
India Defense Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Armed Forces, and Region, 2026-2034
India Defense Market Summary:
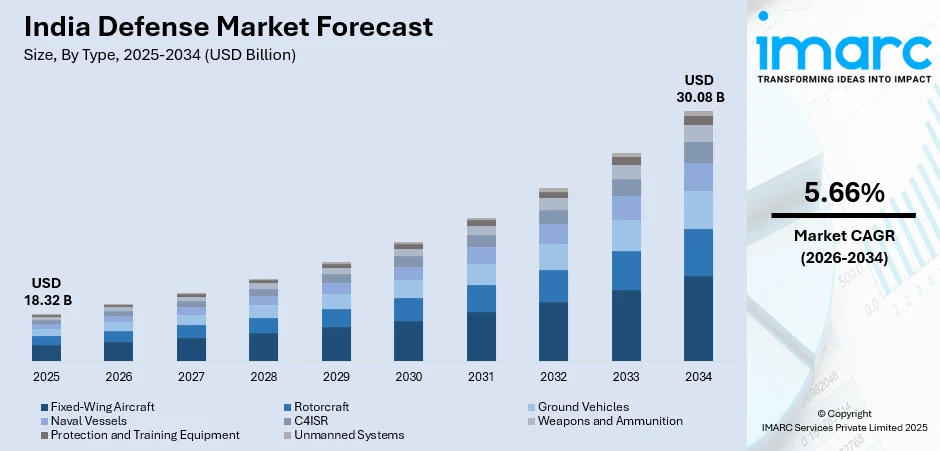
The India defense market size was valued at USD 18.32 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 30.08 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 5.66% from 2026-2034.
The India defense market is experiencing robust expansion, driven by the government's commitment to self-reliance in military capabilities and modernization of the armed forces. Rising geopolitical tensions along land and maritime borders are accelerating procurement activities across air, land, and naval domains. The expanding indigenous manufacturing ecosystem is strengthening domestic production capabilities while reducing dependency on foreign imports.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Type: Fixed-wing aircraft dominates the market with a share of 22% in 2025, owing to the strategic imperative for aerial superiority and surveillance capabilities along extensive borders. Ongoing modernization programs are accelerating procurement of advanced fighter jets, transport aircraft, and unmanned aerial platforms to strengthen aerial defense capabilities.
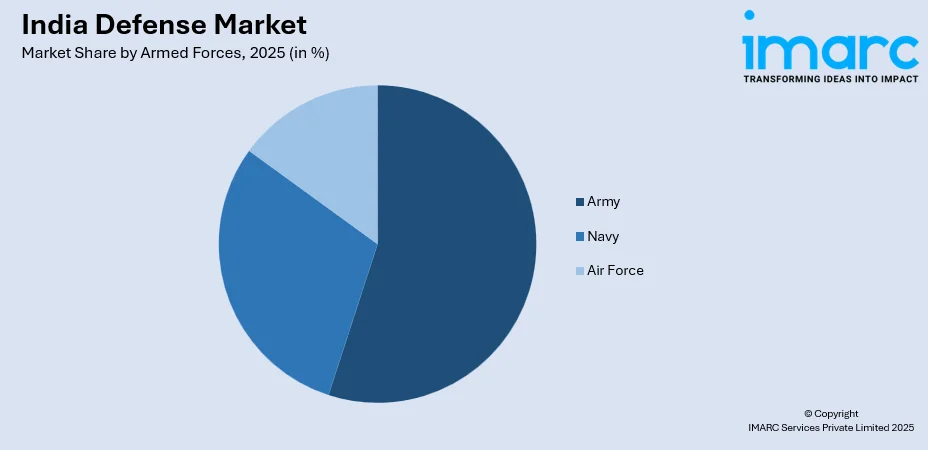
- By Armed Forces: Army leads the market with a share of 50% in 2025, This dominance is driven by the extensive operational requirements across diverse terrain conditions, ongoing modernization of ground combat systems, and the continuous need for advanced armor, artillery, and infantry equipment to secure territorial integrity.
- By Region: North India represents the largest region with 31% share in 2025, owing to the establishment of defense industrial corridors, concentration of major defense manufacturing facilities, and strategic proximity to sensitive border areas requiring enhanced military infrastructure and operational readiness.
