
Australia Biosimilar Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Molecule, Manufacturing Type, Indication, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Biosimilar Market Overview:
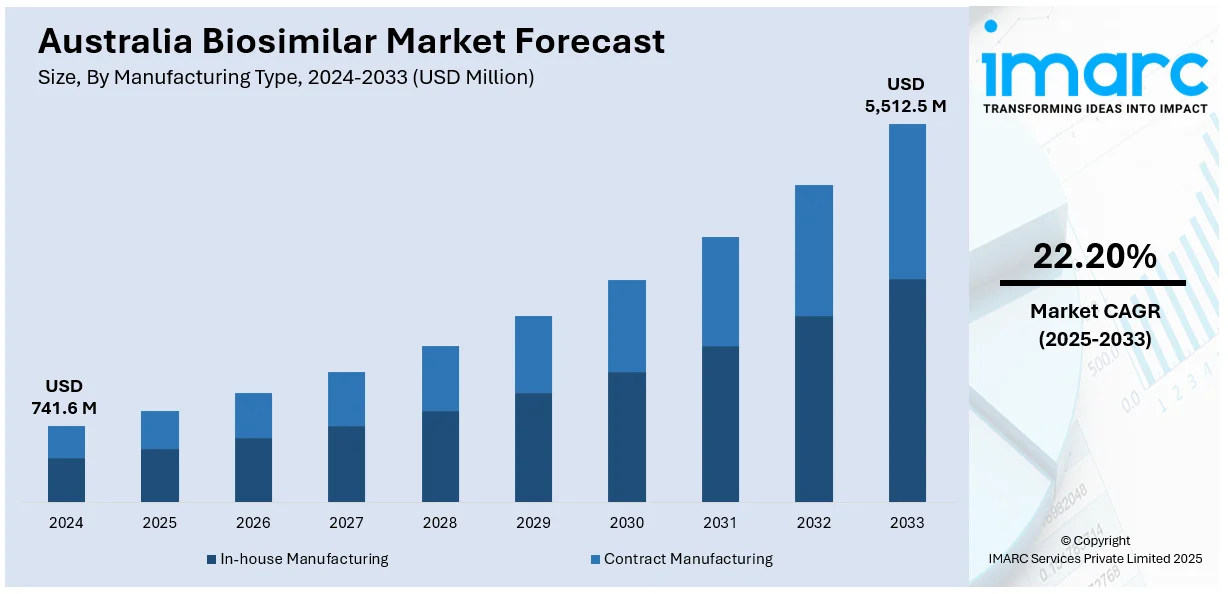
The Australia biosimilar market size reached USD 741.6 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is projected to reach USD 5,512.5 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 22.20% during 2025-2033. Australia’s market is growing steadily, driven by supportive government policies, PBS listings, and rising demand for affordable biologic treatments. Increasing clinical trial activity and broader acceptance among healthcare providers are also encouraging biosimilar development, competition, and early adoption across key therapeutic areas.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 741.6 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 5,512.5 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 22.20% |
Key Trends of Australia Biosimilar Market:
Policy Backing Expands Treatment Access
Australia’s market is being shaped by regulatory support and national reimbursement strategies. The government’s focus on affordable biologics has enabled broader access to advanced therapies while encouraging competition among biosimilar developers. A key driver has been the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee (PBAC), which evaluates medicines for subsidization under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS). These evaluations are essential to ensure patients receive cost-effective treatments without compromising on quality. In May 2024, PBAC recommended Amgen’s Wezlana, the first ustekinumab biosimilar, for PBS listing. This recommendation followed the product’s approval by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) in January 2024. Wezlana was approved for Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, plaque psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis—indications previously served only by higher-cost originator products. This move signaled a turning point, encouraging the integration of biosimilars into frontline treatment plans. The market has since seen greater acceptance among healthcare providers and improved availability across healthcare systems. As a result, patients now have more affordable alternatives, and biosimilar developers gain confidence to enter the Australian market. With continued PBAC endorsements and streamlined pathways for PBS listings, market participants are expected to increase, boosting availability and reducing therapy costs in chronic disease care.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Clinical Research Enhances Market Credibility
Australia’s strong clinical research environment is reinforcing its position in the global biosimilar space. The country’s regulatory stability, experienced trial infrastructure, and high standards of data collection attract international developers to base early-phase studies here. These trials not only bring investment but also affirm Australia’s scientific role in biosimilar validation. A key example is the Phase I study of SELARSDI (ustekinumab-taken), conducted in April 2024 by Alvotech and Teva in both Australia and New Zealand. This trial played a pivotal role in securing the U.S. FDA’s approval of SELARSDI. Though the commercial launch targets the U.S. market in 2025, the research base tied to Australia strengthens its global standing in biosimilar development. The country benefits from being seen as a credible site for high-quality early clinical programs. This encourages international collaboration and improves local expertise in biosimilar protocols. As more companies conduct studies in Australia, data generated here will increasingly influence regulatory decisions worldwide. This raises the country’s profile as not just a consumer of biosimilars but as a foundational part of their development. Growing clinical involvement is likely to result in earlier product availability domestically, improved physician trust, and smoother future regulatory approvals.
