
Australia Digital Twin Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Technology, End Use, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Digital Twin Market Overview:
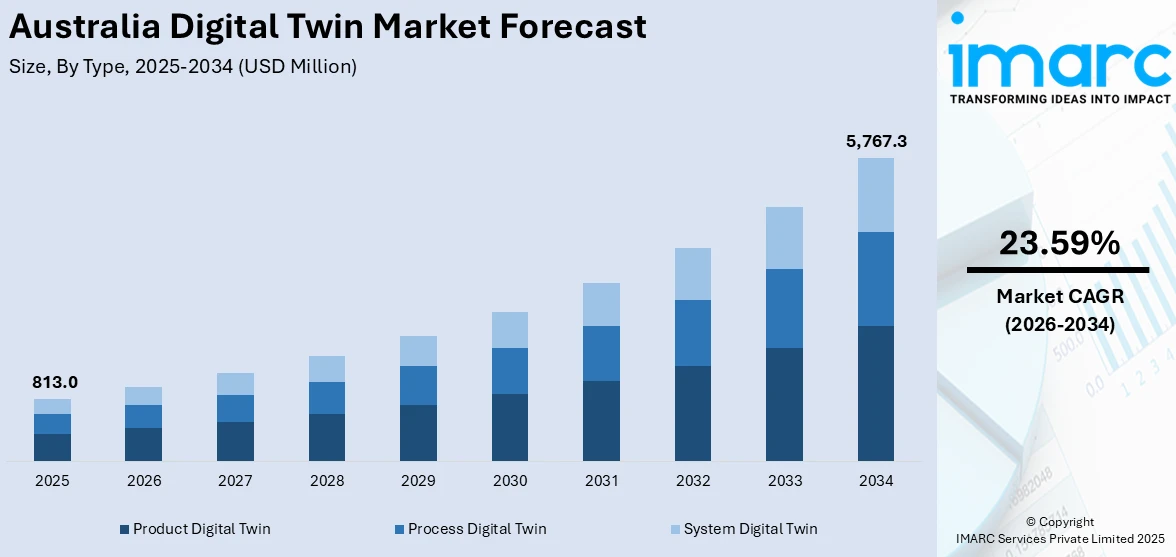
The Australia digital twin market size reached USD 813.0 Million in 2025. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 5,767.3 Million by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 23.59% during 2026-2034. Smart infrastructure development, growing adoption in mining and energy sectors, government investments in digital transformation, increasing use in predictive maintenance, urban planning, and asset management, and rising integration with IoT, AI, and cloud-based platforms are some of the factors propelling the growth of the market.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 813.0 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 5,767.3 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 23.59% |
Key Trends of Australia Digital Twin Market:
Boost in BIM-led Regulatory Efficiency
Australia is seeing increased integration of building information modeling (BIM) within government-led digital infrastructure initiatives. A new framework now guides digital compliance assessment, focusing on faster and more transparent building approvals. This shift promotes uniform practices across planning and construction sectors, strengthening regulatory alignment and project efficiency. The push reflects a broader interest in linking digital twins with real-time data for smarter urban planning. By standardizing digital formats and compliance protocols, the approach reduces delays, lowers administrative overhead, and improves stakeholder collaboration. These moves support a growing ecosystem where digital twins are visual replicas along with being functional tools for governance, especially in construction and asset management sectors across Australian states adopting similar strategies. For example, in November 2024, the Victorian government released the eComply Framework as part of the Digital Twin Victoria program. This framework defines specifications for building information modeling (BIM)-enabled digital compliance assessment practices, aiming to streamline building approvals and enhance regulatory processes.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Expansion of 4D Spatial Modeling for Statewide Planning
Efforts to create highly detailed virtual representations of real-world environments are gaining momentum in Australia. A major investment is supporting the development of a state-wide 4D model integrating time-based spatial data with built and natural assets. This approach strengthens planning capabilities across infrastructure delivery, environmental monitoring, and emergency management. By merging geospatial intelligence with dynamic modeling, decision-makers gain clearer visibility into future project impacts and resource needs. It also enables more responsive policy design and coordinated responses during critical events. The initiative supports broader national momentum toward adopting digital replicas as operational platforms, helping various agencies align strategies, reduce inefficiencies, and improve long-term urban and regional planning outcomes through shared, real-time spatial data systems. For instance, in March 2024, the Western Australian Government announced a USD 140 Million investment in the Spatial WA initiative. This program aims to develop a spatially accurate 4D virtual representation of the state's built and natural environment to enhance decision-making in infrastructure delivery, planning reforms, and emergency preparedness.
