
Vehicle-to-Grid Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Solution Type, Vehicle Type, Charging Type, Application and Region, 2025-2033
Vehicle-to-Grid Market Size and Share:
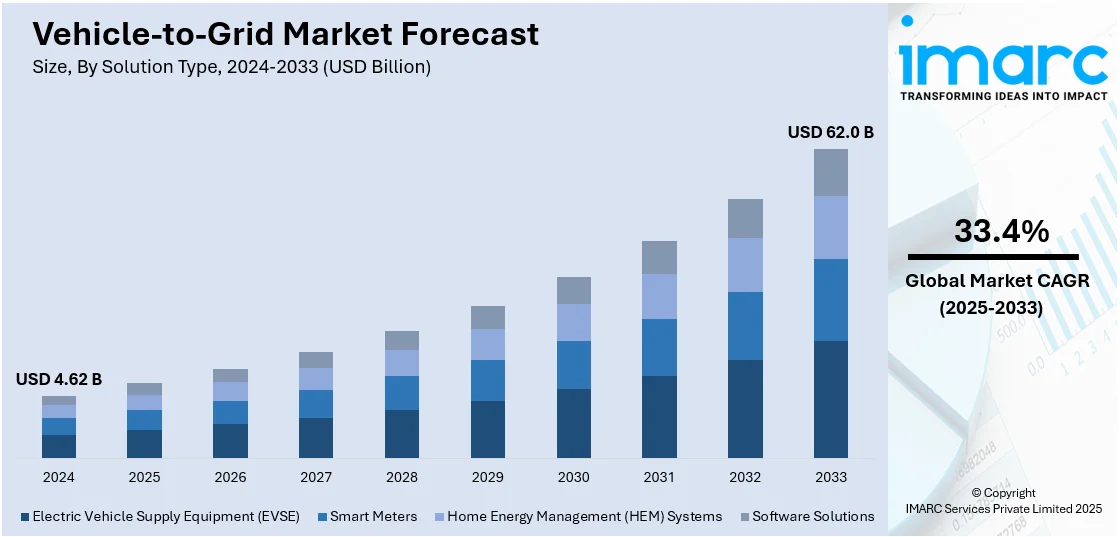
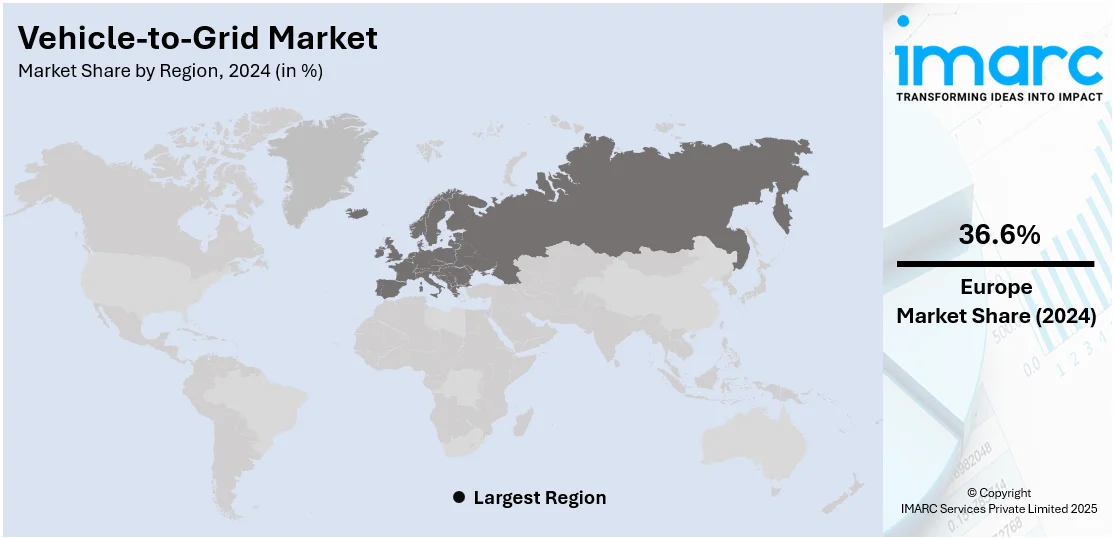
The global vehicle-to-grid market size was valued at USD 4.62 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 62.0 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 33.4% from 2025-2033. Europe currently dominates the market, holding a market share of 36.6% in 2024. At present, as individuals are becoming accustomed to electric vehicles (EVs) and their benefits, the demand for vehicle-to-grid systems is rising. Besides this, the increasing implementation of supportive government initiatives and policies is contributing to the expansion of the vehicle-to-grid market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033 |
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 4.62 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 62.0 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 33.4% |
At present, the market is growing as more people are employing EVs and looking for smart energy solutions. Vehicle-to-grid technology enables electric cars to send unused power back to the grid, which helps balance energy supply and demand. It supports the utilization of renewable energy by storing extra power and sharing it when needed. Besides this, governments and energy companies are promoting this system through incentives and new policies. Fleet operators also find value in using parked vehicles as energy sources. Apart from this, advancements in battery life and smart charging are making vehicle-to-grid more reliable and easier to manage. It reduces electricity costs and helps lower carbon emissions.
