
Indian Ammonia Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Physical Form, End-Use, and States, 2025-2033
Indian Ammonia Market Size and Share:
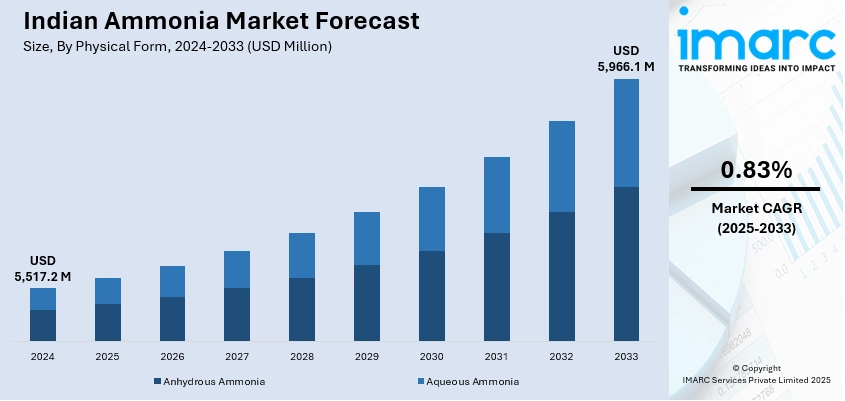
The Indian ammonia market size reached USD 5,517.2 Million in 2024. The market is expected to reach USD 5,966.1 Million by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 0.83% during 2025-2033. The market growth is attributed to the rising agricultural demand for fertilizers, government support for agricultural growth, increasing industrial applications, expansion of urea production, and a growing need for sustainable farming practices, alongside advancements in technology, favorable trade policies, and the growing population, which fuels food demand.
Market Insights:
- Based on states, the market is divided into Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Rajasthan.
- On the basis of physical form, the market is segmented into anhydrous ammonia and aqueous ammonia.
- Based on the end-use, the market is categorized as urea, ammonium phosphate fertilizers, industrial, and others.
Market Size and Forecast:
- 2024 Market Size: USD 5,517.2 Million
- 2033 Projected Market Size: USD 5,966.1 Million
- CAGR (2025-2033): 0.83%
Ammonia is an inorganic, colorless compound with an unpleasant pungent odor. It is naturally sourced from air, soil, water, plants and animals. The gaseous form of ammonia is compressed into liquid form, which dissolves in water to form ammonium hydroxide and is transported in steel cylinders. Ammonia is commonly used in the manufacturing of ammonium nitrate fertilizers, which discharge nitrogen in the soil to promote growth in farm crops and plants. It is also used in the production of plastics, textiles, explosives, coloring agents, household cleaning products and pesticides. Ammonia can absorb heat from its surroundings and can filter and purify impurities from liquid mediums. As a result, it is widely used as a refrigerant in heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems and as a purifying agent in water treatment plants.
To get more information on this market, Request Sample
Significant growth in the agriculture industry across India is one of the key factors creating a positive Indian ammonia market outlook. With the rising population and decreasing arable lands for crop cultivation, there is an increasing demand for efficient nitrogen-rich ammonia-based fertilizers and agrochemicals to ensure optimal food production for the masses. Moreover, the widespread product adoption for the manufacturing of detergents and cleaning products is providing a thrust to the market growth. Ammonia is highly effective in breaking down household grime and removing stains of vegetable oils, fats, cooking grease and wine from tubs, sinks, toilets, countertops and tiles. It also evaporates quickly, thereby facilitating in cleaning glass without leaving any residual streak marks. In line with this, the increasing demand for ammonium nitrate for mining and explosive applications is also contributing to the growth of the market. Other factors, including various product innovations, such as the development of green ammonia through sustainable technologies, are anticipated to drive the market toward growth.
