
India Grid Modernization Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Component, Application, End User, and Region, 2026-2034
India Grid Modernization Market Summary:
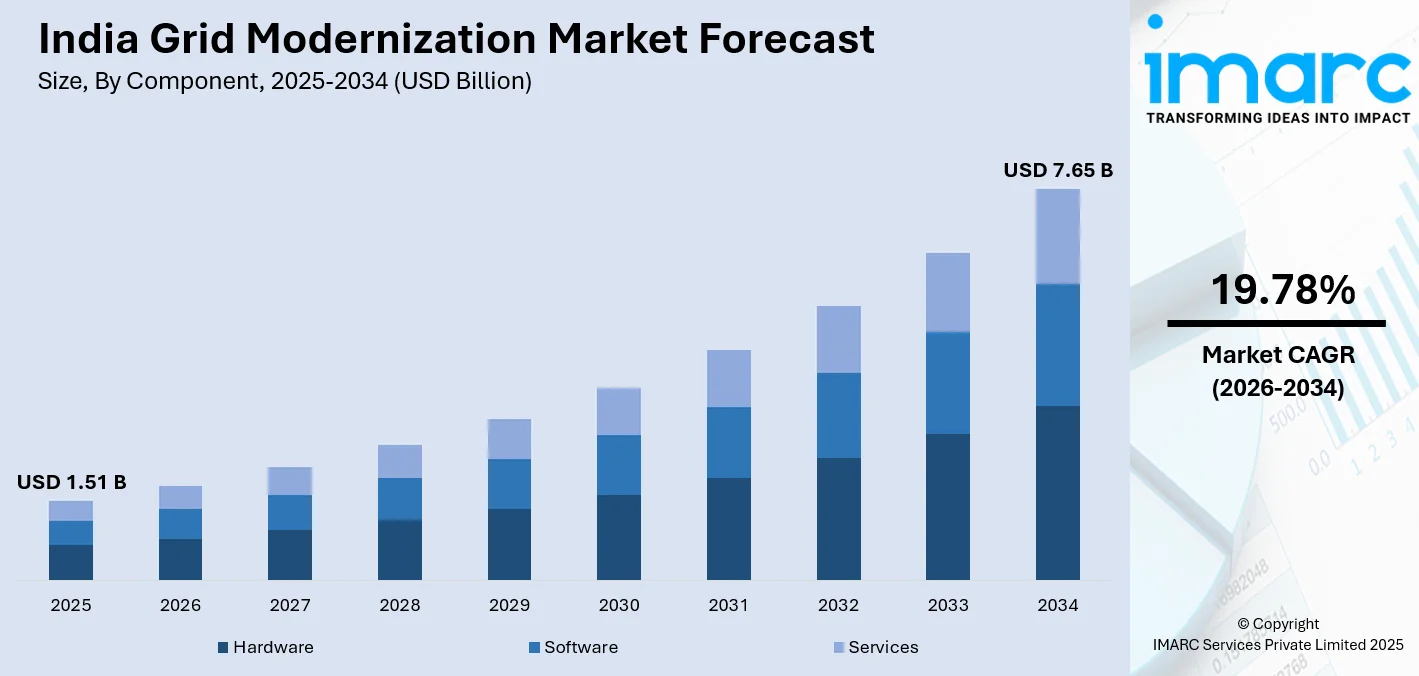
The India grid modernization market size was valued at USD 1.51 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 7.65 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 19.78% from 2026-2034.
The India grid modernization market is experiencing robust growth driven by the nation's accelerating energy transition and ambitious renewable energy integration targets. Rising electricity demand fueled by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the electrification of transport is necessitating substantial investments in advanced grid technologies. Government-led initiatives are encouraging the deployment of smart metering infrastructure, distribution automation systems, and real-time monitoring solutions. The imperative to reduce aggregate technical and commercial losses while enhancing grid stability and reliability is propelling utilities and independent power producers toward comprehensive grid modernization programs, strengthening the market growth.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Component: Hardware dominates the market with a share of 55% in 2025, driven by extensive deployment of smart meters, transformers, SCADA systems, and power electronics equipment essential for grid digitalization and renewable energy integration across transmission and distribution networks.
