
Australia Vegan Food Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Product, Source, Distribution Channel, and Region, 2025-2033
Australia Vegan Food Market Overview:
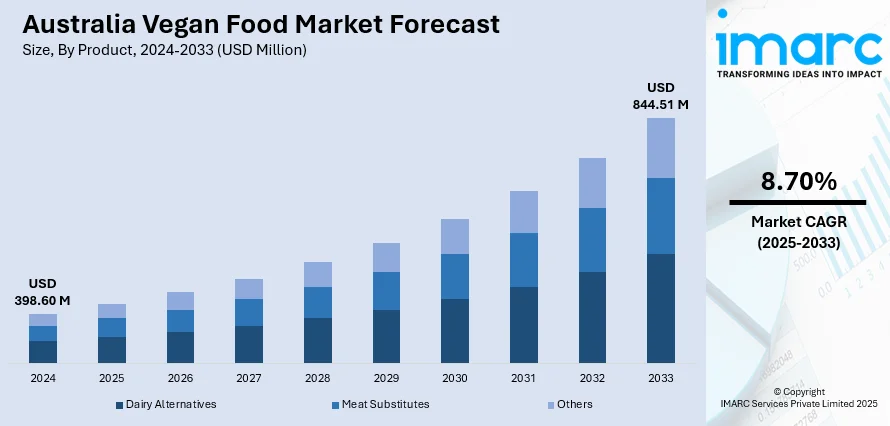
The Australia vegan food market size reached USD 398.60 Million in 2024. Looking forward, the market is expected to reach USD 844.51 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 8.70% during 2025-2033. Rising health consciousness, environmental concerns, and increased availability of innovative plant-based products are driving Australia's vegan food market, supported by growing consumer awareness, mainstream retail adoption, and supportive marketing campaigns that collectively promote sustainable, cruelty-free eating habits across age groups and cultural backgrounds.
|
Report Attribute
|
Key Statistics
|
|---|---|
|
Base Year
|
2024
|
|
Forecast Years
|
2025-2033
|
|
Historical Years
|
2019-2024
|
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 398.60 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2033 | USD 844.51 Million |
| Market Growth Rate 2025-2033 | 8.70% |
Key Trends of Australia Vegan Food Market:
Rising Health Consciousness and Dietary Shifts Among Australians
One of the key drivers of the Australia vegan food market is growing health and nutrition awareness. Australians have expressed a desire for healthier lifestyles in recent years, driven by fears about chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Scientific research that connects vegetable-based diets to better cardiovascular, digestive, and weight health has motivated consumers towards veganism as not only a moral option but also as an approach to prevent diseases. This is reinforced further by the culture of wellness in Australia, where vegan food influencers, health coaches, and fitness groups often advertise vegan diets as a cleaner, healthier alternative to traditional diets. The prevalence of documentaries and literature that discuss the health implications of overconsumption of animal products has also had a critical impact on altering the public's perceptions. Restaurants and supermarkets have quickly adapted to this health-conscious demand by increasing plant-based options. Now, vegan milk, meat, cheese, and even egg alternatives are not only ubiquitous but also cleverly developed with better nutritional profiles. This is especially appealing to millennials and Gen Z shoppers who prefer openness and deliberately search for food items with cleaner labels, reduced cholesterol, and no animal fats.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Environmental and Sustainability Concerns Fueling Ethical Consumption
Another factor driving the vegan food market in Australia is the growing environmental awareness. Climate change is adversely impacting Australia through rising temperatures, severe droughts, and catastrophic bushfires, and it has spurred people and policymakers to re-examine ecological imprints. As the link between livestock production and environmental deterioration becomes evident - most notably greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water use - Australians are extensively adopting veganism as an exercise in climate action. Environmental groups and public campaigns have been vocal regarding the sustainability benefits of plant-based diets. Documentaries and educational materials have brought to light the high land and water needs of animal agriculture and the methane it produces. Consequently, environmentally conscious consumers are now adopting veganism not solely for self-interest, but for the health of the planet. This change is also apparent in government and business policy. Australian food producers and retailers are widely embracing sustainability targets, such as carbon footprint reduction and environmentally friendly sourcing, further driving the market.
