
Australia Banking Market Report by Banking Services (Retail Banking, Commercial Banking, Investment Banking, Corporate Banking, and Others), End User (Individual Consumers, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Large Corporations, Government and Public Sector Entities), and Region 2025-2033
Australia Banking Market Size and Share:
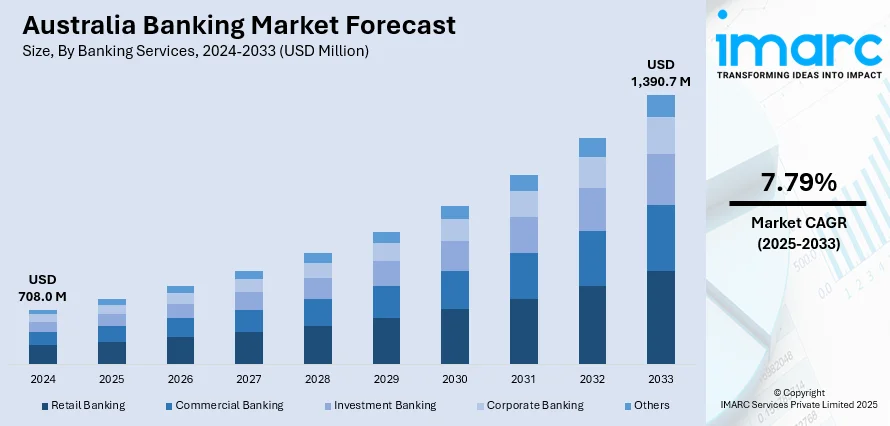
The Australia banking market size reached USD 708.0 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is projected to reach USD 1,390.7 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 7.79% during 2025-2033. The growing focus on improving client experience, rising use of digital wallets, contactless payments, and instant payment solutions, and increasing frequency of cyberattacks, including data breaches and identity theft, are some of the factors impelling the market growth.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
|
Market Size in 2024
|
USD 708.0 Million |
|
Market Forecast in 2033
|
USD 1,390.7 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 7.79% |
Key Trends of Australia Banking Market:
Growing Focus on Client Experience
Banks in Australia are making investments in user-friendly interfaces, around-the-clock user support, and smooth multi-channel experiences on both digital and physical platforms. Banks are improving their client service models to meet the demands of individuals who are seeking more intuitive services and spontaneous issue resolution. Chatbots, virtual assistants, and artificial intelligence (AI)-powered support systems are becoming popular to provide fast and personalized help. Furthermore, by incorporating real-time data analytics, banks can predict user needs in advance and offer custom solutions promptly. By constantly improving their services, banks are not only keeping up with the increasing demand of technology-savvy individuals but also outperforming their rivals. In 2024, National Australia Bank (NAB) introduced its "customer brain," powered by Pega's customer decision hub, to deliver personalized services across digital and human channels. This initiative increased client engagement by 40% and improved service interactions by analyzing user data and preferences.
To get more information of this market, Request Sample
Rise of Digital Payment Systems
The integration of digital wallets, contactless payments, and instant payment solutions is simplifying the payment procedure and providing increased convenience and security. Individuals are opting for cashless transactions, which is encouraging banks to focus on improving their digital payment infrastructure to meet the growing demand. This trend is driving competition within the market as banks compete to offer innovative and seamless payment options across mobile platforms and online services. Improved payment systems are also fostering client loyalty by offering a seamless experience and encouraging increased usage of banking services. Additionally, the ability to offer digital payments is positioning banks as leaders in financial technology, allowing them to capture new revenue streams from businesses and individuals alike. In 2024, NAB and PayPal introduced an in-app feature that enables NAB clients to effortlessly connect their debit and credit cards to their PayPal wallet via the NAB app. This partnership makes it easier to pay online and improve the digital shopping journey for NAB cardholders.
