
Australia Biofuel Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Feedstock, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Biofuel Market Overview:
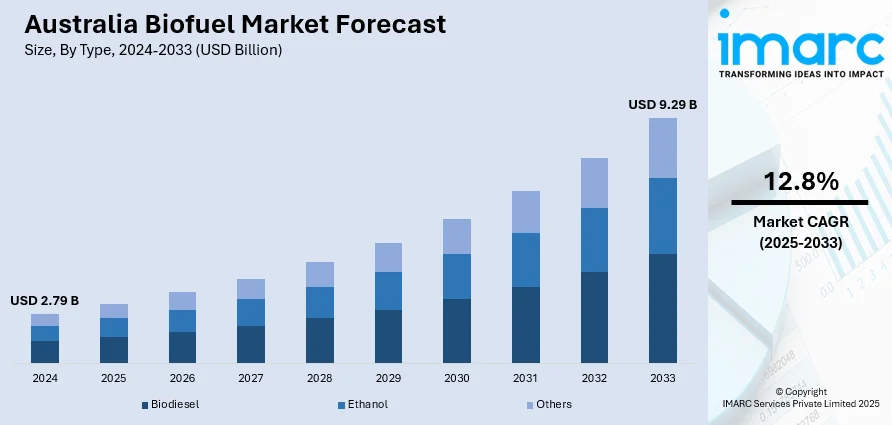
The Australia biofuel market size reached USD 2.79 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 9.29 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 12.8% during 2025-2033. Government policies promoting renewable energy, rising environmental concerns, demand for cleaner fuels in transportation, advancements in biofuel technology, and increased investment in sustainable agricultural practices are some of the factors contributing to Australia biofuel market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 2.79 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 9.29 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 12.8% |
Key Trends of Australia Biofuel Market:
Renewable Feedstock Development in the Biofuel Sector
Australia is seeing growing interest in renewable biofuel feedstocks as companies explore sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. One key development is the cultivation of Pongamia, a promising oilseed crop, to produce renewable diesel. With research focusing on growth conditions and oil yields, these efforts aim to reduce dependence on fossil fuels while supporting the country’s net-zero emissions targets by 2050. Additionally, initiatives are prioritizing local community engagement, including collaboration with Indigenous groups, reflecting a broader commitment to environmental and social responsibility. This focus on biofuel feedstock development in regions like Queensland is helping lay the groundwork for a sustainable, low-carbon energy future in Australia. These factors are intensifying the Australia biofuel market growth. For example, in September 2024, Rio Tinto launched a biofuels pilot in Australia, developing Pongamia seed farms to explore its potential as a renewable diesel feedstock. Located near Townsville in Queensland, the project will study growth conditions and seed oil yields. In partnership with Midway Limited, Rio Tinto aims to reduce fossil fuel reliance and advance its net-zero emissions goal by 2050. The initiative also prioritizes engagement with local communities and Traditional Owners.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Expansion of Sustainable Biofuel Feedstocks
Australia is witnessing increased efforts to scale up the production of sustainable biofuel feedstocks, particularly through the cultivation of Pongamia. With high oil content beans, Pongamia offers a promising alternative for biofuel production. Extensive research into its cultivars has been ongoing for over a decade, with a focus on maximizing oil yields while minimizing input requirements. These efforts are poised to contribute to the development of renewable fuels with lower greenhouse gas emissions, supporting the country’s shift away from fossil fuels. The expansion of such operations in Australia highlights the growing potential for sustainable agriculture to meet the rising demand for biofuels, while also offering environmental and economic benefits. For instance, in October 2024, Terviva Inc. secured backing from Chevron Renewable Energy Group to scale up its pongamia-growing operations in Australia for biofuel feedstock production. The company has spent 15 years researching pongamia cultivars, which yield high oil content beans.
Investment in Regional Refineries
In the changing landscape of Australia’s biofuel industry, there is a notable trend towards investment in regional and decentralized refineries. These smaller biofuel facilities, strategically situated near agricultural areas and sources of organic waste, are optimizing production by cutting transportation costs and reducing feedstock waste. This approach leads to faster processing, lowers carbon emissions associated with transportation, and enhances job opportunities within local communities. It further enables these communities to produce fuel from their own waste or agricultural by-products, thereby improving energy security and promoting sustainability in rural areas. As the demand for low-carbon fuel options rises, the development of region-specific biofuel infrastructure is significantly contributing to the growth of the Australia biofuel market share in both the transportation and industrial sectors.
