
India Two-Wheeler Loan Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Provider Type, Percentage Amount Sanctioned, Tenure, and Region, 2026-2034
India Two-Wheeler Loan Market Summary:
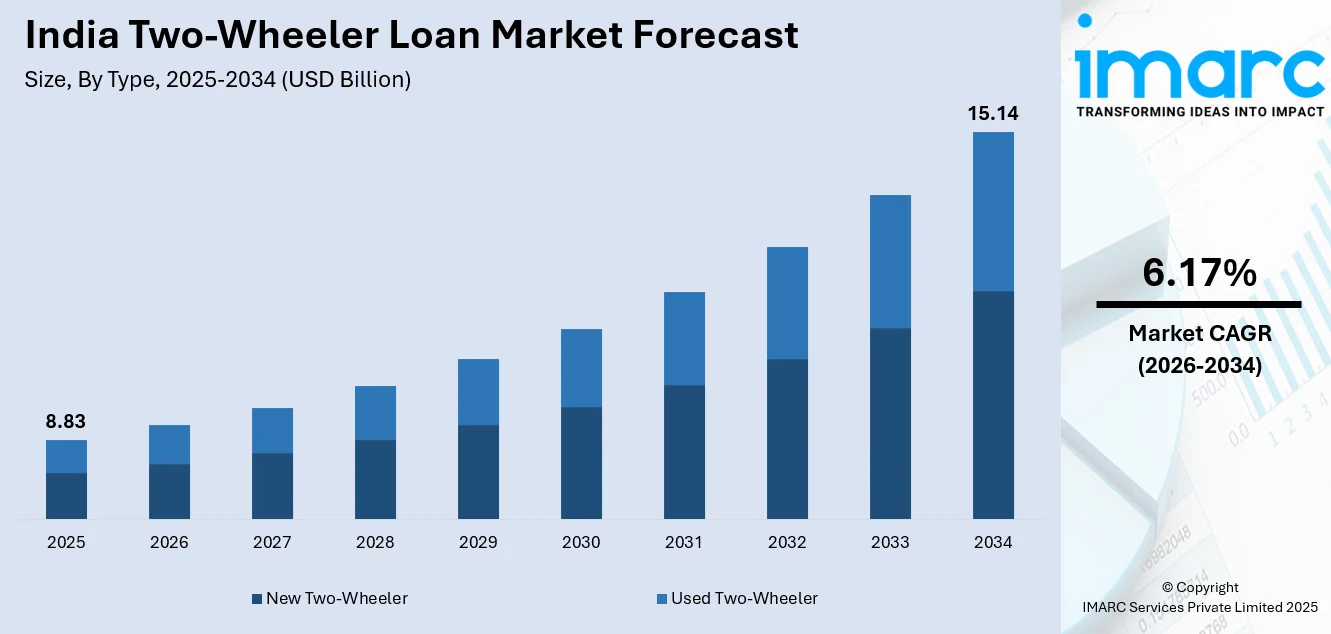
The India two-wheeler loan market size was valued at USD 8.83 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 15.14 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.17% from 2026-2034.
The India two-wheeler loan market is experiencing strong growth, supported by rapid urban development, a widening middle-class base, and a growing preference for cost-effective personal transportation. Lenders are increasingly adopting digital channels and flexible financing approaches to improve credit availability among consumers in semi-urban and rural areas. Collaboration with fintech firms and simplified loan approval processes are further enhancing accessibility, enabling a broader range of buyers to finance two-wheelers and supporting inclusive mobility across varied income groups.
Key Takeaways and Insights:
- By Type: New two-wheeler dominates the market with a share of 68% in 2025, driven by consumer preference for manufacturer warranties, modern safety features, and access to comprehensive financing packages offered by authorized dealerships.
