
Australia Seeds Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Seed Type, Traits, Availability, Seed Treatment, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Seeds Market Overview:
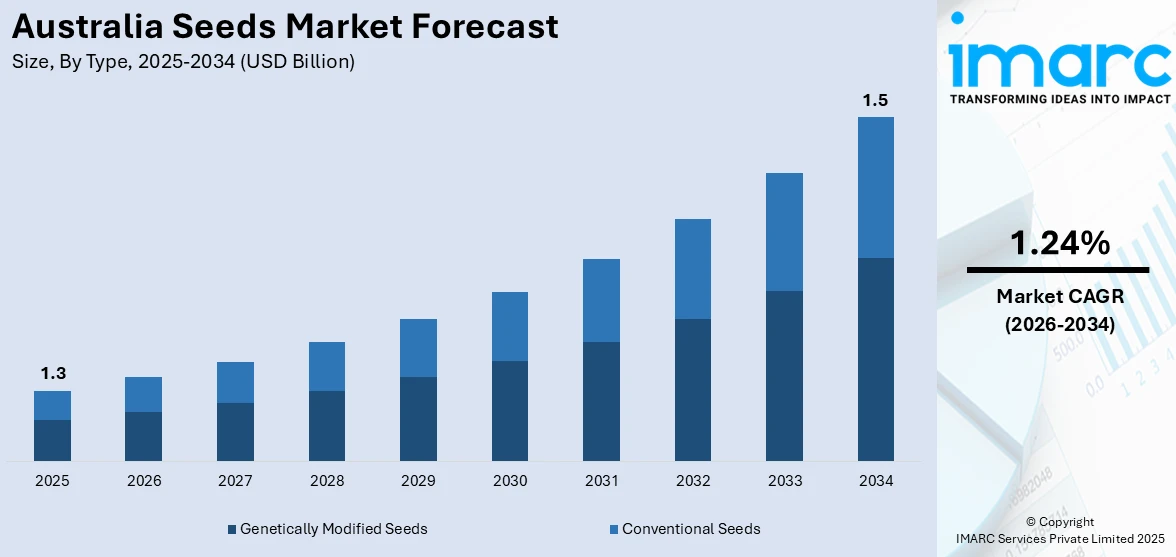
The Australia seeds market size reached USD 1.3 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 1.5 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 1.24% during 2026-2034. The increasing demand for high-yield, disease-resistant crops, rising adoption of genetically modified seeds, government support for sustainable agriculture, technological advancements in seed treatment, expanding organic farming practices, growing population-driven food demand, and climate change adaptation needs are some of the major factors Australia seeds market share.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.3 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 1.5 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 1.24% |
Key Trends of Australia Seeds Market:
Rising Adoption of Genetically Modified (GM) and Hybrid Seeds
The market is witnessing significant growth in the adoption of genetically modified (GM) and hybrid seeds, driven by the need for higher yields, improved resistance to pests and diseases, and enhanced adaptability to climatic variations. Genetically modified crops, such as herbicide-tolerant canola and insect-resistant cotton, are gaining widespread acceptance among Australian farmers due to their ability to reduce production costs and improve efficiency. In addition to this, hybrid seeds are also increasingly used in horticultural and grain crops, offering superior yield potential, uniformity, and better resistance to environmental stressors. Apart from this, supportive government policies and regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in increasing the adoption of GM and hybrid seeds, which is positively impacting the Australia seed market outlook. Besides this, farmers are prioritizing high-performance seed varieties to maximize productivity, thereby driving demand for genetically improved seeds in the Australian market. For instance, according to industry reports, Yandal Farms in West Casuarinas, Western Australia, achieved a yield of 1.7 tonnes per hectare with the new PY422G Optimum GLY Y Series glyphosate-tolerant hybrid canola seeds despite minimal rainfall during the 2023 season. Approximately 50 PY422G crops were cultivated in side-by-side demonstrations across Western Australia to evaluate the hybrid's performance under local conditions. The farm manager noted the hybrid's superior vigor and standability compared to other varieties grown concurrently.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Expansion of Organic and Sustainable Farming Practices
The growing consumer preference for organic and sustainably grown food products is supporting the Australia seeds market growth. There is a rise in demand for organic, open-pollinated seeds. Consumers are increasingly concerned about environmental sustainability, food safety, and pesticide residues, prompting a shift toward organic farming. According to a report by IMARC Group, the organic farming market in Australia is expected to reach USD 5.42 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 7.6% from 2025-2033. This trend is further supported by government initiatives promoting regenerative agriculture and biodiversity conservation. Farmers are investing in climate-resilient seed varieties that require minimal chemical inputs, contributing to long-term soil health and ecological balance. The organic seed market is also benefiting from stringent organic certification standards set by organizations such as Australian Certified Organic (ACO) and the National Association for Sustainable Agriculture, Australia (NASAA). These regulations ensure that seed production adheres to sustainable practices, further reinforcing consumer trust. Additionally, the rise of urban and community gardening initiatives is further increasing the need for heirloom and heritage seeds, allowing small-scale farmers and hobbyist gardeners to cultivate diverse and resilient crops. This shift is gradually transforming seed supply chains, emphasizing sustainability and transparency.