Growth Factors of Australia Biofuel Market:
Government Support and Policy Frameworks
The proactive measures taken by the Australian government regarding renewable energy are crucial for advancing the biofuel sector. Mandates at both national and state levels concerning fuel blending, support for low-emission vehicles, and incentives for clean energy are motivating both producers and consumers to move towards bio-based fuel options. Policies aimed at decarbonizing the transport, aviation, and industrial sectors are enhancing the attractiveness of biofuels as viable and environmentally friendly alternatives. Additionally, the emissions reduction objectives outlined in climate action plans are compelling public and private sectors to adopt cleaner fuel solutions. Funding for pilot initiatives, modifying infrastructure, and developing feedstock are further encouraging market growth. Collectively, these initiatives are driving Australia biofuel market demand, promoting expansion and innovation in low-carbon energy production.
Abundant Agricultural Resources
Australia’s extensive and diverse agricultural sector provides a robust base for the expansion of its biofuel market. Key feedstocks such as sugarcane, canola, sorghum, and organic waste are plentiful and cultivated widely in rural areas. This availability facilitates large-scale production of ethanol and biodiesel and reduces reliance on imported bio-based materials. Farmers and agribusinesses can tap into new revenue opportunities by offering by-products and waste to bio-refineries. Furthermore, advancements in agriculture and crop rotation techniques are enhancing feedstock yields while ensuring food production remains unaffected. As the need for cleaner energy grows, these agricultural resources place Australia in a strong position for sustainable, self-sufficient biofuel manufacturing and bolstering its rural economy.
Rising Energy Security Concerns
Australia’s reliance on imported petroleum has heightened strategic worries regarding energy independence and supply reliability. In response, the country is increasingly focusing on domestic renewable fuel sources, such as biofuels, to mitigate risks associated with fluctuations in global oil prices and potential supply chain disruptions. Biofuels present a trustworthy, locally produced option that can serve the transport, industrial, and even defense sectors with lower environmental consequences. Investing in local bio-refineries and promoting regional feedstock production enhances national energy resilience. This initiative aligns with larger objectives aimed at decarbonizing essential infrastructure. According to Australia biofuel market analysis, energy security is a significant factor driving both governmental and private sector investments in domestic biofuel capacities.
Opportunities of Australia Biofuel Market:
Expansion into Aviation Biofuels
With increasing regulatory and environmental demands for decarbonization in global aviation, sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) has become a vital alternative to traditional jet fuels. Australia, endowed with abundant renewable resources and advancing biofuel production capabilities, is ideally positioned to take advantage of this market. Airlines and airport operators are progressively investing in SAF to achieve carbon reduction objectives and adhere to international emission standards. This presents an excellent opportunity for biofuel manufacturers to create aviation-grade fuels from local feedstocks like agricultural waste and used oils. Furthermore, partnering with airlines and government-supported aviation green initiatives can expedite market entry. As air travel resumes, the call for cleaner fuels is expected to rise, positioning aviation biofuels as a significant growth driver for Australia's biofuel sector.
Export Potential to Asia-Pacific
Australia’s geographical closeness to energy-hungry countries such as Japan, South Korea, and Singapore provides a valuable export opportunity for biofuels. These nations are actively seeking to diversify their energy portfolios and find low-carbon fuel alternatives to fulfill climate commitments. With its extensive agricultural resources, renewable feedstocks, and established trading relationships, Australia can become a notable supplier of bioethanol, biodiesel, and sustainable aviation fuel throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Investing in refining infrastructure for export, ensuring fuel quality standardization, and establishing trade collaborations will enhance global competitiveness. As international markets shift toward greener energy sources, leveraging the export potential will increase revenue for domestic producers and also solidify Australia’s role in the regional transition to clean energy.
Innovation in Advanced Biofuels
Australia has the chance to take the lead in the development and commercialization of second- and third-generation biofuels, which provide higher efficiency and sustainability compared to traditional feedstock-based options. Innovations like algae-derived biofuels, cellulosic ethanol, and waste-to-fuel technologies can utilize non-food biomass, thereby lessening land use pressures and emissions. With strong research capabilities and a growing interest in green technology initiatives, Australia can focus on R&D and pilot-scale facilities to unlock new fuel pathways. Advanced biofuels also promise long-term scalability and compatibility with current fuel infrastructure. As global energy systems evolve, Australia's leadership in biofuel innovation could result in competitive advantages, attract foreign investments, and establish new benchmarks for performance and sustainability within the broader bioenergy landscape.
Government Support of Australia Biofuel Market:
Blending Mandates and Fuel Standards
Australia’s biofuel sector is supported by regulations that require a minimum percentage of biofuels in conventional fuel supplies, particularly in regions like New South Wales and Queensland. These mandates generate consistent demand for ethanol and biodiesel, fostering long-term investments in production infrastructure. Fuel standards are also implemented to ensure quality and compatibility with existing engines, thereby enhancing consumer confidence. By formalizing the use of biofuels in transportation, the government effectively reduces greenhouse gas emissions while also boosting local agricultural economies that furnish the essential feedstocks. Such regulations are vital for cultivating a resilient and scalable biofuel market in Australia.
