
India Mushroom Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Mushroom Type, Form, Distribution Channel, End Use, and Region, 2026-2034
India Mushroom Market Summary:
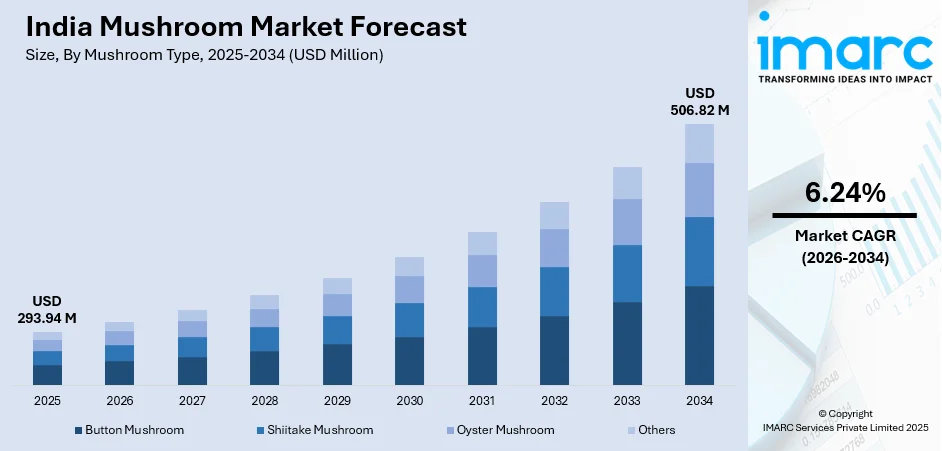
The India mushroom market size was valued at USD 293.94 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 506.82 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.24% from 2026-2034.
The India mushroom market is experiencing robust expansion driven by shifting dietary patterns, heightened nutritional awareness, and favorable cultivation conditions. Consumers increasingly view mushrooms as versatile functional foods offering exceptional protein content, essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidant properties without cholesterol or high caloric density. Government initiatives supporting horticulture development, combined with technological advancements in controlled environment agriculture and cold chain infrastructure, position mushrooms as accessible nutritious options across metropolitan centers, thereby expanding the India mushroom market share.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
-
By Mushroom Type: Button mushroom dominates the market with a share of 59.9% in 2025, reflecting its widespread culinary acceptance, affordability, and cultivation efficiency. Its mild flavor profile seamlessly integrates across traditional Indian recipes.
-
By Form: Fresh mushroom leads the market with a share of 65.4% in 2025, driven by consumer preferences for unprocessed natural ingredients maximizing nutritional benefits and authentic taste profiles.
-
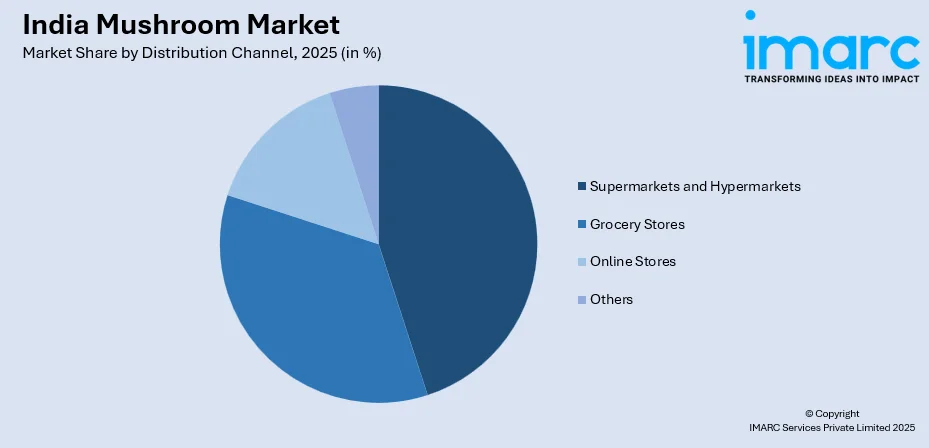
By Distribution Channel: Supermarkets and hypermarkets represent the largest segment with a market share of 44.3% in 2025, as they provide consumers with convenient one-stop shopping experiences and reliable cold storage maintaining product freshness, extensive variety selections, attractive packaging, and promotional activities.
-
By End Use: Direct consumption leads the market with a share of 38.7% in 2025, as households increasingly incorporate mushrooms into daily meal preparations recognizing their versatility as plant-based protein alternatives.
