
Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Blade Material, Blade Length, Location of Deployment, and Region, 2025-2033
Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Size and Share:
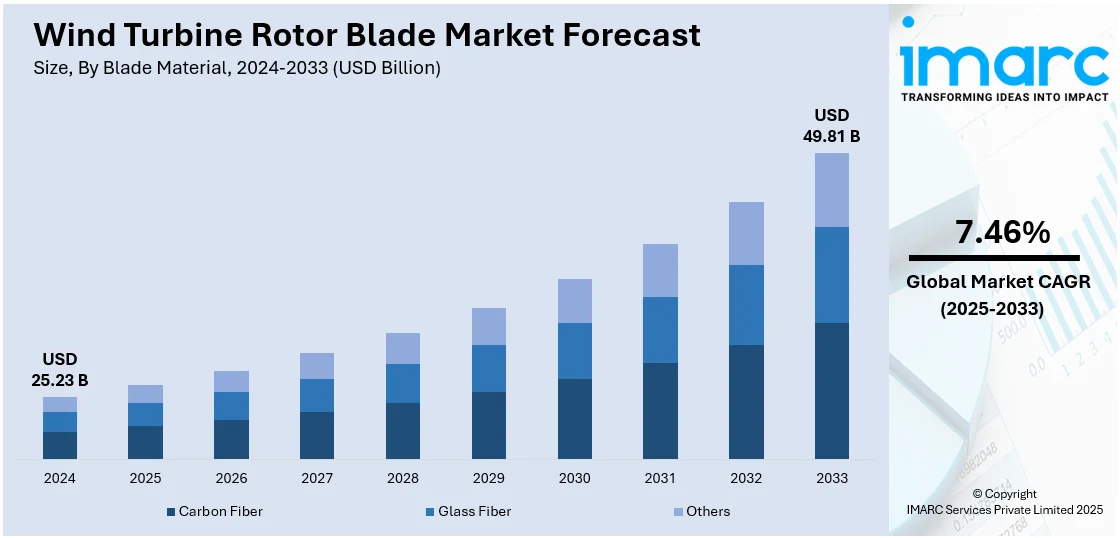
The global wind turbine rotor blade market size was valued at USD 25.23 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market to reach USD 49.81 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 7.46% during 2025-2033. Asia-Pacific currently dominates the market, holding a significant market share of 48.7% in 2024. The market is propelled by the worldwide shift toward renewable energy, increasing demand for clean power, and government schemes favoring wind energy schemes. Improvements in the design and materials of blades, growing investments in wind farms, environmental issues and the need to cut carbon emissions continue to drive adoption which further adds up to the increasing wind turbine rotor blades market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
|
Market Size in 2024
|
USD 25.23 Billion |
|
Market Forecast in 2033
|
USD 49.81 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 7.46% |
The rotor blade market for wind turbine is driven by the global shift to renewable energy and the imperative to cut carbon emissions. Governments across the world are initiating supporting policies, subsidies, and incentives that promote wind energy development, which has direct demand enhancement benefits for rotor blades. Material and design technology improvements, including lightweight composites and aerodynamic advancements, have improved energy efficiency and turbine life. Increasing energy demand, particularly in developing nations, is prompting massive investments in wind power infrastructure. Further, reducing costs of wind energy production make it increasingly competitive with fossil fuels, thereby fueling market growth. Rising concern for sustainability and energy security continues to induce utilities and private industry to increase wind energy use, propelling the wind turbine rotor blade market growth.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
The United States stands out as a key market disruptor, driven by the federal policies, including the Inflation Reduction Act, which have encouraged strong investment in renewable energy, including wind power. This has resulted in the creation and growth of manufacturing centers by corporations such as GE Vernova and Siemens Gamesa in the US with the purpose of providing the increasing demand for locally made components. Political changes, however, have brought uncertainties; an example is that the Trump administration's moves, such as putting offshore wind project approvals on hold and declaring tariffs, have intervened in ongoing and proposed projects, impacting investments as well as project schedules. These policy changes have generated an unstable climate for developers and manufacturers, forcing them to change rapidly to keep up with adapting rules. Notwithstanding these obstacles, the US continues to be a key driver in the wind turbine rotor blade market, and its policies and market processes continue to influence international industry trends
Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Trends:
Growing Demand for Renewable Energy and Wind Technology Adoption
The global wind turbine rotor blade market is undergoing a transformation driven by the increasing need for alternative energy sources. As fossil fuel resources deplete and concerns over energy security rise, many countries are accelerating the transition toward renewable energy. Among these alternatives, wind energy has emerged as a reliable and scalable option, leading to a surge in demand for wind turbines. As per the 2025 Global Wind Report by the Global Wind Energy Council, the wind sector witnessed a remarkable expansion, with 117 GW of new capacity installed in 2024, underscoring the urgency of scaling up renewable energy to meet the global goal of tripling clean energy capacity by 2030. Rotor blades, being a critical component in converting wind into usable power, are seeing significant advancements and higher production volumes. This trend is further reinforced by the extensive employment of wind power generation technology, particularly in regions where natural wind resources are abundant. From large-scale utility projects to decentralized community installations, wind technology is being integrated across various levels. The consistent evolution of rotor blade materials and aerodynamics, aimed at improving energy capture and reducing costs, also reflects the broader trend of innovation supporting this transition.