Increasing Investment in Cybersecurity
Australian banks are placing a high importance on cybersecurity due to the growing dependence on digital banking services. The increased frequency of cyberattacks, including data breaches and identity theft, is encouraging banks to invest heavily in advanced security systems to protect user information. Organizations are implementing strategies like biometric verification, encryption tech, and fraud detection to improve internet safety. These investments are essential not only to comply with regulatory standards but also to build user trust in a market where privacy concerns are on a rise. In 2024, Waave, an Australian fintech firm, introduced biometric verification for its enhanced Pay by Bank service. This function, included in the updated Waave Wallet, provides users with increased security by using fingerprint or Face ID authentication, which helps to reduce fraud and ensure a smooth payment process. In addition, Westpac introduced SaferPay in 2024, a scam detection feature powered by AI that is incorporated into its mobile banking application. This system notifies users about possible scams by showcasing interactive questions while making payments.
Growth Drivers of Australia Banking Market:
Population Growth and Urbanization
Australia is experiencing consistent population growth, primarily within urban areas such as Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane. This trend drives an increased demand for essential banking services, particularly in housing finance, savings accounts, and credit offerings. The expanding urban populace leads to greater residential development, resulting in an increased volume of home loans and infrastructure financing. Furthermore, the influx of migrants introduces new clients to the banking sector, many of whom seek customized banking solutions and multilingual assistance. To address this growing need, banks are enhancing their digital services and expanding their physical locations in rapidly growing suburbs. These changes contribute to a broader customer base and higher transaction volumes across retail banking services, thereby bolstering the overall Australia banking market share.
Rising Mortgage Lending
The aspiration to own property remains strong among many Australians, sustaining the demand for residential mortgages. Banks respond to this need with competitive loan offerings, refinancing alternatives, and expedited approval processes, particularly in urban areas experiencing high growth. Cities like Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane frequently see elevated property prices, which drive up loan amounts. The introduction of first-home buyer incentives and low-deposit loan schemes also attracts new borrowers. As the property market navigates through price fluctuations and regulatory adjustments, banks maintain a substantial portion of household debt through home loans. This ongoing stream of mortgage applications and refinancing significantly enhances Australia banking market demand.
Superannuation System
Australia's mandatory superannuation system obliges employers to allocate a portion of employees' salaries to retirement funds. This mechanism directs billions of dollars yearly into investment channels overseen by banks and financial institutions. The steady flow of funds promotes the growth of wealth management and investment advisory services. Banks derive income through asset management fees, fund administration, and financial planning associated with superannuation portfolios. With an aging demographic, interest in retirement income products, insurance-related services, and estate planning is on the rise. Banks that integrate superannuation services with digital tools and personalized guidance are well-positioned to strengthen client relationships and enhance profits, according to Australia banking market analysis.
Government Support of Australia Banking Market:
Prudential Oversight by APRA
The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) is pivotal in sustaining the resilience of the banking sector. It imposes stringent capital adequacy requirements, ensuring that banks maintain sufficient buffers to absorb losses during economic downturns. APRA also evaluates risk exposures, liquidity positions, and the results of stress tests to identify vulnerabilities early on. To retain their licenses, banks must adhere to internal controls, governance standards, and recovery plans. By concentrating on financial stability, APRA minimizes the risk of institutional failures and systemic crises. Its risk-based supervision fosters enduring confidence among investors, depositors, and global credit rating agencies, contributing to a more stable and trustworthy financial system. This regulatory certainty directly supports Australia banking market growth.
Consumer Protection via ASIC
The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) protects consumers in the financial industry by enforcing equitable practices, transparent disclosures, and ethical standards. It regulates how banks market products, address complaints, and manage conflicts of interest. ASIC mandates that banks acquire appropriate licenses and adhere to responsible lending requirements. It also investigates misconduct, imposes penalties, and publishes enforcement results to hold financial institutions accountable. This oversight enhances service quality and builds trust among individuals and small businesses utilizing retail banking services. ASIC’s focus on transparency and accountability ensures that customers receive fair treatment, promoting long-term engagement and stability in the financial system within the broader context of consumer rights.
