
Indonesia Telecom Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Services and Region, 2026-2034
Indonesia Telecom Market Summary:
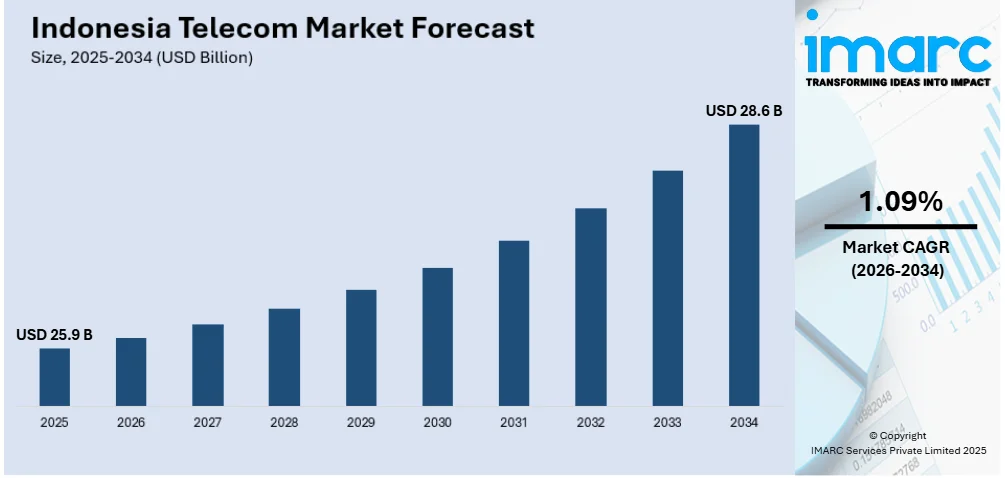
The Indonesia telecom market size was valued at USD 25.9 Billion in 2025. Looking forward, the market is projected to reach USD 28.6 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 1.09% during 2026-2034. The market's growth is attributed to rising mobile internet penetration, increased demand for high-speed connectivity, government-backed infrastructure initiatives, and expanding digital services such as fintech, OTT platforms, and e-commerce.
Market Insights:
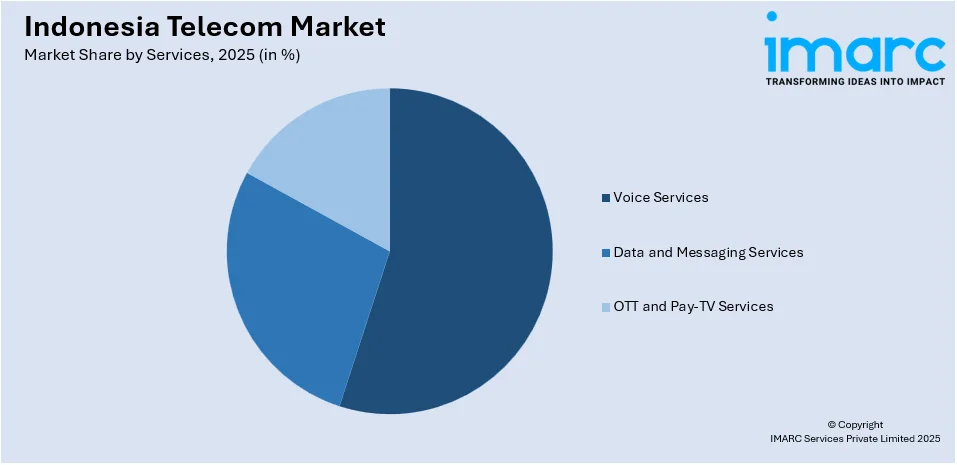
- Services include voice (wired and wireless), data and messaging, and OTT and Pay-TV.
- 4G and early 5G rollout, along with fiber investments, are reshaping network infrastructure.
- Java remains a focal point for telecom development, with high urban demand and dense coverage.
- Sumatra, Sulawesi, and Kalimantan present growth opportunities driven by expanding mobile access.
Market Size & Forecast:
- 2025 Market Size: USD 25.9 Billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 28.6 Billion
- CAGR (2026–2034): 1.09%
The market is primarily driven by escalating mobile internet penetration across the country, fueled by affordable smartphones and competitive data plans. With numerous internet users, demand for high-speed connectivity is accelerating, particularly in urban areas, pushing operators to expand 4G and 5G networks. In early 2025, Indonesia accounted for 212 million internet users, or 74.6% of the population, with 143 million individuals (50.2% of the population) active on social media. Mobile connections hit 356 million, surpassing the nation's overall population, underscoring the rapidly developing digital landscape. These figures underscore the mounting possibilities for telecommunications and digital services operators to ride Indonesia's emerging online space. Government initiatives such as Making Indonesia 4.0 and the Palapa Ring project further accelerate digital infrastructure development. Additionally, the growth of digital services, including e-commerce, fintech, and OTT platforms, creates sustained demand for reliable telecom services. Operators are also investing in fiber-optic networks to cater to enterprises and SMEs adopting cloud and IoT solutions.
