
Australia Shrimp Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Environment, Species, Shrimp Size, Distribution Channel, and Region, 2026-2034
Australia Shrimp Market Size and Share:
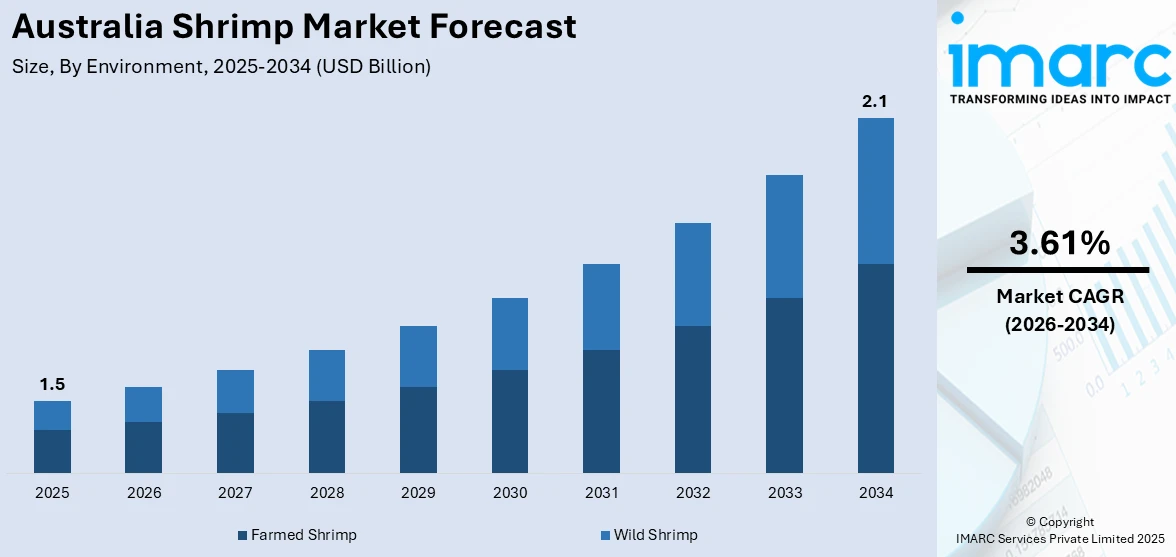
The Australia shrimp market size reached USD 1.5 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 2.1 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 3.61% during 2026-2034. The growing seafood demand, export opportunities, and aquaculture advancements are driving the Australia shrimp market share. Additionally, increasing health consciousness, rising global trade, and improved farming techniques are improving production, strengthening sustainability, and expanding the market growth.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2025 |
|
Forecast Years
|
2026-2034
|
|
Historical Years
|
2020-2025
|
| Market Size in 2025 | USD 1.5 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2034 | USD 2.1 Billion |
| Market Growth Rate 2026-2034 | 3.61% |
Key Trends of Australia Shrimp Market:
Growing Seafood Demand
The escalating demand for seafood in significantly influencing the Australian shrimp market outlook. As consumers are becoming more health-conscious, they are increasingly choosing seafood including shrimp, as a healthier protein alternative. Shrimp is high in protein, low in fat, and packed with essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, making it a preferred choice for individuals focused on balanced nutrition. Additionally, the growing trend of sustainable eating is influencing consumption patterns. Shrimp is viewed as a more environment friendly protein compared to traditional meat sources, further fueling its popularity. Australian consumers are particularly inclined toward seafood that is traceable and sustainably produced, aligning with the nation’s increasing focus on environmental responsibility. Australia’s strong fishing and aquaculture sectors are well-positioned to meet this rising demand through advanced farming techniques and improved harvesting methods. These innovations ensure a steady supply of high-quality shrimp while maintaining sustainability standards. Reflecting this stability, Australia’s fisheries and aquaculture production is projected to remain steady between 2024–25 and 2028–29, with an average value of $3.48 billion. As the seafood industry continues to expand, shrimp remains a key contributor, reinforcing its role in both domestic consumption and the broader market.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
Export Opportunities
Australia’s strategic location in the Asia-Pacific region positions it as a key shrimp exporter to high-demand markets such as Japan, China, and the United States. The rising global consumption of seafood, combined with Australia’s reputation for high-quality, sustainably sourced shrimp, is strengthening its competitiveness in the international market. Trade agreements and reduced tariffs are further facilitating shrimp exports. With established free trade agreements (FTAs) with major economies, Australian shrimp exporters can access foreign markets with fewer restrictions. This is improving profitability, encouraging investments in shrimp farming and processing facilities, and contributing to Australia’s strong trade performance, reflected in its $54.8 billion goods and services surplus in 2023–24. In addition, the growing preference for premium and organic seafood in international markets is further strengthening the Australian shrimp market growth. Consumers, particularly in Asia and North America, are willing to pay higher prices for sustainably farmed shrimp, giving Australian producers a competitive advantage. As export opportunities expand, the shrimp industry is scaling up production to meet foreign demand. This growth is driving advancements in aquaculture techniques, improving supply chain efficiency, and solidifying Australia’s position as a leading shrimp exporter in the global seafood industry.
