
Australia E-Mobility Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product, Voltage, Battery, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia E-Mobility Market Overview:
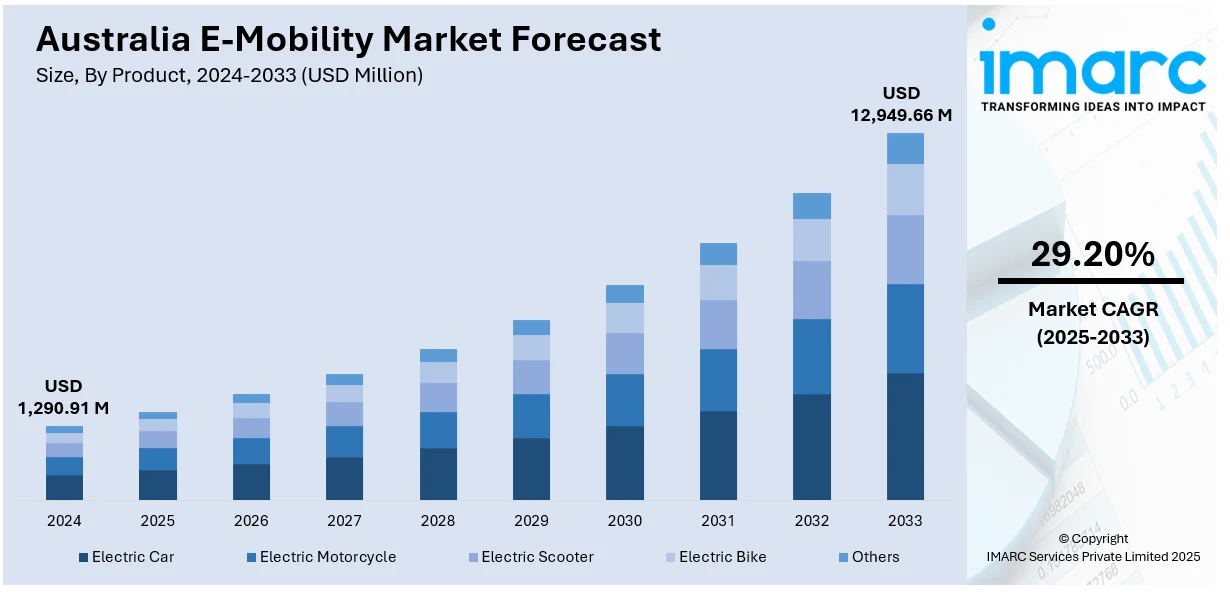
The Australia e-mobility market size reached USD 1,290.91 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is projected to reach USD 12,949.66 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 29.20% during 2025-2033. The market is stimulated by forward-thinking governmental policies focused on lowering carbon emissions, in addition to strategic investments in public charging. Gains in technology with improved battery efficiency and driving range have further driven interest in electric transportation. In addition, the incorporation of renewable energy sources into charging systems reinforces national sustainability goals. Growing eco-awareness among consumers and the growing popularity of micro-mobility solutions drive steady market expansion, which reinforces Australia e-mobility market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 1,290.91 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 12,949.66 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 29.20% |
Key Trends of Australia E-Mobility Market:
Public Charging Infrastructure Expansion
Australia is advancing its national transport goals by expanding the public electric vehicle charging infrastructure network. Governments at all levels are offering policies and financing support to enhance the provision of fast and normal chargers in urban, regional, and remote areas. The objective is to shorten charging time, improve accessibility, and encourage fair service coverage. Integration with mobile apps and mapping utilities also facilitates real-time station availability updates, enhancing user experience and route planning. Infrastructure providers are also focusing on renewable-powered charging stations, which are consistent with the country's wider environmental targets. Concurrently, zoning reforms and commercial collaborations are facilitating installation in residential apartments, shopping malls, and public car parks. This increasing infrastructure ecosystem is critical for securing public trust and take-up, as the charging infrastructure advances, enhancing the sustainability of Australia e-mobility market growth as a reliable part of Australia's changing transport system. For instance, in March 2025, Cadillac officially revealed it would be launching its Optiq and Vistiq electric vehicles in Australia and New Zealand by 2026, playing an important role in growing the Australia e-mobility market.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Merger with Renewable Power Generation
Australia's energy pattern is best placed to enable the intermingling of electric mobility with renewable energy generation. Australia's wealth of solar and wind resources makes it possible to build charging solutions that are both cost-effective and environmentally friendly. On-board solar setups combined with home energy storage enable single-vehicle owners to charge in isolation from the grid, while solar farms on an economy of scale are increasingly powering public and fleet charging points. Time-of-use business models reward off-peak charging when renewable supply is at its peak, promoting efficiency and demand management. This integration saves emissions, improves grid stability, and aids national decarbonisation. As per the sources, in May 2025, Volvo revealed plans to produce Australia's first heavy-duty electric trucks at its Brisbane plant, delivering ten locally produced vehicles as part of the country's largest electric truck order. Furthermore, bi-directional charging technologies are also being investigated, enabling vehicles to supply energy to the grid during peak hours. These developments reflect a wider shift towards a circular energy economy. With the maturation of systems, e-mobility will increasingly support clean energy approaches, assisting in developing a resilient, future-proof transport industry in Australia.