Government Support and Environmental Considerations
Escalating environmental concerns have played a crucial role in shaping the wind turbine rotor blade market outlook. Governments worldwide are under pressure to reduce carbon emissions and achieve sustainability goals, prompting governments to promote the uptake of eco-friendly assets, such as wind turbines, to mitigate carbon emissions. Supporting this trend, the Global Electricity Review 2025 indicates that clean power accounted for over 40% of global electricity generation in 2024, reinforcing the vital role of wind energy in the evolving energy landscape. Moreover, regulatory frameworks, subsidies, and tax incentives have made wind power more attractive for investors and developers, creating fertile ground for market growth. Wind turbine rotor blades are central to this eco-friendly movement, offering an effective means to harness natural energy while reducing environmental impact. Public awareness about climate change has also prompted calls for cleaner infrastructure, compelling energy providers to shift away from carbon-intensive methods. The result is a growing emphasis on developing longer, lighter, and more efficient rotor blades to maximize power generation from wind. As the push for green energy intensifies, wind turbines are becoming a preferred solution, firmly establishing rotor blades as a focal point of technological progress and investment.
Technological Innovation and Strategic Market Expansion
Innovation continues to be a defining factor in the wind turbine rotor blade market forecast, as manufacturers strive to develop blades that are not only efficient but also cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Advances in composite materials like that of carbon fiber and bio-based resins are enabling the production of longer, lighter blades that offer enhanced durability and performance. Simultaneously, digital technologies like sensor integration and predictive maintenance systems are improving operational reliability and reducing downtime. These innovations are helping wind energy compete more effectively with traditional energy sources. In addition, market players are expanding into new geographical areas with high wind potential, particularly in developing regions where infrastructure is rapidly evolving. Localization of manufacturing, strategic partnerships, and adaptation to regional wind profiles are becoming essential practices. With the global push for decarbonization and energy independence, the rotor blade segment remains a critical enabler of clean power, setting the stage for continued growth and diversification in the years ahead.
Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the global wind turbine rotor blade market, along with forecasts at the global, regional, and country levels from 2025-2033. The market has been categorized based on blade material, blade length, and location of deployment.
Analysis by Blade Material:
- Carbon Fiber
- Glass Fiber
- Others
Carbon fiber stands as the largest component in 2024. Carbon fiber has become a prominent segment within the wind turbine rotor blade industry owing to its increased strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and resistance to fatigue. As turbines expand in diameter to capture larger energy yields, the requirement for lighter and longer rotor blades has increased. Carbon fiber is better suited to serve these requirements compared to conventional materials such as fiberglass. Its greater tensile strength enables longer blades to be built without weakening structural integrity, enhancing overall turbine efficiency. Carbon fiber also lowers the overall weight of the blade, resulting in less mechanical stress on the drivetrain and support structures of the turbine. This increases the life of turbines and minimizes maintenance requirements. Even though carbon fiber costs more initially, its performance advantages and eventual cost savings are worth the investment, particularly in offshore wind farms where reliability and durability are paramount. Therefore, carbon fiber is increasingly being accepted as a desirable blade material.