Growth Factors of Australia Seeds Market:
Government Support and Agricultural R&D Investments
The Australian government plays a crucial role in advancing the nation’s seed market through robust support for agricultural research and development. Federal and state programs include tax credits, research funds, and financial grants to foster innovation in seed technology, crop resilience and advanced biotechnology. There has also been cooperation between government departments, agricultural universities, and privately held research organizations that has resulted in the creation of high-production seed varieties that would suit the Australian soil and climatic conditions. Emphasis in these programs is also given on increasing productivity, sustainability, and resistance to diseases. Moreover, this investment is supported by the policy frameworks, which give priority to food security and sustainable practices of farming practices. As a result, farmers gain access to advanced seed solutions that meet evolving agricultural needs, while researchers and breeders benefit from a supportive and innovation-driven ecosystem.
Increased Mechanization and Precision Farming
Australia’s agriculture sector is experiencing a steady shift toward mechanization and precision farming, which is significantly influencing the demand for improved seed varieties. Farmers are increasingly adopting GPS-guided tractors, drone-based crop monitoring, and automated planting technologies to enhance productivity and efficiency, which is further boosting the Australia seeds market demand. These advanced systems require uniform, high-quality seeds that can be sown with precision and perform consistently across large tracts of farmland. In turn, this has spurred demand for certified seeds with uniform germination rates, disease resistance, and enhanced yield potential. Precision farming also relies on data analytics, helping farmers make informed decisions about seed selection, planting density, and fertilization. This integration of smart technologies into agriculture is not only improving operational outcomes but also pushing seed manufacturers to innovate and align their products with evolving mechanized practices.
Shifting Climatic Patterns and Crop Adaptability Needs
Australia’s agriculture sector faces increasing uncertainty due to shifting climate conditions, including prolonged droughts, erratic rainfall, soil salinity, and extreme temperatures. These challenges have elevated the importance of developing and adopting seed varieties that can thrive under unpredictable and harsh environmental conditions. Farmers are now seeking resilient seed strains capable of maintaining productivity despite climate stressors. Seed developers and agribusinesses are responding by breeding varieties that offer drought tolerance, heat resistance, and adaptability to saline soils. Climate-smart seed solutions are also helping reduce crop failure risk and enhance food security across affected regions. As the frequency of climate-related disruptions rises, the demand for high-performance, stress-resistant seeds continues to grow, positioning adaptability as a critical driver of seed innovation and long-term agricultural viability in Australia.
Opportunities of Australia Seeds Market:
Export Potential to Asia-Pacific and Middle East Markets
Australia’s seed industry holds strong export potential, especially in the Asia-Pacific and Middle East regions where food security and agricultural modernization are pressing concerns. The country’s rigorous seed certification systems and strict phytosanitary protocols ensure high-quality, disease-free exports that meet global standards. As nations in these regions experience population growth, shifting diets, and increasing reliance on imported food, the demand for reliable seed varieties—particularly in cereals, pulses, oilseeds, and horticulture—is expanding. Australia's strategic geographic location and trade agreements also offer logistical advantages for exporters. Moreover, climate-adapted Australian seed varieties are well-suited to arid and semi-arid environments found in these regions. Strengthening partnerships with regional distributors and governments can further amplify Australia’s role as a trusted seed supplier in the global agricultural value chain.
Development of Specialty and Niche Crops
The growing demand for alternative, health-focused, and culturally relevant foods presents an exciting opportunity for Australia’s seed sector to diversify into specialty and niche crop segments. Crops like quinoa, hemp, chia, medicinal herbs, bush tomatoes, and native wattleseeds are gaining traction in domestic health food markets and international gourmet, wellness, and nutraceutical industries. According to the Australia seeds market analysis, these underutilized but high-value crops offer premium pricing and attract both traditional farmers and start-ups looking to differentiate their offerings. Developing high-quality, region-specific seed varieties for such crops can help meet rising consumer interest while supporting sustainable land use and indigenous agriculture. By investing in research, partnerships with First Nations communities, and targeted breeding programs, seed producers can position themselves as leaders in these emerging categories and tap into growing export opportunities.
