
Australia Electric Vehicle Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Vehicle Type, Price Category, Propulsion Type, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Electric Vehicle Market Summary:
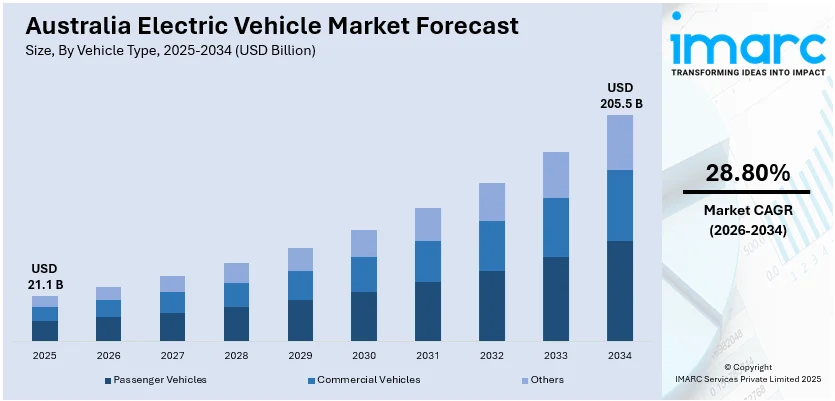
The Australia electric vehicle market size was valued at USD 21.06 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 205.45 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 28.80% from 2026-2034.
The market is driven by the rising adoption of electric vehicles by businesses to meet sustainability objectives and enhance corporate responsibility, along with the growing mass production of EVs to make them more affordable for users. The rapid expansion of charging infrastructure across urban, highway, and regional areas is addressing range anxiety concerns, while the implementation of the New Vehicle Efficiency Standard is encouraging manufacturers to bring more diverse low-emission models to Australia. These factors are collectively contributing to the expansion of Australia electric vehicle market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Vehicle Type: Passenger vehicles dominated the market with 71% revenue share in 2025, driven by increasing consumer preference for SUVs and hatchbacks, expanded model diversity from global automakers, and attractive government incentives including fringe benefits tax exemptions that have made electric passenger cars more accessible to everyday Australians.
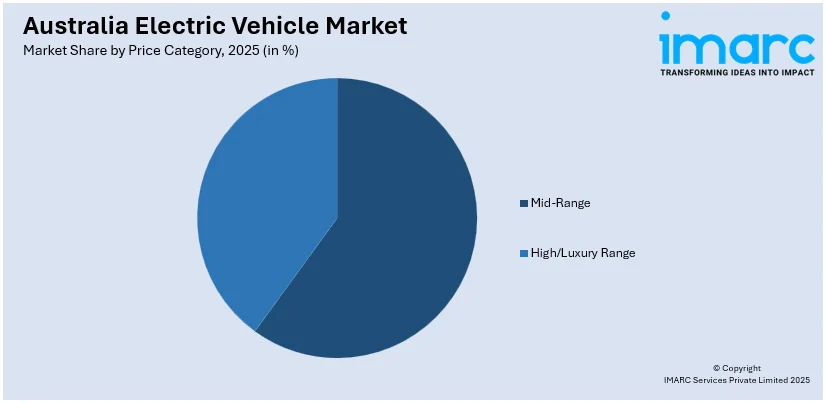
- By Price Category: Mid-range led the market with a revenue share of 58% in 2025, attracting eco-conscious families and commuters with extended range, advanced safety features, and affordability supported by government incentives and tax benefits, making them the preferred choice for mainstream buyers.
- By Propulsion Type: Battery electric vehicles represent the largest share of 50% in 2025, reflecting the country's decisive shift toward zero-emission transportation, supported by advances in battery range, declining production costs, and alignment with national decarbonization goals and renewable energy integration strategies.
- By Region: Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales led the market with a revenue share of 31% in 2025, supported by government incentives, expanding charging networks, rising environmental awareness, and greater availability of electric vehicle models for consumers.
- Key Players: The Australia electric vehicle market exhibits intensifying competitive dynamics, with multinational automakers and emerging Chinese brands competing across price segments. Established manufacturers leverage brand recognition and service networks, while new entrants focus on value-driven offerings and advanced technology features to capture market share.