Growth Factors of Australia Shrimp Market:
Rising Health and Nutrition Awareness
The growing awareness about the nutritional value of shrimp is a major factor supporting market expansion in Australia. Shrimp is recognized as a rich source of lean protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential vitamins and minerals, making it an appealing option for health-conscious consumers. As the trend towards balanced diets, weight control, and prevention of lifestyle diseases has risen, seafood like shrimp is becoming popular as a healthier substitute for red meat and processed meat. Moreover, dietary routines and nutrition awareness on the value of eating seafood are helping boost consumer confidence in shrimp. This increased demand is in line with the overall wellness trends, which promote the use of shrimp more often by households as well as foodservice providers, thus increasing overall constant demand within the domestic food market.
Advancements in Aquaculture Technology
Technological innovation in aquaculture is significantly boosting the Australia shrimp market demand. Modern practices such as biofloc systems and recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) have improved yields while minimizing environmental challenges. These practices are beneficial to water quality, disease risk, and the potential for sustainable shrimp farming with less consumption of resources. Automated and smart monitoring technologies also enable more efficient monitoring of shrimp growth, feed, and health by farmers, thereby limiting production losses. Such opportunities are vital to remove previous limitations in farming, particularly disease outbreaks, as well as ecological issues with the old farming systems. The momentum of introducing these new technologies enables Australia to become a leader in sustainable aquaculture, enhancing the production efficiencies of the industry while ensuring longer-term sustainability. The shift is further enhancing the industry's competitiveness locally and globally.
Expanding Domestic Consumption Channels
The growing diversity of consumption channels in Australia is creating new demand for shrimp products. Shrimp-based dishes are becoming increasingly popular across restaurants, quick-service outlets, and casual dining chains, contributing to stronger foodservice demand. Simultaneously, retail markets are witnessing a surge in ready-to-cook and packaged shrimp products, catering to households seeking convenience without compromising nutrition. E-commerce platforms and online grocery delivery services are further expanding consumer access to shrimp, offering wider product variety and home delivery options. These evolving distribution channels not only improve accessibility but also encourage experimentation with new shrimp-based recipes among consumers. As convenience, variety, and affordability gain importance, expanding domestic consumption avenues are playing a vital role in strengthening the Australian shrimp market’s overall growth.
Opportunities of Australia Shrimp Market:
Sustainable Farming Practices
The growing global demand for responsibly sourced seafood is creating significant opportunities for Australia’s shrimp sector. Consumers are increasingly concerned about sustainability, traceability, and environmental impact, which positions Australian producers to stand out through eco-friendly certifications and transparent supply chains. By adopting sustainable farming techniques—such as reducing water waste, using renewable energy, and implementing low-impact feed alternatives—farmers can appeal to premium markets willing to pay more for ethically produced shrimp. Certification programs like Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) and other eco-labels enhance product credibility, both locally and internationally. These practices not only improve environmental stewardship but also strengthen brand value, helping Australian shrimp producers access high-value markets and secure long-term competitiveness in the global seafood industry.