Increased Acceptance Among Healthcare Providers
In Australia, biosimilars are becoming more recognized as healthcare professionals grow more assured of their safety and effectiveness. This change is fueled by substantial clinical data, favorable real-world results, and clear regulatory direction from organizations like the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). Medical practitioners are increasingly willing to swap originator biologics for biosimilars, especially in managing chronic diseases within oncology, rheumatology, and gastroenterology. Pharmacists also play an essential role by educating patients and ensuring appropriate switching protocols. Ongoing training programs and government initiatives are promoting the adoption of biosimilars in both hospital and retail environments. Consequently, this wider acceptance among providers is significantly contributing to Australia biosimilar market growth.
Growth Drivers of Australia Biosimilar Market:
Patent Expiry of Biologics
With the expiration of patents on high-cost biologic drugs, more affordable biosimilars are entering the market, encouraging competition and innovation. This shift creates opportunities for both local and international manufacturers to launch biosimilars targeting chronic and critical conditions such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes. By emphasizing cost-effectiveness and therapeutic equivalence, these new products are gaining popularity with healthcare providers and patients. Regulatory clarity and expedited approval processes facilitate quicker market entry. As major biologics lose their exclusivity, pricing pressures are increasingly favoring biosimilar adoption, altering competitive dynamics. The Australia biosimilar market share is expected to expand significantly as biosimilars increasingly replace originator biologics across various therapeutic areas.
Rising Chronic Disease Burden
Australia is facing a significant rise in chronic conditions like cancer, autoimmune diseases, and diabetes, which often require long-term biologic therapies. Historically, the high costs of originator biologics have restricted access. However, biosimilars provide comparable safety and efficacy at lower prices, offering a scalable solution to meet the growing therapeutic demands of the population. Both public and private healthcare providers are increasingly looking to biosimilars to manage long-term treatment costs while ensuring broad accessibility. This focus on affordability, alongside increasing physician confidence and government backing, positions biosimilars as essential to future healthcare strategies. The Australia biosimilar market demand is expected to rise in response to this increase in chronic disease and the necessity for sustainable treatment options.
Private Sector Investment
Australia is seeing heightened interest from pharmaceutical companies eager to invest in the development and commercialization of biosimilars. Favorable regulatory conditions, increasing demand for affordable treatments, and a developing healthcare infrastructure make the country an appealing market. Companies are expanding their local operations, forming partnerships, and launching new products to seize market opportunities early. This wave of private sector involvement stimulates innovation and competition and enhances both affordability and supply security. Both start-ups and established companies are investing in clinical trials, manufacturing capabilities, and marketing strategies aimed at biosimilar advancement. According to Australia biosimilar market analysis, this increase in private investment is expected to boost market growth and improve access to advanced biologic therapies.