Growth Factors of Australia Vegan Food Market:
Impact of Animal Welfare Movement and Lifestyle Changes
One of the major drivers of growth in Australia's plant-based food market is the impact of animal welfare movement and lifestyle changes among consumers. Australians are becoming actively involved with ethical debates related to animals' rights, influenced by high-profile campaigns, documentaries, and the actions of local animal welfare groups. This increased consciousness has caused many people to challenge traditional farming methods and lower or cut out their use of animal products. Veganism is being adopted as a diet, and as a lifestyle choice consistent with compassion and ethical accountability. This transformation is particularly evident among younger generations, who are more likely to feel connected to causes involving animal welfare and sustainability. Consequently, retail demand for cruelty-free products—such as plant-based meats, dairy-free alternatives, and egg substitutes—has increased dramatically. Producers in Australia are meeting this demand with open sourcing, animal-free product labeling, and marketing efforts that focus on ethical values. This intersection of personal ethics and food choices is a strong catalyst for the development of vegan options at a rate across the nation, which further contributes to the growth of Australia vegan food market share as well.
Retail Expansion and Accessibility of Plant‑based Offerings
One of the biggest drivers of growth in Australia's vegan food industry is the explosive increase in the availability of plant-based products in conventional retail spaces. Supermarkets and convenience chains are moving fast to expand their vegan offerings, including artisanal nut cheeses, oat milk, Australian soybean-grown tofu, and easy-to-prepare plant-based frozen dinners. Specialty grocers and farmers' markets are also joining in, featuring vegan snacks developed by local producers with native bush foods. Most notably, partnerships between vegan brands and Woolworths or Coles supermarket behemoths have allowed for improved shelf presence in hundreds of stores in both urban and regional Australia. Mass retail penetration within this makes vegan food more commonly available and normalized, even in smaller towns and rural areas. Additionally, vegan-exclusive bakery lines—such as Richards bread or Byron Bay-based patisserie products—are being rolled out through major-chain partnerships. These partnerships build a strong supply chain, providing consumer access to high-quality vegan foods wherever they are located.
Cultural Influence, Innovation, and Education
Cultural interest and marketplace innovation are contributing to the Australia vegan food market demand. With multicultural food becoming more popular, plant-based international foods are thriving. Vegan pho, jackfruit bao, and falafel bowls featuring native lemon myrtle are on the rise in food destinations such as Brisbane's West End and Adelaide's vegan food festivals. This culinary diversity invites experimentation and adoption by fearless eaters. Moreover, university cafeterias and office canteens are adding vegan alternatives to satisfy ethical millennials and Gen Z consumers, solidifying vegan options as normal meals. Australian food tech startups are also leading the charge through new products, such as coconut yoghurt made with locally grown macadamias or pea protein meat alternatives made from domestic pulses. Influencer activations and public cooking classes, led by plant-based chefs and nutritionists, are driving nutritional literacy—showing people how to prepare nutritious vegan meals with Australian-grown produce. With this union of education, culinary innovation, and cultural receptivity, Australia's market for vegan food is transforming at an accelerated pace—redesigning dietary patterns and emerging as a vibrant, forward-looking industry.
Opportunities of Australia Vegan Food Market:
Utilizing Native Ingredients and Food Heritage
Australia has a distinct advantage within the vegan food industry through the incorporation of native and Indigenous ingredients into plant-based food. The nation's high biodiversity provides an abundance of dense nutrient, naturally plant-based foods like wattle seed, finger lime, bush tomato, and quandong. These ingredients, which have been traditionally used by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people, have unique flavors, textures, and nutritional advantages that can help set Australian vegan products apart globally. Integrating Indigenous knowledge and sustainable harvesting techniques into vegan product design may appeal to local and international consumers looking for authenticity and innovation. By establishing ethical collaborations with Indigenous peoples, brands can develop premium product ranges celebrating cultural identity and local economies. This strategy adds value to product narratives and marketability and to responsible sourcing and greater cultural understanding. With consumers globally increasingly demanding origin narratives and ethical sourcing, Australia is best placed to convert its indigenous foods into premium vegan products.
Export Potential Across Asia-Pacific and Beyond
According to the Australia vegan food market analysis, the region’s geographical closeness to rapidly expanding consumer markets in Asia offers an enormous potential for its vegan food sector. Singapore, Japan, South Korea, and Indonesia, among others, are witnessing increasing demand for plant-based foods fueled by health, urbanization, and sustainability trends. Australia, with its clean, green agricultural practices and food safety standards, is best placed to address this need with quality, reliable vegan offerings. There is high potential for plant-based ready-to-eat meals, meat alternatives, snacks, and dairy products made from locally grown Australian produce such as chickpeas, macadamias, and oats. The popularity of "Australian-made" products in most Asian countries provides additional value, particularly when tied to creative packaging and local flavors. Adapting vegan options to accommodate local taste buds—e.g., using Asian spices or developing vegan versions of local comfort foods—can boost acceptance and consumer demand. Furthermore, Australia's established trade network, export infrastructure, and market presence create a strong basis for expanding distribution. This makes regional growth a viable and extremely profitable venture for the nation's vegan food manufacturers.