- Key Players: Key players propel the India defense sector by enhancing local production abilities, channeling funds into cutting-edge technology advancement, and reinforcing research and development (R&D) efforts. Their focus on joint ventures, technology transfers, and public-private partnerships (PPPs) accelerates defense modernization while supporting export growth and ensuring consistent equipment availability across all defense services.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India defense market is witnessing accelerated growth, fueled by the government's sustained commitment to achieving self-reliance in military capabilities through the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative. The strategic focus on indigenous defense manufacturing is transforming the sector from an import-dependent ecosystem into a robust production hub capable of meeting domestic requirements and export demands. Escalating geopolitical tensions along borders with neighboring countries are intensifying the urgency for modernization across all armed forces. The prioritization of domestic procurement under the Defense Acquisition Procedure continues to strengthen the indigenous industrial base while attracting substantial private sector participation. The defense budget for FY 2025-26 allocated INR 6,81,210 Crore, representing a 9.5% increase from FY 2024-2025, with 75% of the modernization budget earmarked for domestic procurement. Technological advancements in emerging domains, including artificial intelligence (AI), cyber capabilities, space-based systems, and unmanned platforms, are reshaping procurement priorities. Additionally, rising defense exports are establishing India as a credible supplier of advanced weapon systems globally.
India Defense Market Trends:
Rising Emphasis on Indigenous Defense Manufacturing
The defense sector is experiencing a fundamental shift towards indigenous manufacturing under government initiatives promoting self-reliance. The establishment of defense industrial corridors is creating specialized production ecosystems that attract domestic and international investments. In August 2025, the Central Government revealed plans to establish two additional defense industrial corridors, one in Maharashtra and the other in Assam, in the coming months. Positive indigenization lists are mandating local manufacturing of thousands of defense items, reducing import dependency while fostering technological capabilities within the domestic industrial base. This transformation is encouraging PPPs and enabling technology transfers that strengthen long-term manufacturing competitiveness.
Integration of Advanced Technologies in Defense Systems
The adoption of cutting-edge technologies is reshaping defense capabilities across all domains. AI and machine learning (ML) are being integrated into surveillance systems, autonomous platforms, and decision-support applications. As per IMARC Group, the India AI market size reached USD 1,251.79 Million in 2024. Unmanned aerial systems are gaining prominence for reconnaissance, strike missions, and force multiplication roles. Directed energy weapons and hypersonic systems are advancing through developmental stages, positioning the armed forces for next-generation warfare requirements. Space-based capabilities are being enhanced for communication, navigation, and reconnaissance applications to support network-centric operations.
Expanding Defense Export Capabilities
The defense sector is transitioning from being a net importer to an emerging exporter of military equipment and technologies. Indigenous weapon systems are gaining international recognition and attracting orders from countries across multiple continents. Simplified export authorizations and streamlined licensing procedures are enabling manufacturers to access global markets efficiently. Strategic partnerships with foreign governments are facilitating defense sales through government-to-government agreements, establishing credibility as a reliable supplier of advanced military hardware and systems integration services.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The India defense market outlook remains positive, as the government maintains its strategic focus on military modernization and self-reliance. Sustained investments in indigenous platforms, including fighter aircraft, naval vessels, armored vehicles, and missile systems, are expected to drive procurement activities throughout the forecast period. The market generated a revenue of USD 18.32 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 30.08 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 5.66% from 2026-2034. The expansion of defense industrial corridors will accelerate manufacturing capabilities while attracting foreign direct investment (FDI). Rising geopolitical challenges and border security requirements will sustain demand for advanced defense systems. The growing emphasis on emerging technologies, including AI, unmanned systems, and cyber capabilities, will reshape procurement priorities across all services.
India Defense Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Type |
Fixed-Wing Aircraft |
22% |
|
Armed Forces |
Army |
50% |
|
Region |
North India |
31% |
Type Insights:
- Fixed-Wing Aircraft
- Rotorcraft
- Ground Vehicles
- Naval Vessels
- C4ISR
- Weapons and Ammunition
- Protection and Training Equipment
- Unmanned Systems
Fixed-wing aircraft dominates with a market share of 22% of the total India defense market in 2025.
Fixed-wing aircraft leads the market, driven by the critical need for aerial superiority, strategic transport capabilities, and long-range surveillance operations across vast territorial expanses. The ongoing modernization of the fighter fleet addresses operational gaps created by the retirement of aging aircraft while enhancing combat readiness along sensitive borders. In May 2025, the Cabinet Committee on Security approved the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) prototype development at a cost of INR 15,000 Crore, marking a significant milestone in indigenous fifth-generation fighter development that will strengthen future aerial capabilities and technological self-reliance.
The acquisition of advanced multi-role fighter aircraft remains a strategic priority to maintain combat effectiveness against evolving threats from neighboring countries. Transport aircraft requirements are expanding to support rapid deployment capabilities and humanitarian operations across diverse operational theaters. The indigenous development of light combat aircraft and training platforms is strengthening domestic manufacturing capabilities while reducing dependency on foreign suppliers. The integration of advanced avionics, precision-guided munitions, and network-centric warfare systems is enhancing overall operational effectiveness of the fixed-wing aircraft across tactical and strategic missions.