Development of Electric Two-Wheelers and Micro-Mobility
Electric two-wheelers and micro-mobility transport are the transforming forces in urban transport in Australia. They comprise electric scooters, bicycles, mopeds, and light personal transport that address short commutes, recreation, and delivery. Their appeal stems from their affordability, parking convenience, and ability to thrive in densely populated urban spaces. Upgrades to supporting infrastructure, like increased bike lanes, specialized micro-mobility corridors, and parking facilities, are boosting their feasibility. Additionally, increasing fuel prices and environmental concerns are encouraging users to switch to smaller electric options. Cities are also bringing these vehicles into comprehensive public transportation networks, facilitating first- and last-mile connectivity. Shared mobility services and online platforms provide on-demand availability, making them more visible and convenient. All these are encouraging behavioral changes in Australians' mode of travel within their cities. With increases in adoption rates and regulatory infrastructures, the role of e-mobility in this sector is likely to be an anchor for sustainable, equitable urban mobility.
Growth Drivers of Australia E-Mobility Market:
Government Policy Support
Government policy has been instrumental in encouraging the uptake of e-mobility throughout Australia. Numerous incentives, including subsidies, rebates, and emission reduction targets, are establishing a favorable environment for both consumers and businesses to shift towards electric mobility. Financial support significantly reduces the initial costs of EVs, while favorable policies regarding clean energy transition motivate companies to modernize their fleets. Both state and federal authorities are advocating for more rigorous emissions standards, enhancing the appeal of electric mobility compared to conventional vehicles. These initiatives encourage vehicle sales and stimulate investment in charging infrastructure and related technologies. As a result, Australia e-mobility market demand continues to accelerate, driven strongly by consistent government backing and long-term sustainability goals.
Rising Fuel Costs
The ongoing increase in petrol and diesel prices has emerged as a significant factor in driving the shift toward electric mobility in Australia. Operating an EV offers considerable long-term savings compared to internal combustion engine vehicles, particularly for businesses with large fleets. This financial benefit makes e-mobility an attractive option for logistics providers, ride-sharing services, and urban commuters looking to minimize daily expenses. As fuel prices fluctuate due to global market dynamics, more individuals and organizations are considering EVs a way to achieve stable and predictable running costs. This change in consumer behavior is directly leading to higher adoption rates, establishing e-mobility as a practical and economical transport solution in the Australian market.
Technological Advancements
Developments in battery technology, charging solutions, and vehicle efficiency are enhancing the practicality and appeal of e-mobility in Australia. Innovations like increased driving ranges, quicker charging times, and reduced battery prices have alleviated previous concerns regarding adoption. Additionally, the incorporation of smart technologies, regenerative braking, and improved connectivity features enhances the overall user experience. Such advancements have solidified the commercial feasibility of electric mobility across passenger, commercial, and shared transport sectors. According to Australia e-mobility market analysis, technological innovations are anticipated to significantly lower ownership barriers while enhancing accessibility, thus accelerating adoption. As vehicles become more reliable and competitively priced, technological progress remains a key factor driving the growth of the e-mobility ecosystem in Australia.