The United States has emerged as a major region in the vehicle-to-grid market owing to many factors. The rising use of EVs is fueling the vehicle-to-grid market growth. As more people and companies are adopting EVs, the potential to employ them as mobile energy sources is increasing. As per industry reports, in 2024, in the United States, the EV market achieved 1.56 Million EV sales, accounting for a 10% share of total light-duty vehicle revenue. Vehicle-to-grid technology helps manage peak electricity demand and supports renewable energy by storing and supplying power when needed. Government programs and clean energy goals are further encouraging the development of this technology. Utilities are also exploring vehicle-to-grid systems to improve grid reliability and reduce energy costs. Advancements in battery performance and smart charging systems are making vehicle-to-grid more practical.
Vehicle-to-Grid Market Trends:
Increasing production and sales of EVs
A surge in EV production and sales is positively influencing the market. According to Livemint, global EV sales grew by approximately 30% annually from 2013 to 2023. Notably, 13 countries surpassed 10% of new light-vehicle sales being electric. The International Energy Agency further reported that in 2023, sales of EVs were 3.5 Million more than in 2022, indicating a 35% increase compared to 2022. Almost 14 Million new EVs were registered worldwide in 2023, with battery electric cars making up 70% of the electric car inventory for the year. The rising user awareness and acceptance of EVs are also fostering a parallel trend for vehicle-to-grid systems. As people are becoming more accustomed to EVs and their advantages, the vehicle-to-grid concept is gaining traction. Vehicle owners are increasingly comfortable with the idea of their car batteries serving dual purposes, both for driving and energy storage/transfer. This shift in user behavior and perception is leading to the expansion of the market.
Supportive government initiatives and policies
Supportive government initiatives and policies are offering a favorable vehicle-to-grid market outlook. These measures lower the cost barriers for users and businesses, encouraging the adoption of vehicle-to-grid technology. Governments are also setting regulations and standards that aid in promoting renewable energy integration and grid stability, creating a conducive environment for vehicle-to-grid systems. Additionally, public investments in research and development (R&D) activities help advance vehicle-to-grid technologies, making them more efficient and accessible, thereby stimulating the market growth. For instance, in 2024, China’s National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) gave an order to set preliminary technical standards for incorporating new energy vehicles into the grid by 2025. The report anticipates that new energy vehicles will form a significant part of the country’s new storage infrastructure by 2030. Furthermore, the NDRC intends to initiate more than 50 pilot projects in areas with positive circumstances for vehicle-to-grid integration, such as the Yangtze River Delta, Beijing, Sichuan, the Pearl River Delta, and Chongqing.
Growing adoption of smart grids
The widespread adoption of smart grids is propelling the market growth. Smart grids excel in intelligently managing energy supply and demand, thereby enhancing grid stability, reliability, and efficiency. Vehicle-to-grid systems leverage this strength by serving as flexible energy resources. When connected to the smart grid, EVs can store surplus energy during low-demand periods and feed this energy back into the grid during peak demand times. This load-balancing capability significantly optimizes power distribution and helps prevent blackouts and power quality issues. Additionally, the widespread employment of smart grids is promoting the usage of renewable energy sources, which is crucial for the success of vehicle-to-grid technology. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), in 2022, spending on electricity grids grew by about 8%, driven by both developed and developing regions to support electrification and assimilate renewable energy. The European Union intended to allocate EUR 584 Billion (USD 633 Billion) by 2030, which included EUR 400 Billion for distribution networks. China revealed USD 77 Billion for 2023 and USD 329 Billion throughout its 14th Five-Year Plan, amounting to a total of USD 442 Billion. Japan launched a YEN 20 Trillion (USD 155 Billion) fund aimed at new grid technologies. India introduced a USD 36.8 Billion program for smart meters. The US Department of Energy suggested a USD 10.5 Billion initiative for enhancing the grid. The World Bank encouraged private sector investments in decentralized renewable energy for Africa.
