
Australia Carbon Credit Market Report by Type (Compliance, Voluntary), Project Type (Avoidance/Reduction Projects, Removal/Sequestration Projects, Nature-based, Technology-based), End-Use (Power, Energy, Aviation, Transportation, Buildings, Industrial, and Others) and Region 2025-2033
Australia Carbon Credit Market Size and Share:
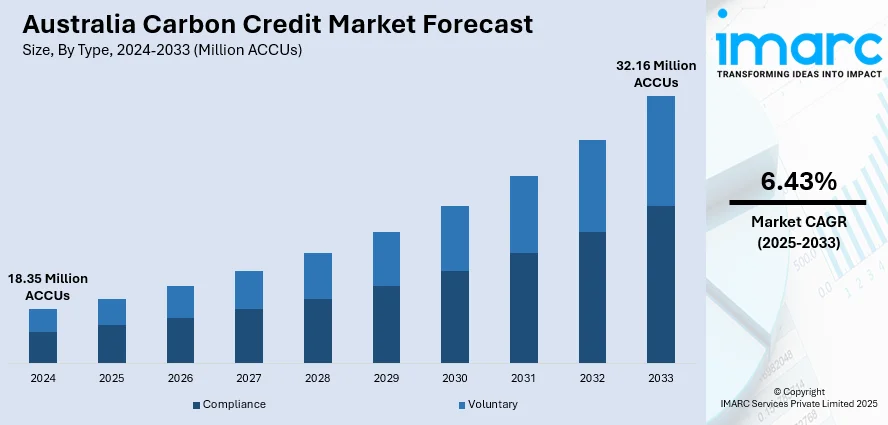
The Australia carbon credit market size reached 18.35 Million ACCUs in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach 32.16 Million ACCUs by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 6.43% during 2025-2033. The industry is expanding significantly due to the favorable government policies and regulations, increased dedication to corporate social responsibility, expanded international trade prospects, and significant expansion in renewable energy projects.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | 18.35 Million ACCUs |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | 32.16 Million ACCUs |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 6.43% |
Key Trends of Australia Carbon Credit Market:
Government Policies and Regulations
Australia’s carbon credit market is primarily driven by government policies and regulatory frameworks, particularly the Emissions Reduction Fund (ERF) and the Safeguard Mechanism. The ERF provides financial incentives for businesses, landowners, and communities to adopt practices that reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Through this, participants can generate Australian Carbon Credit Units (ACCUs), which are tradeable assets in the carbon market. The Safeguard Mechanism complements the ERF by setting baseline emissions for large industrial facilities. When companies exceed their emissions limit, they are required to purchase ACCUs to offset the excess, thus creating demand in the market. These policies foster a regulated environment that encourages innovation and investment in emissions-reducing technologies, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS) and renewable energy projects, further increasing the Australia carbon credit market share.
To get more information of this market, Request Sample
Corporate Sustainability Goals
Corporations across Australia are increasingly adopting ambitious sustainability goals, including pledges to achieve net-zero emissions. This is a significant factor driving the country’s carbon credit market. Businesses in sectors with historically high carbon footprints, such mining, energy, manufacturing, and agriculture, are looking for ways to lessen their environmental effect. Carbon credits offer an effective solution for these companies to offset emissions that cannot be eliminated through operational changes. The growing trend of corporate sustainability reporting and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards is pushing businesses to take meaningful steps toward reducing emissions. Public pressure from stakeholders, including investors, consumers, and regulatory bodies, is also motivating companies to adopt these practices, which adds to the Australia carbon credit market demand.
International Trade Opportunities
Australia’s carbon credit market benefits significantly from international trade opportunities. The country’s carbon credits are recognized globally, which allows Australian businesses to export credits to foreign markets, particularly in regions with more stringent emissions targets. This has opened up new revenue streams for companies participating in carbon reduction projects, as they can sell their Australian Carbon Credit Units (ACCUs) internationally. Australia's competitive advantage is further strengthened by its close proximity to important Asian markets, where there is a growing demand for carbon credits as a result of stringent environmental rules and corporate sustainability pledges. Moreover, international climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, emphasize the importance of cross-border cooperation in emissions reduction, paving the way for international carbon trading.
Growth Drivers of Australia Carbon Credit Market:
International Climate Commitments and Trade Alignment
According to the Australia carbon credit market analysis, the region’s resolve to meet international climate commitments and global trade expectations is a significant factor driving growth of the industry. As a signatory to international climate pacts, such as the Paris Agreement, Australia is increasingly being called upon to show significant reductions in national emissions. To achieve these, the nation is incorporating carbon credits as an essential mechanism for balancing out its emissions mix by sectors. Furthermore, Australia's trading relations—especially with carbon-vigilant markets such as the European Union and sections of Asia—are encouraging the implementation of carbon accountability. Export-oriented sectors like mining and agriculture are increasingly recognizing the imperative to prove low-carbon credentials in order to stay competitive. As carbon border adjustment mechanisms gain traction overseas, capacity to tap and trade credible domestic carbon credits is becoming a commercial necessity. External drivers are also prompting the building of a strong and open carbon credit market serving both compliance and competitiveness.