-
By Region: North India represents the largest segment with a market share of 39.8% in 2025, benefiting from favorable climatic conditions in states like Himachal Pradesh and Haryana where optimal temperature ranges and humidity levels support cultivation.
-
Key Players: The India mushroom market exhibits moderate competitive intensity with multinational agriculture corporations competing alongside regional producers and emerging agri-tech startups. Market participants differentiate through cultivation innovation, quality certifications, organic offerings, value-added processing capabilities, and distribution network development serving diverse consumer segments from premium gourmet varieties to affordable everyday options.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
India's mushroom sector represents a transformative agricultural opportunity bridging nutrition security, sustainable farming practices, and rural income generation. The industry leverages agro-waste recycling capabilities addressing environmental challenges while producing nutrient-dense foods requiring minimal land resources compared to traditional crops. Market dynamics reflect converging trends including urbanization patterns shifting consumption behaviors toward convenience and health, growing vegetarian and vegan populations seeking plant-based protein alternatives, expanding food service sectors incorporating mushrooms across restaurant menus, and pharmaceutical industries exploring medicinal applications. Production systems evolve through adoption of indoor vertical farming technologies, automated climate control mechanisms, and improved spawn quality enabling consistent yields. In 2025, mushroom villages were formed in 50 locations in Kerala under the second phase of a State Horticulture Mission-Kerala (SHM-Kerala) programme. The initiative, Comprehensive Development of Mushroom Villages in Kerala, focuses on empowering rural women, generating income for farmers, ensuring nutritional security, and highlighting business prospects in mushroom farming.
India Mushroom Market Trends:
Rise of Specialty and Exotic Mushroom Cultivation
Growing urban sophistication and culinary experimentation drive demand beyond traditional button varieties toward premium specialty mushrooms including shiitake, oyster, and emerging gourmet options. Metropolitan consumers, fine dining establishments, and health-focused demographics increasingly seek distinctive flavors, textures, and enhanced nutritional profiles associated with exotic varieties. This trend encourages farmers and agricultural entrepreneurs to diversify cultivation portfolios, investing in specialized growing conditions, controlled environment systems, and knowledge transfer programs. The specialty segment creates higher value opportunities for producers while educating consumers about mushroom diversity beyond conventional offerings, gradually shifting market perception from commodity ingredient toward premium functional food category. Mushroom coffee has gained popularity over the past several years. The choices offered in the Indian market depend entirely on powdered extracts or instant mixtures. Maverick and Farmer, an artisanal coffee brand based in Bengaluru, introduced whole bean-infused lion’s mane coffee. In partnership with Nuvedo, these coffee beans utilize a novel technology that combines the two components during the roasting process. The creators are submitting a patent application for this innovative technology.
Integration of Technology-Enabled Cultivation Systems
Modern mushroom farming increasingly adopts precision agriculture technologies including IoT sensors, automated climate control, data analytics, and indoor vertical farming infrastructure. These technological interventions optimize growing conditions, monitor environmental parameters in real-time, reduce labor dependencies, and improve yield consistency throughout production cycles. Smart farming systems enable producers to overcome traditional seasonal limitations, maintain quality standards, and scale operations efficiently. Technology integration particularly benefits small and medium-scale farmers accessing digital platforms providing cultivation guidance, market information, and supply chain connectivity, democratizing advanced agricultural practices previously limited to large commercial operations. IMARC Group predicts that the India precision agriculture market is projected to reach USD 738.7 Million by 2034.
Emergence of Mushroom-Based Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals
Product innovation extends mushroom applications beyond fresh produce into processed functional foods, dietary supplements, protein extracts, and wellness products targeting health-conscious consumers. Manufacturers develop mushroom-enriched snacks, beverages, protein powders, and nutritional bars capitalizing on medicinal properties, immune-boosting compounds, and adaptogenic characteristics. This diversification creates new market segments appealing to preventive health mindsets, fitness enthusiasts, and consumers seeking natural alternatives to synthetic supplements. The functional foods trend elevates mushrooms from culinary ingredients to therapeutic nutrition sources, supported by scientific research validating health benefits and consumer education initiatives promoting medicinal mushroom awareness. In 2024, Miracles Mushroom Superfoods Pvt. Ltd. unveiled its premium line of medicinal mushroom products created for promoting holistic wellness via the efficiency of mushrooms.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The India mushroom market is poised for sustained expansion throughout the forecast period, propelled by converging demographic, economic, and lifestyle factors reshaping food consumption patterns. The market generated a revenue of USD 293.94 Million in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 506.82 Million by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.24% from 2026-2034. Market revenue growth reflects increasing per capita consumption as mushrooms transition from occasional specialty items to regular household staples, expanded distribution reaching previously underserved markets, value-added processing creating premium product categories, and export opportunities for dried and canned varieties meeting global demand.