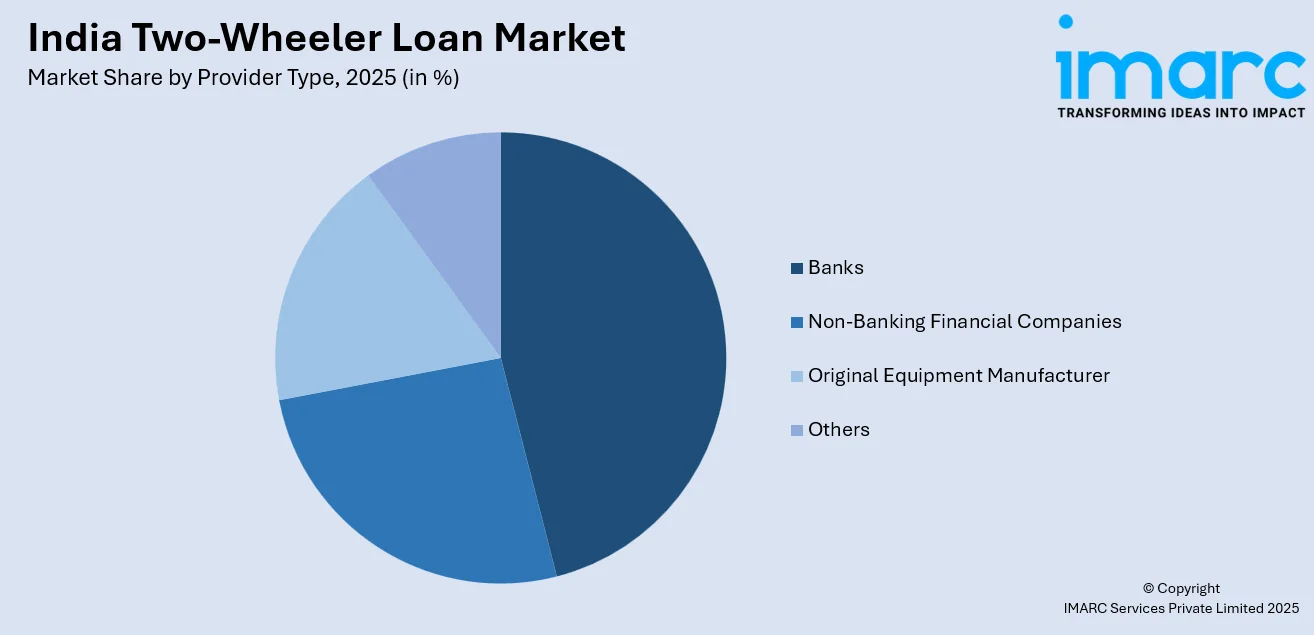
- By Provider Type: Banks lead the market with a share of 43% in 2025, attributed to their extensive branch networks, established consumer trust, competitive interest rates, and integration with digital banking platforms enabling seamless loan processing.
- By Percentage Amount Sanctioned: Less than 50% represents the largest segment with a market share of 56% in 2025, reflecting consumer preference for conservative borrowing approaches and lenders' risk mitigation strategies requiring substantial down payments.
- By Tenure: 3 Years lead the market with a share of 45% in 2025, representing an optimal balance between manageable monthly installments and total interest burden for middle-income borrowers.
- By Region: South India dominates with 33% market share in 2025, supported by rapid economic growth in metropolitan centers like Chennai, Bangalore, and Hyderabad, along with higher disposable incomes and tech-savvy consumer demographics.
- Key Players: The India two-wheeler loan market exhibits a moderately competitive landscape with established public and private sector banks competing alongside non-banking financial companies and emerging fintech platforms. Market participants differentiate through customized loan products, digital processing capabilities, and strategic partnerships with original equipment manufacturers.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
The India two-wheeler loan market continues to evolve with technological innovations transforming the lending landscape. Digital platforms are enabling instant loan approvals through artificial intelligence-driven credit assessments, while Account Aggregator systems facilitate rapid consent-based data sharing, allowing banks to underwrite informal sector workers. The integration of Aadhaar-linked authentication and e-KYC processes has significantly reduced documentation requirements and processing timelines. For instance, in January 2024, Suzuki Motorcycle India Pvt Ltd partnered with SMFG India Credit Co Ltd to provide comprehensive financing solutions for its two-wheeler customers, exemplifying the trend of manufacturer-financier collaborations driving market accessibility. Financial institutions are increasingly targeting Tier II and Tier III cities where two-wheeler ownership is expanding due to limited public transportation infrastructure and improving road connectivity.