The Australia electric vehicle market is undergoing a transformative shift as the country transitions from early adoption to mainstream acceptance. The market is witnessing unprecedented growth driven by favorable government policies, expanding charging infrastructure, and increasing consumer awareness of environmental benefits. Australia now has over 454,000 electric vehicles in its national fleet, with 153 EV models available to buyers including 94 battery electric vehicles and 59 plug-in hybrids. The introduction of new vehicle efficiency standards has enhanced the availability of cleaner vehicles by requiring manufacturers to meet fleet-wide emissions targets. Complementing this, government investments in expanding kerbside and fast-charging infrastructure across urban and regional areas reflect ongoing policy support, aiming to make electric vehicle ownership more convenient and accessible, while reinforcing nationwide efforts to accelerate the transition toward sustainable transportation.
Australia Electric Vehicle Market Trends:
Rising Production of EVs and Model Diversity
Rising electric vehicle production is improving availability and gradually lowering costs for Australian consumers. Expanded manufacturing capacity and broader model lineups, ranging from compact city cars to larger utility-style vehicles, are increasing consumer choice. Efficiency gains from large-scale production are helping make electric vehicles more competitively priced, while product development is increasingly aligned with local driving conditions and preferences. Together, these factors are strengthening affordability, expanding market access, and supporting faster adoption of electric vehicles across different consumer segments in Australia.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Growing Adoption of Sustainability
The increasing focus on sustainability is propelling market growth as individuals and businesses prioritize environmentally responsible choices. Corporate entities are adopting electric vehicles in their fleets to meet sustainability targets and enhance their environmental credentials. Government agencies at federal and state levels are supporting this shift through policies promoting renewable energy and zero-emission transport. The New Vehicle Efficiency Standard passed by the Australian Parliament is projected to deliver over AUD 95 billion in fuel savings and cut carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 321 million tonnes by 2050.
Technological Advancements in Battery Systems
Technological innovation is steadily enhancing electric vehicle performance, affordability, and user convenience. Improvements in battery design are extending driving range and reducing charging times, making electric vehicles more practical for everyday use. The integration of bidirectional charging capabilities allows vehicles to operate as mobile energy storage units, supporting energy management and grid stability. These advancements create additional value for owners, strengthen the role of electric vehicles within the broader energy system, and support wider adoption by improving usability and overall ownership appeal.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Australia electric vehicle market is poised for substantial expansion as the country accelerates its transition toward sustainable transportation. The convergence of supportive government policies, expanding charging networks, advancing battery technologies, and growing consumer acceptance positions the market for continued robust growth. Fleet electrification commitments from major corporations and government agencies are expected to drive significant demand, while the entry of new affordable models will broaden market accessibility. The market generated a revenue of USD 21.06 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 205.45 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 28.80% from 2026-2034.
Australia Electric Vehicle Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Vehicle Type |
Passenger Vehicles |
71% |
| Price Category | Mid-Range |
58% |
| Propulsion Type | Battery Electric Vehicle |
50% |
| Region | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales |
31% |
Vehicle Type Insights:
- Passenger Vehicles
- Commercial Vehicles
- Others
Passenger vehicles dominate with a market share of 71% of the total Australia electric vehicle market in 2025.
Passenger vehicles are driving the electric transition as Australian consumers increasingly embrace sustainable personal mobility. Tax rebates, registration discounts, and financial incentives are encouraging buyers to choose electric options over traditional combustion vehicles. Major automakers are introducing diverse model ranges from affordable compact cars to premium SUVs, catering to varied consumer preferences. Urban centers are leading adoption due to dense populations and extensive charging networks, while advances in battery technology are extending driving ranges and addressing range concerns for suburban commuters.
The Tesla Model Y maintained its position as Australia's best-selling electric vehicle in 2025 with 22,239 units delivered, demonstrating the strong consumer preference for versatile electric SUVs. This trend reflects Australian consumers’ growing preference for practical, spacious vehicles that combine driving range, modern technology, and strong value. The arrival of more affordable electric options has broadened market accessibility, while ongoing improvements across existing electric lineups continue to enhance choice and competitiveness within the market.
Price Category Insights:
To get detailed segment analysis of this market Request Sample
- Mid-Range
- High/Luxury Range
Mid-range leads the market with a share of 58% of the total Australia electric vehicle market in 2025.
The mid-range segment appeals to the mainstream market, attracting eco-conscious families and daily commuters seeking practical electric mobility solutions. Vehicles in this price category offer competitive features including extended driving ranges, advanced safety systems, and modern infotainment options at accessible price points. Government incentives including subsidies and tax exemptions, are reducing upfront costs, while the expansion of charging infrastructure is alleviating range anxiety concerns. Intensifying competition among automakers and continuous improvements in battery efficiency are making mid-range electric vehicles increasingly accessible to average Australian buyers.