Development of Vegan Tourisms and Hospitality Experience
Australia's robust tourism industry and world-class dining reputation present a strong platform for developing the vegan market across hospitality experiences. Cities such as Melbourne, Sydney, and Byron Bay are already famous for their cultural culinary offerings, and vegan fine dining, street food markets, and wellness retreats are becoming more part of that fabric. There is expanding potential to develop immersion-type vegan food experiences—like vegan culinary schools, plant-based food tours, and eco-lodges providing locally sourced vegan meals. This direction follows the increased practice of conscious travel, whereby travelers look for experiences that speak to their values, such as ethical food and sustainability. Local regions also stand to gain by integrating plant-based foods into farm-to-table cuisine, leveraging local ingredients and community narrative. Vegan festivals, pop-up food events, and chef collaborations emphasizing Australian produce can target both domestic tourists and international tourists. By combining gastronomy with ethical lifestyle tourism, Australia can become a market leader in vegan-friendly tourism and hospitality.
Government Support of Australia Vegan Food Market:
Agricultural Innovation and Plant-Based Research Funding
The Australian government contributes significantly to the encouragement of the vegan food market through financing and incentives for agricultural innovation and food technology. With an emphasis on diversification of the national economy and the establishment of sustainable industries, government agencies have been investing resources in research into alternative proteins, plant-based food processing, and crop development. Specifically, funding for research centers and universities has promoted innovation in plant-based meat alternatives from locally produced legumes like lupins, chickpeas, and faba beans. Such efforts produce more sustainable agricultural systems and create opportunities for home-based vegan food production. Grants and research collaborations are being provided to startups and food tech firms that are developing the texture, taste, and nutritional content of vegan foods. This top-down push for R&D is a national effort to future-proof the food industry by lowering dependence on animal-based exports and investing in low-carbon, scalable vegan options that maximize Australia's agricultural strengths.
Encouragement of Sustainable Food Production and Climate Targets
Australia's overall environmental policies are indirectly favoring the vegan food industry, especially through national targets aimed at emissions reduction and sustainable agriculture. In an attempt to combat climate change and lower the nation's carbon footprint, government policies incentivize farmers to practice regenerative agriculture, crop diversification, and lowering methane production—initiatives that directly correlate with plant-based food production. Initiatives that enhance soil health, water use efficiency, and carbon farming are of huge benefits to plant-based ingredient producers, making the production of vegan food more sustainable and competitive. In this regard, the government's climate agenda is forming a positive policy landscape for enterprises investing in vegans, especially those working with indigenous plants and climate-tolerant crops. Moreover, strategic plans for clean energy and sustainable agriculture investments provide plant-based food producers with access to technology and infrastructure improvements. These plans illustrate how sustainability initiatives and food system transformation cross over, promoting the development and competitiveness of Australia's vegan food industry indirectly.
Regulatory Frameworks Promoting Open Labelling and Standards
The Australian government's focus on food transparency labelling and consumer protection also fosters the development of the vegan food industry. Regulatory authorities have been streamlining guidelines for labelling plant-based foods, allergens, and health claims, which is critical to consumer confidence in vegan foods. Vegan, plant-based, and animal-free products being clearly labelled decrease shopper confusion and guarantee observance of dietary needs, particularly for those refraining from eating animal products for ethical, religious, or health grounds. Additionally, the evolution of voluntary certifications like "Vegan Australia Certified" has been facilitated by regulatory certainty, allowing for greater ease in which brands can achieve credibility and visibility. Amidst the controversy surrounding the naming of meat and dairy substitutes, continual consultation with industry players indicates the willingness of the government to evolve and accommodate the expanding vegan market. This positive regulatory framework provides a stable platform for innovation, promotion, and export of vegan foods, which serves to establish consumer confidence locally and overseas.
Australia Vegan Food Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the region/country level for 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on product, source, and distribution channel.
Product Insights:
- Dairy Alternatives
- Cheese
- Desserts
- Snacks
- Others
- Meat Substitutes
- Tofu
- Texturized Vegetable Protein (TVP)
- Seiten
- Quorn
- Others
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the product. This includes dairy alternatives (cheese, desserts, snacks, and others), meat substitutes (tofu, texturized vegetable protein (TVP), seiten, Quorn, and others), and others.