India Two-Wheeler Loan Market Trends:
Digital Lending Platform Proliferation
The rapid adoption of digital lending platforms is transforming the two-wheeler loan ecosystem by enabling paperless applications, instant credit decisions, and doorstep disbursement services. Fintech companies and traditional lenders are utilizing artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics to evaluate borrower creditworthiness within minutes, reducing reliance on conventional assessment methods. The partnership between digital lenders and e-commerce platforms allows consumers to apply for financing while purchasing vehicles online, significantly simplifying the acquisition process. These technological innovations are expanding credit access to first-time buyers, gig economy participants, and individuals with limited formal credit histories. For instance, in October 2025, Home Credit India expanded its consumer finance offerings by entering the two-wheeler loan segment. Timed with the festive period, this move is designed to improve access to cost-effective mobility options for households and individual buyers across the country, strengthening the company’s presence in vehicle financing and supporting broader two-wheeler ownership.
Electric Two-Wheeler Financing Expansion
Rising interest in electric two-wheelers is opening new avenues for specialized financing, supported by increasing environmental awareness and the appeal of lower running costs. Banks and non-banking financial companies are rolling out dedicated electric vehicle loan products with flexible structures, attractive pricing, and longer repayment periods to encourage adoption. Supportive policy measures and incentive programs are further improving affordability, making financed electric two-wheelers more accessible to a wider consumer base. Together, these factors are strengthening the role of tailored financing solutions in accelerating electric two-wheeler uptake. For instance, in September 2025, Ecofy Finance Pvt Ltd announced a strategic collaboration with electric two-wheeler manufacturer Motovolt Mobility to provide comprehensive financing solutions for both individual buyers and institutional customers. As part of the agreement, the green-focused NBFC will serve as the principal lending partner for Motovolt’s full electric two-wheeler portfolio, including its recently introduced MVS7 e-scooter.
Rural and Semi-Urban Market Penetration
Financial institutions are increasingly focusing on rural and semi-urban regions, where rising two-wheeler ownership is driven by limited public transport options and gradually improving income conditions. To attract borrowers in these areas, lenders are easing documentation norms, offering flexible eligibility criteria, and providing higher loan coverage for customers without formal income records. The use of digital platforms, mobile-based applications, and collaborations with local dealerships is further improving loan reach, enabling smoother credit access and supporting two-wheeler adoption across underserved and emerging markets.
Market Outlook 2026-2034:
The India two-wheeler loan market is expected to maintain steady expansion, supported by ongoing urban growth, increasing aspirational spending among younger consumers, and supportive policies aimed at widening financial inclusion. Improvements in electric mobility ecosystems, such as better charging access and alternative energy solutions, are likely to encourage greater financing uptake for electric two-wheelers. In addition, evolving ownership models, including leasing and subscription-based options, are set to broaden financing choices and reshape the overall lending landscape for two-wheelers. The market generated a revenue of USD 8.83 Billion in 2025 and is projected to reach a revenue of USD 15.14 Billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 6.17% from 2026-2034.
India Two-Wheeler Loan Market Report Segmentation:
| Segment Category | Leading Segment | Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Type | New Two-Wheeler | 68% |
| Provider Type | Banks | 43% |
| Percentage Amount Sanctioned | Less Than 50% | 56% |
| Tenure | 3 Years | 45% |
| Region | South India | 33% |
Type Insights:
- New Two-Wheeler
- Used Two-Wheeler
The new two-wheeler dominates with a market share of 68% of the total India two-wheeler loan market in 2025.
