
Australia Housing Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Provider, Size of Unit, Location, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Housing Market Summary:
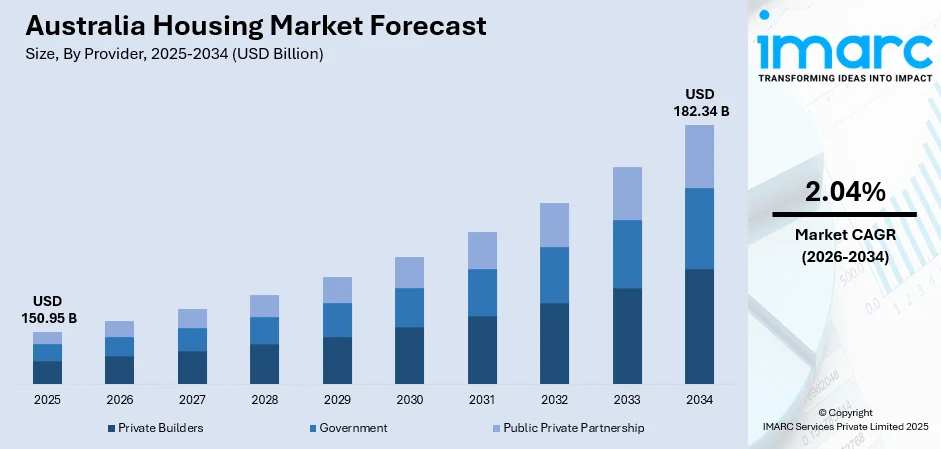
The Australia housing market size was valued at USD 150.95 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 182.34 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 2.04% from 2026-2034.
The market is driven by rising population growth, increasing urbanization trends, and growing demand for affordable residential properties across major metropolitan areas. Government initiatives supporting first-home buyers, favorable mortgage lending conditions, and sustained infrastructure development continue to bolster housing demand. Lifestyle preferences shifting toward convenient urban living arrangements and strong investor confidence in real estate assets further strengthen the Australia housing market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Provider: Private builders dominate the market with a share of 50% in 2025, driven by their ability to deliver diverse housing options, superior customization capabilities, and efficient project delivery timelines.
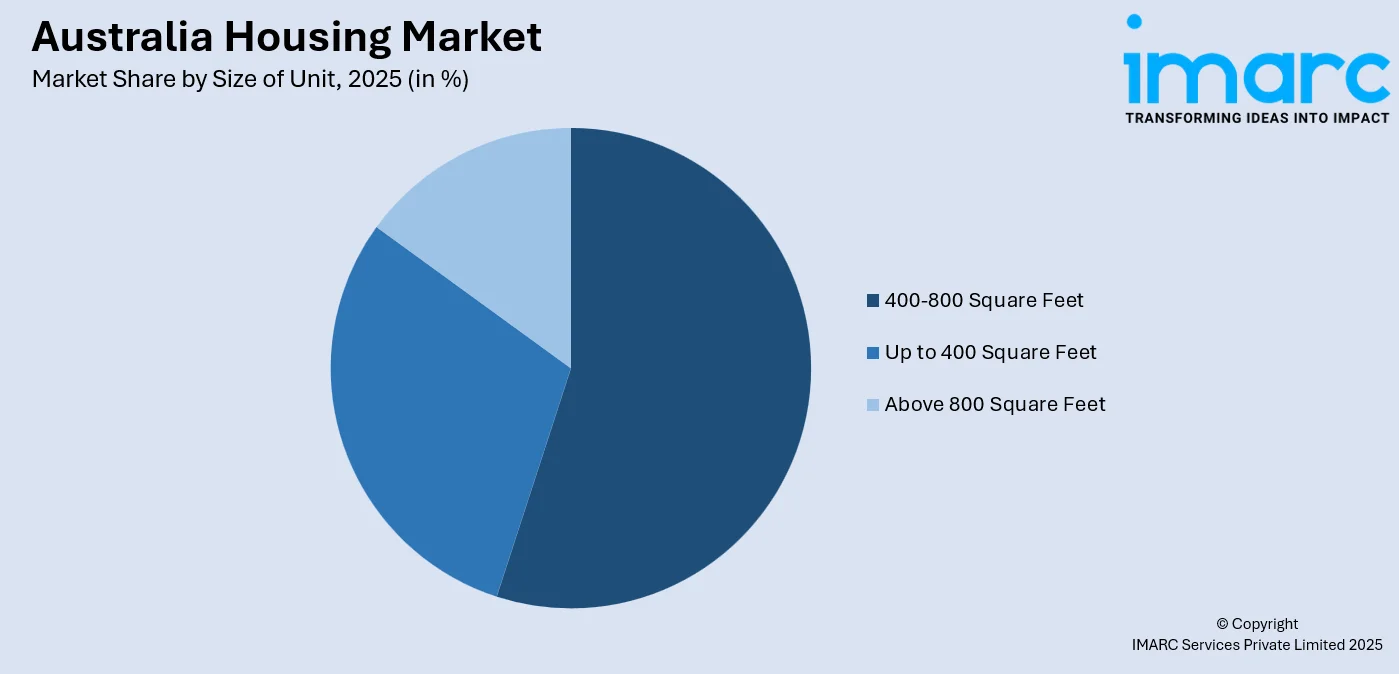
- By Size of Unit: 400-800 square feet leads the market with a share of 48% in 2025, owing to affordability alignment for first-time homebuyers and appeal to young professionals seeking practical living spaces.