Opportunities of Australia Biosimilar Market:
Growth in Oncology and Autoimmune Therapies
Australia's biosimilar market is experiencing significant growth potential in therapeutic areas like oncology and autoimmune conditions. These fields are marked by high treatment expenses and long-term therapy needs, making them ideal candidates for more affordable alternatives. As an increasing number of biologics lose their patent protections, biosimilars can bridge the gap in affordability while maintaining efficacy. Healthcare systems and insurers are increasingly endorsing biosimilar prescriptions in cancer and chronic disease management to control expenses. The rising incidence of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and breast cancer ensures a steady demand, creating a favorable landscape for biosimilar manufacturers to broaden their presence and offer large-scale, affordable solutions.
Enhanced Tender and Hospital Adoption
Public procurement via hospital tenders offers a substantial opportunity for biosimilar manufacturers in Australia. With public healthcare budgets under pressure, tender-based purchasing enables government and hospital networks to acquire biosimilars at competitive rates while expanding patient access. This procurement method is particularly effective in high-demand areas like oncology, nephrology, and endocrinology. Biosimilar suppliers that adhere to rigorous quality and supply standards can secure long-term institutional contracts, resulting in stable revenue streams. Government initiatives promoting biosimilar adoption are positioning hospitals as critical distribution channels, making hospital and tender-based entry a potent strategy for market penetration.
Local Manufacturing Potential
Australia's commitment to domestic biomanufacturing presents an encouraging opportunity for biosimilar developers. As international supply chain disruptions highlight vulnerabilities in healthcare procurement, establishing local facilities can offer manufacturers a competitive advantage. Local production ensures quicker delivery times, better regulatory responsiveness, and less reliance on overseas logistics. It also facilitates public-private partnerships and government incentives aimed at strengthening the country’s healthcare sovereignty. Building domestic manufacturing capabilities supports long-term cost efficiencies and fosters trust among regulators and prescribers, aligning with Australia's broader goals of enhancing self-sufficiency in essential healthcare supplies.
Challenges of Australia Biosimilar Market:
Physician Reluctance
A major challenge confronting the biosimilar market in Australia is the hesitance of physicians to recommend these alternatives over originator biologics. Despite regulatory assurances regarding their safety and effectiveness, some healthcare providers are cautious about switching stable patients due to concerns about potential immunogenic responses and varying clinical outcomes. This cautious mindset is particularly prevalent in complex treatment areas such as oncology and autoimmune diseases. Physicians often seek extensive peer-reviewed data and post-marketing surveillance before feeling secure in prescribing biosimilars. Without increased clinician acceptance, the uptake of biosimilars may be hindered, delaying cost savings and limiting access to more affordable therapies for patients.
Limited Patient Awareness
Another considerable barrier in the Australian market is patient unfamiliarity with biosimilars. Many individuals mistakenly equate biosimilars with generic drugs or lack awareness of how these products compare in quality and effectiveness to originator biologics. This misunderstanding can lead to skepticism, mistrust, or reluctance when physicians suggest a switch. In chronic or life-threatening conditions, patients might prefer to stick with familiar treatments rather than consider new, untested options—even if they are more economical. Implementing effective public education campaigns and ensuring clear communication from healthcare providers are essential to improving patient confidence in biosimilars and promoting wider market acceptance across therapeutic areas.
Loyalty to Originator Brands
The established presence of originator biologics gives them an advantage in terms of brand recognition, physician preference, and patient trust. These companies often implement strong marketing strategies, loyalty programs, and continuing education initiatives that reinforce their market dominance and impede biosimilar adoption. Even when biosimilars present cost benefits, strong brand loyalty among both healthcare professionals and patients can slow their uptake. Furthermore, originator firms may use strategies like minor reformulations or extended patent protections to maintain their market position. Overcoming this loyalty will require biosimilar manufacturers in Australia to adopt aggressive pricing, present robust clinical evidence, and engage strategically with stakeholders.
Government Initiatives of Australia Biosimilar Market:
Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) Listing
The integration of biosimilars into the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) is crucial for improving patient access throughout Australia. By subsidizing the expenses of approved biosimilars, the government guarantees that patients can afford these medications while encouraging healthcare providers to explore cost-effective alternatives to original biologics. The PBS listing depends on stringent regulatory approvals that verify the safety, quality, and effectiveness of the biosimilar. This fosters trust among prescribers and promotes increased adoption. Additionally, the financial savings from PBS-supported biosimilars significantly support the long-term viability of Australia’s healthcare system. As more biosimilars are included in the PBS, competition increases, resulting in lower costs, a broader range of treatment options, and enhanced accessibility—thus bolstering the commercial environment of the Australian biosimilar market.