India Mushroom Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Mushroom Type |
Button Mushroom |
59.9% |
|
Form |
Fresh Mushroom |
65.4% |
|
Distribution Channel |
Supermarkets and Hypermarkets |
44.3% |
|
End Use |
Direct Consumption |
38.7% |
|
Region |
North India |
39.8% |
Mushroom Type Insights:
- Button Mushroom
- Shiitake Mushroom
- Oyster Mushroom
- Others
Button mushroom dominates with a market share of 59.9% of the total India mushroom market in 2025.
Button mushroom’s dominance stems from remarkable versatility across diverse culinary applications, from traditional Indian curries and gravies to continental preparations and Asian stir-fries, making it universally acceptable across regional taste preferences and cooking styles. Economic accessibility positions button mushrooms within reach of middle-income households, while mild flavor profiles appeal to consumers unfamiliar with stronger mushroom varieties, facilitating gradual market adoption and repeat purchasing behavior. Production economics strongly favor button mushroom cultivation with relatively straightforward farming techniques requiring moderate infrastructure investments compared to exotic varieties.
Farmers benefit from shorter cultivation cycles enabling rapid turnover, established supply chains connecting rural production zones with urban markets, and abundant technical support through government agricultural extension programs and research institutions. Climate adaptability allows cultivation across varied geographical conditions, from controlled environments in plains to natural growing conditions in hillier regions, democratizing production opportunities for small and medium agricultural enterprises. In 2025, Gachwala, a leading name in India's mushroom farming industry, unveiled its newest innovation, Button Mushroom Spawn (Sylvan A15 variety). Through this initiative, Gachwala seeks to support Indian farmers, small-scale cultivators, and mushroom lovers by providing high-quality spawn technology that improves yield, quality, and profitability.
Form Insights:
- Fresh Mushroom
- Canned Mushroom
- Dried Mushroom
- Others
Fresh mushroom leads with a share of 65.4% of the total India mushroom market in 2025.
The fresh category dominates the market, reflecting strong consumer preferences for natural unprocessed ingredients maximizing nutritional integrity, authentic flavors, and optimal textures for culinary preparations. Fresh varieties dominate household purchasing decisions driven by perceptions of superior quality, health benefits, and versatility enabling diverse cooking applications from sautéing and grilling to incorporation in complex multi-ingredient dishes requiring specific texture profiles. Consumer behavior increasingly emphasizes organic and minimally processed foods aligning with wellness lifestyles, preventive health approaches, and clean eating philosophies gaining traction across urban demographics. Fresh mushrooms satisfy these preferences by delivering complete nutritional profiles without preservatives, additives, or processing modifications potentially diminishing health benefits.
This segment particularly appeals to cooking enthusiasts, restaurant chefs, and health-conscious families willing to manage shorter shelf lives in exchange for perceived quality advantages. Market growth faces logistical challenges requiring robust cold chain infrastructure, refrigerated transportation networks, and rapid distribution systems minimizing spoilage between farm gate and consumer purchase points. Premium positioning opportunities emerge through organic certifications, farm-fresh branding emphasizing traceability, and experiential marketing connecting consumers with production processes. The segment benefits from increasing disposable incomes enabling premium purchases, urbanization concentrating populations within reach of reliable cold chain networks, and evolving shopping behaviors favoring quality over extended shelf lives in fresh produce categories.
Distribution Channel Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Supermarkets and Hypermarkets
- Grocery Stores
- Online Stores
- Others
Supermarkets and hypermarkets exhibit a clear dominance with a 44.3% share of the total India mushroom market in 2025.
Supermarkets offer comprehensive shopping experiences where mushrooms integrate within broader fresh produce selections, enabling convenient one-stop purchasing for weekly grocery needs. Strategic product placement near vegetables and salad ingredients promotes impulse purchases and recipe inspiration, while promotional activities, sampling programs, and nutritional information displays educate consumers about preparation methods and health benefits. Organized retail's professional merchandising, attractive packaging, and quality assurance mechanisms build consumer trust compared to traditional unbranded market channels, particularly resonating with urban middle-class demographics prioritizing food safety and hygiene standards.