- By Location: Urban represents the largest segment with a market share of 69% in 2025, driven by proximity to employment centers, access to essential amenities, well-developed transportation networks, and lifestyle preferences favoring connected communities.
- By Region: Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales leads the market with a share of 22% in 2025, owing to its economic hub function and employment opportunities in Sydney, with a continuous flow of population.
- Key Players: The Australia housing market exhibits a fragmented competitive structure with numerous private builders, government housing authorities, and public-private partnerships operating across different price segments and geographic regions, each targeting specific consumer demographics through varied service offerings.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The Australia housing market continues to experience robust growth propelled by fundamental demographic and economic factors shaping residential property demand. Sustained population growth through natural increase and immigration creates ongoing requirements for new housing stock across diverse price points and dwelling configurations. As per sources, in 2025, the Australian Government launched the Help to Buy Scheme, supporting up to 40,000 eligible households with shared-equity contributions of up to 40% for new homes. Moreover, urbanization trends concentrate demand in major metropolitan areas where employment opportunities and lifestyle amenities attract residents seeking convenient living arrangements. Government policies supporting homeownership accessibility, including first-home buyer schemes and stamp duty concessions, actively stimulate market activity and encourage household formation. Low unemployment rates and consistent wage growth enhance household purchasing capacity while favorable lending environments maintain mortgage affordability for prospective buyers.
Australia Housing Market Trends:
Rising Demand for Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Homes
The Australia housing market is witnessing increasing consumer preference for environmentally sustainable residential properties incorporating energy-efficient design principles. In February 2025, the Albanese Government expanded the Nationwide House Energy Rating Scheme to existing homes with CSIRO and industry partners, enabling better energy efficiency assessments and upgrades that reduce running costs and carbon emissions. Moreover, homebuyers are prioritizing properties featuring solar panel installations, water harvesting systems, improved insulation standards, and smart home technologies that reduce utility consumption. Builders are responding by integrating green building certifications and sustainable materials into new developments.
Growing Preference for Mixed-Use Integrated Developments
Australian housing preferences are evolving toward integrated mixed-use developments combining residential units with retail, commercial, and recreational facilities within unified precincts. According to reports, ALAND won the Cherrybrook Metro Station precinct tender in Sydney, planning a 410-home transit-oriented neighbourhood with retail, public spaces, and community amenities, reflecting growing demand for walkable, lifestyle-focused housing. These developments offer residents convenient access to essential services, dining options, and entertainment venues without requiring extensive travel. Urban planners and developers recognize the appeal of walkable communities that reduce car dependency while fostering neighbourhood connectivity.
Increasing Adoption of Modular and Prefabricated Construction Methods
The Australia housing market is experiencing growing adoption of modular and prefabricated construction techniques offering accelerated project completion timelines and enhanced quality control. These manufacturing-based approaches involve producing building components in controlled factory environments before assembly at construction sites. Benefits include reduced material waste, minimized weather-related delays, improved workplace safety, and consistent construction quality. According to sources, in March 2025, the Australian Government allocated $54 Million to advance prefabricated and modular home manufacturing, including $4.7 Million for a national certification process, supporting faster, high-quality housing supply.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The Australia housing market revenue is projected to demonstrate sustained growth throughout the forecast period, supported by persistent demand fundamentals and favorable economic conditions. Population growth through immigration and natural increase will continue generating new housing requirements across metropolitan and regional areas. Government housing affordability initiatives and infrastructure investments will expand development opportunities in emerging growth corridors. Evolving consumer preferences toward sustainable construction and integrated community developments will shape product offerings. Interest rate stabilization and employment market resilience will maintain buyer confidence and mortgage accessibility. The market generated a revenue of USD 150.95 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 182.34 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 2.04% from 2026-2034.
Australia Housing Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Provider |
Private Builders |
50% |
| Size of Unit | 400-800 Square Feet |
48% |
| Location | Urban |
69% |
| Region | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales |
22% |
Provider Insights:
- Private Builders
- Government
- Public Private Partnership
Private builders dominate with a market share of 50% of the total Australia housing market in 2025.
