
India School Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Level of Education, Ownership, Board of Affiliation, Fee Structure, and Region 2026-2034
India School Market Summary:
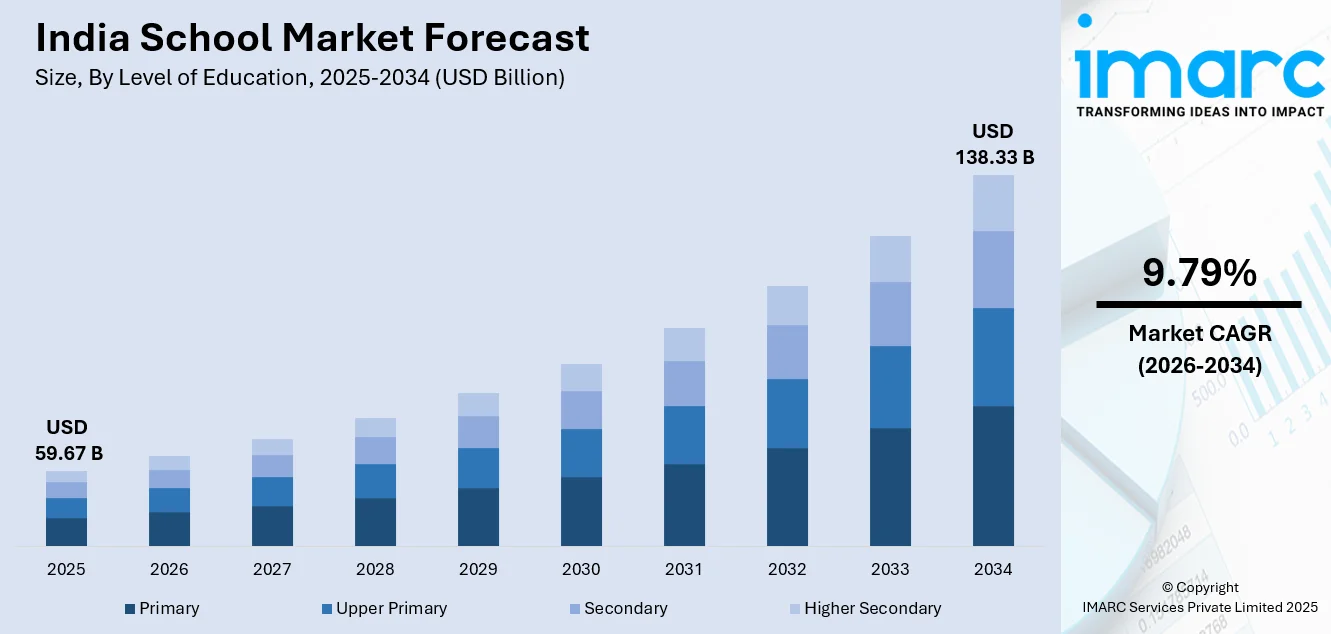
The India school market size was valued at USD 59.67 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 138.33 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 9.79% from 2026-2034.
The India school market is witnessing strong growth supported by the country’s demographic dividend, ongoing education policy reforms, and sustained public investment in school infrastructure. Expanding access to digital learning, curriculum modernization, and improved teacher training are further reinforcing system capacity. Apart from this, the rising parental aspirations for quality education and steadily increasing household spending on schooling are boosting enrollment levels across primary, secondary, and senior secondary segments nationwide.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Level of Education: Primary dominates the market with a share of 42% in 2025, supported by universal enrollment mandates, government-led literacy programs, and sustained public funding schemes.