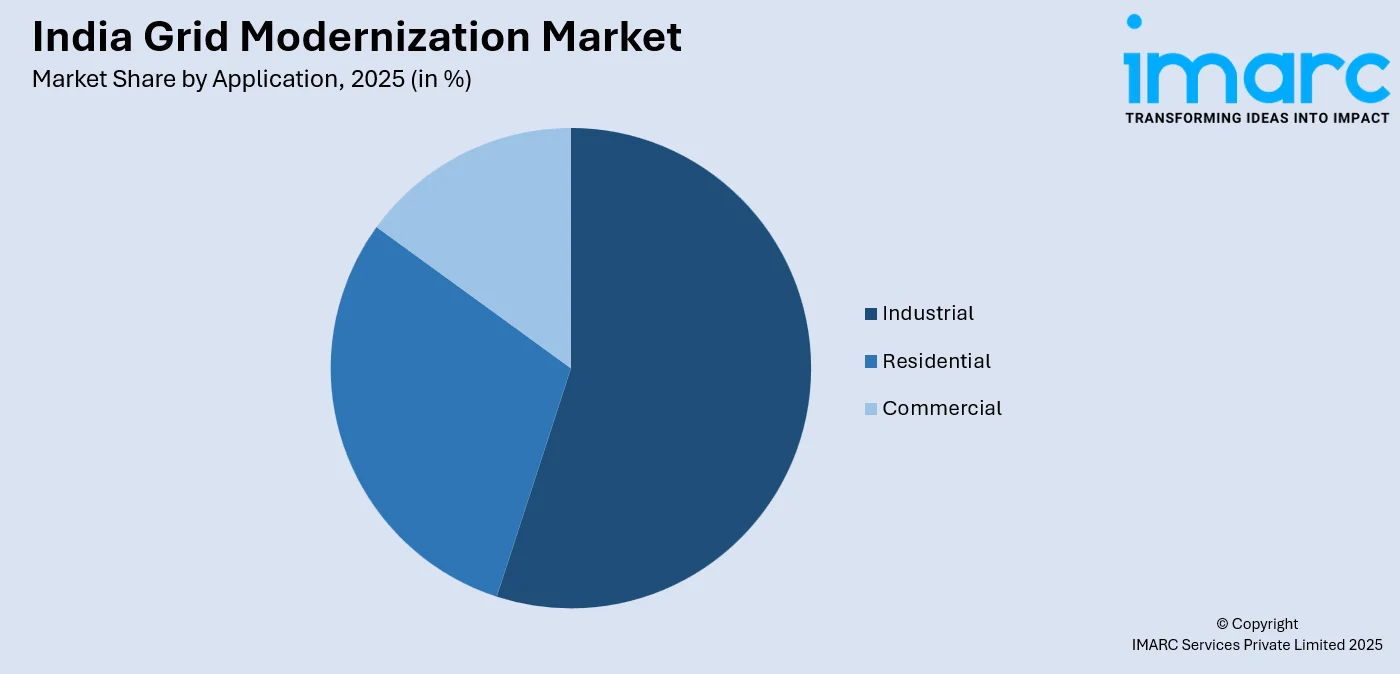
- By Application: Industrial leads the market with a share of 45% in 2025, reflecting the critical need for reliable power supply and advanced grid solutions to support manufacturing growth, industrial corridors, and energy-intensive operations across key economic zones.
- By End User: Utilities represent the largest segment with a market share of 52% in 2025, as distribution companies nationwide spearhead grid modernization efforts through smart metering rollouts, distribution automation deployments, and infrastructure upgrades under central government schemes.
- By Region: West India dominates the market with a share of 30% in 2025, underpinned by substantial renewable energy capacity in Gujarat and Maharashtra, progressive transmission infrastructure investments, and strong industrial demand driving grid enhancement initiatives.
- Key Players: The India grid modernization market exhibits moderate to highly competitive intensity, with established global technology providers and domestic engineering conglomerates competing across smart grid solutions, transmission equipment, distribution automation, and energy storage systems to capture market share.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India grid modernization market is witnessing strong momentum as the country advances energy security goals, expands renewable capacity, and upgrades aging transmission and distribution networks to handle rising power demand. Large-scale integration of solar and wind generation is driving the need for digital monitoring, automation, and real-time load management across utilities. A major driver is the nationwide rollout of smart metering under the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme. Under RDSS, 20.33 crore smart meters have been sanctioned across 28 States and Union Territories, reflecting the scale of planned infrastructure upgrades. As of July 15, 2025, 2.41 crore smart meters had already been installed, enabling improved billing accuracy, loss reduction, and demand-side management. These deployments are strengthening data visibility at the distribution level and supporting grid stability. Continued investment in advanced metering, substations, and digital control systems is expected to improve operational efficiency, support renewable integration, and enhance reliability across India’s evolving power grid.