Source Insights:
- Almond
- Soy
- Oats
- Wheat
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the source have also been provided in the report. This includes almond, soy, oats, wheat, and others.
Distribution Channel Insights:
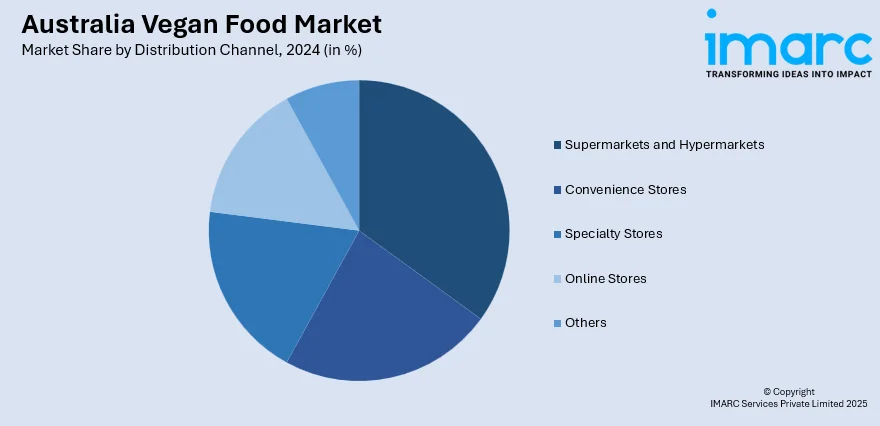
- Supermarkets and Hypermarkets
- Convenience Stores
- Specialty Stores
- Online Stores
- Others
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the distribution channel. This includes supermarkets and hypermarkets, convenience stores, specialty stores, online stores, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales
- Victoria & Tasmania
- Queensland
- Northern Territory & Southern Australia
- Western Australia
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, and Western Australia.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Australia Vegan Food Market News:
- October 2024: Australian plant-based meat producer Aussie Plant Based Co, encompassing brands vEEF and Love Buds, was acquired by Queensland-based Smart Foods.
- June 2024: Adelaide startup Vege-Tables launched an app to simplify dining for those with dietary preferences. The app categorizes nearly 3,000 South Australian venues based on vegan, vegetarian, and gluten-free options, aiding users in finding suitable meals. With regular updates and user contributions, Vege-Tables supports the growing demand for plant-based dining and sustainable food choices in the region.
- January 2024: v2food acquired ready meal brands Soulara and MACROS, forming a new entity called Flexitarian Meal Solutions. This strategic move expands v2food's offerings beyond meat analogues to include a diverse range of plant-based ready meals, catering to the growing demand for convenient, healthy, and sustainable food options. Soulara, known for its chef-designed vegan meals, complements v2food's mission to make plant-based eating more accessible and appealing.
- October 2023: v2food introduced RepliHue. This is a patented technology that enables plant-based meats to change color during cooking, mimicking the behavior of animal meat. This innovation, derived from red algae and plants, aims to enhance the cooking experience for consumers and chefs alike.
Australia Vegan Food Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Products Covered |
|
| Sources Covered | Almond, Soy, Oats, Wheat, Others |
| Distribution Channels Covered | Supermarkets and Hypermarkets, Convenience Stores, Specialty Stores, Online Stores, Others |
| Regions Covered | Australia Capital Territory & New South Wales, Victoria & Tasmania, Queensland, Northern Territory & Southern Australia, Western Australia |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Australia vegan food market from 2019-2033.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Australia vegan food market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Australia vegan food industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The Australia vegan food market was valued at USD 398.60 Million in 2024.
The Australia vegan food market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 8.70% during 2025-2033.
The Australia vegan food market is expected to reach a value of USD 844.51 Million by 2033.
The Australia vegan food industry is adopting trends such as native ingredient inclusion, gourmet plant-based cuisine, and ready-to-consume convenience foods. Increasing need for clean labels, allergen-free choices, and sustainable sourcing is redefining product innovation. Consumer demand for sustainable, locally produced, and worldwide-inspired vegan food is also fueling innovation and market growth.
The Australia vegan food market is powered by ethical consumerism, greater health awareness, and increased environmental sustainability consciousness. Rising demand for plant-based, cruelty-free options and strong backing from local producers utilizing indigenous ingredients drive its growth. Social media and food influencers are also instrumental in influencing consumer choices.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