To get more information on this market Request Sample
In addition, the country’s young, tech-savvy population, driving the consumption of data-heavy applications, is propelling the Indonesia telecom market share. Regulatory support, including spectrum reallocation and simplified licensing, encourages market competition and innovation. The shift from voice to data-centric services compels telcos to adopt dynamic pricing and bundling strategies. Rural connectivity remains a growth opportunity, with satellite and fixed-wireless solutions bridging gaps. Indonesia's telecommunications tower industry is still developing, with major players such as Mitratel and Protelindo expanding their reach through acquisitions, as seen in the recent purchase of 803 towers by Mitratel for USD 112 Million. A key focus is rural coverage, as seen with Mitratel's spending of USD 69.5 Million on rural towers and the expansion of Protelindo's fiber network to 170,000 kilometers. Despite significant efforts at consolidation, Indonesia's telecommunications industry continues to face challenges in adequately serving the country's far-reaching and diverse networks. Furthermore, partnerships between telcos and tech firms enhance service ecosystems. Rising foreign investment in digital infrastructure and increasing smartphone affordability ensure sustained market expansion despite economic fluctuations.
Indonesia Telecom Market Trends:
Rapid Growth in Mobile Penetration and Smartphone Adoption
Indonesia's telecom market is being significantly driven by the rise in mobile penetration, largely fueled by the widespread adoption of smartphones and mobile devices. In 2023, Indonesia recorded 352 million mobile cellular subscriptions, reflecting a substantial increase in mobile connectivity. The rise in mobile usage is complemented by the rapid expansion of 4G networks, which have enhanced connectivity across the archipelago. As mobile internet access becomes increasingly accessible, approximately 69% of Indonesia's population had internet access in 2023. This broad digital adoption is propelling Indonesia telecom market demand and encouraging operators to improve their infrastructure. The ongoing shift towards mobile-first digital solutions in sectors such as banking, e-commerce, and education further supports this growth trend, driving up the need for stronger network capabilities to accommodate growing data traffic.
Government-Led Push for Digital Transformation and Rural Connectivity
The Indonesian government’s efforts to strengthen digital infrastructure are playing a pivotal role in shaping the telecom market. One of the major initiatives involves improving rural connectivity, with the government aiming to deliver 4G internet to every village by 2025. This ambitious goal is being realized through the construction of new data transmission and reception stations across 4,200 villages, along with the upgrading of existing stations in 1,209 villages. As of 2023, the Ministry of Communications and Informatics has been working tirelessly to bridge the digital divide and extend telecom services to underserved rural areas. By enhancing internet access in these regions, the government is not only expanding market reach but also contributing to a more equitable and sustainable telecom landscape. These developments are creating a positive Indonesia telecom market outlook, as rural consumers increasingly become part of the digital economy.
Digital Services, IoT Adoption, and the Changing Telecom Landscape
Indonesia's telecom market is also experiencing growth due to the increasing demand for digital services and the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. The adoption of IoT across sectors including agriculture, healthcare, and manufacturing is opening up new opportunities for telecom operators to provide the necessary infrastructure to support these technologies. As industries integrate IoT solutions, they require a robust telecom network capable of handling high volumes of data traffic and ensuring seamless connectivity. This trend is being fuelled by the rise in online transactions, social media use, and remote work, with Indonesia’s mobile data traffic per user expected to double to 25 GB per month by 2028. Telecom operators are therefore investing in next-generation networks and infrastructure to meet the rising demand for digital connectivity. With IoT solutions becoming integral to industries, telecom companies are tapping into this market potential by offering specialized services designed to support IoT growth, positioning themselves for long-term success in a changing digital economy.
Indonesia Telecom Industry Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the Indonesia telecom market, along with forecasts at the regional and country/country and regional levels from 2026-2034. The market has been categorized based on services.
Analysis by Services:
Access the comprehensive market breakdown Request Sample
- Voice Services
- Wired
- Wireless
- Data and Messaging Services
- OTT and Pay-TV Services
Voice services remain a foundational segment in Indonesia’s telecom market, though growth has slowed due to the shift toward data-driven communication. Traditional voice revenue is declining as over-the-top (OTT) apps such as WhatsApp and Zoom displace conventional calls, yet prepaid voice bundles remain popular in rural areas with limited internet access. Telcos are countering this trend by integrating voice into unlimited data plans, ensuring retention among price-sensitive users. The enterprise segment still relies on voice for customer service and internal communications, sustaining demand for VoIP and cloud-based solutions. Regulatory measures, such as lower interconnection rates, aim to stabilize the segment, while 4G VoLTE (Voice over LTE) adoption improves call quality. Despite challenges, voice services contribute steady revenue, particularly among older demographics and businesses, ensuring its relevance in the near term.