Armed Forces Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Army
- Navy
- Air Force
Army leads with a share of 50% of the total India defense market in 2025.
The Army's market dominance reflects the extensive operational requirements across thousands of kilometers of disputed borders requiring continuous vigilance and rapid response capabilities. Modernization programs are addressing critical gaps in armored warfare, artillery systems, infantry equipment, and air defense capabilities. In September 2024, the Defence Acquisition Council approved ten capital acquisition proposals totaling INR 1,44,716 Crore, with the Future Ready Combat Vehicle (FRCV) program representing a significant upgrade for the Army's armored corps to enhance mobility, firepower, and protection against contemporary battlefield threats.
The armed forces are undergoing comprehensive transformation incorporating advanced artillery systems, infantry combat vehicles, tactical communications equipment, and integrated air defense networks. Night-fighting capabilities, soldier modernization programs, and battlefield surveillance systems are receiving priority attention to enhance operational effectiveness in challenging terrain and weather conditions. The integration of unmanned ground vehicles and drone detection systems is strengthening border security while reducing personnel exposure to threats in high-risk areas. Logistics modernization is improving supply chain efficiency across dispersed operational areas.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- West and Central India
- South India
- East and Northeast India
North India exhibits a clear dominance with a 31% share of the total India defense market in 2025.
North India leads the India defense market due to the high concentration of military infrastructure, strategic command centers, and defense establishments across the region. The presence of major Army formations, air bases, and border-facing operational zones drives sustained demand for defense equipment, logistics, and maintenance services. Proximity to sensitive borders increases the need for continuous modernization, surveillance, and readiness. The region also hosts key research institutions, training academies, and ordnance facilities, creating a strong ecosystem that supports defense procurement, testing, and operational deployment activities.
The region’s leadership is further strengthened by the concentration of public sector undertakings, private defense manufacturers, and policy-making institutions. North India benefits from close coordination between the armed forces, defense production units, and government agencies, accelerating decision-making and project execution. Industrial corridors, skilled workforce availability, and strong transport connectivity support manufacturing and supply chains. In addition, rising participation of private players and startups in defense electronics, drones, and advanced systems reinforces North India’s dominant role in shaping the market growth.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Defense Market Growing?
Government Push for Indigenous Defense Manufacturing
The government's sustained commitment to achieving self-reliance in defense manufacturing through comprehensive policy initiatives is fueling the market expansion in India. The establishment of defense industrial corridors is providing specialized infrastructure, streamlined approvals, and fiscal incentives that attract both domestic and international investments into manufacturing operations. Positive indigenization lists have created protected market opportunities for local manufacturers by restricting imports of thousands of defense items, compelling procurement from domestic sources. The liberalization of FDI norms is enabling technology partnerships and joint ventures that transfer advanced manufacturing capabilities to Indian entities. Private sector participation has expanded significantly with simplified licensing procedures and increased engagement opportunities through dedicated programs supporting startups and small enterprises. The allocation of substantial portions of modernization budgets exclusively for domestic procurement is providing revenue certainty that encourages long-term capacity building investments. These coordinated policy measures are creating sustainable growth momentum by reducing import dependency while establishing globally competitive manufacturing capabilities within the country.
Escalating Geopolitical Tensions and Security Challenges
The complex security environment, characterized by border tensions, territorial disputes, and regional instability, is driving sustained demand for advanced military capabilities across all domains. Unresolved boundary issues with neighboring countries require maintaining robust conventional deterrence through continuous modernization of ground, air, and naval forces. The evolving nature of threats, including hybrid warfare tactics, cross-border infiltration, and terrorism, necessitates acquiring sophisticated surveillance systems, precision strike capabilities, and rapid response platforms. Maritime security concerns in the Indian Ocean region are accelerating naval expansion programs, including aircraft carriers, submarines, frigates, and coastal defense systems, to protect strategic sea lanes and exclusive economic zones. The growing strategic competition in the Indo-Pacific region is influencing defense planning and procurement priorities with emphasis on power projection capabilities. Border infrastructure development programs are expanding to improve accessibility and operational mobility in challenging terrain conditions along sensitive frontiers. In December 2025, Defense Minister Rajnath Singh inaugurated 125 newly finished Border Roads Organization (BRO) infrastructure projects for the nation.