Affordability has become a key factor shaping electric vehicle purchase decisions, with stronger demand concentrated in lower-priced segments while higher-end models experience slower adoption. Compact and practical vehicle formats are attracting first-time buyers, supported by accessible pricing and dependable after-sales support. Growing interest in value-oriented electric SUVs and hatchbacks highlights consumer preference for vehicles that balance everyday usability, driving range, and cost efficiency, reinforcing the importance of competitively priced offerings in expanding electric vehicle adoption across the broader market.
Propulsion Type Insights:
- Battery Electric Vehicle
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle
- Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Battery electric vehicles exhibit clear dominance with a 50% share of the total Australia electric vehicle market in 2025.
Battery electric vehicles represent Australia's decisive shift toward zero-emission transportation, relying exclusively on electric power without internal combustion engines. Popular models appeal to both urban and suburban users due to significant advances in battery range and the ongoing expansion of charging infrastructure. As Australia continues investing heavily in renewable energy generation, battery electric vehicles are increasingly aligned with the nation's decarbonization objectives, making them particularly attractive to environmentally conscious buyers seeking to minimize their carbon footprint.
Australia's battery electric vehicle sales exceeded 100,000 units for the first time in 2025, reaching 103,269 deliveries according to the Federal Chamber of Automotive Industries and the Electric Vehicle Council. This milestone represents a 13.1% increase from the previous year's 91,495 units, with battery electric vehicles now accounting for 8.3% of all new vehicle deliveries compared to 7.4% in 2024. Plug-in hybrid vehicle sales demonstrated even stronger growth, surging 134.5% to reach 53,484 units as buyers sought electric capability with petrol backup for extended journeys or limited charging access situations.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & South Australia
- Western Australia
Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales represent the largest share with 31% of the total Australia electric vehicle market in 2025.
The Australia Capital Territory and the New South Wales region demonstrate strong electric vehicle adoption supported by progressive government policies and robust charging infrastructure networks. Incentives including rebates, stamp duty exemptions, and substantial investments in charging stations, have accelerated uptake throughout the region. The focus on public transport electrification and fleet transformation is creating broader ecosystem effects. Urban centers including Sydney and Canberra, serve as hubs for electric vehicle activity, hosting large private and commercial fleets alongside expanding fast-charging networks.
New South Wales maintains its position as Australia's infrastructure leader with 357 total charging locations as of mid-2025. The state government announced in November 2025 an additional AUD 5.9 million in grants combined with AUD 3.2 million in private investment to install electric vehicle chargers across regional hotspots, with six companies including NRMA and Woolworths, participating in the infrastructure rollout. The Shoalhaven local government area will receive the most charging ports at 19 units, followed by Kempsey with 11 and Lismore with nine, demonstrating a commitment to extending charging accessibility beyond metropolitan areas.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Australia Electric Vehicle Market Growing?
Government Incentives and Policy Support
The support provided by the government is promoting the use of electric vehicles through incentives and policies. These incentives and policies provided by the government include the concession of buying the vehicles, lowered costs of owning them, and other working advantages that make it easier for people and companies to make use of them. The policies and standards put forth by the government, like lower emissions and efficiency standards for vehicles, make it easier for people to adopt them and thus make the transition to electric vehicles.
Expansion of EV Charging Infrastructure
Australia's electric vehicle market growth is being significantly driven by the rapid expansion of public and private charging networks. Both federal and state governments, in partnership with private firms, are investing substantially in fast-charging stations across highways, urban centers, and regional areas. The country had 1,272 fast-charging locations with over 3,436 plugs by mid-2025, representing approximately 20% growth from the previous year. The Australian Government announced a AUD 40 million investment in September 2025 to expand kerbside and fast-charging infrastructure across suburbs and regional communities as part of its broader Net Zero Plan. Western Australia completed its Electric Vehicle Highway connecting Perth to regional areas including Kalgoorlie, Geraldton, and Albany, with strategically placed charging stations at intervals matching typical electric vehicle ranges.
