
Australia Meat Substitutes Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Distribution Channel, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Meat Substitutes Market Overview:
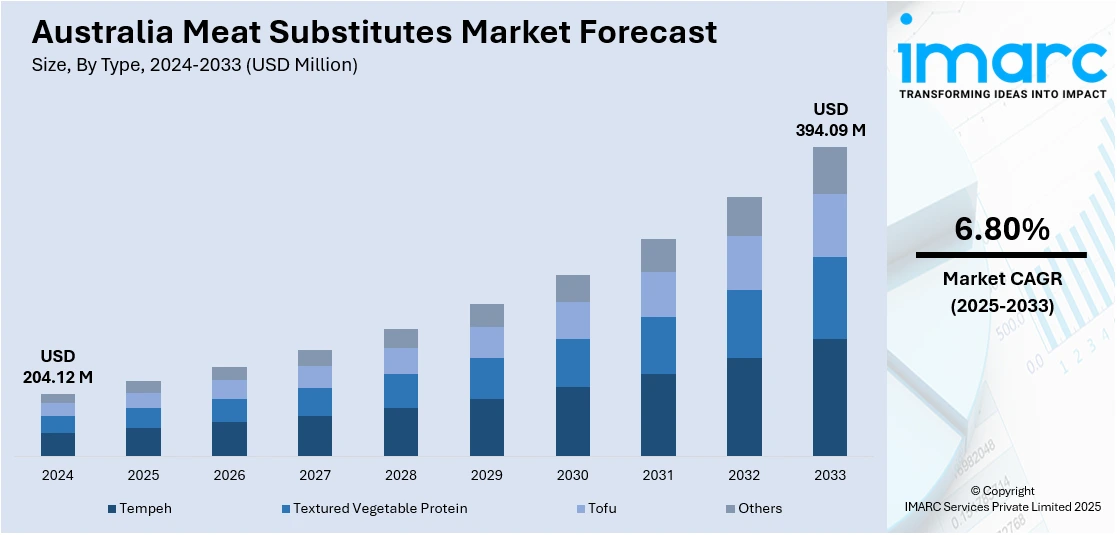
The Australia meat substitutes market size reached USD 204.12 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 394.09 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 6.80% during 2025-2033. At present, Australian consumers are becoming more health and wellbeing-conscious, driving the need for meat alternatives. Moreover, the increasing focus on environmental sustainability among consumers is propelling the market growth. This trend, along with the heightened product innovation and increasing variety is expanding the Australia meat substitutes market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 204.12 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 394.09 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 6.80% |
Key Trends of Australia Meat Substitutes Market:
Growing Health Awareness
Australian consumers are becoming more health and wellbeing-conscious, driving the need for meat substitutes. The changing dietary habits are mainly linked to increased worries related to the health implications of eating products from animal sources, including high cholesterol and saturated fats, and the connections to chronic health conditions like heart disease and diabetes. Consequently, people are actively looking for substitute protein products that contain less fat and calories yet provide adequate nutritional benefits. As awareness about plant-based nutrition rises, people are turning towards meat substitutes to enhance health and well-being. The trend is further supported by research on the benefits of plant-based diets, leading health-aware people to look for more sustainable and health-promoting food options. Increased demand for plant-based foods, together with an expanding awareness of the necessity for nutritional intake, is also fueling market growth for meat substitutes in Australia.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Heightened Environmental Awareness
Environmental sustainability is propelling the Australia meat substitutes market growth. With increased knowledge among consumers about the environmental effects of meat production such as deforestation, emission of greenhouse gases, and water consumption, there is an evident movement towards embracing environmentally friendly options. Individuals are becoming increasingly aware about how food can affect the health of the planet, leading to the transition from traditional meat products to plant-based alternatives with a smaller carbon footprint. The common fear of climate change is inspiring people to adopt meat substitutes as a means of curtailing individual contributions to environmental degradation. In response to this, various food companies are innovating and developing more sustainable alternatives, sustaining the call for plant-based proteins. The trend is becoming more prominent as more Australians embrace sustainability in their food choices, thereby playing a major role in supporting the growth of the market. Moreover, the recent Food Frontier consumer survey from 2024 indicated that about 5% of Australians were following a vegan diet. With the rise in veganism, 44% of Australians think that animal farming affects climate change, and a notable 79% chose to abstain from meat at least one day each week, which further contributes to the Australia meat substitutes market demand.