Vehicle-to-Grid Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global vehicle-to-grid market, along with forecast at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on solution type, vehicle type, charging type, and application.
Analysis by Solution Type:
- Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE)
- Smart Meters
- Home Energy Management (HEM) Systems
- Software Solutions
Electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) held 83.5% of the market share in 2024. It serves as the main link between EVs and the power grid. This equipment controls the flow of electricity, allowing two-way charging and energy transfer. It supports communication between the vehicle and the grid, enabling smart energy management. As EV adoption is growing, the demand for reliable and intelligent charging systems is increasing. EVSE includes features like load balancing, real-time monitoring, and remote control, which are essential for vehicle-to-grid operations. Manufacturers continue to develop advanced charging units that handle bidirectional energy flow efficiently. Utilities and energy providers also prefer EVSE because it ensures safe and stable energy exchange. It plays an important role in peak shaving, grid balancing, and renewable energy integration. With its central role in enabling vehicle-to-grid functions, EVSE is becoming the leading solution in the market, supporting both residential and commercial applications.
Analysis by Vehicle Type:
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV)
- Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
Battery electric vehicle (BEV) accounts for 64.4% of the market share. It holds dominance because of its substantial battery capacities, offering considerable energy storage capabilities. Vehicle-to-grid technology enables BEVs to efficiently retain and release energy to the grid, stabilizing supply and demand. Furthermore, the rising uptake of BEVs, supported by improvements in battery technology, governmental support, and heightened environmental awareness, is strengthening their leadership in the vehicle-to-grid market. The IEA's yearly outlook report estimated that by 2035, BEVs and PHEVs were set to make up nearly two-thirds of worldwide automobile sales. In 2024, the sales of these vehicles grew by more than 20%, attaining 17 Million, up from nearly 14 Million in 2023. The forecast indicates that by 2030, close to one in three vehicles on Chinese streets and around one in five in the US and EU will be electric, according to existing policy conditions. Additionally, as per an article released by Electric Autonomy in May 2024, Canada saw 130,000 BEVs sold in 2023, representing a 35% rise compared to 2022 sales. According to the vehicle-to-grid market forecast, with the increasing awareness about the benefits of BEVs, the segment will continue to lead the market.
Analysis by Charging Type:
- Unidirectional Charging
- Bidirectional Charging
Bidirectional charging holds 78.4% of the market share. It allows EVs to receive and deliver power to the grid. This feature enables EVs to function as portable energy storage solutions, offering adaptability in energy management and improving grid stability. It facilitates the incorporation of renewable energy sources by retaining surplus energy during times of low usage and distributing it during high demand periods. Moreover, bidirectional charging can aid in lowering electricity expenses for users and create income, which in turn assists in promoting its uptake. For example, in June 2023, Renault revealed its intentions to implement bidirectional charging in the all-electric Renault 5, which was set to be the inaugural Renault model featuring this technology. The vehicle-to-grid service was set to debut with the Renault 5 in France and Germany in 2024, and then in the UK in 2025. This project was managed by Renault's mobility brand, Mobilize. Apart from this, as smart grids and clean energy goals are expanding, bidirectional charging is becoming essential for efficient energy management.