Financial Incentives and Grants
The Australian government provides various financial tools to accelerate the development of biofuels, including capital grants, tax rebates, and public-private co-investment initiatives. These incentives alleviate the financial pressures on companies involved in building bio-refineries, feedstock supply chains, and innovative fuel projects. Initiatives like the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) offer targeted funding for low-carbon endeavors, promoting scalability and commercial feasibility. By diminishing initial capital expenses and encouraging shared risks, these financial instruments attract private sector investment and foster the growth of local biofuel ecosystems. Such measures are crucial for creating economic pathways for clean fuel solutions and reinforcing the domestic bioenergy industry.
Research and Development Funding
Australia's dedication to innovation is reflected in the strong government backing for research and development in advanced biofuels. Organizations like CSIRO and ARENA provide funding for university-led initiatives and startups concentrating on next-generation technologies such as algae-based fuels, lignocellulosic ethanol, and waste-to-energy systems. These investments seek to address technical and commercial challenges while cultivating local expertise. By aligning biofuel research with national decarbonization strategies, the government guarantees that public funding yields scalable, future-oriented solutions. R&D support boosts Australia’s global competitiveness in renewable energy and establishes a solid foundation for sustainable fuel production tailored to local resources.
Investment and Development of Australia Biofuel Market:
Expansion of Domestic Bio-refineries
Developing domestic bio-refineries is integral to Australia’s biofuel strategy, with substantial investment being allocated for the construction of new facilities and technological enhancements. These initiatives aim to boost processing capabilities, lower energy consumption, and utilize a variety of feedstocks such as sugarcane, canola, and agricultural waste. Renovated facilities will be capable of producing both first-generation and advanced biofuels, improving overall supply stability. Long-term prospects, supported by government incentives and growing domestic demand, are attracting investors. As infrastructure expands, local economies benefit from job creation and better resource use. Enhancing refinery capabilities also aids Australia in reducing its reliance on imported fuels and reaching decarbonization targets through locally sourced renewable alternatives.
Private Sector Partnerships
Collaboration within the private sector is crucial for propelling Australia’s biofuel industry forward. Energy companies, agricultural tech providers, and clean technology startups are forming partnerships to drive innovation throughout the value chain, from cultivating feedstocks to processing and distributing fuels. These collaborations enable the transfer of technology, co-investment opportunities, and the commercialization of pilot projects. Joint ventures are particularly important in scaling advanced biofuels, such as those derived from algae or waste, which demand significant R&D and infrastructure investments. By tapping into the expertise and resources of the private sector, the biofuel market becomes more agile and economically viable. These partnerships also help mitigate risks, speed up market entry, and ensure alignment with industry needs and sustainability objectives.
Feedstock Supply Chain Strengthening
A robust and localized feedstock supply chain is vital for the sustained growth of Australia’s biofuel industry. Current investments are directed towards ensuring dependable sources of biomass, which include agricultural residues, oilseeds like canola, and food waste. Collaborations with farmers, cooperatives, and waste management organizations are fostering the development of integrated supply systems. Efforts are also being made to create logistics networks that facilitate timely and cost-effective transportation of raw materials to processing sites. This improves operational efficiency and lowers greenhouse gas emissions associated with long-distance shipping. Additionally, a varied feedstock base helps mitigate seasonal supply challenges and ensures continuous fuel production, while bolstering rural development by providing farmers with new income opportunities.
Challenges of Australia Biofuel Market:
High Production Costs
The production of biofuels in Australia frequently faces obstacles due to elevated input and operational costs, which render it less competitive against fossil fuels. Factors such as costly feedstock processing, limited economies of scale, and high logistics costs contribute to the increased overall production expenses. In contrast to traditional fuels, which benefit from established infrastructure and subsidies, biofuels often require considerable initial investments in specialized technology and equipment. These financial pressures lead to reduced profit margins for producers and higher prices for consumers, hampering widespread adoption in transportation and industrial sectors. Addressing this issue necessitates focused government support, advancements in technology, and broader market incentives to enhance cost-effectiveness.
Feedstock Availability and Consistency
Reliable and sustainable feedstock availability is a primary concern for Australia's biofuel industry. Sources like sugarcane, canola, and organic waste can be impacted by seasonal variations, climate conditions, and regional disparities. Furthermore, competition with the food and livestock industries can limit supply, leading to price fluctuations and challenges in production planning. Regional supply chain constraints exacerbate the unpredictability of raw material availability, complicating stable production for manufacturers. To ensure a steady and consistent supply, investments are required to diversify feedstock sources, improve logistics, and establish long-term agreements with agricultural suppliers to minimize reliance and mitigate supply risks.