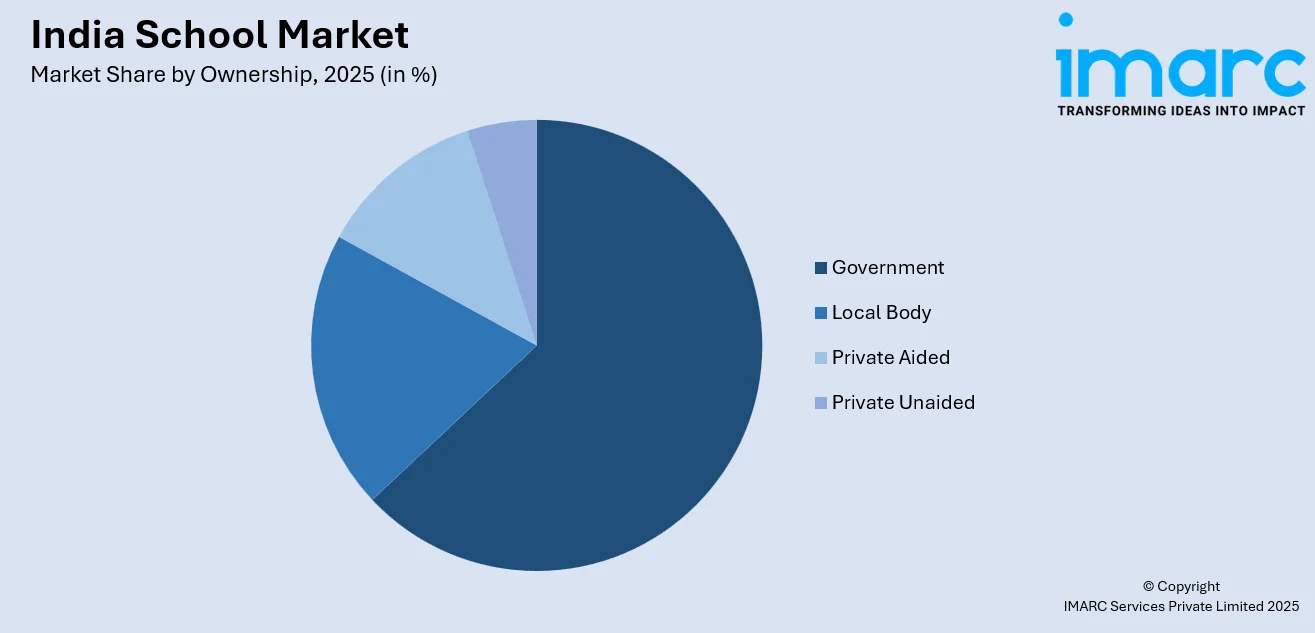
- By Ownership: Government leads the market with a share of 63% in 2025, reflecting its extensive school network, free or subsidized education provision, and strong focus on improving access in rural and economically weaker regions.
- By Board of Affiliation: State government boards represent the largest segment with a market share of 62% in 2025, due to curriculum alignment with regional languages, affordability, and widespread recognition for public examinations.
- By Fee Structure: Low-income dominates the market with a share of 56% in 2025, driven by high dependence on government schools, free education policies, and targeted support for economically disadvantaged households.
- By Region: South India leads the market with a share of 32% in 2025, owing to higher literacy rates, stronger education infrastructure, proactive state policies, and greater household spending on schooling.
- Key Players: The India school market exhibits a highly fragmented competitive landscape, characterized by the dominance of government-operated institutions alongside a growing presence of private school chains, international board affiliates, and technology-enabled education providers expanding their footprint across metropolitan and tier-two cities.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India school market is shaped by sustained enrollment demand, higher household prioritization of education, and system wide reforms focused on learning quality. Public investment in physical and digital infrastructure is strengthening access and reducing dropouts, particularly at the upper primary and secondary levels. In addition to this, pedagogical reform is influencing how schools position themselves. Reflecting this shift, in 2025, a government primary school in Sabarkantha, Gujarat introduced the ‘Year of Questions’ initiative under NEP 2020, encouraging students to engage through classroom dialogue and structured question boxes. The approach improved confidence, reasoning ability, and independent learning, earning positive response from parents and teachers. Such outcome focused practices, combined with the growing acceptance of organized pre schooling, international curricula, technology exposure, and experiential learning, are expanding the role of formal schooling. Corporate and institutional partnerships further reinforce academic support and inclusion, sustaining long term market growth.
India School Market Trends:
Expansion of High-End International School Infrastructure
The rising preference for integrated residential schooling with international exposure is supporting expansion of premium school infrastructure in India. Families increasingly seek institutions that offer academic continuity from early childhood through senior secondary levels, supported by boarding facilities, global curricula, and strong governance. This demand is encouraging investment in large, purpose-built campuses designed to deliver end to end education under a single system. Reflecting this trend, in 2025, UK based Bedford School announced plans to open its first international campus in India, the country’s first British girls’ school. The Mohali campus offered education from ages three to eighteen, combining British and national curricula with day and boarding options through a partnership with the Doon International Education Society.