Lender of Last Resort (RBA)
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) serves as a lender of last resort, providing emergency funding to solvent banks experiencing short-term liquidity challenges. This function is crucial in preventing short-term liquidity issues from developing into full-scale financial crises. In stressful situations such as market freeze or economic shocks the RBA can inject funds into the system through repurchase agreements or other liquidity facilities. This intervention restores confidence in interbank lending and lessens the risk of bank runs. The RBA’s safety net guarantees the continuity of credit flows and payment systems, both essential for economic stability. Its role enhances trust in the financial system during uncertain times.
Opportunities of Australia Banking Market:
Expansion in Regional Markets
As the major cities of Australia experience growing saturation, banks have the opportunity to tap into regional and rural areas that remain largely unexplored. These locations often possess unique financial requirements that are distinct from those in urban environments, including needs for agricultural financing, land loans, and small business loans tailored to local industries. By establishing a firm presence in these communities, banks can cultivate long-lasting relationships with individuals and businesses, providing specialized products such as farm mortgages, rural insurance, and community banking services. Engaging in regional expansion enables banks to benefit from local growth, nurture loyalty in underserved markets, and leverage the distinctive economic activities found in rural areas, ultimately aiding in market diversification and expanding their customer base.
Open Banking and Consumer Data Right (CDR)
The launch of open banking regulations and the Consumer Data Right (CDR) offers banks the chance to utilize customer data in a more effective manner, unveiling significant growth potential. By securely accessing and sharing customer data with consent, banks can provide customized financial products that are more aligned with individual needs. This data-driven strategy facilitates personalized services such as tailored savings plans, optimized loan products, and adaptive credit scoring. Moreover, the transparency introduced by open banking enhances customer trust and loyalty. With advancements in data analytics and AI, banks can elevate customer experiences, streamline their product offerings, and strengthen their relationships with clients, ultimately driving innovation and competitive edge in the financial services landscape.
Expansion of Wealth Management Services
Given Australia’s aging demographic and the increasing complexity of finances, there is a rising demand for wealth management services. Banks are well-positioned to broaden their offerings by delivering personalized retirement planning, investment guidance, and superannuation solutions. As individuals seek ways to secure their financial future, there is an escalating need for expert assistance in asset management, portfolio diversification, and retirement planning. Banks can provide customized advisory services, educational materials, and innovative investment options tailored to the requirements of retirees or those preparing for retirement. This shift towards personalized wealth management enhances customer relationships and creates a profitable revenue stream through fees, commissions, and asset management services.
Challenges of Australia Banking Market:
Regulatory Compliance and Oversight
The Australian banking sector is continuously challenged by rigorous regulatory standards set by organizations such as the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) and the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC). Adherence to capital adequacy norms, risk management protocols, and consumer protection legislation necessitates that banks allocate considerable resources toward monitoring, reporting, and upholding their financial practices. Non-compliance with these regulations can lead to severe penalties, legal issues, or damage to reputation. Furthermore, as regulations frequently change, banks are required to proactively adjust their operations to meet new expectations. While these regulations contribute to the stability and integrity of the banking system, they also elevate operational costs and complexity, highlighting the importance of specialized knowledge in risk management.
Rising Competition from Fintechs
Fintech firms and neobanks are swiftly reshaping the financial landscape by providing services like digital payments, personal loans, wealth management, and insurance offerings. This influx of fintech innovation has amplified competition for traditional banks, particularly in segments once dominated by established players. These fintech entities utilize advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics to offer quicker, more tailored, and cost-efficient financial solutions. Consequently, banks feel pressured to innovate rapidly to keep customers, enhance service efficiency, and maintain competitiveness. Institutions that resist adapting to this evolving competitive climate risk losing market share to more nimble, technology-driven challengers, compelling them to reassess their product offerings and business strategies.