The channel provides market access for producers through consolidated procurement systems, quality specifications, and contractual arrangements offering production predictability compared to fragmented traditional distribution networks. Retail chains increasingly develop cold chain infrastructure extending distribution reach into tier-two and tier-three cities, democratizing access to fresh mushrooms beyond metropolitan markets. Furthermore, the expansion of supermarkets in the country is increasing accessibility of mushroom. In 2025, More Retail, a prominent food and grocery retailer in India, unveiled the opening of its newest supermarket in Kazipara, situated on Taki Road, Barasat, Kolkata (West Bengal). The new shop will officially welcome customers on June 20, 2025. The launch represents another important milestone in More Retail’s ongoing growth and dedication to providing an enhanced, community-oriented shopping experience.
End Use Insights:
- Food Processing Industry
- Food Service Sector
- Direct Consumption
- Others
Direct consumption leads with a share of 38.7% of the total India mushroom market in 2025.
Growing health consciousness drives direct consumption as households recognize mushrooms' nutritional density, particularly protein content appealing to vegetarian populations seeking plant-based alternatives to animal proteins. Consumers appreciate mushrooms' versatility enabling incorporation across traditional Indian dishes including curries, biryanis, and parathas alongside continental preparations like pastas, pizzas, and salads, supporting dietary variety without compromising cultural food preferences. This adaptability encourages repeat purchases and regular consumption patterns, transitioning mushrooms from occasional purchases to routine grocery list items competing with established vegetable categories.
The segment benefits from increased cooking at home, accelerated by pandemic-era behavioral changes and sustained through economic considerations, wellness focuses, and family meal priorities. Home cooks experiment with mushroom recipes facilitated by online cooking content, social media recipe sharing, and celebrity chef endorsements normalizing mushroom usage across mainstream households. Nutritional education campaigns highlighting mushrooms' immune-boosting properties, vitamin D content, antioxidant capacities, and cardiovascular benefits resonate with preventive health mindsets, particularly among middle-aged consumers managing chronic disease risks and parents prioritizing children's nutritional intake.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- West and Central India
- South India
- East India
North India exhibits a clear dominance with a 39.8% share of the total India mushroom market in 2025.
North India dominates with a market, establishing the country's mushroom cultivation powerhouse through favorable agro-climatic conditions and institutional infrastructure. States like Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Punjab, and Uttar Pradesh provide ideal temperature ranges and humidity levels essential for optimal button mushroom growth. Solan in Himachal Pradesh, known as the "Mushroom City of India," serves as the research epicenter through ICAR-Directorate of Mushroom Research, providing technical knowledge transfer and comprehensive farmer training programs.
Government initiatives offer substantial support including subsidized infrastructure development, spawn production facilities, and compost preparation training, reducing entry barriers for agricultural entrepreneurs. Established cold chain networks connecting production zones with metropolitan consumption markets ensure minimal post-harvest losses and consistent product quality. The region's strategic proximity to large urban centers, combined with agricultural extension services and organized farmer cooperatives, creates efficient distribution systems supporting robust domestic supply chains and expanding export-oriented production capabilities across diverse mushroom varieties.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Mushroom Market Growing?
Expanding Health Awareness and Nutritional Consciousness
India experiences profound health consciousness evolution as consumers increasingly recognizes dietary choices' direct impact on wellness outcomes, disease prevention, and quality of life across all age demographics. Mushrooms emerge as ideal functional foods offering comprehensive nutritional profiles including high-quality proteins with all essential amino acids, B-complex vitamins supporting energy metabolism, minerals like selenium and potassium, and bioactive compounds including beta-glucans providing immune modulation benefits. Growing awareness of chronic lifestyle diseases including diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, and obesity drives consumers toward nutrient-dense low-calorie foods, positioning mushrooms as strategic dietary inclusions. Public health campaigns like the launch of Swasth Nari, Sashakt Parivar Abhiyaan, strengthening healthcare and nutrition services for women, adolescent girls, and children across India in 2025, are increasing awareness about the consumption of healthy food products like mushrooms.