India Grid Modernization Market Trends:
Growing Electricity Demand and Urbanization Pressure
Rising electricity usage from rapid urbanization, industrial growth, and increased household appliance usage is placing sustained pressure on India’s existing grid infrastructure. Urban centers are facing higher peak loads, network congestion, and reliability concerns, driving the need for capacity upgrades and automated distribution systems. This requirement is evident in ongoing infrastructure expansion, with Power Grid Corporation of India’s subsidiary launching the Khavda Phase-II Part-B Interstate Transmission Project in 2025 to strengthen interstate connectivity and enable more efficient power transfer across states. It reflects the company’s commitment to developing reliable infrastructure for India’s growing energy needs. As demand patterns grow more complex, grid modernization remains essential to ensure reliable power delivery across residential, commercial, and industrial users.
Government Policy Support and Public Investment
Strong policy support continues to support grid modernization across India by providing clear regulatory direction and sustained financial backing. Central programs targeting transmission expansion, distribution reform, and smart grid adoption are enabling utilities to upgrade legacy infrastructure and deploy digital systems. This policy momentum translated into concrete action in 2025, when Maharashtra State Electricity Distribution Company partnered with the Global Energy Alliance for People and Planet to modernize the state grid using artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and advanced analytics, alongside battery energy storage integration. This initiative enhanced grid reliability, scalability, and consumer service through digital innovation. Together, long-term planning frameworks and public sector participation reduce investment risk, attract private involvement, and align grid upgrades with national energy security and development goals.
Rapid Expansion of Renewable Energy Integration
India’s rapid expansion of renewable energy capacity is placing new technical demands on the power grid, making modernization a priority. Large solar and wind installations introduce variability and two-way power flows that traditional networks cannot manage efficiently. This requirement is reflected in projects, such as the 250 MW/1,000 MWh Battery Energy Storage System commissioned in 2025, at West Bengal’s Goaltore Substation, designed to manage peak loads and support renewable integration during non-solar hours. Supported by flexible substations, real-time monitoring, and advanced forecasting, modern transmission corridors are also enabling efficient power transfer from renewable-rich regions to demand centers. As renewable penetration rises, grid upgrades remain critical to maintain stability, reduce curtailment, and ensure reliable clean energy utilization nationwide.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The India grid modernization market demonstrates strong growth potential over the forecast period, driven by sustained government investment, rapid expansion of renewable energy capacity, and steadily rising electricity demand across residential, industrial, and commercial segments. Increasing integration of solar and wind power is driving the need for advanced transmission, distribution automation, and digital grid technologies. The market generated a revenue of USD 1.51 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 7.65 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 19.78% from 2026-2034.
India Grid Modernization Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Component |
Hardware |
55% |
|
Application |
Industrial |
45% |
|
End User |
Utilities |
52% |
|
Region |
West India |
30% |
Component Insights:
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
Hardware dominates with a market share of 55% of the total India grid modernization market in 2025.
Hardware represents the largest segment due to the immediate need for physical infrastructure upgrades across transmission and distribution networks. Utilities are making substantial investments in smart meters, advanced transformers, substations, sensors, and communication equipment to reduce technical losses and improve grid reliability. These hardware components are essential for supporting renewable energy integration, enabling automation, and providing the foundation for digital grid technologies, making them critical to comprehensive grid modernization initiatives.
Large-scale deployment of advanced metering infrastructure, distribution automation equipment, and grid monitoring systems continues to drive the demand for hardware solutions. Government-supported programs and utility-led investments emphasize tangible assets that deliver immediate operational improvements, such as loss reduction and improved reliability. Hardware upgrades also create the necessary foundation for later integration of software, analytics, and control platforms, reinforcing hardware’s dominant role and long-term importance within India’s grid modernization market.
Application Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
Industrial leads with a market share of 45% of the total India grid modernization market in 2025.