Growth Drivers of Australia Digital Twin Market:
Infra Modernization and Smart City Programs
The region’s infrastructure modernization and smart city program is a key growth driver of the Australia digital twin market share. With urbanization and population growth in cities such as Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane, there is mounting pressure on public infrastructure, transport networks, and utilities. Digital twins provide an advanced method for simulating, monitoring, and optimizing city assets in real-time, enhancing long-term planning and minimizing operational risk. Local governments and planning authorities are using digital twins to simulate city landscapes, predict traffic, manage energy usage, and improve public services. Government investment in large-scale infrastructure projects, including urban rail, roads, and water supply infrastructure, forms a solid platform for digital twin integration. New South Wales and Victoria are at the forefront with state plans that include digital twin platforms as crucial tools to manage infrastructure in an efficient way. Demand for digital twin technologies is increasing in both private and public sectors.
Mining, Energy, and Natural Resource Management
The Australia digital twin market growth is also driven by the nation's high emphasis on natural resource extraction and energy production, where safety and efficiency are paramount. Australia's economy-dependent mining and oil & gas industries are increasingly leveraging digital twin solutions to streamline complicated operations in remote and risky environments. Digital twins are being employed by companies to build real-time simulations of machinery, track structural health, forecast breakdowns, and schedule maintenance—albeit all of these reduce downtime and costs of operation. In countries such as Western Australia and Queensland, where mining is a prominent industry, digital twin applications are being implemented throughout entire mine operations and supply chains. Moreover, the drive toward clean energy is also encouraging energy companies to employ digital twins to maximize the efficiency of solar farms, wind farms, and energy storage facilities. Digital twins' integration into environmental monitoring—e.g., simulating groundwater networks or bushfire-risked areas—also aids Australia's national sustainability and climate resilience agenda.
Advance in Research, Technology, and Local Innovation
Australia's solid research capabilities, paired with a highly qualified tech workforce, are also fueling growth in the digital twin market. Research institutions and universities, including CSIRO and major public universities, are playing an active role in developing digital twin applications across industries such as health, construction, transport, and manufacturing. These research partnerships are yielding solutions that are customized to Australia's specific geographic and economic situation while also being ready for worldwide application. Digital twin technologies, for instance, are being applied in precision agriculture to model crop yields, conserve water resources, and track the health of soil, which are applications highly applicable in Australia's arid agricultural basins. Moreover, local startups and tech firms are emerging as key contributors, offering custom-built digital twin solutions for industries ranging from logistics to urban planning. Government support through innovation grants and digital transformation strategies encourages continued investment and experimentation. Australia is positioned to play a major role in the changing global digital twin scene owing to its combination of research, talent, and governmental backing.
Opportunity of Australia Digital Twin Market:
Urban Resilience and Disaster Preparedness
Australia's vulnerability to natural disasters like bushfires, floods, and cyclones offers a large potential market for digital twin technologies to help urban resilience and emergency preparedness. Digital twins are able to create real-time models of environmental hazards and simulate disaster scenarios to enhance response planning and resource allocation. State and local governments are more interested in employing digital twin platforms to forecast the effects of weather events on infrastructure and communities. For example, digital twins can be incorporated into emergency management software to map possible flood areas or fire routes so evacuation plan and asset protection can be better managed. In a nation where climate events consistently interrupt transportation, utilities, and homes, having the capacity to anticipate vulnerabilities through data-based simulations is incredibly useful. The increasing use of digital twins in disaster planning also presents tech vendors, city planners, and data analysts with opportunities to work together on bespoke solutions suited to Australia's varied and often difficult geography.
Sustainable Development and Environmental Monitoring
Australia's continued focus on sustainability and environmental protection presents large opportunities for digital twin uses in monitoring ecosystems, water resources, and carbon emissions. With the nation's rich biodiversity and natural scenery, ranging from the Great Barrier Reef to the parched interior, there is an expanding demand for technologies able to manage these delicate environments with delicacy and accuracy. Digital twins make real-time monitoring of ecological states and anthropogenic influences possible, facilitating government departments, scientists, and conservation groups making better-informed decisions. In regions facing water scarcity or soil degradation, digital twins can simulate different land-use strategies or agricultural practices to promote sustainability. Furthermore, with Australia’s push toward net-zero emissions and a circular economy, industries are looking for ways to monitor and reduce their environmental footprint. Digital twins present a scalable solution for the visualization of energy usage, carbon offset management, and environmental performance reporting, presenting an excellent opportunity for expansion in the green technology industry, which further increases the Australia digital twin market demand.