Product Innovation and Variety Advancements
The Australian meat substitutes sector is driven by product innovation progress and increasing variety. There are ongoing improvements as companies innovate new plant-based foodstuffs that bear a strong resemblance to the taste, texture, and look of regular meat. This can cater to wider audiences, including those not necessarily being vegan or vegetarian but seeking to minimize their meat intake. These developments are making meat alternatives more convenient and desirable, with better flavor, convenience, and nutritional profiles. Moreover, new product categories are being launched, including plant-based seafood and dairy products, which are widening the applicability of the meat substitutes market. The steady investment in research is assisting in the development of improved production processes, higher-quality products, and meeting a broader range of dietary requirements. In 2024, Australian plant-based meat brand vEEF introduced a line of four carbon-neutral products, all priced at the same level as or less than their animal-based alternatives. The items comprise plant-based classic sausages, plant-based beef mince, plant-based smokey sausages, and plant-based chorizo sausages. They are reportedly crafted by chefs and filled with nutrients, featuring 50% less plastic packaging compared to earlier vEEF items.
Growth Drivers of Australia Meat Substitutes Market:
Emergence of Ethical Consumerism and Consciousness of Animal Welfare
One of the major drivers of growth in the meat substitutes market in Australia is growing concern about the welfare of animals and the ethics of rearing livestock. Australian consumers, particularly younger people and city residents are increasingly outspoken in raising concerns about the ethical nature of factory farming and conventional meat production. Social media campaigns, animal rights advocacy, and documentaries have helped fuel this social change. Consequently, numerous Australians are opting for plant-based options for health or environmental purposes and to match food values. This trend is especially prevalent in states such as Victoria and New South Wales, where ethical food markets and community-supported agriculture are on the rise. In addition, Australian brands are answering with cruelty-free labeling and animal-friendly certification marketing. Restaurants, cafes, and food trucks also market meat-free foods as "ethical" or "compassionate options," driving greater adoption of meat substitutes outside of vegetarian and vegan circles.
Export Potential and Regional Trade Opportunities
According to the Australia meat substitutes market analysis, another key driver of the industry is its growing position as a producer and exporter within the Asia-Pacific region. With its robust agricultural foundation and established food manufacturing infrastructure, Australia is well placed to build high-quality, plant-based protein products for both national and export markets. Alliances with neighboring nations like Singapore, Japan, and South Korea also provide increasing export markets for Australia-produced meat substitutes as these countries increasingly experience rising demand for sustainable protein. Support from the government for agrifood innovation and export diversification has also spurred investment in the production of meat substitutes. Besides, Australia's geographical strength enables it to become a food innovation center for the region, combining indigenous ingredients such as wattleseed or macadamia into meat-free foods acceptable to Pacific and Asian tastes. Having the capacity to ride on its clean, green image and commitment to quality assurance provides Australia with competitive advantage in regional trade, which also encourages domestic production and investment in the expanding category.
Technological Advancement and Food Innovation Ecosystem
Australia's expanding network of food tech innovation is a driving force behind the advancement of meat substitutes. Through institutions like CSIRO and university-startup collaborations, the nation is seeing the development of sophisticated meat-free proteins that better replicate the texture, flavor, and nutritional content of actual meat. Food tech accelerators in Sydney and Brisbane foster startups testing fermentation-based protein, cellular agriculture, and new plant-based formulations. State-funded resources and the ability to leverage nearby expertise in bioprocessing, flavor science, and sustainable agriculture enable Australian firms to scale faster and create products localized for local taste profiles. In addition, increased cooperation between conventional meat producers and plant-based businesses indicates a national food industry-wide move towards diversification. These technological advancements improve the quality of available meat substitutes, while establishing Australia as a global leader in sustainable protein innovation, drawing both consumer and investor attention.
Opportunities of Australia Meat Substitutes Market:
Expansion into Regional and Rural Consumer Markets
One of the key opportunities for Australia's meat substitutes industry is to push into rural and regional towns, where plant-based meals have historically been less common. With health and sustainability consciousness spreading further than major urban areas, meat substitute demand is beginning to pick up in Queensland, Victorian, and South Australian towns and agricultural centers. Retailers and local supermarkets in these countries are increasingly carrying plant-based equivalents such as burger patties, sausages, and ready-to-heat meals, offering new points of access for consumers who might not have had access to them before. Additionally, school food programs and news stories on healthy eating are slowly changing attitudes among families and older age groups. The presence of meat alternatives that offer similar texture and flavor to familiar foods such as meat pies or BBQ-style items, which provides a connection between old diets and new food ways. Leveraging this opportunity enables companies to expand their customer bases while promoting more inclusive eating options nationwide.