Analysis by Blade Length:
- Below 45 Meters
- 45-60 Meters
- Above 60 Meters
45-60 meters leads the market share in 2024. 45 to 60-meter wind turbine blades have emerged as the leading segment within the global rotor blade market, as they are the optimal size for balancing energy capture, structural construction, and logistical practicability and is well suited to new onshore and offshore wind farms. Blades in this range are widely employed in 4–6 MW turbines, which form the lion's share of recent onshore installations. These turbines are especially widespread in areas with middling wind conditions, where big blades are impractical owing to transportation limitations. The 45–60 meter blades provide better energy output than shorter blades without being too big in terms of production, transportation, and installation. Innovations in design and materials further augmented the popularity of this blade length category. Companies are now using light yet strong materials, like carbon fiber composites, to enhance performance and save on maintenance. Furthermore, technological innovations in blade design, such as aerodynamic features, have resulted in greater efficiency and energy harnessing.
Analysis by Location of Deployment:
- Onshore
- Offshore
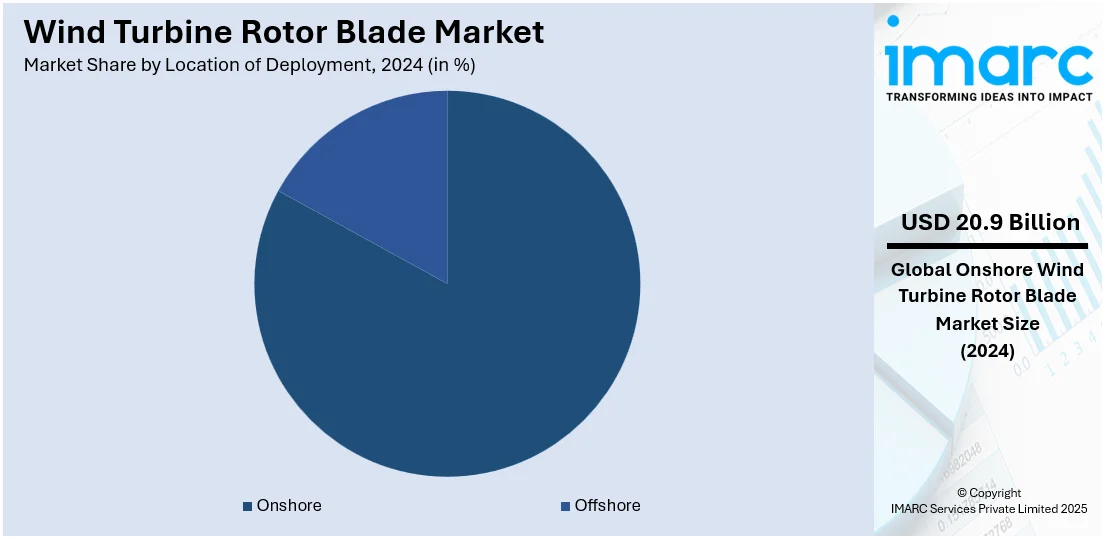
Onshore leads the market with 82.7% of market share in 2024. Onshore installation is the most dominant segment of the wind turbine rotor blade market because it is more accessible, cost-effective, and convenient with regard to logistics. Mounting wind turbines on land is typically simpler and less expensive compared to offshore ventures that need specialized vessels and equipment. Onshore wind farms can enjoy easier transportation of rotor blades and parts, as well as greater ease of maintenance and repair access. This practicality renders onshore locations particularly favorable to developers seeking to maximize budgets and timelines. The expansion of onshore wind power is further enabled by existing infrastructure and beneficial regulatory frameworks in most nations. Moreover, developments in rotor blade design have enabled the capture of wind power efficiently in a vast array of onshore locations, even locations with moderate wind velocities. Consequently, onshore wind continues to be very attractive for investment and the choice of many of the world's wind power projects.