Industrial dominates the market owing to high electricity usage, complex load profiles, and the need for reliable power supply. For instance, peak electricity load in India has grown significantly, rising from 148 GW in 2014 to 250 GW in 2024, with industrial expansion being a vital contributor. Manufacturing plants, refineries, and heavy industries require advanced grid infrastructure to manage demand fluctuations, reduce downtime, and support automation, driving early adoption of smart grid technologies.
Industrial users continue to invest heavily in energy management systems, real-time monitoring tools, and advanced power quality solutions to optimize energy usage and reduce operating costs. Integration of renewable energy sources, captive power generation, and energy storage systems further increases the need for grid modernization. These requirements drive upgrades in transmission and distribution infrastructure, automation, and control systems, making industrial applications a major contributor to sustained investment and technological advancement across India’s power networks.
End User Insights:
- Utilities
- Independent Power Producers (IPPs)
- Government and Municipalities
Utilities exhibit a clear dominance with a 52% share of the total India grid modernization market in 2025.
Utilities hold the biggest market share attributed to their central role in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution across the country. Both state-owned and private utilities are responsible for modernizing aging infrastructure, reducing technical and commercial losses, and enabling large-scale renewable energy integration. These responsibilities require consistent investment in advanced grid technologies, automation solutions, and digital monitoring systems, positioning utilities as the primary adopters and key drivers of grid modernization initiatives nationwide.
Large-scale government programs and evolving regulatory mandates are encouraging utilities to accelerate deployment of smart meters, automation technologies, and advanced control systems across power networks. Utilities play a central role in maintaining grid reliability, operational efficiency, and system stability, which necessitates continuous investment in modernization initiatives. Their responsibility for network planning, asset management, and capital expenditure decisions allows utilities to drive technology adoption at scale, reinforcing their dominant position in the market.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
West India dominates with a market share of 30% of the total India grid modernization market in 2025.
West India leads the market, driven by high industrial concentration, rising electricity demand, and early adoption of advanced grid technologies. States, such as Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Rajasthan, operate extensive transmission and distribution networks that require regular upgrades to support large-scale renewable energy integration, rapid urbanization, and industrial growth. Significant investment in grid automation, smart substations, and digital monitoring systems continues to strengthen regional leadership and improve overall power reliability and efficiency.
The region also benefits from proactive state utilities, private sector participation, and large-scale renewable energy deployment, particularly solar and wind projects. Strong regulatory support and infrastructure readiness further reinforce West India’s leadership in grid modernization across transmission and distribution networks. For example, in 2024, Gujarat’s ₹1 lakh crore transmission investment strengthened grid capacity, enables 100 GW renewable integration by 2030, and supports rising electricity demand across agriculture, industry, and consumers.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Grid Modernization Market Growing?
Private Sector Participation and Technology Innovation
The growing participation from private companies and technology providers is strengthening the India grid modernization efforts. Equipment manufacturers, software developers, and engineering firms are delivering advanced solutions across transmission, distribution, and grid management, while private capital brings digital platforms and operational expertise. This collaboration translated into measurable outcomes in 2025, when AmpereHour Energy and Indigrid commissioned a 20 MW/40 MWh battery energy storage system in Delhi, delivering up to four hours of daily backup and improving reliability for more than 100,000 residents. Executed under a long-term agreement with BSES Rajdhani Power Limited, the project demonstrated how public–private partnerships accelerate deployment, support renewable integration, and enhance grid resilience, contributing to long-term stability and growth of India’s power sector.
Integration of Advanced Transmission Technologies
Adoption of advanced transmission technologies is playing a key role in modernizing India’s power grid and improving system efficiency at scale. Solutions like high-voltage direct current links, flexible AC transmission systems, and digital substations enable long-distance power transfer with lower losses and stronger grid stability. This shift toward next-generation infrastructure was reinforced in 2025, when Epsilon Composite established its Indian subsidiary, HindEpsilon Composite, in Chennai to locally manufacture HVCRC high-performance composite conductors. Local production supports higher transmission capacity, faster project execution, and improved efficiency. As transmission expansion continues to meet rising demand, integration of advanced materials and technologies strengthens grid resilience, operational flexibility, and long-term performance nationwide.