Investment in Digital School Infrastructure
Sustained government funding for education infrastructure is impelling the school market growth by improving capacity, quality, and learning delivery. Large scale public investment reduces infrastructure gaps, raises baseline standards, and encourages higher student retention within formal schooling systems. In 2025, the Delhi Cabinet approved over ₹900 crore to expand Smart Classrooms across government schools and implement the National Education Policy 2020. The plan included installing over 2,400 smart blackboards and creating nearly 19,000 additional smart classrooms for senior secondary grades. Such initiatives modernize teaching environments, support technology enabled instruction, and reinforce confidence in public education, indirectly stimulating overall market expansion.
Emphasis on Innovation and Experiential Learning
Increasing focus on innovation led education is driving the demand for structured schooling that goes beyond traditional academics. Schools are expected to provide platforms for problem solving, creativity, and practical application of knowledge. In 2025, the Ministry of Education announced the Viksit Bharat Buildathon 2025, a nationwide school level innovation event engaging students from Classes 6 to 12 across India. The initiative aimed to involve nearly one crore students in ideation and prototype development aligned with national development themes. Such programs elevate the role of schools as innovation hubs, enhance student engagement, and reinforce the relevance of formal education systems, supporting the market growth.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The India school market shows strong growth potential across the forecast period, supported by favorable population trends, continued policy support, and rising household spending on education. Expanding urbanization, higher enrollment rates, and greater emphasis on quality schooling are strengthening the demand across both public and private institutions. The market generated a revenue of USD 59.67 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 138.33 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 9.79% from 2026-2034. The growing investments in infrastructure, curriculum upgrades, and digital learning tools further reinforce long-term expansion prospects.
India School Market Report Segmentation:
|
Segment Category |
Leading Segment |
Market Share |
|
Level of Education |
Primary |
42% |
|
Ownership |
Government |
63% |
|
Board of Affiliation |
State Government Boards |
62% |
|
Fee Structure |
Low-Income |
56% |
|
Region |
South India |
32% |
Level of Education Insights:
- Primary
- Upper Primary
- Secondary
- Higher Secondary
Primary dominates with a market share of 42% of the total India school market in 2025.
Primary holds the biggest market share owing to its universal mandate and foundational role within the formal education system. Government policy places strong emphasis on enrolment, retention, and basic learning outcomes at this stage, supported by nationwide programs and compulsory education norms. High demand is further reinforced by public and private investment aimed at literacy, numeracy, and early cognitive development. For example, in 2025, the central government released guidelines to co-locate Anganwadi Centres with primary schools to strengthen early childhood care and education. The framework promoted joint planning between teachers and Anganwadi workers, aligned curricula, and child-friendly infrastructure to ensure smoother transitions into Grade 1.
Another contributing factor is the relatively lower cost structure and scalability of primary schooling compared to secondary and higher levels. Infrastructure, curriculum requirements, and teacher specialization are less complex, allowing wider geographic penetration, including rural and semi-urban areas. Parental priorities tend to favor early schooling as a minimum educational standard, driving consistent intake levels. Demographic factors also play a role, as the population size within primary-age cohorts remains substantial. In addition, policy continuity and sustained funding ensure stability at the primary level, supporting its dominance within the overall school education market.
Ownership Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Government
- Local Body
- Private Aided
- Private Unaided
Government leads with a market share of 63% of the total India school market in 2025.
Government represents the largest segment due to constitutional obligations and long-standing public policy commitments to universal education. The state bears primary responsibility for ensuring access, equity, and continuity across regions and income groups. Extensive public funding mechanisms, centralized standards, and regulatory authority enable large-scale provisioning of schools. Public systems are designed to absorb population growth and regional disparities, sustaining high enrolment capacity. This dominance is reflected by the data provided by the Economic Survey 2024-25, which stated that government schools comprised 69 % of the total, enrolling 50 % of students and employing 51 % of teachers.
Another reason for government dominance lies in policy-driven expansion objectives and administrative control over schooling networks. Public ownership allows coordinated planning, standardized implementation, and alignment with national development priorities. Government systems also benefit from assured land access, workforce deployment mechanisms, and long-term operational support. Regulatory influence further strengthens public presence by setting entry barriers and compliance requirements, which limits rapid ownership expansion by non-government participants across diverse regions and administrative jurisdictions nationwide under unified governance structures and long-term oversight mechanisms.
Board of Affiliation Insights:
- Central Board of Secondary Education
- Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations
- State Government Boards
- Others
State government boards exhibit a clear dominance with a 62% share of the total India school market in 2025.