Limited Infrastructure and Distribution Network
The development of Australia’s biofuel sector is constrained by insufficient infrastructure for blending, distribution, and retail. Much of the existing fuel infrastructure is designed for conventional petrol and diesel, creating challenges for biofuel integration. The lack of dedicated pipelines, fueling stations, and storage facilities, especially in remote and regional areas, limits access and usage. Moreover, facilities for blending biofuels and logistical support are underdeveloped, increasing costs and time within the supply chain. To expand this infrastructure, collaboration between public and private sectors, along with policy incentives and strategic investments, will be essential.
Australia Biofuel Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on type and feedstock.
Type Insights:
- Biodiesel
- Ethanol
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes biodiesel, ethanol, and others.
Feedstock Insights:
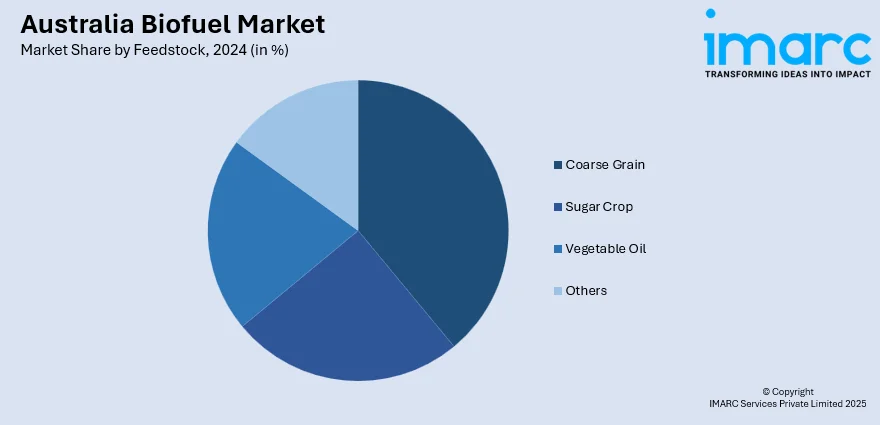
- Coarse Grain
- Sugar Crop
- Vegetable Oil
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the feedstock have also been provided in the report. This includes coarse grain, sugar crop, vegetable oil, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory and New South Wales
- Victoria and Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory and Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory and New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory and Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Biofuel Market News:
- In May 2025, Viva Energy Australia launched the nation's first commercial biofuel trial for cruise ships, utilizing a marine biofuel blend on Royal Caribbean's Celebrity Edge. The B20 blend, comprising 80% marine distillate and 20% biodiesel from used cooking oil, aims to support maritime decarbonization and promote sustainable fuel solutions.
- In April 2025, Virgin Australia and Qatar Airways, in partnership with Renewable Developments Australia, announced their plans to develop a Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) production facility in North Queensland's Charters Towers Region. The plant aims to produce up to 96 million litres of SAF annually, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- In September 2024, Comstock Fuels announced its partnership with Southern Asian Carbon Limited to construct three biofuel plants in Australia, with a focus on Sustainable Aviation Fuel. The USD 2.4 Billion project will produce over 160 million gallons of fuel annually, utilizing advanced biomass refining technology.
- In November 2024, S&W Seed Company completed the voluntary administration process for its Australian subsidiary, S&W Seed Company Australia. The company would now focus on its core operations, including a biofuels joint venture with Shell. S&W continues to explore sustainable biofuel feedstocks, particularly camelina, through its partnership. The restructuring involves transferring assets and providing transitional support to ensure S&W Australia operates as a standalone entity.
Australia Biofuel Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Biodiesel, Ethanol, Others |
| Feedstocks Covered | Coarse Grain, Sugar Crop, Vegetable Oil, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory and New South Wales, Victoria and Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory and Southern Australia, and Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia biofuel market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia biofuel market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia biofuel industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The biofuel market in Australia was valued at USD 2.79 Billion in 2024.
The Australia biofuel market is projected to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.8% during 2025-2033.
The Australia biofuel market is expected to reach a value of USD 9.29 Billion by 2033.
Rising focus on carbon neutrality, energy independence, and sustainable transport solutions are major drivers of Australia biofuel market. Supportive government policies, availability of local feedstock, and rising fuel blending mandates are encouraging investment and adoption, thereby driving the market growth.
The Australia biofuel market is witnessing a shift toward advanced biofuels, with increased interest in algae-based and waste-derived options. Integration of digital technologies for process optimization, growing collaboration with the aviation sector for sustainable fuels, and rising focus on lifecycle emissions tracking are also key emerging trends in the market.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