Regional Analysis:
- North America
- United States
- Canada
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Australia
- Indonesia
- Others
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Russia
- Others
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Others
- Middle East and Africa
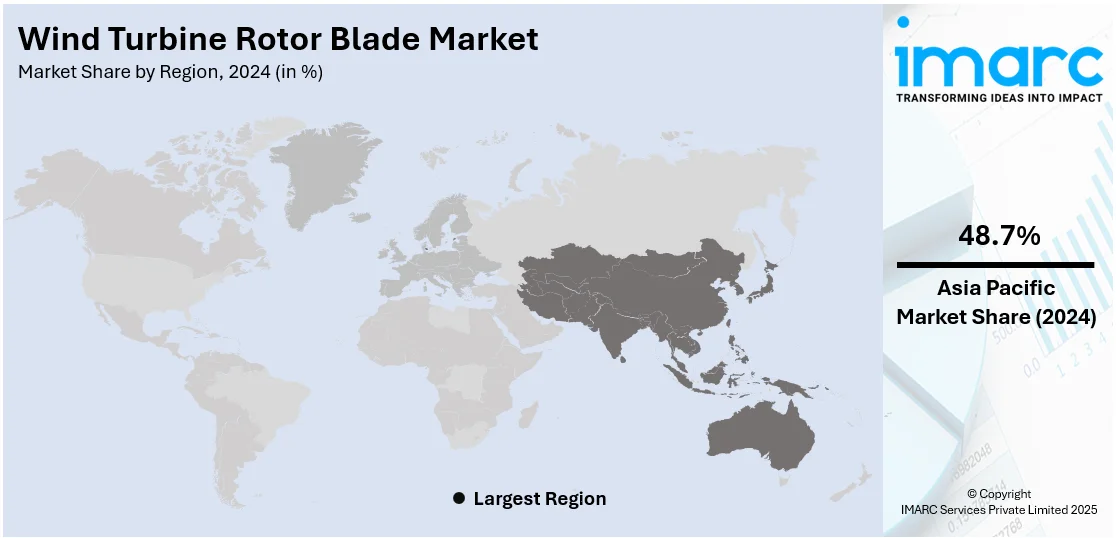
In 2024, Asia-Pacific accounted for the largest market share of 48.7%. The Asia Pacific region is the prime regional segment of the wind turbine rotor blade market due to its fast-growing industrialization, good government policies, and strong initiatives push toward the adoption of renewable energy. China, India, Japan, and South Korea are the leaders in this shift, with increased investments in wind energy infrastructure. China, however, has become a world leader in wind turbine production, with Mingyang Smart Energy and Goldwind as major industry players. The country's leadership is also explained through the large land space, allowing the construction of onshore wind farms, and its proximity to major manufacturing centers, providing direct supply chain efficiency to rotor blades. Additionally, the Asia Pacific region's pledge to go carbon neutral and lower its reliance on fossil fuels further propelled the demand for wind power solutions. Asia Pacific's strategic investments, combined with its strong manufacturing base and supportive policies, reinforce its dominance in the wind turbine rotor blade market.
Key Regiobnal Takeaways:
United States Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Analysis
In 2024, the United States accounted for 78.80% of the wind turbine rotor blade market in North America. The United States wind turbine rotor blade market is witnessing strong growth, driven by increased investments in large-scale wind energy projects and the rapid modernization of aging power infrastructure. The nation’s emphasis on grid decarbonization is fostering demand for high-efficiency rotor blades capable of generating more energy at lower wind speeds. Advancements in composite materials and aerodynamic blade design are supporting the trend toward longer, lighter blades, which enhance turbine performance. 30 active wind component manufacturing projects in the United States are monitored by the Clean Investment Monitor as of Q1 2025. These projects have the capacity to manufacture 4 GW of blades, 10 GW of towers, and 17 GW of nacelles annually. The market adoption is being further reinforced by the use of digital monitoring technology for performance optimization. Government incentives focused on renewable energy deployment and state-level clean energy standards are accelerating installations across various terrains. Offshore wind development, especially in deeper waters, is creating a surge in demand for specialized, high-durability rotor blades. Corporate procurement of wind energy is driving turbine technology upgrades, including rotor blade enhancements. Domestic supply chain expansion, transportation innovations, and modular assembly improve scalability, preparing for sustained expansion.