Accelerating Vegetarianism and Plant-Based Diet Adoption
India’s substantial vegetarian population creates inherent demand for diverse plant-based protein sources, with mushrooms uniquely positioned through meat-like textures and umami flavor profiles satisfying sensory expectations traditionally associated with animal proteins. The World Atlas states that India possesses the highest percentage of vegetarians globally, with 38% of its population recognizing themselves as vegetarians. Beyond traditional vegetarianism, emerging vegan movements among younger urban demographics reject all animal-derived products including dairy, actively seeking plant-based alternatives across food categories. Mushrooms provide essential proteins, vitamins, and minerals often challenging to obtain from purely plant-based diets, making them invaluable for nutritionally balanced vegan eating patterns. Environmental consciousness increasingly influences dietary choices as consumers recognize animal agriculture's substantial carbon footprint, water consumption, and deforestation contributions, driving deliberate shifts toward lower-impact plant-based foods like mushrooms requiring minimal resources compared to conventional livestock farming.
Government Support and Agricultural Development Initiatives
Central and state government programs actively promote mushroom cultivation through comprehensive support mechanisms recognizing the sector's potential for rural income generation, agricultural diversification, and nutritional security enhancement. Financial assistance schemes including subsidies covering infrastructure setup costs reduce entry barriers for aspiring mushroom farmers, democratizing access to agricultural entrepreneurship opportunities particularly for small and marginal landholders seeking high-value crop alternatives. Technical training initiatives conducted through agricultural universities, extension services, and specialized research institutions provide scientific knowledge transfer on cultivation techniques, pest management, quality spawn production, and post-harvest handling, building farmer capabilities and production consistency. Government-backed credit facilities through NABARD and cooperative banking structures enable working capital access for operational expenses, equipment purchases, and expansion investments, addressing financial constraints limiting agricultural innovation adoption. In 2025, Farmers in Bihar are receiving a new chance to boost their earnings as the state's horticulture department initiates a program to encourage mushroom farming in Bhagalpur. The initiative will offer training, mushroom kits, and financial support to farmers interested in this farming method.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India Mushroom Market is Facing?
Limited Cold Chain and Post-Harvest Infrastructure
Mushrooms' high perishability with typical shelf lives of one to three days under ambient conditions necessitates sophisticated cold chain infrastructure throughout production, distribution, and retail stages, capabilities remaining underdeveloped across India's fragmented agricultural supply chains particularly affecting rural and semi-urban markets. Many production regions particularly in emerging cultivation zones lack adequate cold storage facilities, forcing farmers to accept distressed sales at unfavorable prices rather than storing inventory for optimal market timing. Traditional retail channels including wet markets and small grocery stores typically operate without refrigeration, limiting product quality maintenance and shortening consumer purchase windows, restricting market penetration among price-sensitive segments prioritizing affordability over premium cold-chain-enabled offerings.
Fragmented Supply Chains and Market Access Challenges
India's mushroom sector operates through highly fragmented supply chains involving multiple intermediaries between producers and end consumers, each extracting margins while adding limited value, ultimately increasing consumer prices while reducing farmer realizations. Small-scale producers particularly struggle with direct market access, depending on local aggregators and commission agents who possess superior market information and bargaining power, creating asymmetric relationships disadvantaging cultivators. Limited producer organizations and collective marketing mechanisms prevent farmers from achieving economies of scale in procurement, transportation, and negotiations with retailers or processors. Geographic dispersion of production zones combined with concentrated urban consumption creates logistical inefficiencies, particularly during peak harvest periods when supply surges exceed immediate demand, leading to price crashes and production disincentives.
High Initial Investment and Technical Knowledge Requirements
Establishing commercial mushroom cultivation units requires substantial upfront capital investments in infrastructure including growing rooms, climate control systems, pasteurization equipment, and spawn production facilities, creating entry barriers for resource-constrained farmers despite high potential returns. Technical complexity of mushroom cultivation involving precise environmental controls, substrate preparation, spawn quality management, and pest disease prevention demands specialized knowledge often unavailable in traditional agricultural communities, limiting adoption rates. Many farmers lack awareness about modern cultivation practices, quality standards, and market requirements, resulting in suboptimal production outcomes, quality inconsistencies, and marketing difficulties even when cultivation attempts are made. Access to quality spawn, the fundamental input for mushroom production, remains limited outside established production regions, forcing farmers to rely on unreliable sources or undertake expensive procurement from distant suppliers, increasing operational complexity.