Data services impact the market positively, fueled by rising smartphone penetration and demand for high-speed internet. With millions internet users, operators are aggressively expanding 4G coverage and rolling out 5G in major cities, catering to bandwidth-heavy applications such as video streaming and mobile gaming. Affordable data packages and bundling strategies drive consumption, particularly among younger users. Meanwhile, traditional SMS usage has declined due to OTT messaging apps, though A2P (application-to-person) SMS remains vital for banking alerts and authentication. The enterprise segment is adopting IoT and cloud-based data solutions, further improving B2B revenue. As digital transformation accelerates, data services will remain the primary growth engine, with operators investing in fiber and wireless broadband to meet escalating demand.
The OTT and Pay-TV segment is expanding rapidly, driven by Indonesia’s growing digital content consumption. Local and international platforms compete for subscribers, leveraging partnerships with telcos for bundled data-content packages. Pay-TV adoption is rising in urban households, with IPTV and satellite services gaining traction, though cost sensitivity limits growth in lower-tier cities. Meanwhile, live sports and original local content drive engagement, with telcos including Telkomsel and Indosat integrating OTT subscriptions into their ecosystems. Advertising-based video-on-demand (AVOD) models are also gaining popularity, targeting budget-conscious users. As broadband penetration increases, OTT and Pay-TV services will further disrupt traditional media, with telcos playing a pivotal role in content distribution and monetization.
Regional Analysis:
- Java
- Sumatra
- Kalimantan
- Sulawesi
- Others
As Indonesia's most populous and economically developed island, Java in the telecom market, accounts for a significant number of subscribers. The region benefits from extensive 4G coverage and early 5G deployments in Jakarta, Bandung, and Surabaya, driven by high smartphone penetration and dense urban demand. Operators prioritize Java for fiber-optic expansion, catering to enterprises and digital-native consumers. However, network congestion remains a challenge in major cities, prompting investments in small cells and spectrum optimization. Rural areas in Central and East Java still face connectivity gaps, but government-backed initiatives including Palapa Ring aim to bridge this divide. With a concentration of tech startups, financial hubs, and OTT service users, Java remains the focal point for innovation, shaping national telecom trends through its outsized influence on data consumption and digital service adoption.
Sumatra represents a high-growth telecom market, fueled by rising mobile internet adoption across its resource-rich provinces. Urban centers such as Medan and Palembang have near-complete 4G coverage, while operators are expanding into secondary cities such as Pekanbaru and Jambi. The region’s underpenetrated rural areas present opportunities, with satellite and fixed-wireless access (FWA) bridging gaps in mountainous and remote zones. Demand is driven by a young population, increasing e-commerce activity, and the growth of local digital services. However, infrastructure challenges persist, including fiber backhaul limitations and frequent undersea cable disruptions affecting connectivity. Telcos are leveraging Sumatra’s economic potential—linked to agriculture, mining, and trade to push B2B solutions including IoT and cloud services, making it a key battleground for market share beyond Java.
Kalimantan’s telecom market is shaped by its vast geography and uneven population distribution, with demand concentrated in urban hubs such as Balikpapan and Banjarmasin. The region’s 4G coverage is expanding, but rural and inland areas—particularly in Central and West Kalimantan remain underserved due to challenging terrain and low ROI for infrastructure. Mining and palm oil industries drive B2B demand for reliable connectivity, prompting operators to deploy private networks and satellite solutions. Consumer growth is steady but slower than in Java or Sumatra, limited by lower smartphone penetration and disposable income. However, government projects such as Indonesia Maju aim to improve digital inclusion, while undersea cables enhance international bandwidth capacity. As resource-based industries digitize, Kalimantan’s telecom sector is poised for gradual but sustained growth, with niche opportunities in industrial IoT and rural broadband.
Sulawesi’s telecom market is emerging as a strategic growth area, with Makassar serving as the primary hub for 4G and early 5G trials. The region’s archipelagic geography complicates infrastructure rollout, but undersea cables and microwave links are improving connectivity in key economic zones including Manado and Kendari. Youth-driven demand for social media and video streaming is rising, though prepaid users dominate, requiring cost-sensitive data bundling strategies. Rural electrification and tower-sharing agreements are expanding coverage in provinces such as Southeast Sulawesi, where fishing and agriculture communities remain underserved. Telcos are also targeting tourism hotspots such as Tana Toraja with localized digital services. With the government prioritizing eastern Indonesia’s development, Sulawesi’s telecom market is set to benefit from increased investment in backbone infrastructure and maritime connectivity solutions.