Corporate and Fleet Electrification Commitments
Large corporations and government bodies are increasingly committing to fleet electrification as part of broader environmental, social, and governance objectives and carbon neutrality goals. Major companies in logistics, car rental, utilities, and rideshare sectors are leading the transition by integrating electric vehicles into their operations, often supported by dedicated leasing and financing models. These bulk purchases significantly increase demand, create a used electric vehicle supply for resale markets, and accelerate public exposure to electric mobility. For instance, IKEA Australia currently delivers 83% of its orders using zero-emission vehicles and is progressing toward its goal of reaching 90% zero-emission deliveries by the final weeks of 2025, demonstrating steady advancement in decarbonizing its logistics operations.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Australia Electric Vehicle Market is Facing?
Limited Charging Infrastructure in Regional Areas
Despite advances in urban charging networks, rural and regional areas remain underserved, limiting consumer confidence in owning electric vehicles outside cities. Australia’s vast geography poses challenges for establishing widespread charging coverage across remote locations. Ongoing maintenance and reliability issues further affect driver trust, highlighting the need for robust infrastructure to support consistent and convenient EV use nationwide.
High Upfront Vehicle Costs
Although the Australian electric vehicle market is growing, it continues to offer limited options in the entry-level and compact car segments. High pricing restricts affordability, making EVs less accessible to budget-conscious consumers. This limits widespread adoption, keeping the market largely confined to early adopters and higher-income buyers, and slowing broader penetration across the general population.
Policy Inconsistency Across Jurisdictions
A significant barrier to seamless electric vehicle adoption remains the fragmented policy landscape across different states and territories. Each jurisdiction maintains its own set of incentives, taxes, and regulations, with some offering purchase subsidies and free registration while others have implemented road-user charges on electric vehicles. This inconsistency creates confusion for consumers and complicates strategic planning for automakers and infrastructure providers seeking to deploy resources efficiently across the national market.
Competitive Landscape:
The electric vehicle market in Australia is advancing as a wide range of new models are being introduced to meet diverse consumer needs and budgets. Expansion of charging infrastructure, including fast-charging stations across urban and highway networks, is reducing range anxiety. Government incentives, subsidies, and support for public and private charging networks encourage adoption, while fleet operators transition to EVs to cut emissions and operational costs. Integration of renewable energy for charging and increasing consumer awareness is further strengthening the ecosystem, driving sustainable growth, and accelerating the shift toward electric mobility nationwide.
Recent Developments:
- January 2026: Mazda announced plans to introduce a new mid-size electric SUV, produced in China, to the Australian market in 2026, aiming to compete directly with leading models in the segment. Named the Mazda CX-6e, this vehicle will mark the company’s second fully electric offering in Australia, joining the forthcoming Mazda 6e sedan. The CX-6e is scheduled for release in 2026, with pricing details and final specifications for the Australian market yet to be disclosed.
- November 2025: BYD launched the Atto 1, known globally as the Seagull, in Australia at a starting price of AUD 23,990, making it the country's most affordable electric vehicle. The compact city hatchback features BYD's Blade Battery technology, 10.1-inch touchscreen, and vehicle-to-load capabilities, significantly undercutting petrol alternatives including the Toyota Yaris and Mazda 2.
- August 2024: Cadillac opened its first experience center in Australia, an 841-square-metre facility in southern Sydney designed to showcase the new electric Lyriq in right-hand drive configuration, featuring contemporary design elements alongside advanced showroom and service spaces.
Australia Electric Vehicle Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Vehicle Types Covered | Passenger Vehicles, Commercial Vehicles, Others |
| Price Categories Covered | Mid-Range, High/Luxury Range |
| Propulsion Types Covered | Battery Electric Vehicle, Hybrid Electric Vehicle, Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia electric vehicle market size was valued at USD 21.06 Billion in 2025.
The Australia electric vehicle market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 28.80% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 205.45 Billion by 2034.
Passenger vehicles dominated the market with 71% revenue share in 2025, driven by increasing consumer preference for electric SUVs and hatchbacks, expanded model diversity from global automakers, and attractive government incentives.
Key factors driving the Australia electric vehicle market include supportive government policies and incentives such as the New Vehicle Efficiency Standard and fringe benefits tax exemptions, rapid expansion of charging infrastructure, corporate fleet electrification commitments, and technological advances in battery systems.
Major challenges include limited charging infrastructure coverage in regional and remote areas, high upfront vehicle costs with insufficient affordable model options below AUD 50,000, policy inconsistencies across different states and territories, and ongoing consumer concerns about battery longevity and resale value depreciation.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