Private builders represent the leading provider within the Australia housing market, maintaining dominance through comprehensive service offerings spanning land acquisition, design, construction, and property settlement. These entities demonstrate superior market responsiveness, quickly adapting development strategies to address evolving consumer preferences and demographic requirements. Their established supply chain relationships ensure consistent material availability and competitive pricing structures. In September 2025, Metricon Homes led Australia’s residential construction sector for the tenth consecutive year, commencing 4,015 new homes across four states, reflecting sustained leadership among the Housing 100 builders.
Private builders leverage extensive industry experience and technical expertise to deliver diverse housing products ranging from entry-level apartments to premium detached residences. Strong relationships with financial institutions facilitate buyer financing solutions while marketing capabilities effectively reach target consumer categories. Operational efficiencies achieved through standardized processes and volume purchasing enable competitive positioning across various price points. Their ability to navigate regulatory requirements and manage complex development projects reinforces market leadership, ensuring continued dominance within the Australian residential construction landscape through responsive and innovative approaches.
Size of Unit Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Up to 400 Square Feet
- 400-800 Square Feet
- Above 800 Square Feet
400-800 square feet leads with a share of 48% of the total Australia housing market in 2025.
The 400-800 square feet dominates the Australia housing market, reflecting alignment with affordability priorities and practical living requirements among key buyer demographics. This size offers optimal balance between functional living space and manageable purchase prices, particularly appealing to first-time homebuyers entering property ownership. Urban apartment developments extensively utilize this size range to maximize dwelling yield while meeting minimum livability standards. As per sources, in 2025 the NSW government launched nine new apartment design patterns for small lots to fast‑track building approvals, encouraging development of compact, efficient units within this size range.
This unit size addresses growing household formation among young professionals and couples establishing independent residences without requiring extensive space. Lower maintenance obligations and reduced utility costs enhance ongoing affordability beyond initial purchase considerations. Investment properties within this size category demonstrate strong rental demand from students and young workers, providing attractive yields that encourage investor participation. The practical configuration suits contemporary lifestyle preferences emphasizing convenience and accessibility over expansive floor plans, sustaining strong market preference and continued dominance within Australian residential property transactions.
Location Insights:
- Urban
- Rural
Urban exhibits a clear dominance with a 69% share of the total Australia housing market in 2025.
Urban represents the overwhelmingly dominant choice within the Australia housing market, reflecting concentrated population distribution and economic activity within major metropolitan areas. Cities including Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, and Perth attract residents through superior employment opportunities across diverse industry sectors. Comprehensive infrastructure supporting transportation, healthcare, education, and retail services enhances urban living convenience and desirability. As per sources, the NSW Government launched nine architect-designed mid-rise apartment patterns, reducing approval times by 15 percent and accelerating delivery of high-quality, affordable housing, supporting urban densification across Sydney and surrounding areas.
Urban demand benefits from lifestyle preferences emphasizing accessibility to cultural amenities, entertainment venues, and social opportunities concentrated in city environments. Public transportation networks reduce vehicle dependency while enabling efficient commuting to employment centers. Government planning policies supporting urban densification through apartment and townhouse developments facilitate supply responsiveness to concentrated demand. Young professionals, families seeking quality education access, and retirees desiring convenient amenity proximity collectively sustain urban preference, reinforcing metropolitan dominance within the national housing market structure through persistent demographic and economic fundamentals.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales dominates with a market share of 22% of the total Australia housing market in 2025.
Australia Capital Territory and New South Wales represent the leading regional market, anchored by Sydney's position as the nation's largest city and primary economic center. This region benefits from diverse employment opportunities spanning finance, professional services, technology, and creative industries attracting domestic migrants and international immigrants. Established infrastructure and amenity provision support premium property values reflecting location desirability. The combination of economic dynamism, cultural vibrancy, and lifestyle appeal ensures sustained housing demand across various dwelling types and price categories throughout this prominent region.
The region provides stable government sector employment supporting consistent housing demand within the coastal areas and regional centers experience additional demand from lifestyle-motivated relocations and tourism-related economic activity. Population concentration and wealth accumulation within this region drive premium pricing and sophisticated development offerings. Strong educational institutions, world-class healthcare facilities, and diverse entertainment options enhance residential attractiveness, maintaining leading market position through sustained demand fundamentals and continued population growth from domestic and international migration sources.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the Australia Housing Market Growing?
Strong Population Growth and Immigration Trends
Australia's consistent population growth represents a fundamental driver propelling housing market expansion through sustained demand generation. The nation maintains attractive immigration policies drawing skilled workers, students, and family migrants who require residential accommodation upon arrival. As per sources, in 2025, Australia’s temporary visa population reached a record 2.93 Million, intensifying housing demand and underscoring the importance of initiatives like the Interim Development Fund to support urban housing supply. Further, natural population increase through births further compounds housing requirements across family-oriented dwelling types. Metropolitan areas particularly experience immigration concentration as new arrivals seek established community networks and employment opportunities.