Top Telecom Companies in Indonesia:
The competitive landscape in market is characterized by aggressive infrastructure expansion and service diversification as operators vie for dominance in this high-growth sector. Leading players are accelerating 4G network densification while selectively deploying 5G in urban centers, coupled with substantial investments in fiber-optic backhaul to support increasing data demand. Competition has intensified around digital ecosystems, with providers bundling connectivity with OTT content, mobile payments, and cloud services to enhance customer stickiness. Value-added services targeting SMEs and corporate clients, such as IoT solutions and enterprise cloud platforms, have become key differentiators. Price competition remains fierce in the prepaid segment, driving operators to innovate with flexible data packages and loyalty programs. Meanwhile, strategic partnerships with tech firms and content providers are reshaping service offerings, particularly in video streaming and gaming. Rural coverage expansion through innovative technologies such as fixed wireless access and satellite solutions has emerged as both a competitive frontier and regulatory imperative. The market is also seeing increased foreign investment in digital infrastructure, particularly for submarine cables and data centers, as players position themselves for Indonesia's ongoing digital transformation.
The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the Indonesia telecom market with detailed profiles of all major companies, including:
- PT Bakrie Telecom Tbk
- PT Elang Mahkota Teknologi Tbk
- PT Smartfren Telecom Tbk (Sinar Mas)
- PT Telkom Indonesia (Persero) Tbk
- PT XL Axiata Tbk (Axiata Group Berhad)
- PT. Indosat Tbk
Latest News and Developments:
- May 2025: Telkomsel announced the establishment of 73 new 5G base stations in Makassar, significantly expanding its 5G network coverage across the city. The installation of these new stations will enable Telkomsel to provide 5G coverage across numerous residential localities, tourist areas, and industrial zones in the region. The network will also cover the Sultan Hasanuddin International Airport.
- March 2025: Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison, together with Nokia and Nvidia, announced plans to deploy an AI-powered Radio Access Network (AI-RAN) infrastructure across Indonesia. The project integrates Nokia's 5G Cloud RAN with Nvidia's AI Aerial platform, setting a unified computing framework for AI and RAN functions. The program aims to enhance network performance, spectral efficiency, and energy consumption, setting the stage for next-generation development in 6G technology.
- February 2025: Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison, Telkomsel, Smartfren, and XL Axiata established an alliance to launch three Application Programming Interface (API) services, Device Location, SIM Swap, and Number Verify, as part of the international GSMA Open Gateway program. The project is a collection of standard network APIs created to give enterprise developers the ability to utilize operator networks from anywhere.
- December 2024: Axiata Group and Sinar Mas finalized a USD 6.5 Billion merger of their Indonesian telecom units—XL Axiata, Smartfren, and SmartTel—forming PT XLSmart Telecom Sejahtera (XLSmart). The new entity aims to enhance Indonesia's digital infrastructure through investments in 5G, AI, and cloud services.
- December 2024: Nokia and Indosat Ooredoo Hutchison signed a two-year agreement to expand 4G and 5G networks across Indonesia. The deal also includes deploying Fixed Wireless Access solutions to improve broadband access in underserved areas, supporting Indonesia's digital inclusion efforts.
Indonesia Telecom Market Report Scope:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2025 |
| Historical Period | 2020-2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2034 |
| Units | Billion USD |
| Scope of the Report |
Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment:
|
| Services Covered |
|
| Regions Covered | Java, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Others |
| Companies Covered | PT Bakrie Telecom Tbk, PT Elang Mahkota Teknologi Tbk, PT Smartfren Telecom Tbk (Sinar Mas), PT Telkom Indonesia (Persero) Tbk, PT XL Axiata Tbk (Axiata Group Berhad), PT. Indosat Tbk, etc. |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Indonesia telecom market from 2020-2034.
- The research study provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Indonesia telecom market.
- Porter's Five Forces analysis assists stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Indonesia telecom industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
Key Questions Answered in This Report
The telecom market in Indonesia was valued at USD 25.9 Billion in 2025.
The Indonesia telecom market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 1.09% during 2026-2034, reaching a value of USD 28.6 Billion by 2034.
The key drivers of the Indonesia telecom market include rising mobile internet penetration, the increasing demand for high-speed connectivity, government initiatives to develop infrastructure, the growing adoption of digital services including e-commerce and fintech, and strategic partnerships between telecom and tech companies.
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
 Request Customization
Request Customization
 Speak to an Analyst
Speak to an Analyst
 Request Brochure
Request Brochure
 Inquire Before Buying
Inquire Before Buying




.webp)




.webp)