Healthcare and Smart Campus Applications
The healthcare industry and the emerging smart campus trend also represent a significant area of opportunity for Australia's digital twin market. Australian hospitals and healthcare research institutions are investigating digital twin uses to enhance operational effectiveness, patient outcomes, and medical education. Digital twins of hospital structures can maximize the use of space, regulate the use of energy, and allow equipment maintenance schedules to be fulfilled. At the clinical level, the combining of patient-specific digital twins—virtual copies of organs or biological systems—is predicted to transform personalized medicine and surgical planning. In addition, Australia's top universities are converting their campuses into smart, networked spaces, where digital twins are employed to control building systems, monitor occupancy behavior, and design for future growth. These campuses are frequently proof of concept sites for wider smart city deployments, offering a platform for collaboration between government, academia, and industry. The education and healthcare industries provide rich terrain for long-term digital twin implementation, driven by continuous research and digital change investment.
Government Investment of Australia Digital Twin Market:
Government Strategic Funding of Infrastructure and Urban Planning
The Australian government has been heavily investing in digital twin technology to assist the infrastructure and urban planning requirements of the country. With continuous population increase and urbanization in cities such as Melbourne, Sydney, and Perth, there is an urgent need for intelligent means of managing transport infrastructures, housing complexes, and public utilities. Government authorities at federal and state levels are investing in digital twin initiatives that allow for thorough modelling of urban habitats and support planning long-term infrastructure demands. These investments enable planners to model traffic flows, estimate the effect of zoning reforms, and optimize land use to a high level of accuracy. New South Wales, for instance, has created a whole-of-government spatial digital twin that combines real-time information to enhance decision-making on infrastructure projects. As per the Australia digital twin market analysis, these publicly subsidized programs simplify planning activities while also increasing transparency and interdepartmental collaboration between government ministries, industry players, and the community.
Financing Research and Innovation via National Programs
Government investment in Australia's digital twin sector also encompasses research and development. Government investment in the country's digital twin market includes several national programs and research grants designed to encourage innovation in the sector. Organisations like the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) are funded by the government in order to work together on digital twin implementation across industries like mining, agriculture, and energy. These partnerships are usually formed with universities, start-ups, and larger industry players to establish an ecosystem where research at the academic level is being converted very quickly into commercial solutions. The Australian government has identified digital twins as an important facilitator of its wider digital shift and Industry 4.0 agenda, which involves funding for new technologies that enhance productivity and environmental efficiency. These investments also support other policy objectives, such as stimulating regional development, enhancing STEM education, and narrowing the digital divide. Through investments in pilot projects and innovation hubs, the government is assuring that digital twin capability is built locally and tailored to Australia's specific economic and environmental circumstances.
Climate Action and Environmental Policy Integration
Another key aspect of government investment in digital twin technology is in relation to Australia's environment and climate change agenda. While the nation experiences increasing threats from natural disasters, water shortages, and loss of biodiversity, federal and state governments are incorporating digital twins into environmental monitoring and policy-making frameworks. Government-funded projects are employing digital twins to monitor industrial facilities' emissions, simulate the effect of climate policy, and monitor ecosystems like coastal areas and wetlands. Such utilization of technology complements Australia's sustainability and carbon reduction commitments through the presentation of more precise data for the purpose of environmental regulation as well as conservation. For example, digital twins are being increasingly combined with satellite and sensor information to model climate situations and develop adaptive measures at both local and national levels. These investments by governments enhance environmental resilience and create new business opportunities for technology companies, environmental consultants, and research centers operating in climate-related sectors.
Australia Digital Twin Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the region/country level for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on type, technology, and end use.
Type Insights:
- Product Digital Twin
- Process Digital Twin
- System Digital Twin
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes product digital twin, process digital twin, and system digital twin.