Cybersecurity Risks
As digital banking continues to expand, cybersecurity threats have emerged as a critical concern for Australian banks. With an increasing number of consumers using online platforms for banking transactions, the likelihood of cyberattacks, data breaches, and fraud escalates significantly. Banks retain sensitive customer information, such as financial records, personal identification, and transaction histories, which makes them attractive targets for cybercriminals. Safeguarding these digital infrastructures is essential for maintaining customer trust and protecting their data. Banks must consistently invest in state-of-the-art cybersecurity solutions, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and real-time fraud detection systems. Failure to secure customer data can result in substantial financial losses, legal consequences, and irreparable damage to reputation. Therefore, tackling cybersecurity is an ongoing challenge for the banking industry.
Australia Banking Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on banking services, and end user.
Banking Services Insights:
- Retail Banking
- Commercial Banking
- Investment Banking
- Corporate Banking
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the banking services. This includes retail banking, commercial banking, investment banking, corporate banking, and others.
End User Insights:
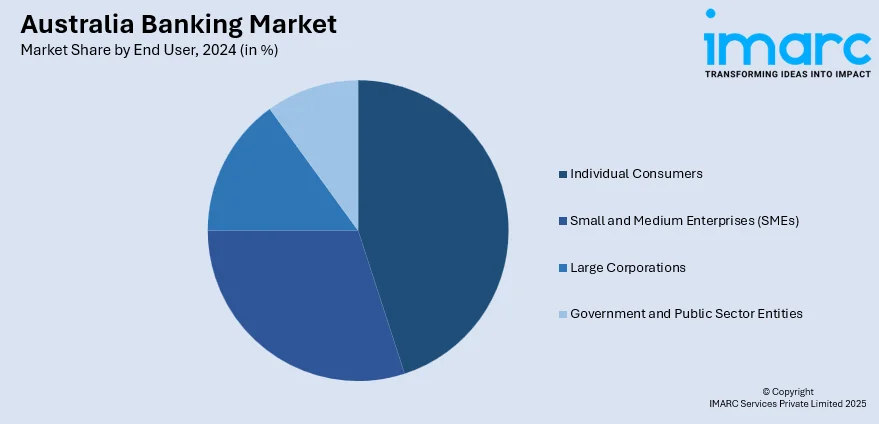
- Individual Consumers
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
- Large Corporations
- Government and Public Sector Entities
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end user have also been provided in the report. This includes individual consumers, small and medium enterprises (SMEs), large corporations, and government and public sector entities.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Banking Market News:
- October 2023: NAB had collaborated with Trovata, a US fintech firm, to introduce NAB Liquidity+, an online tool designed for managing corporate cash and predicting finances. This AI-driven solution aimed to enhance capital management and provide instant cash visibility for NAB's corporate clients.
- March 2024: The Great Southern Bank introduced the Business+ app, the initial all-inclusive online banking platform in Australia created for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The app provides services like transaction accounts, savings, and loans with the goal of simplifying banking for small business owners.
Australia Banking Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Banking Services Covered | Retail Banking, Commercial Banking, Investment Banking, Corporate Banking, Others |
| End Users Covered | Individual Consumers, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), Large Corporations, Government and Public Sector Entities |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia banking market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia banking market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia banking industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The banking market in Australia was valued at USD 708.0 Million in 2024.
The Australia banking market is projected to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.79% during 2025-2033.
The Australia banking market is expected to reach a value of USD 1,390.7 Million by 2033.
The Australia banking market is witnessing a shift toward digitalization, with more customers preferring mobile and online banking services. There is also a rise in fintech collaborations, as well as the growth of open banking.
Key growth drivers include population growth in urban areas, which fuels demand for housing loans and retail banking services. Rising mortgage lending, driven by homeownership goals, and the expanding wealth management sector, due to an aging population, also contribute to the market’s growth potential.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