Encouraging Prescribing Practices
The Australian government is actively pursuing educational programs aimed at boosting physician confidence in prescribing biosimilars. These initiatives encompass seminars, assessments of clinical evidence, and continuing medical education (CME) programs that clarify the standards of biosimilarity and protocols for switching. By equipping healthcare professionals with transparent data and straightforward guidelines, policymakers intend to normalize the incorporation of biosimilars into standard treatment practices. Informed switching—transitioning patients from original biologics to biosimilars— is strongly advocated when clinically suitable, helping to lower treatment costs without sacrificing therapeutic results. These incentives for prescribing help eliminate barriers to adoption and facilitate the integration of biosimilars into daily clinical routines. Consequently, this initiative fosters trust and accelerates the acceptance of biosimilars across the Australian biosimilar market.
Substitution Policies at Pharmacy Level
The Australian government permits the substitution of biosimilars at the pharmacy level under specific conditions to facilitate adoption and minimize administrative hurdles. When a biosimilar is considered interchangeable and clinically appropriate, pharmacists are allowed to substitute it for the reference product, particularly when the prescribing physician does not explicitly object. This approach lessens the need for prescriber approval for each switch, promoting smoother access and improving efficiency in dispensing practices. To ensure safety and transparency, substitution protocols are supported by robust pharmacovigilance and diligent patient record-keeping. By empowering pharmacists, the government enhances the distribution of biosimilars while contributing to the efficiency of the healthcare system. This substitution policy directly aids in the expansion of the Australian biosimilar market.
Australia Biosimilar Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on molecule, manufacturing type, and indication.
Molecule Insights:
- Infliximab
- Insulin Glargine
- Epoetin Alfa
- Etanercept
- Filgrastim
- Somatropin
- Rituximab
- Follitropin Alfa
- Adalimumab
- Pegfilgrastim
- Trastuzumab
- Bevacizumab
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the molecule. This includes infliximab, insulin glargine, epoetin alfa, etanercept, filgrastim, somatropin, rituximab, follitropin alfa, adalimumab, pegfilgrastim, trastuzumab, bevacizumab, and others
Manufacturing Type Insights:
- In-house Manufacturing
- Contract Manufacturing
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the manufacturing type have also been provided in the report. This includes in-house manufacturing and contract manufacturing.
Indication Insights:
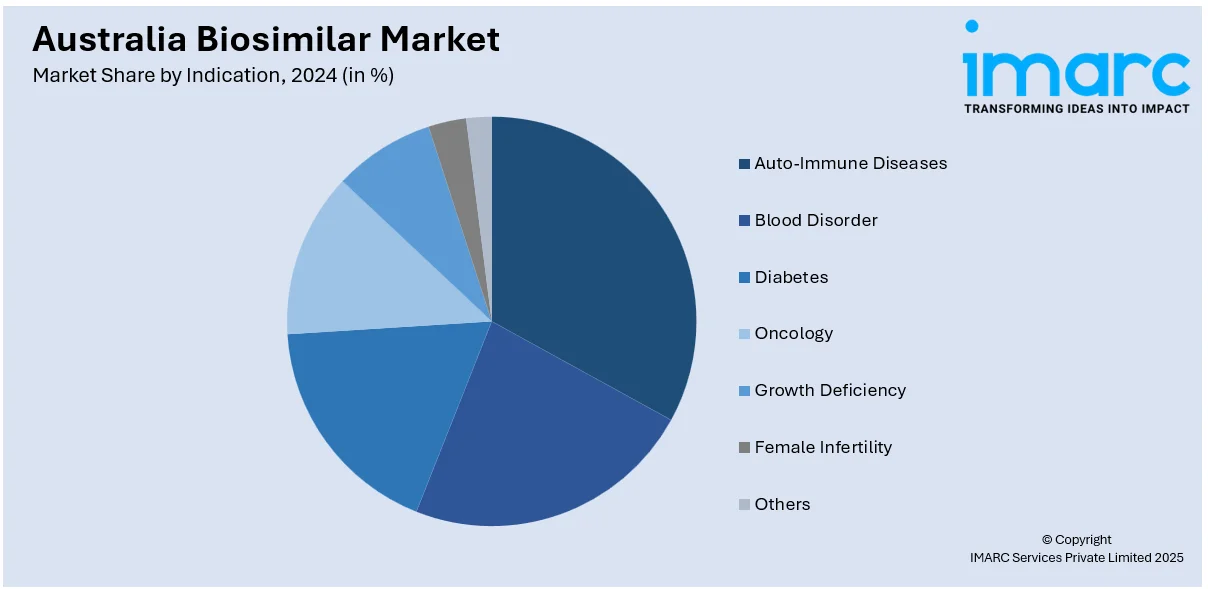
- Auto-Immune Diseases
- Blood Disorder
- Diabetes
- Oncology
- Growth Deficiency
- Female Infertility
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the indication have also been provided in the report. This includes auto-immune diseases, blood disorder, diabetes, oncology, growth deficiency, female infertility, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia Canada
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Biosimilar Market News:
- In April 2025, Sandoz's Tyruko become the first biosimilar to natalizumab approved in Australia, receiving TGA approval. This 300mg/15mL concentrate is indicated for treating relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. Sandoz has exclusive commercialization rights through its 2019 agreement with Polpharma Biologics.
- In April 2025, Celltrion's denosumab biosimilars, Stoboclo and Osenvelt, received approval from Australia's TGA, marking a significant milestone as the second sponsor to do so.
- In February 2025, Australia’s TGA approved Uteknix, a biosimilar to Stelara® (ustekinumab) by Alvotech and Cipla, available in 90 mg and 45 mg formulations. Indicated for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, Uteknix is the fifth ustekinumab biosimilar approved in Australia.
- In November 2024, Australia’s ARTG approved five new denosumab brands by Amgen, signaling anticipation of biosimilar competition. This followed August 2024 approvals of Sandoz’s biosimilars, Jubbonti and Wyost. The development boosted market readiness, increasing competition and paving the way for wider biosimilar access.
- In October 2024, Australia’s TGA approved Samsung Bioepis’ Epyztek, a ustekinumab biosimilar, in three formulations. This marked the fourth ustekinumab biosimilar approval, strengthening biosimilar competition. The move expanded treatment options and was expected to reduce costs, supporting broader market acceptance and adoption of biosimilars.
Australia Biosimilar Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Molecules Covered | Infliximab, Insulin Glargine, Epoetin Alfa, Etanercept, Filgrastim, Somatropin, Rituximab, Follitropin Alfa, Adalimumab, Pegfilgrastim, Trastuzumab, Bevacizumab, Others |
| Indications Covered | In-house Manufacturing, Contract Manufacturing |
| Manufacturing Types Covered | Auto-Immune Diseases, Blood Disorder, Diabetes, Oncology, Growth Deficiency, Female Infertility, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia biosimilar market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia biosimilar market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia biosimilar industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The biosimilar market in Australia was valued at USD 741.6 Million in 2024.
The Australia biosimilar market is projected to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.20% during 2025-2033.
The Australia biosimilar market is expected to reach a value of USD 5,512.5 Million by 2033.
Key factors contributing to growth include support from government through PBS listings, increasing demand for affordable biologic treatments, and a rise in chronic disease cases. Efforts to educate healthcare providers, coupled with clearer regulations, are facilitating greater acceptance in the market. The expansion of biosimilar products across various therapeutic areas is further enhancing commercial potential and ensuring long-term market presence.
The major key trends of the Australia biosimilar market are the rising adoption of biosimilars due to patent expirations of major biologics, enhanced clinical data supporting interchangeability, and broader payer support. Digital platforms and telehealth are also increasing awareness and accessibility, while pharmacy-level substitutions are streamlining patient access and reducing costs.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