Indian Ammonia Market Trends:
Regional Industrial Integration through State-Level Synergies
The market is experiencing increased regional alignment through state-specific industrial synergies, which is significantly influencing both production and distribution dynamics. Gujarat, a hub for petrochemicals and fertilizers, plays a crucial role in ammonia value chains through its strategic chemical corridors and Special Economic Zones. These corridors facilitate integrated manufacturing clusters, ensuring proximity to feedstock suppliers, ports, and ancillary chemical industries, thereby improving ammonia production efficiency and reducing logistical costs. Meanwhile, Punjab leverages its extensive canal-based irrigation network to streamline fertilizer distribution, including ammonia-based urea. This canal infrastructure enables cost-effective movement of fertilizers from centralized storage facilities to agricultural zones, enhancing last-mile delivery and minimizing nutrient losses. Moreover, the Punjab State Farmers' Commission actively supports ammonia nitrate formulations in areas practicing precision agriculture. These state-led models foster localized ammonia applications, while also driving inter-state collaborations for infrastructure sharing and demand aggregation. Such synergies position individual states as critical nodes in the broader national ammonia framework.
Advancements in Ammonia Production Technologies
Technological innovation is propelling Indian ammonia market growth, with a focus on reducing emissions and enhancing efficiency. Electrochemical synthesis, a novel production route gaining traction, allows ammonia to be synthesized directly from nitrogen and water using renewable electricity under ambient conditions. Moreover, the country's research institutions and start-ups are piloting modular systems that decouple ammonia production from fossil fuels, presenting a viable pathway toward distributed green ammonia units. In addition to this, retrofitting conventional Haber-Bosch plants with carbon capture and storage (CCS) systems is enabling the transition to blue ammonia. Also, several public-private partnerships are exploring CO₂ sequestration in depleted oil fields or mineralization in saline aquifers, especially in industrial zones of Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh. These retrofits aim to reduce carbon intensity without decommissioning legacy infrastructure. Additionally, advanced process analytics and digital twin technologies are being integrated to optimize plant operations. Together, these innovations are redefining ammonia production paradigms, aligning them with India's decarbonization commitments and net-zero industrial strategies.
Strengthening the Water-Agriculture Nexus through Ammonia Applications
As per the Indian ammonia market forecast, water-agriculture nexus is set to become important in the market, particularly through the integration of ammonia-based compounds into precision irrigation and water treatment systems. Ammonia is utilized in drip irrigation setups, especially in arid regions such as Rajasthan and parts of Karnataka, where efficient nutrient delivery is critical. These systems incorporate ammonium nitrate or ammonium phosphate in fertigation units, improving nitrogen use efficiency while conserving water. The controlled application also minimizes runoff and leaching, aligning with sustainable agriculture protocols. Additionally, ammonia plays a crucial role in municipal and industrial water treatment processes as a reagent in chloramination, which is gaining preference over traditional chlorination due to its stability and reduced disinfection byproducts. States like Tamil Nadu and Telangana are adopting integrated models where treated wastewater is reused for agriculture, creating a circular ecosystem between water purification and ammonia-fertilizer usage. This nexus enhances resource optimization while supporting India's broader goals of sustainable rural development and climate-resilient agriculture.
Growth Drivers of the Indian Ammonia Market:
The market is driven by the country’s growing demand for nitrogen-based fertilizers, especially urea, to support intensive agricultural practices. Furthermore, government subsidies and initiatives like the Nutrient Based Subsidy (NBS) scheme enhance the affordability and accessibility of ammonia derivatives across rural economies. This, in turn, is augmenting the Indian ammonia market share. Additionally, India’s policy-energy landscape is fostering significant cross-sectoral linkages that are accelerating ammonia market development, especially through green and transitional energy initiatives. Under the National Hydrogen Mission, substantial subsidies are being directed toward the production of green ammonia, which uses renewable electricity to split water for hydrogen before synthesizing it into ammonia. This initiative aims to reduce dependency on imported fertilizers and fossil fuels while promoting self-reliance in clean energy. In parallel, the FAME-III (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) scheme introduces incentives for innovative EV thermal management systems, including those that utilize ammonia-based refrigerants in battery cooling mechanisms. These systems offer higher thermal conductivity and lower environmental impact compared to conventional coolants. In addition to this, rapid industrialization has led to increased ammonia consumption in sectors such as textiles, refrigeration, mining, and water treatment. Besides that, the push toward self-reliance in fertilizers under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative is encouraging domestic production, while infrastructure upgrades like new ammonia pipelines and integrated chemical parks reduce logistical constraints.