Europe Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Analysis
The Europe wind turbine rotor blade market is expanding steadily due to the continent's early adoption of renewable energy and its evolving energy transition strategies. According to Wind Europe, installations in the EU would need to reach 425 GW by 2030 in order to satisfy the 42.5% renewable energy objective set by the EU. The need for new rotor blades with increased efficiency and longer operating lifespans is one of the major investments in wind infrastructure being driven by this ambitious target. Emphasis on repowering existing wind farms is further fueling this demand. A rising focus on circular economy practices is encouraging the development of recyclable blade materials and sustainable end-of-life solutions. Additionally, the increasing role of wind in hybrid renewable energy systems is influencing blade design, favoring components that maximize output in variable wind conditions. Europe's leadership in floating wind projects is enhancing the need for adaptable rotor blade structures in complex offshore environments. Regional research hubs foster innovation, while energy independence and reducing fossil fuel imports support the European rotor blade market.
Asia Pacific Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Analysis
The Asia Pacific wind turbine rotor blade market is witnessing accelerated growth, driven by large-scale investments in renewable infrastructure and the region’s expanding power demand. According to the Press Information Bureau, wind power capacity in the region crossed the 50 GW mark, reaching 50,038 MW in Q1 2025, signaling the growing momentum of wind energy adoption. Utility-scale projects across diverse geographical zones are fostering the need for rotor blades tailored to varying wind profiles and terrain conditions. Rapid urbanization and industrialization are increasing pressure on energy systems, driving interest in high-capacity wind turbines with optimized blade geometries. Policy incentives are enhancing domestic manufacturing capabilities and promoting localization and innovation in technology. Advances in blade length and load-bearing capacity are enabling turbines to operate efficiently in low-wind areas. Public awareness about clean energy and supportive financing mechanisms are promoting adoption across emerging economies. Predictive maintenance technologies improve rotor blade lifecycle efficiency.
Latin America Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Analysis
The Latin American wind turbine rotor blade market is gaining traction, propelled by regional electrification goals and the growing appeal of wind energy as a cost-competitive power source. Expansive land availability and favorable wind conditions in inland areas are encouraging the deployment of large turbines with extended rotor blades. Brazil’s energy sector has reached a significant milestone, with the country’s installed electricity generation capacity surpassing 210 gigawatts (GW) in April 2025, wherein wind farms have become a major contributor, offering 33.74 GW (15.91%). Local governments are prioritizing infrastructure development to improve grid integration, increasing the demand for advanced rotor technology. Environmental considerations are influencing blade materials, and academic and technical partnerships are fostering innovation in blade testing and performance optimization.
Middle East and Africa Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Analysis
The Middle East and Africa wind turbine rotor blade market is developing steadily, supported by strategic national plans aiming to reduce dependency on fossil fuels. According to the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), the region is expected to install a total of 2.9 gigawatts (GW) of new onshore wind capacity in 2025, which is significantly driving the demand for rotor blades. Utility-scale wind installations in the desert and coastal areas demand optimized rotor blades for extreme temperatures and sand-laden environments. Aerodynamic optimization, global research collaborations, and rural electrification opportunities drive blade adoption. Rapid capacity growth and innovative solutions are expected to boost the market.
Competitive Landscape:
Major market players in the wind turbine rotor blade industry are implementing strategic efforts to increase product efficiency, minimize costs, and fulfill increasing demands on renewable energy. These players, including Vestas Wind Systems A/S, Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, S.A.U., and LM Wind Power, are spending largely on research and development to create longer, lighter, and more resilient rotor blades that boost energy yield and reduce the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE). These companies are also embracing high-tech materials such as carbon fiber composites to enhance blade strength and minimize weight. Strategic partnerships and collaborations are facilitating technology advancements and global outreach, and certain manufacturers are prioritizing blade designs that are modular to ease transportation and installation. Sustainability is also becoming a focus, with initiatives toward creating recyclable blade technologies and lowering production emissions. Moreover, manufacturers are also increasing manufacturing capacities, particularly in developing markets like India, China, and Brazil, to serve local demand and regional content requirements. Digitalization, such as the deployment of sensors and AI-based maintenance systems, is being adopted for integrating into blade technology to monitor performance and manage lifecycle more effectively. All these collectively play a significant role in staying competitive and facilitating the global transition toward cleaner energy forms.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the wind turbine rotor blade market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- Acciona S.A.