The new two-wheeler financing segment maintains a commanding market presence driven by consumer preference for manufacturer warranties, access to the latest technology features, and comprehensive after-sales support networks. Financial institutions offer preferential interest rates for new vehicle purchases, given the lower risk profiles associated with factory-backed products. The availability of zero down payment schemes and bundled insurance packages through dealer-financier partnerships enhances the value proposition for consumers seeking hassle-free ownership experiences.
Original equipment manufacturers are increasingly working with banks and non-banking financial companies to offer embedded financing options that simplify the vehicle purchase process. These arrangements enable customers to access loans directly at dealerships, often receiving quick eligibility decisions at the point of sale. The adoption of digital identity checks and real-time credit evaluation tools has shortened approval and disbursement timelines, enhancing buyer convenience. As a result, dealerships across urban, semi-urban, and rural areas are witnessing improved conversion rates and smoother financing experiences for two-wheeler buyers. For instance, in September 2025, L&T Finance introduced three new two-wheeler loan schemes in time for the festive season, as reported in its exchange filings. The non-banking financial company stated that these initiatives aim to simplify vehicle ownership and provide customers with more accessible financing options during the peak demand period.
Provider Type Insights:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Banks
- Non-Banking Financial Companies
- Original Equipment Manufacturer
- Others
Banks leads with a share of 43% of the total India two-wheeler loan market in 2025.
Banks maintain market leadership through established consumer trust, extensive branch infrastructure, and competitive interest rate offerings typically ranging from nine to fifteen percent annually. Public sector banks leverage their widespread presence in semi-urban and rural territories to serve agricultural communities and informal sector workers seeking vehicle financing. The integration of digital banking platforms enables existing account holders to access pre-approved loan offers with minimal documentation requirements and expedited processing timelines.
Private sector banks are enhancing their offerings with technology-driven services such as mobile app-based loan applications, instant eligibility assessments, and doorstep document collection. They provide specialized two-wheeler financing products with flexible repayment tenures, making loans more accessible to a wider range of customers. Collaborations between banks and authorized dealerships streamline the purchase process, allowing buyers to secure financing directly at the point of sale. These innovations improve convenience, speed up loan approvals, and strengthen customer engagement during critical purchase decision moments.
Percentage Amount Sanctioned Insights:
- Less Than 50%
- More Than 50%
Less than 50% exhibits a clear dominance with a 56% share of the total India two-wheeler loan market in 2025.
The prevalence of conservative loan sanctioning reflects both lender risk mitigation strategies and borrower preferences for maintaining lower debt burdens. Financial institutions typically require down payments of twenty to forty percent for standard loan applications, ensuring borrowers demonstrate financial commitment and reducing default probabilities. This approach aligns with Reserve Bank of India guidelines promoting responsible lending practices while protecting consumers from over-indebtedness situations that could strain household finances.
Higher down payments allow borrowers to benefit from lower interest rates and reduced processing charges, encouraging more cautious borrowing practices. Meanwhile, non-banking financial companies and fintech lenders are offering elevated loan-to-value ratios, sometimes covering most of the vehicle cost, to attract cost-conscious buyers. These higher-risk products come with correspondingly higher interest rates. Overall, the structure of financing options highlights the pragmatic mindset of Indian consumers, who carefully balance affordability with long-term financial stability when acquiring vehicles.
Tenure Insights:
- Less Than 3 Years
- 3 Years
- More Than 3 Years
The 3 years represent the largest share with 45% of the total India two-wheeler loan market in 2025.
The three-year tenure represents an optimal equilibrium between monthly installment affordability and cumulative interest expenditure for middle-income borrowers. This duration aligns with typical two-wheeler ownership cycles and allows borrowers to build equity in their vehicles while maintaining manageable monthly outflows. Financial institutions frequently promote thirty-six-month terms as standard offerings, given the balanced risk-return profiles these products generate for their lending portfolios.