Government Housing Affordability Initiatives and Incentive Programs
Government interventions supporting housing affordability significantly stimulate market activity by enhancing buyer purchasing capacity and reducing transaction barriers. First-home buyer grant programs provide direct financial assistance enabling deposit accumulation and reducing mortgage requirements. In 2025, the Australian Government expanded the Home Guarantee Scheme by removing place limits and increasing property price caps, enabling first home buyers nationwide to access 5% deposit option. Furthermore, stamp duty concessions and exemptions decrease transaction costs that otherwise impede market entry for price-sensitive buyers. Shared equity schemes allow government co-investment reducing individual borrowing requirements while maintaining ownership benefits. These initiatives particularly target younger demographics facing affordability challenges in competitive metropolitan markets, effectively expanding the addressable buyer pool and accelerating household formation rates.
Infrastructure Development and Urban Expansion Programs
Substantial infrastructure investment programs drive housing market growth by unlocking development potential in emerging suburban and regional areas. Transportation improvements including new rail lines, road upgrades, and public transit extensions reduce commuting burdens, enhancing residential desirability in previously peripheral locations. As per sources, in January 2025, the Albanese Government committed $182 Million to critical infrastructure in New South Wales that will unlock more than 25,000 new homes through roads, sewage, water, and transport links. Moreover, educational facility construction and healthcare service expansion improve community amenity provision supporting family-oriented housing demand. Utility infrastructure extensions enable residential development on previously unserviced land parcels.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the Australia Housing Market is Facing?
Persistent Housing Affordability Challenges in Major Markets
Housing affordability constraints in major metropolitan markets represent significant restraints limiting buyer participation and market accessibility. Property price appreciation outpacing income growth creates expanding deposit requirements that delay household formation among younger demographics. Elevated mortgage servicing costs relative to incomes reduce borrowing capacity. Rental market tightness further impedes savings accumulation among prospective buyers.
Skilled Labor Shortages Affecting Construction Capacity
The Australian construction industry faces persistent skilled labor shortages constraining housing delivery capacity and project timelines. Competition from infrastructure and commercial projects diverts tradesperson availability from residential construction. Training pipeline inadequacies fail to replace retiring experienced workers across critical trades. Labor shortages inflate construction costs through wage pressures while extending project completion schedules.
Regulatory Complexity and Planning Approval Delays
Complex regulatory environments governing residential development impose significant time and cost burdens restraining market supply responsiveness. Planning approval processes involving multiple government levels create uncertainty and delays affecting project feasibility assessments. Environmental, heritage, and community consultation requirements extend development timelines unpredictably. Regulatory compliance costs add to overall development expenses ultimately reflected in property pricing.
Competitive Landscape:
The Australia housing market demonstrates a fragmented competitive structure characterized by numerous participants operating across distinct geographic markets and product segments. Large-volume private builders capture significant market positions through operational scale advantages enabling cost-competitive pricing and extensive geographic coverage. Medium-sized regional builders maintain competitive presence through local market expertise and personalized customer service approaches. Government housing authorities address social and affordable housing segments through direct construction programs and land release initiatives. Public-private partnerships increasingly bridge capability gaps between government objectives and private sector delivery expertise. Competition occurs across multiple dimensions including pricing, location quality, design innovation, construction quality, and customer service experience.
Recent Developments:
- In January 2026, Cameron Brae Group revealed plans for a $67 Million commercial and retail centre at Bringelly, Sydney West, within the Birling Village masterplanned community, supporting 2100 homes with retail, health, recreation, and dining facilities, alongside residential subdivisions and infrastructure to enhance suburban living.
Australia Housing Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Providers Covered | Private Builders, Government, Public Private Partnership |
| Size of Units Covered | Up to 400 Square Feet, 400-800 Square Feet, Above 800 Square Feet |
| Locations Covered | Urban, Rural |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia housing market size was valued at USD 150.95 Billion in 2025.
The Australia housing market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 2.04% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 182.34 Billion by 2034.
Private builders held the largest market share, driven by their comprehensive service capabilities, diverse housing product offerings, established financial institution relationships, and superior market responsiveness addressing evolving consumer preferences across various price segments.
Key factors driving the Australia housing market include strong population growth through immigration, government affordability initiatives and incentive programs, sustained urbanization trends, favorable mortgage lending conditions, infrastructure development unlocking new areas, and investor confidence in residential property assets.
Major challenges include persistent housing affordability constraints in metropolitan areas, skilled labor shortages affecting construction capacity, regulatory complexity and planning approval delays, rising construction material costs, interest rate sensitivity affecting borrowing capacity, and land supply limitations in established urban areas.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