Integration of Indigenous Ingredients and Culinary Identity
Australia's rich biodiversity and Indigenous culinary heritage offer a unique opportunity for innovation within the meat substitutes market. By incorporating native ingredients such as wattle seed, bush tomatoes, and saltbush into plant-based protein products, manufacturers can differentiate their offerings with distinctly Australian flavors. These ingredients not only enhance taste profiles but also resonate with local consumers seeking authenticity and connection to the land. Partnerships with Indigenous groups can also push ethical sourcing and cultural understanding, producing products that honor Australia's culinary heritage and generate economic benefits for local communities. Examples include a plant-based sausage flavored with lemon myrtle or a pepper berry-spiced burger patty to engage curious consumers and visitors alike. Such food storytelling through plant-based innovation constructs a distinct Australian identity within the global meat alternatives marketplace. As demand increases for sustainable, culturally relevant food, the incorporation of traditional knowledge in product development provides commercial interest as well as social worth.
Export Growth Through Asia-Pacific Partnerships
Australia is well placed to be a leading exporter of meat alternatives to the rapidly expanding Asia-Pacific market. Japan, South Korea, Singapore, and China are witnessing increased demand for plant protein due to health issues, urbanization, and changing food habits. With its excellent record in food safety, quality, and soil-through-plate cleanliness, Australia can utilize trade relationships to ship value-added, innovative meat alternatives to neighboring markets. Free trade agreements and intimate logistical connections complement this potential, especially for frozen, shelf-stable, and pre-cooked plant-based products. Australian businesses that customize their products to regional tastes, like soy-based foods for East Asia or gluten-free versions for export to health-conscious markets, can gain a competitive advantage. Furthermore, highlighting Australian-grown crops and eco-friendly cultivation methods allows these products to be marketed as premium, eco-friendly options. This export-led growth potential provides a valuable dimension to Australia's local plant-based sector, allowing production upscaling and global recognition.
Challenges of Australia Meat Substitutes Market:
Cultural Attachment and Consumer Perception of Meat
One of the largest challenges that the meat substitutes market in Australia has is the cultural predisposition towards eating traditional meat. Barbecues, roasts, and meals featuring meat are an institution within Australian culture, particularly in rural and suburban areas. This cultural convention presents a psychological hurdle for most consumers, who will either perceive plant-based substitutes as inferior, over-processed, or lacking taste and texture. In spite of improvements in product innovation, persuading long-established meat consumers to change or even try alternatives is a gradual process. Opposition is usually greater among the elderly population and in families that value value for money as well as cooking convenience. In addition, Australian food culture, shaped by British and Mediterranean cuisine, has strong focus on animal proteins, and therefore, the scope of substitutability is narrow unless a product can successfully duplicate the total sensory and culinary experience of the meat. Shattering these images takes significant education, improved product quality, and more innovative marketing that respects regional food culture.
Price Sensitivity and Accessibility in Regional Areas
Affordability and availability remain major concerns for increasing Australia's meat substitutes market, especially beyond the capital cities. Even though plant-based products are growing in major city supermarkets, they tend to be higher in price than conventional meat, less appealing to budget-conscious consumers. In rural and regional areas, where incomes at home could be lower and food prices higher because of transport costs, premium-priced meat substitutes find it difficult to catch on. Also, narrow product range in smaller stores hampers exposure to newer, more innovative plant-based alternatives. Such unequal access perpetuates the belief that meat substitutes are luxury or specialty goods. Even among city consumers, affordability is still a restraint to frequent consumption, particularly when consuming in larger family groups. Manufacturers and retailers need to overcome this obstacle by enhancing supply chain effectiveness, investing in domestic production, and making access-oriented entry-level products available to suit budget-conscious everyday Australian consumers.
Regulatory and Labelling Uncertainty
A further major challenge facing the Australian meat substitutes market is the consistent controversy surrounding product labelling, regulation, and classification of food. Industry associations for conventional meat manufacturers have complained about plant-based alternatives employing labels such as "sausage," "burger," or "meat," claiming it confuses consumers. This has resulted in demands for tighter labelling regulations and intervention by regulators, which leaves uncertainty among plant-based brands based in the nation. Such regulatory uncertainty can slow down product releases, raise costs of compliance, and make marketing more complex. Further, the absence of an overarching framework for nutritional claims, processing standards, and ingredient origin complicates the task of gauging the health value or sustainability of a wide range of products. Food standards and labelling legislation being under federal and state jurisdiction complicates this process for local producers as well as global brands seeking entry in the market. Overcoming these regulatory hurdles will take industry cooperation, well-crafted guidelines, and customer-centric policies that encourage transparency without inhibiting innovation.
Australia Meat Substitutes Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country and regional levels for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on type and distribution channel.
Type Insights:
- Tempeh
- Textured Vegetable Protein
- Tofu
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes tempeh, textured vegetable protein, tofu, and others.