Shorter tenures below three years appeal to borrowers seeking rapid debt elimination and minimized total interest payments, though higher monthly installments may strain household budgets. Extended tenure options beyond three years are gaining traction among entry-level buyers prioritizing reduced monthly financial commitments, with some NBFCs offering repayment periods extending to five or seven years. Customization of tenure options based on individual financial circumstances represents a key competitive differentiator among market participants.
Regional Insights:
- North India
- South India
- East India
- West India
The South India region exhibits a clear dominance with a 33% of the total India two-wheeler loan market in 2025.
South India's market leadership stems from concentrated economic activity in metropolitan centers including Chennai, Bangalore, and Hyderabad, where the technology sector employment generates substantial disposable incomes. The region is home to major two-wheeler production hubs such as TVS Motor Company, which has a head office in Chennai, developing strong dealer networks and financing systems. An increase in literacy and adoption of technology helps in penetrating the digital lending platforms, which ensure the smooth processing of loans, and through which more people can access credit in both the urban and semi-urban areas.
Tamil Nadu's automotive manufacturing ecosystem attracts specialized financing providers targeting the regional consumer base with customized loan products. The favorable startup culture and young practitioner population in Karnataka are the factors that encourage the high demand for two-wheeler segments that are financed by innovative lending patterns. The tendency of the South Indian consumer to have scooters, which is encouraged by the fact that there is an improved road system and women have to work in the country, opens the possibility of various financing options in terms of the category and the price of the vehicle.
Market Dynamics:
Growth Drivers:
Why is the India Two-Wheeler Loan Market Growing?
Rising Urbanization and Middle-Class Expansion
India's accelerating urbanization trajectory is propelling demand for affordable personal mobility solutions as millions migrate to metropolitan and semi-urban centers seeking employment and educational opportunities. The expanding middle-class population segment possesses growing aspirational consumption patterns but may lack immediate liquidity for outright vehicle purchases, creating substantial financing opportunities. Congested public transportation infrastructure and increasing commute distances make two-wheeler ownership essential for daily mobility. Banks and NBFCs have simplified loan accessibility through reduced documentation requirements, competitive interest rates, and flexible repayment structures that accommodate varying income profiles. Low down payment schemes and attractive EMI options influence consumers to leverage financing rather than depleting savings, democratizing vehicle ownership across socioeconomic segments.
Digital Transformation and Fintech Innovation
The rapid digitalization of financial services is transforming the two-wheeler loan market by introducing technology-driven processes that improve convenience and accessibility. Fintech firms and traditional lenders are leveraging artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics to assess creditworthiness instantly, significantly shortening approval timelines. Innovations such as digital wallets, biometric authentication, and secure transaction technologies have enhanced transparency and trust in loan disbursements. Paperless documentation, integrated financing platforms, and doorstep service models are removing traditional barriers, enabling first-time buyers and gig economy workers to obtain affordable credit regardless of formal employment or income documentation.
Government Support for Electric Mobility
Government initiatives promoting electric vehicle adoption are creating specialized financing opportunities within the two-wheeler loan market. For instance, the PM E-DRIVE scheme launched in October 2024 with an outlay of Rs 10,900 crore provides demand incentives of Rs 5,000 per kilowatt-hour for electric two-wheelers, effectively reducing upfront costs for financed purchases. The NITI Aayog has recommended that EV lending by banks and NBFCs should qualify under Reserve Bank of India priority sector lending guidelines, potentially unlocking significant credit flows. State-level policies offering additional subsidies, road tax exemptions, and registration fee waivers compound the affordability advantages. Financial institutions are responding with tailored loan products featuring lower interest rates, extended tenures, and reduced payment requirements specifically designed for electric two-wheeler acquisition, accelerating the transition toward sustainable mobility.
Market Restraints:
What Challenges the India Two-Wheeler Loan Market is Facing?