Modernization Requirements Across Armed Forces
The pressing need to replace aging military equipment and upgrade existing platforms with contemporary systems is generating substantial procurement demand across all three services. The fighter aircraft fleet faces critical shortages due to retirement of legacy platforms without adequate replacements, compelling accelerated acquisition programs to restore authorized squadron strength. Artillery modernization addresses capability gaps with advanced towed and self-propelled gun systems incorporating precision guidance and extended range features essential for contemporary battlefield requirements. Naval fleet expansion encompasses aircraft carriers, destroyers, frigates, corvettes, and submarines to strengthen blue-water capabilities and regional power projection. Infantry modernization programs are equipping soldiers with advanced assault rifles, body armor, communication systems, and night-vision devices that enhance individual and unit effectiveness. Helicopter acquisitions are addressing requirements for troop transport, attack missions, and search-and-rescue operations across varied operational environments. Air defense modernization encompasses integrated missile systems, radars, and command-and-control networks providing layered protection against aerial threats.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges is the India Defense Market Facing?
Complex Procurement Procedures and Delays
The defense acquisition process remains constrained by lengthy procurement cycles, extensive documentation requirements, and multi-stage approval procedures that delay equipment induction. Risk-averse decision-making stemming from past controversies creates bureaucratic bottlenecks affecting timely capability development. The complexity of technical evaluations, trials, and contract negotiations extends timelines significantly, leaving operational gaps and affecting force modernization schedules across services.
Limited Indigenous Technological Capabilities
Despite progress in domestic manufacturing, critical technology gaps persist in advanced propulsion systems, high-end electronics, and specialized materials requiring continued foreign dependency. The domestic semiconductor industry remains nascent, constraining indigenous development of sophisticated electronic warfare and precision guidance systems. Technology transfer restrictions from supplier nations limit absorption of cutting-edge capabilities, affecting development timelines for next-generation indigenous platforms.
Budgetary Constraints and Pension Burden
The defense budget allocation as a share of national expenditure faces competing demands from socioeconomic development priorities, limiting funds available for capital acquisitions. Rising pension expenditures consume substantial portions of the overall defense allocation, reducing resources for modernization programs. The allocation for procurement remains insufficient to address accumulated capability gaps across all services simultaneously, forcing prioritization and deferrals.
Competitive Landscape:
The India defense market features a competitive landscape, comprising defense public sector undertakings, private sector manufacturers, and international original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) operating through partnerships and joint ventures. The ecosystem has evolved significantly with growing private sector participation supported by liberalized policies encouraging domestic manufacturing. Public sector entities maintain dominant positions in strategic platforms, including aircraft, naval vessels, and missile systems, while expanding production capabilities through capacity modernization. Private manufacturers are increasingly participating in complex system integration projects and component manufacturing under indigenization programs. International collaborations are facilitating technology transfers enabling domestic production of advanced platforms through licensed manufacturing and co-development arrangements.
Recent Developments:
- In January 2026, the Indian Army revealed plans to establish 15-20 Shaktibaan regiments that would be fitted with swarm drones, loitering munitions, and long-range UAVs capable of hitting targets from 5 Km to 500 Km. The significant force restructuring, envisioned by Indian Army Chief Gen Upendra Dwivedi, is integral to the forces' evolution to address the demands of contemporary warfare. Indian companies, such as Solar Defence and Aerospace, AdDefence, and RapheM, are expected to be the contenders for this INR 2,000 Crore initiative.
- In October 2025, Defense Minister Shri Rajnath Singh and Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister Shri Yogi Adityanath jointly inaugurated the initial set of BrahMos missiles produced at the BrahMos Integration and Testing Facility Centre in Lucknow. The missile is equipped with a conventional warhead and a sophisticated guidance system, allowing it to hit targets at great distances at supersonic speeds.
India Defense Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | Fixed-Wing Aircraft, Rotorcraft, Ground Vehicles, Naval Vessels, C4ISR, Weapons and Ammunition, Protection and Training Equipment, Unmanned Systems |
| Armed Forces Covered | Army, Navy, Air Force |
| Regions Covered | North India, West and Central India, South India, East and Northeast India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India defense market size was valued at USD 18.32 Billion in 2025.
The India defense market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.66% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 30.08 Billion by 2034.
Fixed-wing aircraft dominated the market with a share of 22%, driven by the strategic importance of aerial superiority, ongoing fighter fleet modernization programs, and the critical need for reconnaissance and transport capabilities along extensive borders.
Key factors driving the India defense market include government initiatives promoting indigenous manufacturing, escalating geopolitical tensions requiring military modernization, expanding defense budgets supporting procurement programs, and rising emphasis on self-reliance in defense production.
Major challenges include complex procurement procedures causing acquisition delays, limited indigenous technological capabilities in critical domains, budgetary constraints from competing socioeconomic priorities, high pension expenditures reducing modernization funds, and technology transfer restrictions from supplier nations.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