State government boards dominate the market attributed to their statutory authority and widespread administrative integration. These boards are designed to align schooling with regional governance structures, language requirements, and standardized assessment frameworks. Affiliation processes are streamlined and accessible, enabling broad institutional participation. Curriculum oversight, examination management, and certification functions are centralized, ensuring uniformity and predictability. Public funding linkages and regulatory recognition further strengthen adoption. The emphasis on inclusivity and standardized progression pathways sustains high affiliation volumes, reinforcing the dominance of state boards across the school education system.
Another factor supporting state government boards dominance is policy continuity and institutional familiarity among schools and administrators. Long-established governance mechanisms provide clarity in compliance, inspection, and academic regulation. Affiliation with state boards offers alignment with localized academic calendars and administrative processes, reducing operational complexity. Examination structures and evaluation criteria are integrated with state-level oversight, supporting consistency in outcomes. In addition, recognition across public institutions and higher education pathways encourages sustained preference.
Fee Structure Insights:
- Low-Income
- Medium-Income
- High-Income
Low-income dominates with a market share of 56% of the total India school market in 2025.
Low-income exhibits a clear dominance in the market because of the overarching objective of ensuring broad access to basic education across socio-economic segments. Policy measures emphasize affordability, cost control, and inclusion, influencing institutional fee frameworks. Public funding support, subsidies, and regulatory oversight further constrain pricing levels. Schools operating within this structure prioritize scale and accessibility over margin expansion, reinforcing the prevalence of low-fee models within the overall education market and sustaining high enrolment volumes nationwide.
Another driver of low-income dominance is the structural composition of the education ecosystem, where affordability remains central to long-term participation and retention. Cost-sensitive enrolment patterns encourage institutions to maintain modest fee levels to ensure stability and continuity. Operational models are designed around controlled expenditure, standardized delivery, and efficient resource utilization. Regulatory scrutiny on fee increases also limits upward pricing flexibility. These conditions collectively support widespread adoption of low-income fee structure, positioning it as the dominant segment within the market across diverse geographic and administrative settings.
Breakup by Region:
To get detailed regional analysis of this market, Request Sample
- North India
- East India
- West and Central India
- South India
South India leads with a market share of 32% of the total India school market in 2025.
South India dominates the market, driven by its relatively higher concentration of educational infrastructure and sustained emphasis on formal schooling. The region benefits from stronger administrative focus on education planning, higher literacy orientation, and consistent policy implementation. Demographic trends support steady enrolment across age groups, while institutional density enables greater access and continuity. Investment patterns favor long-term capacity building, contributing to a well-established schooling ecosystem. These factors collectively result in higher participation rates and stronger market presence compared to other regions within the national education system.
Another contributing factor is the region’s structured approach to governance, curriculum adoption, and institutional management. Efficient implementation of education policies supports stability in operations and enrolment flows. The presence of diverse management models across public and private segments enhances capacity absorption. A significant development in this landscape occurred in 2025, when the Western Australian Certificate of Education announced its entry into India, with three schools in Karnataka launching the curriculum at the kindergarten level. By offering an Australian-recognized pathway at a competitive cost, such international boards cater to the social prioritization of global education standards.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India School Market Growing?
Strengthening of Organized Preschool Networks
India’s preschool segment is witnessing steady growth as operators move toward structured, system-led early education models. Parents increasingly prefer institutions with defined teaching philosophies, standardized classroom practices, and consistent learning outcomes over fragmented play-based formats. This shift is driving the demand for professionally managed preschool networks that combine pedagogy with operational discipline. In 2025, Finnish early education company HEI Schools established HEI India to support the domestic preschool market through localized academic practices, educator capacity building, and school management support aligned with national guidelines. Such initiatives formalize early education delivery, enhance trust in preschool quality, and contribute to scalable growth within the organized early learning segment.
Integration of Workforce-Oriented Digital Education
Alignment of school curricula with future workforce requirements is expanding the functional role of schools beyond academic instruction. Stakeholders increasingly view technology exposure as essential for employability readiness and digital inclusion. This is resulting in partnerships that embed applied digital skills within middle school education. In 2025, Lenovo India and Motorola Mobility collaborated with Muskaan Dreams to launch the “Innovators of Tomorrow” programme in government schools in Lucknow. The initiative introduced structured ICT, coding, and AI-ML learning through IoT labs for students in Classes 6 to 8, alongside teacher training. Such interventions broaden curriculum relevance, strengthen institutional value, and support sustained participation in formal schooling systems.