Stringent Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Financial institutions face complex regulatory frameworks governing lending practices, interest rate structures, and borrower eligibility criteria established by the Reserve Bank of India. Compliance requirements, including customer verification protocols, credit scoring standards, and documentation mandates, increase operational complexity and processing timelines. Interest rate caps and lending amount restrictions can limit competitive positioning and product innovation, particularly affecting NBFCs serving higher-risk customer segments in rural and semi-urban markets.
Credit Assessment Challenges for Informal Workers
A significant portion of India's workforce operates within the informal economy, lacking traditional income documentation and formal credit histories required by conventional lending assessments. Despite advancements in alternative data analytics and artificial intelligence-driven credit scoring, accurately evaluating repayment capacity for self-employed individuals, agricultural workers, and gig economy participants remains challenging. Higher perceived risk profiles result in elevated interest rates or loan rejections, limiting market penetration among populations with genuine financing requirements.
Interest Rate Volatility and Economic Sensitivity
Fluctuations in policy interest rates and macroeconomic conditions directly impact borrowing costs and consumer demand for financed vehicle purchases. Rising inflation and monetary policy tightening can elevate lending rates, reducing affordability and suppressing loan origination volumes. Economic uncertainties affecting employment stability and household income levels increase default probabilities, compelling lenders to adopt conservative underwriting standards that restrict credit availability during challenging periods.
Competitive Landscape:
The India two-wheeler loan market features a moderately fragmented competitive structure with public sector banks, private banks, non-banking financial companies, and emerging fintech platforms competing across customer segments and geographic territories. Established players differentiate through extensive branch networks, brand trust, and integrated banking relationships, while NBFCs leverage operational flexibility, faster processing capabilities, and willingness to serve underbanked populations. Strategic partnerships between financial institutions and original equipment manufacturers create captive financing channels that capture customers at the point of sale. Digital-first platforms are disrupting traditional distribution models through technology-enabled underwriting, paperless processes, and embedded financing within e-commerce ecosystems. Competition intensifies around interest rate offerings, tenure flexibility, documentation simplicity, and disbursement speed as market participants seek to expand portfolio share amid growing demand.
Recent Developments:
- September 2024: OLX India partnered with IDFC FIRST Bank to launch an end-to-end financing solution for pre-owned vehicles, enabling convenient loan access directly on the OLX platform to stimulate used two-wheeler ownership through affordable financing options.
- April 2024: CASHe launched 'CASHe Green', providing customized financial options for electric two-wheeler purchases in India, offering loans up to INR 2 lakh with interest rates starting below one percent per month to promote electric vehicle adoption.
India Two-Wheeler Loan Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical Trends and Market Outlook, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Future Market Assessment:
|
| Types Covered | New Two-Wheeler, Used Two-Wheeler |
| Provider Types Covered | Banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies, Original Equipment Manufacturer, Others |
| Percentage Amounts Sanctioned Covered | Less Than 50%, More Than 50% |
| Tenures Covered | Less Than 3 Years, 3 Years, More Than 3 Years |
| Regions Covered | North India, South India, East India, West India |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The India two-wheeler loan market size was valued at USD 8.83 Billion in 2025.
The India two-wheeler loan market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.17% from 2026-2034 to reach USD 15.14 Billion by 2034.
New two-wheeler dominated the market with a 68% share in 2025, driven by consumer preference for manufacturer warranties, latest technology features, and comprehensive after-sales support networks provided by authorized dealerships.
Key factors driving the India two-wheeler loan market include rising urbanization and middle-class expansion, digital transformation enabling instant loan approvals, government incentives for electric two-wheelers, flexible financing options, and expanding financial inclusion in semi-urban and rural areas.
Major challenges include stringent regulatory compliance requirements, credit assessment difficulties for informal sector workers lacking traditional income documentation, interest rate volatility affecting borrowing costs, and economic uncertainties impacting household financial stability and loan repayment capacities.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