Opportunities of Australia E-Mobility Market:
Fleet Electrification
Fleet electrification presents a substantial opportunity within the Australian e-mobility landscape. Logistics companies, public transportation systems, and corporate fleets face increasing pressure to cut operational costs and meet sustainability objectives. Making the switch to electric vehicles allows these sectors to enjoy reduced fuel and maintenance costs while contributing to national emission reduction goals. For logistics operations, electric vehicles provide long-term cost savings in last-mile and intercity delivery services. The electrification of public transport enhances urban air quality and addresses the growing commuter demand for environmentally friendly options. Likewise, corporate adoption elevates ESG performance and improves brand perception. This widespread transition in fleet management can significantly increase e-mobility adoption across Australia.
Battery Recycling and Second Life Use
Battery recycling and second-life applications present a transformative opportunity for the Australian e-mobility sector. With the rise of electric vehicle use, effective management of end-of-life batteries becomes essential for sustainability and resource efficiency. Recycling facilitates the recovery of important materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which decreases reliance on imports and bolsters local supply chains. Concurrently, second-life applications—like repurposing EV batteries for renewable energy storage or backup systems—prolong their usefulness and provide economical energy solutions. Establishing specialized recycling facilities and second-life projects aligns with circular economy principles, delivering both economic and environmental advantages. This opportunity positions Australia as a leader in sustainable practices while fostering long-term growth in the e-mobility market.
Smart Mobility Solutions
Smart mobility solutions signify a forward-thinking opportunity in the Australian e-mobility sector. As digital integration progresses, electric vehicles are increasingly connecting to wider smart city ecosystems. Merging electric mobility with technologies such as AI, IoT, and autonomous driving creates new business models in ride-sharing, vehicle-as-a-service, and mobility-on-demand. Such advancements enhance transport efficiency in urban areas while also lessening congestion and emissions. In addition, data-driven platforms allow for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized fleet utilization, generating additional value for both businesses and consumers. Aligning smart mobility with EV adoption supports government efforts for sustainable urban development, making this field a promising area for innovation and investment.
Government Support for Australia E-Mobility Market:
Purchase Incentives
Government-driven purchase incentives such as subsidies, rebates, and tax benefits are essential in mitigating the high initial costs associated with electric vehicles (EVs). By reducing these financial barriers, these initiatives enhance the affordability of EVs for both consumers and businesses. Additional measures like lowered registration fees, exemptions from fringe benefits tax, and import duty reductions further improve financial viability. These incentives stimulate demand among consumers and motivate automakers and dealers to broaden their EV selections in Australia. Consequently, this heightened demand leads to the necessity for expanded charging infrastructure and related services, creating a broader impact on the e-mobility ecosystem. Ultimately, these initiatives accelerate the adoption of EVs, significantly advancing the growth of the Australian e-mobility market.
Infrastructure Investment
Investment in charging infrastructure is fundamental to the development of Australia’s e-mobility landscape, ensuring that electric vehicles are a viable option for everyday usage. Both federal and state governments are actively financing the establishment of fast-charging networks throughout urban centers, highways, and regional areas. This alleviates consumer worries related to range anxiety and bolsters the confidence in EV ownership. A well-developed charging ecosystem also facilitates the electrification of fleets, public transportation, and logistics services. Enhancing infrastructure fosters adoption and encourages participation and innovation from the private sector in charging solutions. By addressing accessibility challenges, government-led infrastructure initiatives are pivotal in making EVs feasible at scale and promoting sustained long-term growth in the Australian e-mobility market.