Opportunities in the Indian Ammonia Market:
According to the Indian ammonia market report, the market presents expansive opportunities across multiple verticals, driven by evolving end-use applications, technological innovation, and policy support for clean energy. The shift toward green ammonia production using renewable electricity and water electrolysis offers considerable investment potential, particularly as India expands its solar and wind capacities. Export prospects are also growing, with global demand rising for low-carbon ammonia as a hydrogen carrier and maritime fuel, positioning India as a future supply hub. In agriculture, there is significant scope for precision farming solutions using ammonia-based fertigation in drip and sprinkler systems, improving nutrient efficiency and water conservation. Industrial opportunities are expanding in refrigeration, power generation, and wastewater treatment, where ammonia-based formulations offer environmental and operational advantages. Furthermore, state-level industrial clusters, including chemical corridors in Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, provide a foundation for public-private partnerships and innovation. These opportunities collectively enhance India’s potential to become a leading player in the global ammonia economy.
Challenges in the Indian Ammonia Market:
Despite promising growth prospects, as per the Indian ammonia market analysis, the market faces several challenges that may constrain its trajectory. A major constraint lies in the sector's dependence on imported natural gas, which exposes ammonia production to price volatility and supply disruptions. The capital-intensive nature of setting up ammonia synthesis plants, especially those utilizing green technologies, poses financial risks, further complicated by limited access to long-term financing for decarbonization projects. Additionally, regulatory inconsistencies between state and central authorities on environmental clearances, land acquisition, and infrastructure provisioning can delay project timelines. Technological gaps persist in scaling up electrochemical synthesis and carbon capture systems at commercial levels. Moreover, inadequate storage and transportation infrastructure, particularly for handling hazardous ammonia, creates bottlenecks in distribution. In agriculture, inefficient application practices contribute to nitrogen losses, reducing overall efficacy. Also, awareness and capacity-building deficits among farmers and industries regarding sustainable ammonia use present a barrier to demand optimization and environmentally responsible utilization.
Indian Ammonia Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each sub-segment of the Indian ammonia market report, along with forecasts at the country and state level from 2025-2033. Our report has categorized the market based on physical form and end-use.
Breakup by Physical Form:
- Anhydrous Ammonia
- Aqueous Ammonia
Breakup by End-Use:
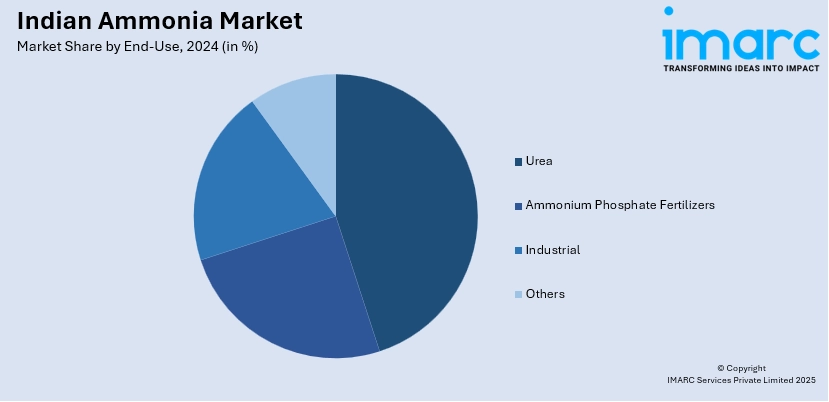
- Urea
- Ammonium Phosphate Fertilizers
- Industrial
- Others
Breakup by States:
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- Rajasthan
- Others
Competitive Landscape:
The competitive landscape of the industry has also been examined with some of the key player being Chambal Fertilizers and Chemicals Ltd., GNFC (Gujarat Narmada Valley Fertilizers and Chemicals), IFFCO (Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative Limited), KRIBHCO (Krishak Bharati Cooperative Limited), NFCL (Nagarjuna Fertilizers and Chemicals Limited), RCFL (Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd) and Southern Petrochemicals Industries Limited (SPIC).
Latest News and Developments:
- June 2025: India-headquartered hydrogen company Hygenco Green Energies inaugurated a green ammonia production facility at Gopalpur Industrial Park in Odisha, with plans to scale up to an annual capacity of 1.1 Million Tonnes. The project follows the company’s earlier commissioning of a commercial-scale green hydrogen plant in Hisar, reflecting its strategic commitment to expanding clean energy infrastructure. For this initiative, Hygenco has partnered with Denmark-based Topsoe as the technology licensor, integrating advanced green ammonia synthesis technologies to support India’s decarbonization goals.
