration, where companies oversee manufacturing, launch coordination, and data services on their own. This approach is allowing participants to differentiate their offerings and capture a larger share of the growing demand for commercial and government-focused space applications.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the United States small satellite market with detailed profiles of all major companies.
Latest News and Developments:
- June 2025: SpaceX successfully scheduled the launch of Starlink Group 12-24 smallsats aboard Falcon 9 from Cape Canaveral. A USD 69.75 Million mission aimed to expand the Starlink constellation. Favorable weather and a planned drone ship landing supported this addition to the growing U.S. small satellite ecosystem.
- May 2025: Rocket Lab launched iQPS’s QPS-SAR-10 satellite aboard Electron from New Zealand, marking the third mission for the Japanese company. This was part of an eight-launch contract through 2026, showcasing Rocket Lab’s growing role in supporting the rapid deployment of small satellite constellations with precise, reliable launches.
- March 2025: SpaceX’s Transporter-13 mission launched 74 small satellites, including payloads from U.S. military and intelligence agencies. Notable deployments included NRO cubesats, Albedo’s Clarity-1, MuonSpace’s FireSat Protoflight, and Turion Space’s Droid.002, reflecting increasing government investment in commercial space technologies with dual-use and defense applications.
- February 2025: NASA selected SpaceX to launch the Pandora smallsat mission under the VADR contract. Designed to study exoplanet atmospheres via transmission spectroscopy, Pandora featured a 45-cm telescope and aimed for a fall launch as a rideshare payload into sun-synchronous orbit, advancing low-cost astrophysics missions.
United States Small Satellite Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Payloads and Structures, Electric Power System, Solar Panels and Antenna System, Propulsion System, Others |
| Types Covered | Mini Satellite, Micro Satellite, Nano Satellite, Others |
| Frequencies Covered | L-Band, S-Band, C-Band, X-Band, Ku-Band, Ka-Band, Q/V-Band, HF/VHF/UHF-Band, Others |
| Applications Covered | Communication, Earth Observation and Remote Sensing, Science and Exploration, Mapping and Navigation, Space Observation, Others |
| End Users Covered | Commercial, Academic, Government and Military, Others |
| Regions Covered | Northeast, Midwest, South, West |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the United States small satellite market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the United States small satellite market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the small satellite industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The small satellite market in the United States was valued at USD 167.6 Million in 2025.
The United States small satellite market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 13.59% during 2026-2034, reaching a value of USD 533.4 Million by 2034.
Drivers for the United States small satellite market include accelerating demand for economical space missions, mounting defense and government spending on satellite communications, and wider applications of satellites in Earth observation, navigation, and data analysis. The increasing demand for swift deployment, technology demonstrations, and enhanced connectivity between civil and commercial industries further drives market growth and innovation in the United States.
Communication is the dominant application segment of the U.S. small satellite market, holding a 95.4% share in 2025. The growth is driven by amplified requirements for real-time connectivity, secure data communications, and worldwide internet services. These satellites enable broadband access, remote sensing, and navigation services, particularly in defense, commercial telecom, and emergency response networks.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