Emission Reduction Targets
Australia’s national and state-level emission reduction goals are key policy drivers for the adoption of e-mobility. With aspirations of achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century, governments are increasing their focus on sustainable transportation solutions. Electric vehicles, recognized for their lower lifecycle emissions, play a vital role in this transition. Stricter vehicle emission standards, the integration of renewable energy, and decarbonization policies align closely with the uptake of EVs. These targets guide consumer choices and impact corporate strategies, decisions regarding fleet electrification, and infrastructure planning. By connecting transport electrification with climate objectives, emission reduction policies secure a consistent long-term demand for electric vehicles and associated technologies, thus enhancing the growth prospects of the Australian e-mobility market.
Challenges of Australia E-Mobility Market:
High Upfront Costs
While electric vehicles (EVs) offer long-term savings, their uptake in Australia is hindered by high initial expenses. EVs typically come with a higher price tag compared to traditional petrol and diesel vehicles due to costly batteries and sophisticated technologies. Additionally, the installation of home charging units or the development of commercial charging infrastructure demands significant investment, which can deter early adopters. For businesses, transitioning to electric fleets can be capital-intensive, making it less appealing without government support. Although subsidies and rebates can help bridge the cost gap, affordability continues to pose a significant barrier for middle-income families and small businesses. Addressing concerns about upfront costs is essential for increasing adoption rates and ensuring sustainable growth in Australia’s e-mobility market.
Limited Charging Infrastructure
The growth of the Australia e-mobility market is hampered by the insufficient number of charging stations, especially in rural and regional areas. While major cities are beginning to see improvements in fast-charging networks, challenges remain for long-distance travel due to range anxiety and uneven infrastructure coverage. This situation discourages many individuals from viewing EVs as viable primary vehicles. Moreover, businesses encounter operational challenges when switching to electric fleets, as dependable access to charging is critical for logistics and transport efficiency. Without a comprehensive and accessible charging infrastructure, adoption will likely remain concentrated in urban areas. Increasing investment in regional charging networks is vital for achieving balanced adoption across the nation and supporting the long-term sustainability of electric mobility.
Battery Supply Constraints
Battery supply represents a significant obstacle for the Australia e-mobility market, as the country largely depends on imported battery cells and components. Variations in global demand, supply chain disruptions, and shortages of materials particularly lithium, cobalt, and nickel lead to price fluctuations and restricted availability. This reliance creates challenges for vehicle affordability and for the expansion of charging infrastructure that necessitates battery storage solutions. Despite Australia’s abundance of raw materials like lithium, the lack of local processing and battery manufacturing capabilities limits its ability to maintain a stable supply. Without enhanced domestic production and diversified sourcing strategies, the market remains susceptible to global trade disputes and supply interruptions, which could hinder the speed of EV adoption.
Australia E-Mobility Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on product, voltage, and battery.
Product Insights:
- Electric Car
- Electric Motorcycle
- Electric Scooter
- Electric Bike
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the product. This includes electric car, electric motorcycle, electric scooter, electric bike, and others.