- June 2025: AVTL, a joint venture between Aegis Logistics Limited and Vopak India, has unveiled plans to develop India’s first standalone ammonia storage terminal. The facility, a brownfield project located in Pipavav, Gujarat, will have an estimated storage capacity of 36,000 metric tonnes. The terminal is slated for commissioning by the end of 2026.Fully funded by AVTL at an estimated investment of EUR 53 Million (INR 5.3 Billion), the terminal is designed as a third‑party, open‑access facility to support ammonia imports for India’s robust fertilizer sector.
- January 2025: The Andhra Pradesh cabinet approved a suite of strategic renewable energy projects, including a 1 Million Tonne per annum green ammonia manufacturing facility in Kakinada developed by AM Green Ammonia, under an INR 2,723 Crore investment package aimed at transforming the Amaravati capital region. This development underscores Andhra Pradesh’s aggressive push toward clean energy, with significant focus on green ammonia infrastructure as key pillars of its evolving renewable energy strategy.
- January 2025: Avaada Group has entered into a strategic partnership with Casale, a Swiss leader in ammonia technology, to establish India’s largest green ammonia production facility in Gopalpur, Odisha. The plant will have a planned production capacity of 1,500 tonnes per day and will operate entirely on renewable energy sources. It will incorporate Casale’s cutting-edge technologies to enable a fully carbon-neutral production process. This collaboration represents a significant advancement in Casale’s global green ammonia initiatives and is expected to expand the ammonia market size in India.
Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2024 |
| Historical Period | 2019-2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2033 |
| Units | Million USD, Million Tons |
| Segment Coverage | Physical Form, End-Use, State |
| States Covered | Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Others |
| Companies Covered | Chambal Fertilizers and Chemicals Ltd., GNFC (Gujarat Narmada Valley Fertilizers and Chemicals), IFFCO (Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative Limited), KRIBHCO (Krishak Bharati Cooperative Limited), NFCL (Nagarjuna Fertilizers and Chemicals Limited), RCFL (Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd) and Southern Petrochemicals Industries Limited (SPIC) |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The ammonia market size was observed to be approximately USD 5,517.2 Million in 2024. The rising demand for nitrogen-rich, ammonia-based fertilizers and agrochemicals to ensure optimal food production, on account of the increasing population levels, is primarily driving the India ammonia market. Additionally, the emerging adoption of ammonia in manufacturing detergents and cleaning products is also propelling the market growth. Moreover, the rising utilization of ammonia in breaking down household grime and eliminating stains of vegetable oils, fats, cooking grease, etc., from tubs, sinks, toilets, countertops, and tiles is further augmenting the regional market. Besides this, the growing demand for ammonium nitrate for mining and explosive applications is acting as a significant growth-inducing factor. Additionally, the continuous development of green ammonia through sustainable technologies for reducing carbon emissions is expected to drive the India market for ammonia.
The rising utilization of ammonia for manufacturing numerous cleaning products on account of its high pH value, along with the ongoing development of green ammonia through sustainable technologies, is primarily driving the Indian ammonia market.
The sudden outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic had led to the implementation of stringent lockdown regulations across the nation, resulting in the temporary closure of numerous end-use industries for ammonia.
Based on the physical form, the Indian ammonia market has been segmented into anhydrous ammonia and aqueous ammonia. Currently, anhydrous ammonia holds the majority of the total market share.
Based on the end-use, the Indian ammonia market can be divided into urea, ammonium phosphate fertilizers, industrial, and others. Among these, urea exhibits a clear dominance in the market.
On a regional level, the market has been classified into Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, and others, where Gujarat currently dominates the Indian ammonia market.
Some of the major players in the Indian ammonia market include Chambal Fertilizers and Chemicals Ltd., GNFC (Gujarat Narmada Valley Fertilizers and Chemicals), IFFCO (Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative Limited), KRIBHCO (Krishak Bharati Cooperative Limited), NFCL (Nagarjuna Fertilizers and Chemicals Limited), RCFL (Rashtriya Chemicals and Fertilizers Ltd), and Southern Petrochemicals Industries Limited (SPIC).
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