- Aeris Energy
- ENERCON Global GmbH
- LM Wind Power
- Moog Inc.
- Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, S.A.U.
- Sinoma Science & Technology Co., Ltd
- TPI Composites, Inc.
- Vestas Wind Systems A/S
Latest News and Developments:
- April 2025: JSW Energy announced their plans to commission two wind turbine blade manufacturing plants in Karnataka by 2025. These facilities aim to ensure a steady supply of rotor blades for the company's renewable energy projects, reduce reliance on imports, and optimize costs.
- February 2025: Senvion India partnered with Germany’s Voodin Blade Technology to develop wooden wind turbine rotor blades for its 4.2 MW platform. The initiative aims to enhance blade recyclability using engineered wood and Voodin’s mold-free LVL technology, with prototype testing planned to follow a detailed feasibility study.
- February 2025: Siemens Gamesa invested EUR 200 million to expand its Le Havre facility in France to manufacture 115-metre rotor blades (B115) for 14 MW offshore turbines. Construction began with completion expected in 2026, aiming to meet over 16 GW in orders and support France’s growing offshore wind sector.
- February 2025: As part of a 3,000 MW wind energy development project, Suzlon Group announced plans to build a wind turbine blade manufacturing facility in Vijayapura, Karnataka. The initiative marks a major boost to renewable energy manufacturing in the region.
- January 2025: We4Ce completed validation tests for its 2.5-3MW rotor blade design in India, collaborating with Suzlon and InDutch Composites Technology. The blade passed extreme fatigue tests, meeting IEC 61400-5:2020 certification standards.
Wind Turbine Rotor Blade Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Blade Materials Covered | Carbon Fiber, Glass Fiber, Others |
| Blade Lengths Covered | Below 45 Meters, 45-60 Meters, Above 60 Meters |
| Locations of Deployment Covered | Onshore, Offshore |
| Regions Covered | Asia Pacific, Europe, North America, Latin America, Middle East and Africa |
| Countries Covered | United States, Canada, Germany, France, United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, Russia, China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Indonesia, Brazil, Mexico |
| Companies Covered | Acciona S.A., Aeris Energy, ENERCON Global GmbH, LM Wind Power, Moog Inc., Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, S.A.U., Sinoma Science & Technology Co., Ltd, TPI Composites, Inc., Vestas Wind Systems A/S, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the wind turbine rotor blade market from 2019-2033.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the global wind turbine rotor blade market.
- The study maps the leading, as well as the fastest-growing, regional markets. It further enables stakeholders to identify the key country-level markets within each region.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the wind turbine rotor blade industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The wind turbine rotor blade market was valued at USD 25.23 Billion in 2024.
The wind turbine rotor blade market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 7.46% during 2025-2033, reaching a value of USD 49.81 Billion by 2033.
The wind turbine rotor blade market is driven by rising global demand for clean energy, government incentives, and technological advancements in blade design and materials. Increasing investments in wind power infrastructure and the push to reduce carbon emissions further support the market’s growth and long-term sustainability.
Asia Pacific currently dominates the wind turbine rotor blade market, driven by strong government policies, high levels of investment in renewable energy infrastructure, and improvements in blade design technology. China and India are at the forefront of the region's development, driven by rising energy requirements and carbon neutrality goals. The geographically diverse region with high coastlines and suitable wind patterns also supports the growth of onshore as well as offshore wind projects. All these factors combined are responsible for the Asia Pacific region leading the global wind turbine rotor blade market.
Some of the major players in the wind turbine rotor blade market include Acciona S.A., Aeris Energy, ENERCON Global GmbH, LM Wind Power, Moog Inc., Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, S.A.U., Sinoma Science & Technology Co., Ltd, TPI Composites, Inc., Vestas Wind Systems A/S, etc.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