Integration of Digital Platforms for Seed Distribution
The rise of digital agriculture and e-commerce is transforming how seeds are marketed and distributed in Australia, creating new opportunities for both producers and farmers. Digital platforms—ranging from specialized seed marketplaces to agri-retail apps—allow small and mid-sized seed companies to reach a broader, geographically diverse customer base. These platforms provide easy product comparisons, transparent pricing, and traceability features that increase buyer confidence. Additionally, integration with farm management software enables data-driven seed selection based on soil type, climate, and cropping history. For farmers, this translates into improved decision-making and crop outcomes. Real-time delivery tracking, customer reviews, and loyalty programs further enhance the user experience. The expansion of digital distribution channels also reduces intermediaries, lowers costs, and empowers producers to build stronger, direct-to-farmer relationships in a competitive seed market.
Challenges of Australia Seeds Market:
Stringent Regulatory and Biosecurity Requirements
Australia’s seed industry operates under one of the world’s most rigorous regulatory and biosecurity frameworks, designed to protect native ecosystems, crops, and biodiversity. While these regulations are critical for ensuring agricultural safety, they also pose significant hurdles for seed producers and international partners. Import restrictions, prolonged quarantine procedures, and complex documentation often delay the introduction of new seed varieties and slow innovation. Additionally, strict controls on genetically modified organisms (GMOs) create further limitations on what can be developed or imported. For seed companies—especially smaller or international entrants—navigating these regulatory pathways requires deep expertise, considerable investment, and substantial time. Although these frameworks maintain high-quality standards, the complexity of compliance can inadvertently stifle growth, limit global collaboration, and reduce the pace of product diversification in the market.
Limited Awareness Among Smallholder Farmers
Despite technological advances and seed innovation, a significant portion of Australia’s smallholder and mid-sized farmers continue to depend on traditional seed-saving methods. This reliance is often driven by limited access to agricultural education, lack of exposure to improved seed varieties, and financial constraints. Many growers are unaware of the benefits that scientifically bred seeds can offer in terms of higher yields, better pest and disease resistance, and climate adaptability. As a result, the adoption rate of commercial seeds remains suboptimal in several regions, particularly in remote or economically disadvantaged farming communities. Bridging this gap requires targeted extension services, farmer training programs, and accessible demonstration trials to showcase the effectiveness of modern seed technologies. Without such efforts, market growth potential remains constrained by information and accessibility barriers.
High Production Costs and Market Consolidation
Producing high-quality seeds in Australia involves considerable investment in research, development, testing, and regulatory compliance. From breeding programs to field trials and quality certification, each step incurs rising operational costs. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), these expenses often represent a barrier to market entry or expansion. At the same time, increasing market consolidation has resulted in a few large players dominating seed production and distribution, which can limit competition and the diversity of available seed options. This concentration may also hinder innovation, as larger firms typically focus on high-volume commercial crops over niche or emerging varieties. The combination of financial pressure and competitive imbalance poses challenges for smaller firms and farmers alike, ultimately affecting affordability, accessibility, and the overall resilience of the seed supply chain.
Australia Seeds Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on type, seed type, traits, availability, and seed treatment.
Type Insights:
- Genetically Modified Seeds
- Conventional Seeds
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the type. This includes genetically modified seeds and conventional seeds.