Voltage Insights:
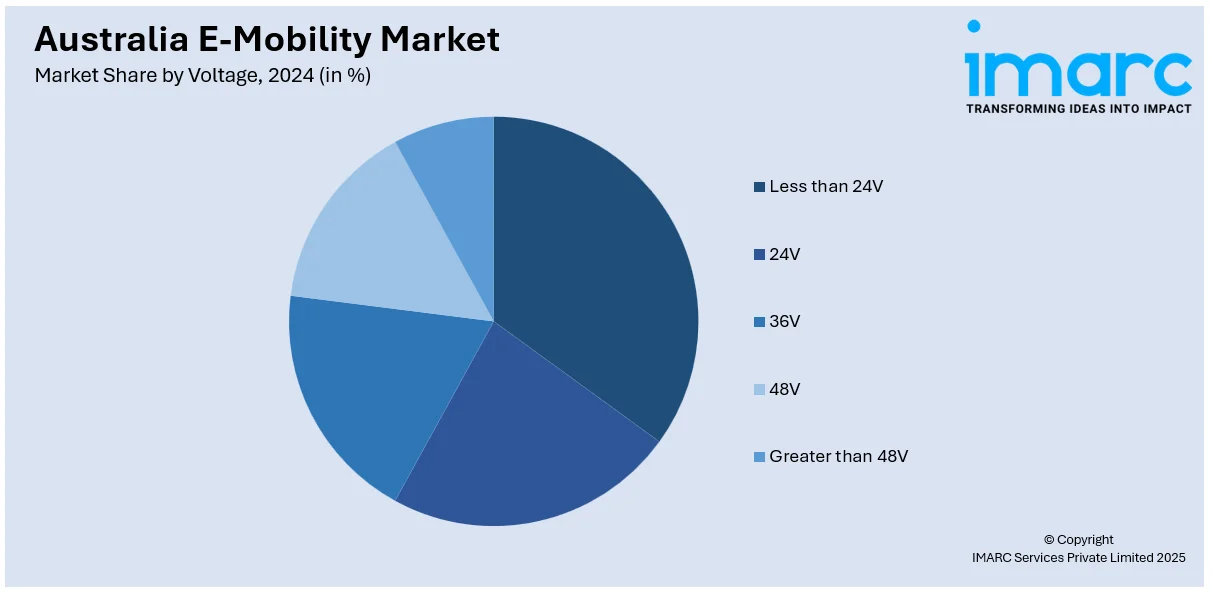
- Less than 24V
- 24V
- 36V
- 48V
- Greater than 48V
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the voltage have also been provided in the report. This includes less than 24V, 24V, 36V, 48V, and greater than 48V.
Battery Insights:
- Sealed Lead Acid
- Li-ion
- NiMH
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the battery. This includes sealed lead acid, Li-ion, and NiMH.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided, including:
- BMW Group Australia
- BYD Australia Pty. Ltd
- Dyson Bikes
- Lexus Australia
- Mercedes-Benz Australia/Pacific Pty Ltd
- MG Motor Australia
- Savic Motorcycles
- Super SOCO
- Tesla, Inc
- Toyota Australia
Australia E-Mobility Market News:
- In January 2025, BYD launched the Dolphin Essentials trim officially in Australia, which is Australia's first electric vehicle under \\$30,000. Deliveries will commence in March, further solidifying BYD's market position in the Australian e-mobility sector with budget-friendly, long-distance electric vehicles following increasing demand.
- In May 2024, XPeng announced that the G6 electric SUV would enter Australia by Q4 2024, with a mission to drive EV adoption with cutting-edge features and cost-effective pricing. This is a major milestone for the Chinese electric vehicle brand's push into the Australian market.
Australia E-Mobility Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Products Covered | Electric Car, Electric Motorcycle, Electric Scooter, Electric Bike, Others |
| Voltages Covered | Less than 24V, 24V, 36V, 48V, Greater than 48V |
| Batteries Covered | Sealed Lead Acid, Li-ion, NiMH |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Companies Covered | BMW Group Australia, BYD Australia Pty. Ltd, Dyson Bikes, Lexus Australia, Mercedes-Benz Australia/Pacific Pty Ltd, MG Motor Australia, Savic Motorcycles, Super SOCO, Tesla, Inc, Toyota Australia, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia e-mobility market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia e-mobility market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia e-mobility industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The e-mobility market in Australia was valued at USD 1,290.91 Million in 2024.
The Australia e-mobility market is projected to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29.20% during 2025-2033.
The Australia e-mobility market is expected to reach a value of USD 12,949.66 Million by 2033.
Australia’s e-mobility market is witnessing trends such as the expansion of fast-charging corridors, integration of renewable energy with EV infrastructure, rising adoption of shared e-mobility services, and technological advancements in connected vehicles. Growing focus on fleet electrification and digital mobility platforms is also reshaping transport ecosystems.
The market is driven by the declining battery costs, government-backed emission reduction targets, rising fuel prices encouraging EV preference, and consumer demand for sustainable transport. Corporate sustainability initiatives and investments in local EV assembly are accelerating adoption, making e-mobility a critical part of Australia’s clean energy transition.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