Technology Insights:
- IoT and IIoT
- Blockchain
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality
- Big Data Analytics
- 5G
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology. This includes IoT and IIoT, blockchain, artificial intelligence and machine learning, augmented reality, virtual reality and mixed reality, big data analytics, and 5G.
End Use Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Aerospace and Defense
- Automotive and Transportation
- Healthcare
- Energy and Utilities
- Oil and Gas
- Agriculture
- Residential and Commercial
- Retail and Consumer Goods
- Telecommunication
- Others
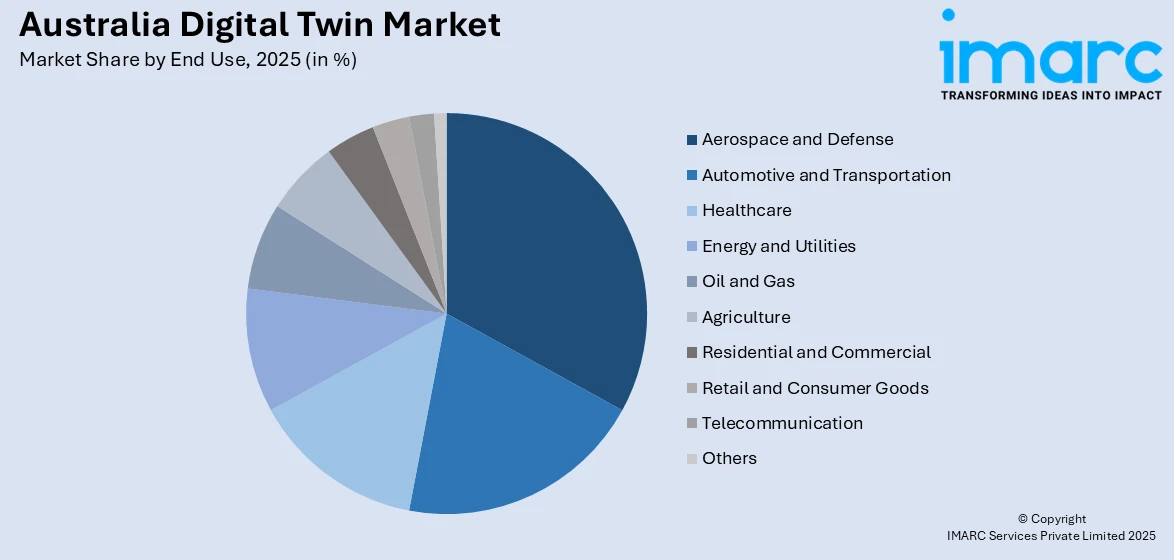
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end use have also been provided in the report. This includes aerospace and defense, automotive and transportation, healthcare, energy and utilities, oil and gas, agriculture, residential and commercial, retail and consumer goods, telecommunication, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Digital Twin Market News:
- In February 2025, the Digital Transformation Agency highlighted the Australian Government's efforts in harnessing innovative investment models and emerging technologies to create a future-ready data and digital portfolio. This includes trials of AI technologies and the development of policies for responsible AI use in government.
- In July 2024, the Digital Twin Consortium announced that its members would lead sessions at Smart Cities Week Asia Pacific in Adelaide. These sessions focused on the future of digital twin technology and its applications in smart city development.
Australia Digital Twin Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Product Digital Twin, Process Digital Twin, System Digital Twin |
| Technologies Covered | IoT and IIoT, Blockchain, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality, Big Data Analytics, 5G |
| End Uses Covered | Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Healthcare, Energy and Utilities, Oil and Gas, Agriculture, Residential and Commercial, Retail and Consumer Goods, Telecommunication, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia digital twin market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia digital twin market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia digital twin industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia digital twin market was valued at USD 813.0 Million in 2025.
The Australia digital twin market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 23.59% during 2026-2034.
The Australia digital twin market is expected to reach a value of USD 5,767.3 Million by 2034.
The Australia digital twin market trends include growing use in climate resilience and infrastructure planning. Integration with AI, IoT, and geospatial data is also enhancing real-time simulation capabilities. Government-backed initiatives and academic-industry collaborations are further accelerating innovation and nationwide implementation.
The Australia digital twin market is driven by smart city initiatives, robust research ecosystem, and growing adoption in sectors like mining, healthcare, and energy. Digital transformation goals and sustainability efforts are also key contributing factors.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