Corporate-Led Support for Public School Performance
Private sector engagement is emerging as a complementary force in improving public school outcomes and scale. Corporations are adopting long term education programs that address academic gaps, guidance needs, and student continuity rather than short term interventions. In 2025, Sumadhura Foundation launched the “Sumadhura Nirman Shatha Shatham” program across Telangana, supporting more than 7,000 government school students in 25 schools through academic mentoring, career guidance, and scholarships. Implemented with state authorities and non-profit partners, such initiatives enhance school performance, improve completion rates, and strengthen confidence in government education systems, contributing to broader market stability and sustained enrollment.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India School Market is Facing?
Persistent Urban-Rural Educational Divide
Significant disparities in educational infrastructure, teacher availability, and learning outcomes continue to persist between urban and rural regions. Schools in rural areas frequently contend with multi-grade classrooms, chronic shortages of qualified teachers, and inadequate physical facilities. Limited internet connectivity and restricted access to digital learning tools further widen this gap, constraining student performance, reducing retention rates, and limiting the reach and growth potential of education-focused solutions in underserved rural markets.
Teacher Shortages and Quality Concerns
Inadequate teacher recruitment, persistent retention challenges, and limited access to structured professional development continue to constrain educational quality across government schools. Teacher absenteeism remains a widespread issue, disrupting classroom continuity and student engagement. At the secondary level, gaps in subject-specific expertise weaken academic depth and exam preparedness. Together, these workforce limitations reduce teaching effectiveness and restrict the sector’s ability to fully benefit from rising student enrollment and policy-driven expansion.
Infrastructure Gaps in Remote and Economically Disadvantaged Areas
Despite substantial public and private investments, many schools in remote and economically backward regions still lack basic infrastructure, including functional toilets, reliable drinking water, electricity, and adequate classroom space. These gaps directly affect student health, safety, and daily attendance, particularly among girls. Poor infrastructure also discourages teacher retention and community trust, limiting access to quality education for vulnerable groups and slowing overall education market growth.
Competitive Landscape:
The market exhibits a highly fragmented competitive landscape characterized by the dominant presence of government-operated institutions alongside a diverse ecosystem of private providers. Market dynamics are shaped by regulatory frameworks, including the Right to Education Act mandating reservation for economically weaker sections in private schools, state-level fee regulations, and affiliation requirements from education boards. Competition is intensifying as private school chains expand their footprint in metropolitan and tier-two cities, international board affiliates increase their presence, and technology-enabled education providers offer supplementary learning solutions. Strategic differentiation through curriculum innovation, infrastructure modernization, and technology integration is becoming increasingly important for market positioning across segments.
Recent Developments:
- January 2026: Historic UK grammar school Queen Elizabeth’s, founded in 1573, announced its entry into India with a new campus planned in Gurugram in partnership with GEDU Global Education. The school will offer an independent K–12 curriculum rooted in academic rigor, discipline, and holistic development, drawing on over 450 years of institutional legacy.
- January 2026: The Municipal Corporation of Delhi announced plans to establish ‘MCD Shri’ schools, aligned with PM Shri and CM Shri models, to promote academic excellence in civic schools. In the first phase, two schools will be set up in each MCD zone, with admissions focused on identifying and supporting meritorious students. The initiative aims to nurture academic, sports, and co-curricular talent while strengthening preparation for higher education and long-term student development.
India School Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Levels of Education Covered | Primary, Upper Primary, Secondary, Higher Secondary |
| Ownership Covered | Government, Local Body, Private Aided, Private Unaided |
| Board of Affiliation Covered | Central Board of Secondary Education, Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations, State Government Boards, Others |
| Fee Structure Covered | Low-Income, Medium-Income, High-Income |
| Region Covered | North India, West and Central India, South India, East India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India school market size was valued at USD 59.67 Billion in 2025.
The India school market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 9.79% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 138.33 Billion by 2034.
Primary holds the largest revenue share at 42% in 2025, driven by near-universal enrollment rates, government initiatives under foundational literacy programs, and compulsory elementary education provisions under the Right to Education Act.
Key factors driving the India school market include the rising demand for integrated residential education with international exposure. Parents prefer end-to-end schooling with boarding and global curricula. Reflecting this trend, in 2025, UK-based Bedford School announced its first Indian campus in Mohali, serving ages three to eighteen.
Major challenges include persistent urban-rural educational divide, teacher shortages and quality concerns in government schools, infrastructure gaps in remote and economically disadvantaged areas, and ensuring equitable access to quality education across diverse socioeconomic segments.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