Competitive Landscape:
The India mushroom market demonstrates moderate competitive intensity characterized by diverse participant profiles ranging from multinational agricultural corporations with established cultivation technologies and distribution networks to regional players leveraging local market knowledge and emerging agritech startups introducing innovative production and marketing approaches. Large-scale commercial operations compete through economies of scale, advanced farming infrastructure including automated climate control and spawn production facilities, and established supply chain partnerships with organized retail chains and food processing companies. These industry leaders invest substantially in quality certifications, food safety standards, and brand development differentiating premium offerings commanding higher price points among discerning consumers. Regional producers maintain competitive advantages through proximity to local markets enabling fresher products, relationships with traditional distribution channels including wet markets and small retailers, and adaptation to regional taste preferences and consumption patterns. Price competition remains significant particularly in commodity segments like button mushrooms where product differentiation is limited, encouraging efficiency improvements in cultivation practices, input procurement, and distribution optimization. Innovation becomes increasingly important as market participants develop value-added products including organic certified offerings, exotic variety introductions, processed formats like dried and powdered mushrooms, and convenience products such as pre-washed pre-sliced varieties appealing to time-constrained urban consumers. Strategic collaborations emerge between producers and research institutions for variety development, cultivation technology improvements, and disease management solutions addressing production challenges while enhancing yield consistency. Export-oriented players focus on compliance with international quality standards, certifications including Global GAP, and relationship building with overseas buyers particularly in Gulf markets and Western countries demanding dried and canned varieties. Market consolidation pressures gradually increase as successful players pursue acquisitions of smaller operations to expand production capacities, geographic coverage, and market share, though the sector remains relatively fragmented compared to global benchmarks, offering continued opportunities for differentiated new entrants and niche players.
Recent Developments:
-
In December 2025, The Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK), Anjaw has, for the initial time, performed an experiment on oyster mushroom farming utilizing maize cobs, finger millet straw, and large cardamom stalks with leaves as substrate. The KVK announced in a statement that the demonstration has exhibited promising and robust mycelium development, suggesting that the trial is advancing well and is anticipated to reach complete success.
-
In September 2025, Tripura is making significant progress toward self-reliance in mushroom production by starting an organic cultivation program, as announced by Agriculture and Farmer’s Welfare Minister. The declaration was made at the opening of the state’s inaugural training workshop on organic mushroom farming at the Horticulture Research Complex, Nagichhara. The initiative involved 53 Farmer Producer Companies (FPCs) and showcased mushrooms as a nutrient-dense “superfood” loaded with vitamin D, iron, and various crucial nutrients.
India Mushroom Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Million USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Mushroom Types Covered | Button Mushroom, Shiitake Mushroom, Oyster Mushroom, Others |
| Forms Covered | Fresh Mushroom, Canned Mushroom, Dried Mushroom, Others |
| Distribution Channels Covered | Supermarkets and Hypermarkets, Grocery Stores, Online Stores, Others |
| End-Uses Covered | Food Processing Industry, Food Service Sector, Direct Consumption, Others |
| Regions Covered | North India, West and Central India, South India, East India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India mushroom market size was valued at USD 293.94 Million in 2025.
The India mushroom market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.24% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 506.82 Million by 2034.
Button mushroom dominated the India mushroom market in 2025, accounting for 59.9% of total market share due to its widespread culinary acceptance, affordability, and ease of cultivation across diverse climatic conditions.
Key factors driving the India Mushroom market include expanding health consciousness among consumers recognizing mushrooms' nutritional benefits and functional food properties, accelerating vegetarianism and plant-based diet adoption positioning mushrooms as essential protein alternatives, growing food service sector integration featuring mushroom-based dishes across restaurant menus, technological advancements in controlled environment cultivation improving production efficiency and year-round availability, and comprehensive government support through subsidies, training programs, and infrastructure development reducing entry barriers for agricultural entrepreneurs.
Major challenges include inadequate cold chain infrastructure causing substantial post-harvest losses and limiting market reach particularly in semi-urban and rural areas, fragmented supply chains involving multiple intermediaries reducing farmer profitability while increasing consumer prices, high initial investment requirements for commercial cultivation setup deterring potential producers, limited technical knowledge and quality spawn availability constraining production optimization, and perishability concerns requiring rapid distribution systems that remain underdeveloped across many production regions.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