Seed Type Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
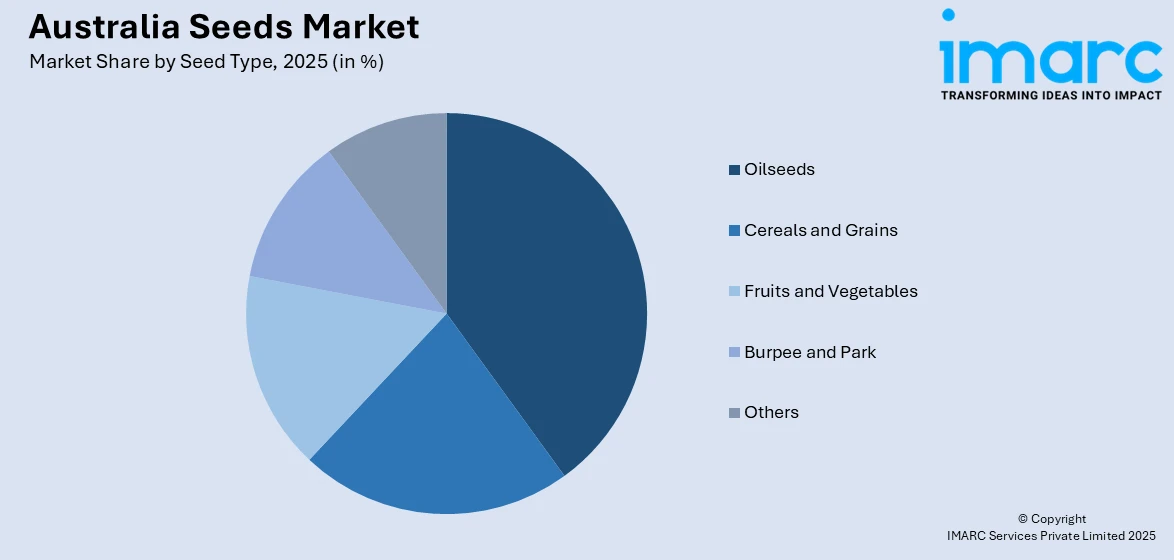
- Oilseeds
- Soybean
- Sunflower
- Cotton
- Canola/Rapeseed
- Cereals and Grains
- Corn
- Wheat
- Rice
- Sorghum
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Tomatoes
- Lemons
- Brassica
- Pepper
- Lettuce
- Onion
- Carrot
- Burpee and Park
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the seed type have also been provided in the report. This includes oil seeds (soybean, sunflower, cotton, and canola/rapeseed), cereals and grains (corn, wheat, rice, and sorghum), fruits and vegetables (tomatoes, lemons, brassica, pepper, lettuce, onion, and carrot), burpee and park, and others.
Traits Insights:
- Herbicide-Tolerant (HT)
- Insecticide-Resistant (IR)
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the traits. This includes herbicide-tolerant (HT), insecticide -resistant (IR), and others.
Availability Insights:
- Commercial Seeds
- Saved Seeds
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the availability have also been provided in the report. This includes commercial seeds and saved seeds.
Seed Treatment Insights:
- Treated
- Untreated
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the seed treatment. This includes treated and untreated.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided, including:
- AlfaGen Seeds Company Pty Ltd
- Australian Seed Supplier Pty Ltd
- Bejo Australia Pty Ltd
- DLF Seeds Australia
- Fairbanks Seeds
- Nindethana Seed Service Pty Ltd
- Pioneer Seeds
- Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel B.V.
- Royston Petrie Seeds
- Terranova Seeds Australia
- The Seed Collection Pty Ltd
Australia Seeds Market News:
- On October 25, 2024, Rijk Zwaan, in collaboration with Van der Hoeven Horticultural Projects, commenced construction of a new seed production facility near Melbourne, Australia. The facility will incorporate both traditional and semi-closed greenhouse technologies to optimize cooling and pest control. The hybrid seeds produced will be exported to the Netherlands for processing and sales.
- On November 25, 2024, S&W Seeds Australia announced its rebranding to AlfaGen Seeds following its acquisition by Avior Capital Partners. The company will focus on producing seed varieties such as lucerne, pasture legumes, ryegrass, forage sorghum, forage cereals, and sunflowers. The company plans to consolidate operations in Keith, South Australia, and Deniliquin, New South Wales.
Australia Seeds Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Genetically Modified Seeds, Conventional Seeds |
| Seed Types Covered |
|
| Traits Covered | Herbicide-Tolerant (HT), Insecticide-Resistant (IR), Others |
| Availabilities Covered | Commercial Seeds, Saved Seeds |
| Seed treatments Covered | Treated, Untreated |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Companies Covered | AlfaGen Seeds Company Pty Ltd, Australian Seed Supplier Pty Ltd, Bejo Australia Pty Ltd, DLF Seeds Australia, Fairbanks Seeds, Nindethana Seed Service Pty Ltd, Pioneer Seeds, Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel B.V., Royston Petrie Seeds, Terranova Seeds Australia, The Seed Collection Pty Ltd, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia seeds market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia seeds market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia seeds industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The seeds market in Australia was valued at USD 1.3 Billion in 2025.
The Australia seeds market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 1.24% during 2026-2034.
The Australia seeds market is projected to reach a value of USD 1.5 Billion by 2034.
The major trends of the Australia seeds market are increased adoption of climate-smart seed varieties, along with rising use of digital farming platforms for precision planting. Additionally, collaborative research in seed genetics and a push for native and specialty crop seeds are gaining traction.
The expanding international trade agreements and rising demand for food security are fueling seed innovation. Government-backed climate adaptation initiatives, along with growing investment in vertical farming and controlled-environment agriculture, are further supporting market expansion. The shift toward plant-based diets is also increasing the demand for diverse, high-protein seed varieties.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