Value-Added Product Development
Innovation in product formats presents a promising growth avenue for Australia’s shrimp industry. Shifting consumer preferences toward convenience, health, and variety are fueling demand for ready-to-eat, marinated, and frozen shrimp products. According to the Australia shrimp market analysis, these offerings cater to busy lifestyles while retaining nutritional benefits, making shrimp more attractive to a broader customer base. By diversifying into flavored, portion-controlled, and premium packaging solutions, producers can capture new segments in retail and foodservice. The rise of e-commerce and online grocery platforms further supports the distribution of value-added seafood, enabling direct access to consumers. Such product development not only boosts domestic sales but also strengthens Australia’s positioning in export markets where processed, high-quality shrimp products are in demand. This innovation-driven approach provides resilience against price competition from raw shrimp suppliers.
Tourism and Hospitality Sector Growth
The continued growth of Australia’s tourism and hospitality industries offers a strong platform for expanding shrimp demand. Seafood is a key attraction for international visitors, and shrimp dishes often feature prominently in coastal dining, resorts, and luxury hotels. As domestic and global tourism rebounds, demand for premium, locally sourced shrimp in foodservice channels is set to rise. The industry can leverage partnerships with restaurants, cruise lines, and resorts to highlight Australian shrimp as a signature product, enhancing its reputation and value. Additionally, the popularity of culinary tourism provides an avenue for promoting shrimp-based cuisines, further integrating seafood into Australia’s cultural experience. This growing synergy between tourism and aquaculture creates long-term opportunities to elevate shrimp consumption and strengthen market presence.
Challenges of Australia Shrimp Market:
High Production Costs
The Australian shrimp industry faces significant challenges from rising production costs, particularly in areas such as feed, energy, and labor. Feed expenses account for a large proportion of aquaculture operations, and fluctuations in raw material prices often increase the financial burden on farmers. Similarly, high labor costs, driven by strict wage regulations, further elevate overall expenses compared to low-cost producing nations. Energy requirements for maintaining water quality, aeration, and advanced aquaculture systems also add to operational costs. These financial pressures reduce Australia’s price competitiveness in international markets, where imported shrimp is often cheaper. Addressing this challenge requires innovations in cost-efficient farming practices, adoption of sustainable feed alternatives, and technological improvements to enhance efficiency while maintaining product quality.
Disease Outbreak Risks
Disease outbreaks pose a persistent threat to shrimp farming in Australia, significantly impacting productivity and profitability. Conditions such as white spot syndrome can spread rapidly across farms, leading to mass mortalities, supply shortages, and revenue losses. Despite stringent biosecurity measures, disease prevention remains difficult due to factors such as water contamination, climate variability, and global pathogen transmission risks. Outbreaks not only disrupt production but also damage farmer confidence and industry reputation, potentially reducing market demand. To address this challenge, farmers are increasingly investing in advanced biosecurity systems, genetic research for disease-resistant shrimp species, and early detection technologies. Collaboration between industry stakeholders, research institutions, and government agencies is crucial for minimizing risks and ensuring the long-term stability of shrimp production.
Environmental Concerns
Balancing aquaculture growth with environmental preservation remains a key challenge for Australia’s shrimp sector. Expanding shrimp farming operations can place pressure on natural ecosystems through waste generation, water pollution, and habitat disruption. Maintaining water quality is particularly critical, as excessive nutrient discharge can damage surrounding aquatic environments. Additionally, concerns about land use, biodiversity, and greenhouse gas emissions create public scrutiny, requiring farmers to adopt more sustainable practices. Addressing these environmental challenges involves implementing advanced water treatment systems, adopting recirculating aquaculture technologies, and improving waste management techniques. Certification programs promoting eco-friendly production also help enhance consumer trust. By aligning operations with sustainability goals, the industry can strengthen resilience while minimizing its ecological footprint and ensuring long-term growth potential.
Australia Shrimp Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the regional level for 2026-2034. Our report has categorized the market based on environment, species, shrimp size, and distribution channel.
Environment Insights:
- Farmed Shrimp
- Wild Shrimp
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the environment. This includes farmed shrimp and wild shrimp.
Species Insights:
- Penaeus Vannamei
- Penaeus Monodon
- Macrobrachium Rosenbergii
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the species have also been provided in the report. This includes Penaeus Vannamei, Penaeus Monodon, Macrobrachium Rosenbergii, and others.
Shrimp Size Insights:
- <21
- 21-25
- 26-30
- 31-40
- 41-50
- 51-60
- 61-70
- >70
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the shrimp size. This includes <21, 21-25, 26-30, 31-40, 41-50, 51-60, 61-70, and >70.