Increasing Land Sector Involvement and Natural Resource Capability
Australia's expansive and varied terrain offers a special set of carbon sequestration opportunities, especially within the land sector. Australia's large rangelands, agricultural regions, and forests give it a perfect location for nature-based carbon offset initiatives like reforestation, soil carbon increase, and savanna fire management. These projects are particularly dominant in areas such as Northern Australia and Western Queensland, where landholders have the opportunity to be economically rewarded while contributing to environmental objectives. The growing engagement of Indigenous communities, who control vast amounts of land, also enhances the potential of the carbon credit system. These communities are using traditional knowledge to adopt sustainable land management strategies that earn credits while advancing ecological and cultural outcomes. The increasing consciousness of the land sector and its ability to engage in carbon markets, fostered by government initiatives, NGOs, and carbon project developers, have opened fresh opportunities, contributing significantly to the Australia carbon credit market growth.
Financial Sector Engagement and Carbon as an Asset Class
The other significant force behind the expansion of Australia's carbon credit market is the growing participation of financial institutions and investors who today see carbon credits as a legitimate asset class. Banks, investment houses, and superannuation funds are seeing the potential of carbon markets as an asset class for diversification as well as long-term return. This has resulted in increased interest in funding carbon farming projects and investing in projects with high-integrity credits. Financial institutions are also offering custom products and advisory services to landholders and project developers so that they may more easily pass through the technical and regulatory complexities of the market. In addition, the emergence of carbon credit exchanges and blockchain-based tracking platforms is improving the transparency and liquidity in the market, drawing even more institutions into the market. As carbon credits get incorporated into financial risk approaches and green investment models, their function in Australia's economy is increasing—driving expansion in market size, sophistication, and long-term stability.
Australia Carbon Credit Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on type, project type, and end-use.
Type Insights:
- Compliance
- Voluntary
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes compliance and voluntary.
Project Type Insights:
- Avoidance/Reduction Projects
- Removal/Sequestration Projects
- Nature-based
- Technology-based
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the project type have also been provided in the report. This includes avoidance/reduction projects and removal/sequestration projects (nature-based and technology-based).
End-Use Insights:
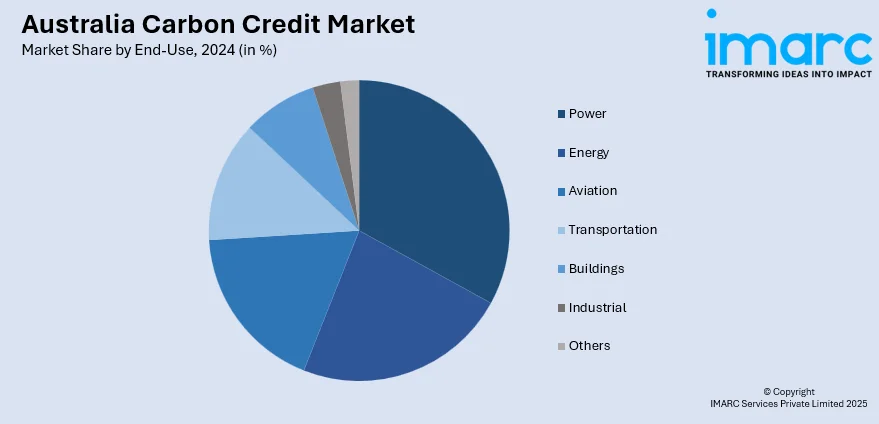
- Power
- Energy
- Aviation
- Transportation
- Buildings
- Industrial
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end-use. This includes power, energy, aviation, transportation, buildings, industrial, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Carbon Credit Market News:
- In December 2023, Clean Energy Regulator signed a contract with Trovio Group to develop the Unit & Certificate Register that will house the registries of different credits, including the Australian Carbon Credit units (ACCUs) and large-scale generation certificates (LGCs).
- In August 2024, Australian airline Qantas announced its plan to fund carbon credit projects. The company will contribute to a new fund, which is designed to develop high-integrity, nature-based carbon projects in the country.
Australia Carbon Credit Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million ACCUs |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Compliance, Voluntary |
| Project Types Covered |
|
| End-Uses Covered | Power, Energy, Aviation, Transportation, Buildings, Industrial, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia carbon credit market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia carbon credit market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia carbon credit industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia carbon credit market reached 18.35 Million ACCUs in 2024.
The Australia carbon credit market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.43% during 2025-2033.
The Australia carbon credit market is expected to reach 32.16 Million ACCUs by 2033.
The Australia carbon credit market is growing due to strengthened emissions policies, expanding land-based offset projects, and increasing corporate demand for sustainable solutions. Advances in carbon accounting and financial sector interest are also boosting market transparency and investment, driving a robust and evolving market that supports the nation’s climate commitments and economic goals.
The Australia carbon credit market is driven by strong government climate policies, vast natural landscapes suitable for carbon sequestration, and growing corporate commitments to sustainability. Additionally, increasing investor interest and international trade pressures encourage the development and adoption of carbon offset projects, supporting both environmental goals and economic growth across the country.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