Analysis by Application:
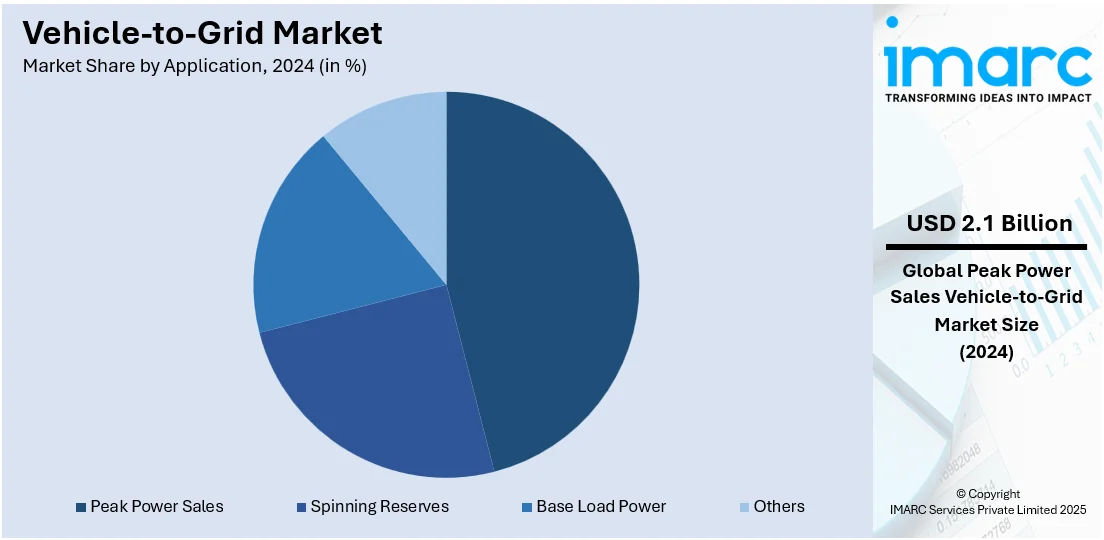
- Peak Power Sales
- Spinning Reserves
- Base Load Power
- Others
Peak power sales account for 46.3% of the market share. They offer an attractive income source for EV owners and utility providers. During high demand times, the grid needs extra power, and EVs can provide this energy from their batteries, allowing owners to receive compensation for their input. This method improves grid stability and effectiveness, decreases dependence on conventional power stations, and facilitates the incorporation of renewable energy sources. The economic advantages and grid advantages make peak power sales a key component in the vehicle-to-grid market. For example, in February 2024, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. revealed the introduction of the Nissan Energy Share service in Japan to increase the value of EVs. This service employed cutting-edge energy management technology to oversee EV battery charging and discharging, aimed at benefiting businesses and local governments. It provided load shifting via intelligent charging, peak reduction by controlling discharge in peak demand periods, optimal use of renewable energy through integration with solar panels, and synchronized charging schedules using bidirectional charging technology, assisting businesses in reaching renewable energy objectives.
Regional Analysis:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Asia-Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
Europe, accounting for a share of 36.6%, enjoys the leading position in the market. The market is experiencing robust growth, fueled by aggressive decarbonization targets, the rapid rise in EV adoption, and strong regulatory support for smart grid integration. According to Eurostat, the European Union attained a 2.6% decrease in GHG emissions during Q2 2024 compared to Q2 2023. The European Union’s Green Deal and Fit for 55 package mandate significant reductions in carbon emissions, encouraging member states to employ technologies that enhance energy efficiency and renewable integration, roles that vehicle-to-grid systems are well-suited to fulfill. Countries, such as the Netherlands, the UK, Germany, and France, are leading vehicle-to-grid deployment through pilot programs, dedicated funding, and inclusion of vehicle-to-grid in national energy strategies. Additionally, increasing renewable energy penetration, particularly wind and solar, is creating the need for demand-side flexibility, enabling grid operators to utilize vehicle-to-grid to manage intermittency and stabilize frequency. According to industry reports, in 2024, Europe added 16.4 GW of new wind power capacity, bringing the total to 285 GW. Between 2025 and 2030, Europe is projected to incorporate 187 GW of new wind energy capacity, increasing the total installations to 450 GW by 2030. Apart from this, automakers and energy companies are also forming partnerships to co-develop vehicle-to-grid solutions, facilitating overall industry expansion.
Key Regional Takeaways:
North America Vehicle-to-Grid Market Analysis
The region is noted for its strong EV adoption, advanced technology development, and supportive government policies. The region has a well-established EV infrastructure, including a growing network of smart charging stations. Major automakers and technology companies in North America are investing heavily in vehicle-to-grid research and innovations, creating advanced systems that connect vehicles to the grid. Utilities across the region are showing strong interest in using EVs to support grid stability and reduce peak energy demand. Government initiatives are promoting clean energy, offering incentives for EV use and funding for vehicle-to-grid pilot projects. The presence of key industry players, research institutions, and start-ups also helps drive progress. In addition, North America's focus on renewable energy and grid modernization owing to rising electricity demand is creating the need for flexible energy solutions. According to the Statistics Canada, in December 2024, Canadian electricity utilization increased by 7.4% compared to 2023, reaching 59.9 Million MWh. With a combination of innovations, investments, and policy support, North America is building a strong foundation for the growth of vehicle-to-grid technology and market leadership.