Distribution Channel Insights:
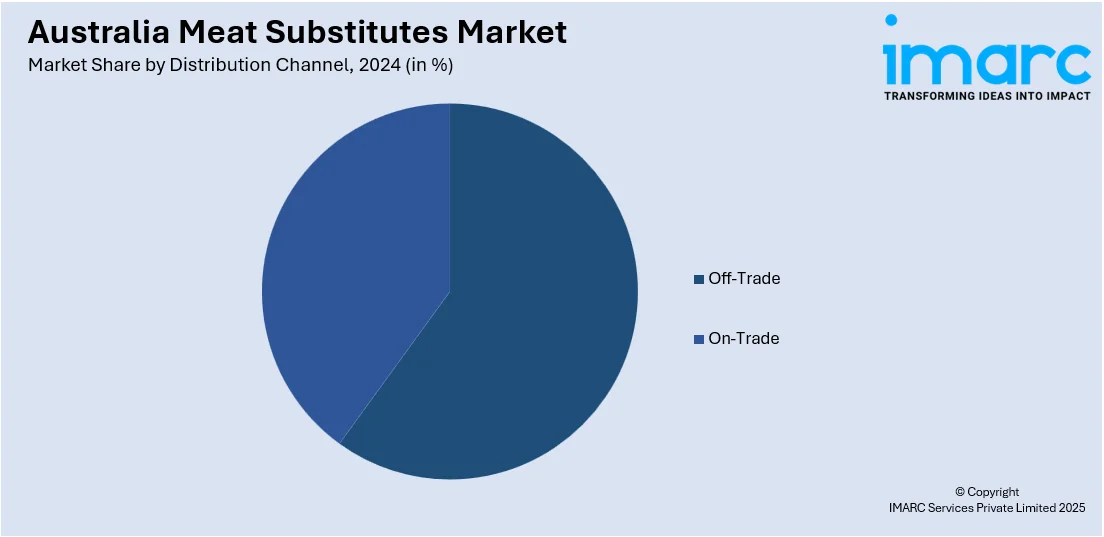
- Off-Trade
- Convenience Stores
- Online Channels
- Supermarkets and Hypermarkets
- Others
- On-Trade
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the distribution channel have also been provided in the report. This includes off-trade (convenience stores, online channels, supermarkets and hypermarkets, and others) and on-trade.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Meat Substitutes Market News:
- In September 2024, the Australian plant-based meat company vEEF introduced a selection of four carbon-neutral items, all priced similarly to or less than their animal-derived equivalents. The items include Plant Based Ground Beef, Plant Based Traditional Sausages, Plant Based Smoky Sausages, and Plant Based Chorizo Sausages. They are described as being created by chefs and packed with nutrients, featuring 50% reduced plastic packaging compared to earlier vEEF offerings.
- In May 2024, new findings from a 2023 State of the Industry report by Food Frontier indicate that Australia's plant-based meat sector remains resilient despite macroeconomic challenges and maintains a hopeful outlook – underscoring its lasting appeal and increasing future possibilities. Findings indicated that Australia’s plant-based meat production sector added $45.8 million in value to the economy during the 2023 financial year and predicted that it might contribute over half a billion dollars to the economy by 2033.
- In February 2023, food tech firm Harvest B inaugurated Australia’s inaugural plant-protein factory. The facility located in Sydney is a cutting-edge area outfitted with the most recent manufacturing technology, backed by a USD 1 Million co-investment from the Australian Government's Advanced Manufacturing Growth Centre. Harvest B claims their goal is to build a world where food is more nutritious, environmentally friendly, and easier to obtain. The concept for the company emerged when its founders identified a significant gap in Australia’s plant-based protein industry, specifically, there was no Australian business providing locally produced plant proteins to domestic food manufacturers.
Australia Meat Substitutes Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Tempeh, Textured Vegetable Protein, Tofu, Others |
| Distribution Channels Covered |
|
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia meat substitutes market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia meat substitutes market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia meat substitutes industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia meat substitutes market was valued at USD 204.12 Million in 2024.
The Australia meat substitutes market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 6.80% during 2025-2033.
The Australia meat substitutes market is expected to reach a value of USD 394.09 Million by 2033.
The Australia meat substitutes market trends showcase advanced plant-based formulation and fermentation technologies appealing to mainstream consumers. Products increasingly feature native Australian ingredients and flavors, aligning with local taste preferences. Retail shelves spotlight dedicated meat-alternative aisles, while foodservice collaborations bring creative offerings to menus. Sustainability, transparency, and innovation also define the market’s direction.
The Australia meat substitutes market is driven by rising ethical consumerism, food innovation, and demand for sustainable protein sources. Increased awareness about animal welfare, support for local plant-based startups, and government-backed research into alternative proteins are encouraging consumers to shift away from traditional meat, fueling steady growth in the sector.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