Smart Meter Rollout and Consumer-Centric Grid Management
Large-scale deployment of smart meters is transforming grid operations and accelerating modernization across India. These meters support real-time utilization monitoring, remote services, and dynamic pricing, enabling utilities to manage demand more effectively and improve forecasting accuracy. This shift is evident in deployment progress, with 47.6 million smart meters installed nationwide by November 15, 2025, and approvals in place for 203.3 million additional meters under the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme. Integrating this scale of metering requires upgraded communication networks and data platforms. As people participation becomes central to power sector reforms, smart metering is driving responsive, data-enabled electricity systems across residential, commercial, and industrial segments.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India Grid Modernization Market is Facing?
High Capital Investment Requirements and Financial Constraints
Grid modernization requires significant upfront capital investment for advanced technologies, network upgrades, and system integration. Many distribution companies face financial constraints that limit their ability to fund large-scale modernization initiatives. In addition, returns on investment often accrue gradually through efficiency gains and loss reduction, creating longer payback periods. These financial pressures can slow adoption, delay project execution, and restrict the pace of grid modernization despite strong long-term benefits.
Technical Integration Challenges with Legacy Infrastructure
Integrating advanced metering infrastructure and digital grid solutions with legacy billing and operational systems presents major technical challenges for utilities. Many power distributors rely on outdated platforms that lack compatibility with modern smart grid technologies. Upgrading or replacing these systems requires complex system integration, skilled expertise, and careful execution, increasing costs and implementation timelines while raising operational risk during the transition period.
Skilled Workforce Shortage and Capacity Limitations
The shift toward digitalized energy systems requires specialized expertise in data analytics, cybersecurity, power electronics, and advanced grid operations. Many utilities face a shortage of skilled professionals capable of deploying, operating, and maintaining complex smart grid infrastructure. Limited availability of trained personnel increases reliance on external support, raises implementation costs, and slows the pace of grid modernization across power distribution and transmission networks.
Competitive Landscape:
The India grid modernization market exhibits moderate to highly competitive intensity characterized by the participation of established multinational technology providers alongside domestic engineering conglomerates. Market dynamics reflect strategic positioning across smart grid solutions, transmission equipment, distribution automation, and energy storage systems. Competition is increasingly shaped by technological capabilities, project execution expertise, local manufacturing presence, and alignment with government procurement requirements. Companies are focusing on expanding service offerings, enhancing digital capabilities, and establishing strategic partnerships to strengthen market presence and capture opportunities emerging from India's energy transition. The competitive landscape is evolving as players invest in research and development (R&D), localize manufacturing operations, and develop integrated solutions addressing the comprehensive requirements of grid modernization programs.
Recent Developments:
- December 2025: Digital twins created a real-time virtual replica of India’s power grid, enabling predictive monitoring, self-healing, and AI-driven decision-making. They enhanced grid resilience, integrated renewable energy, and optimized operations across generation, transmission, and distribution. Implemented under India’s Smart Grid Mission, these technologies aimed for a sustainable, intelligent, and efficient energy system.
- July 2025: Bajel Projects Ltd won a Rs. 300 crore order from Power Grid Corporation of India (PGCIL) to build the 400 kV double-circuit Siwani–Jind transmission line in Haryana under the REZ Ph-IV, Bikaner Complex scheme. The 99 km project, part of India’s green energy and grid modernization initiatives, was scheduled for completion in 18 months. This order reinforces Bajel Projects’ role in high-value transmission infrastructure supporting India’s renewable energy evacuation and grid expansion.
India Grid Modernization Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Components Covered | Hardware, Software, Services |
| Applications Covered | Residential, Commercial, Industrial |
| End-Users Covered | Utilities, Independent Power Producers (IPPs), Government and Municipalities |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India grid modernization market size was valued at USD 1.51 Billion in 2025.
The India grid modernization market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 19.78% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 7.65 Billion by 2034.
Hardware holds the largest market share at 55% in 2025, driven by extensive deployment of smart meters, transformers, SCADA systems, and power electronics equipment essential for grid digitalization and renewable energy integration.
Key factors driving the India grid modernization market include strong policy support through regulatory guidance and funding. For example, in 2025, Maharashtra State Electricity Distribution Company partnered with the Global Energy Alliance to use AI, ML, and battery storage, enhancing reliability, scalability, and consumer service through digital innovation.
Major challenges include high capital investment requirements constraining utility modernization budgets, technical integration difficulties with legacy infrastructure systems, skilled workforce shortages for operating advanced digital technologies, and implementation delays affecting smart metering rollout timelines.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