United States Vehicle-to-Grid Market Analysis
The United States vehicle-to-grid market, holding a share of 88.90%, is primarily driven by the growing adoption of EVs, supportive government policies, and increasing focus on grid resilience and energy decentralization. According to the Smart Electric Power Alliance (SEPA), during Q1 2023, 320,000 EVs were sold in the United States, registering a growth of 60% in comparison to Q1 2022. As EV penetration is rising, their potential as distributed energy storage assets is gaining traction among utilities and grid operators. Vehicle-to-grid technology enables bidirectional power flow between EVs and the grid, allowing stored energy in EV batteries to support peak load demands, integrate renewable sources, and provide ancillary services, such as frequency regulation. Additionally, federal and state-level initiatives are also fostering vehicle-to-grid pilot projects and infrastructure development. Utilities are beginning to offer incentives for vehicle-to-grid compatible chargers, while automakers are launching vehicle-to-grid-ready models, boosting technology availability. Increasing frequency of extreme weather events and associated power outages has also highlighted the importance of decentralized energy storage, with vehicle-to-grid providing a backup power source. Apart from this, advancements in battery durability and charging technologies are addressing concerns around battery degradation, making vehicle-to-grid more commercially viable. Fleet operators, particularly in school transportation and logistics, are also adopting vehicle-to-grid systems to monetize idle battery capacity, supporting the market growth.
Asia-Pacific Vehicle-to-Grid Market Analysis
In the Asia-Pacific region, the market is expanding due to the rising penetration of EVs, increasing renewable energy deployment, and strong government support for smart energy infrastructure. As per industry reports, renewable energy sources held a 29% share in the electricity generation sector in Asia in 2024. Countries, such as China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia, are at the forefront, investing heavily in EV ecosystem development and grid modernization. Japan has been a pioneer in vehicle-to-grid innovations, leveraging its advanced EV fleet and disaster-preparedness policies to promote bidirectional charging. China’s aggressive EV targets, combined with large-scale solar and wind projects, have heightened the need for flexible energy storage solutions, making vehicle-to-grid a strategic fit. In 2024, wind and solar energy accounted for 18% of electricity generation in China, as per industry reports. Besides this, the region’s increasing interest in distributed energy systems and peak load management is also encouraging vehicle-to-grid adoption.
Latin America Vehicle-to-Grid Market Analysis
In Latin America, the market is driven by increasing EV adoption, government focus on grid modernization, and the growing need for energy resilience in urban centers. For instance, Brazil registered 52,000 new registrations of EVs in 2023, reporting a growth of 181.1% in comparison to 2022. Countries, such as Brazil, Chile, and Colombia, are expanding EV infrastructure while exploring smart grid solutions to manage fluctuating energy demand and integrate renewable power sources. Vehicle-to-grid technology offers a cost-effective way to enhance grid stability, particularly in regions with variable solar and hydroelectric output. Additionally, regional interest in decentralized energy systems and partnerships with international energy firms are encouraging the development of pilot projects aimed at demonstrating the economic and technical viability of vehicle-to-grid in Latin America.
Middle East and Africa Vehicle-to-Grid Market Analysis
In the Middle East and Africa region, the market is witnessing growth on account of the growing investments in electric mobility, renewable energy expansion, and efforts to enhance energy security. For instance, in 2022, Saudi Arabia incorporated 2,100 MW of renewable energy capacity into the grid, increasing the overall installed capacity to 2,800 MW (2.8 GW). This signified a 300% rise in installed capacity, generating sufficient energy to supply over 520,000 homes. Moreover, countries, such as the UAE, are promoting EV adoption alongside ambitious solar and wind energy targets, creating the need for grid-balancing technologies like vehicle-to-grid. It is also being explored as a tool for optimizing energy utilization in high-demand urban centers and reducing reliance on fossil fuel-based power during peak hours.