Distribution Channel Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
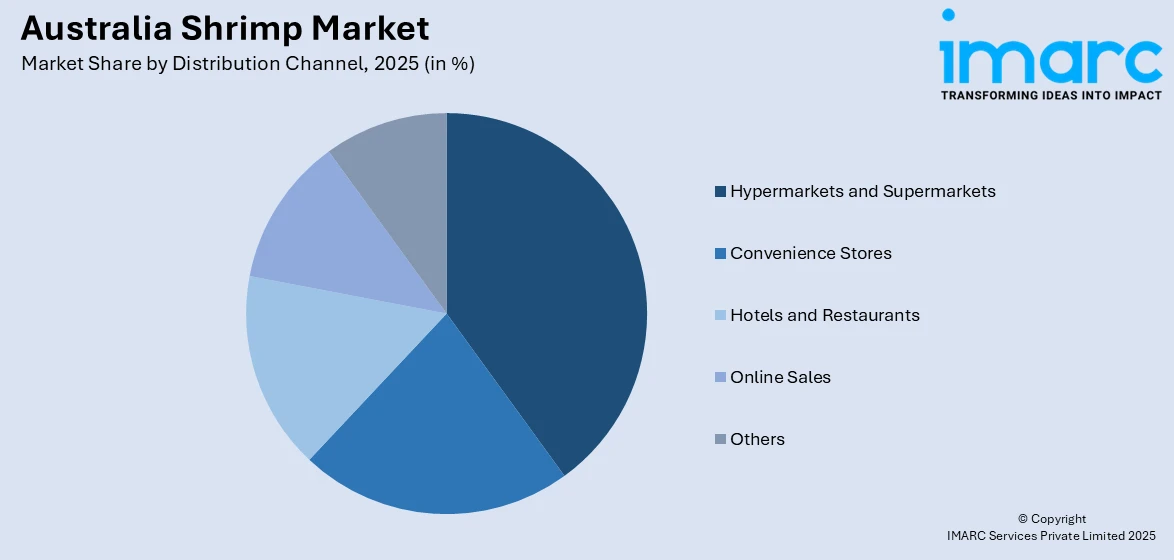
- Hypermarkets and Supermarkets
- Convenience Stores
- Hotels and Restaurants
- Online Sales
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the distribution channel have also been provided in the report. This includes hypermarkets and supermarkets, convenience stores, hotels and restaurants, online sales, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Shrimp Market News:
- In January 2024, Australian biotech company Genics launched Shrimp MultiPath2.0, a technology that detects 18 shrimp pathogens early, weeks before visible symptoms appear. This advancement helps farmers proactively manage diseases, potentially preventing significant losses. By improving disease control, the technology supports the sustainability and productivity of the Australian shrimp market, ensuring healthier stock and higher-quality products.
Australia Shrimp Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Environments Covered | Farmed Shrimp, Wild Shrimp |
| Species Covered | Penaeus Vannamei, Penaeus Monodon, Macrobrachium Rosenbergii, Others |
| Shrimp Sizes Covered | <21, 21-25, 26-30, 31-40, 41-50, 51-60, 61-70, >70 |
| Distribution Channels Covered | Hypermarkets and Supermarkets, Convenience Stores, Hotels and Restaurants, Online Sales, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia shrimp market from 2020-2034.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia shrimp market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia shrimp industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The shrimp market in Australia was valued at USD 1.5 Billion in 2025.
The Australia shrimp market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 3.61% during 2026-2034.
The Australia shrimp market is projected to reach a value of USD 2.1 Billion by 2034.
The Australia shrimp market is witnessing trends such as rising consumer preference for protein-rich seafood, growing demand for sustainably farmed shrimp, and expanding exports to Asian markets. Advancements in aquaculture practices, adoption of eco-friendly production methods, and increasing popularity of value-added shrimp products are further shaping industry growth and competitiveness.
The Australia shrimp market is driven by increasing seafood consumption, rising health awareness, and growing demand for high-protein diets. Expanding aquaculture production, supportive government initiatives, and strong export opportunities to Asia further fuel market growth, while innovations in sustainable farming enhance competitiveness and industry development.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