Competitive Landscape:
Key players work on developing innovative solutions to meet the high demand. EV manufacturers are designing vehicles with bidirectional charging features that support energy transfer to the grid. Charging infrastructure companies are creating smart charging stations that enable smooth energy exchange. Battery manufacturers are improving energy storage capabilities to support frequent charging and discharging. Software companies are creating platforms that manage energy flow and connect vehicles with the grid in real time. Governments and regulatory bodies are also partnering with key players to create supportive policies and pilot programs. Moreover, energy companies and utilities are teaming up with technology providers to test and scale vehicle-to-grid systems. Through innovations, collaborations, and investments, these key players are moving the market forward and helping to build a cleaner, more flexible, and efficient energy system. For instance, in June 2024, Toyota Motor North America partnered with local energy provider Pepco for vehicle-to-grid research in Maryland, employing the Toyota bZ4X BEV. This project sought to investigate bidirectional power flow technology, allowing BEV owners to charge their vehicles and supply power back to the local grid. The vehicle-to-grid technology offered improved energy reliability, incorporation of renewable sources, and possible decreases in electricity expenses. Moreover, the alliance aimed to comprehend the charging behaviors and vehicle utilization of EV owners to promote the broad acceptance of vehicle-to-grid technology.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the vehicle-to-grid market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- AC Propulsion Inc.
- Coritech Services Inc.
- DENSO Corporation
- Enerdel Inc.
- ENGIE Group
- EV Grid
- Hitachi Ltd.
- Nissan Motor Company Ltd.
- NRG Energy Inc.
- OVO Energy Ltd.
Latest News and Developments:
- May 2025: Mercedes-Benz and the Mobility House revealed a Europe-wide collaboration aimed at promoting innovative solutions for vehicle-to-grid integration. Through this collaboration, the firms were set to merge their expertise in charging technologies and electromobility to seamlessly connect Mercedes-Benz EVs with the energy infrastructure. The joint initiative aimed to provide private homes with both unidirectional and bidirectional smart charging solutions.
- April 2025: The Kerala State Electricity Board (KSEB) formed a collaboration with IIT Bombay to initiate a pilot project assessing the viability of vehicle-to-grid technology in Kerala. KSEB sought to employ EVs to possibly enhance grid management and promote the incorporation of renewable energy sources in the state.
- April 2025: Essential Energy, partnering with CSIRO, Sigenergy, and AUSEV, revealed the successful incorporation of vehicle-to-grid technology into its system. By linking AUSEV's Ford F-150 Lightning to a CCS2 DC bi-directional charger and Sigenergy's storage system, this innovation enabled EVs to return power to the grid, improving renewable energy use and grid stability.
- April 2025: China revealed its intention to initiate trial projects in nine cities that could utilize the country’s growing EV fleet as batteries to assist the grid's power supply during peak demand periods. Vehicle-to-grid projects constituted the majority of the 30 initiatives located in cities, such as Beijing, Shenzhen, Shanghai, and Guangzhou.
- January 2025: Nuvve Holding Group introduced its latest lineup of products, expanding its selection of advanced unidirectional and bidirectional charging solutions. The latest chargers, with power levels between 20 kW and 360 kW, were aimed at fulfilling the distinct requirements of public infrastructure, school buses, commercial and private fleets, and microgrid functions.
Vehicle-to-Grid Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Solution Types Covered | Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), Smart Meters, Home Energy Management (HEM) Systems, Software Solutions |
| Vehicle Types Covered | Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV), Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV), Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) |
| Charging Types Covered | Unidirectional Charging, Bidirectional Charging |
| Applications Covered | Peak Power Sales, Spinning Reserves, Base Load Power, Others |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Russia, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | AC Propulsion Inc., Coritech Services Inc., DENSO Corporation, Enerdel Inc., ENGIE Group, EV Grid, Hitachi Ltd., Nissan Motor Company Ltd., NRG Energy Inc., OVO Energy Ltd., etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the vehicle-to-grid market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global vehicle-to-grid market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's five forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the vehicle-to-grid industry and its attractiveness.
- The competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The vehicle-to-grid market was valued at USD 4.62 Billion in 2024.
The vehicle-to-grid market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 33.4% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 62.0 Billion by 2033.
Government agencies and utility companies are encouraging vehicle-to-grid development through supportive policies, pilot programs, and investments in smart grid infrastructure. In addition, the rise of electric fleets in public transport and corporate logistics is making large-scale energy exchange more feasible. Moreover, advancements in battery performance and smart charging technologies are also enhancing the practicality of vehicle-to-grid systems.
Europe currently dominates the vehicle-to-grid market, accounting for a share of 36.6% in 2024, driven by rapid rise in EV adoption, and strong regulatory support for smart grid integration.
Some of the major players in the vehicle-to-grid market include AC Propulsion Inc., Coritech Services Inc., DENSO Corporation, Enerdel Inc., ENGIE Group, EV Grid, Hitachi Ltd., Nissan Motor Company Ltd., NRG Energy Inc., OVO Energy Ltd., etc.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












